Silvopastoral Agroforestry with Cattle [英国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Alan Radbourne
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6347 - 英国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
co-compiler:
Fisher Karen
Soil Association
土地使用者:
Hope Joe
Cefn Coch
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
European Interreg project FABulous Farmers有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - 英国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A mixture of silvopastoral agroforestry approaches, including extensive and rotational cattle grazing around trees, provide benefits for biodiversity as well as leaf fodder for cattle, edible fruits and nuts, and wood fuel.
2.2 技术的详细说明
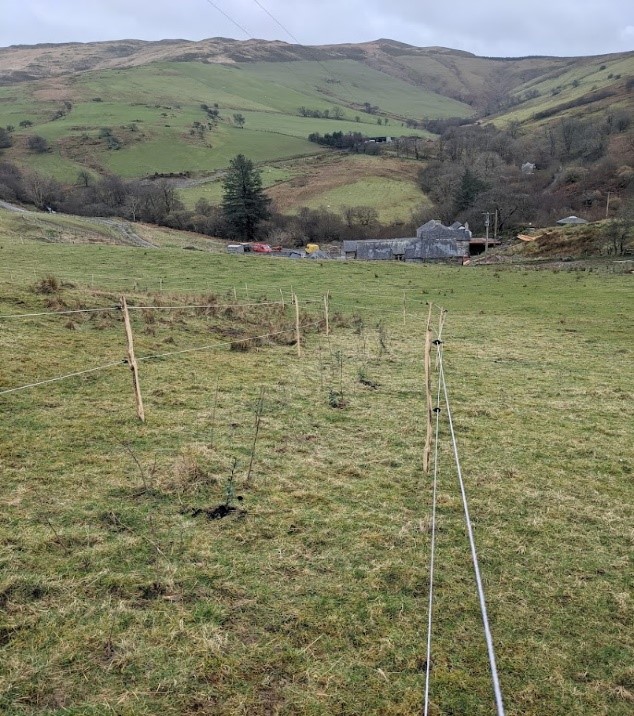
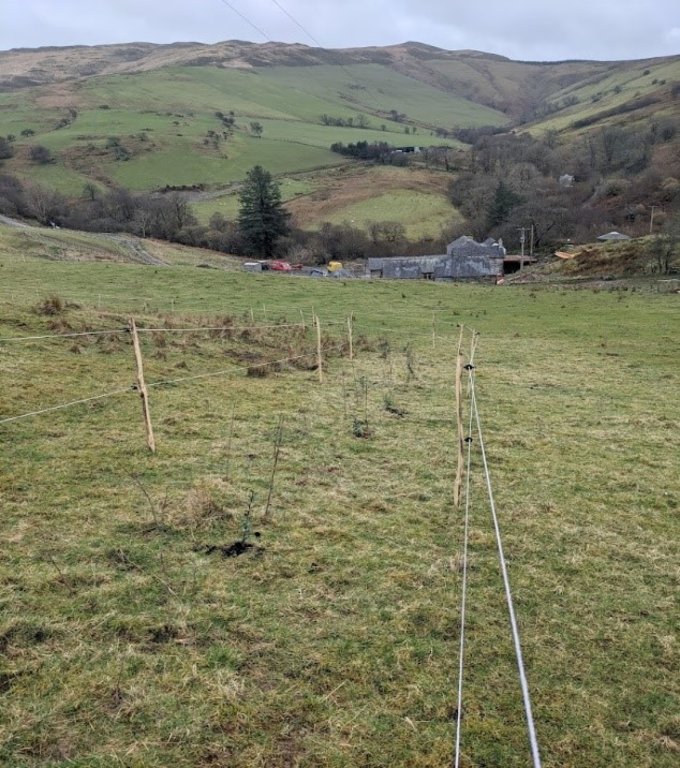
说明:
A first generation farmer with a mixed 36 hectare farm has been exploring the establishment of a regenerative silvopastoral agroforestry system.
Under this system the farm has been divided into four zones:
1. Cae mawr- 4.3 ha field. Formerly semi-improved permanent pasture with occasional scattered trees. The field has been divided with hedges into 8 rotational grazing units for Highland and Welsh White cattle. Hedges are of mixed edible fruit and nut varieties. The more distant hedges are composed of mixed native species.
2. Cae Ceirch – 5.4 ha field. Semi-improved permanent pasture with scattered trees and gorse bush. New planting of native species amongst the gorse, creating enclosures by planting native trees at a variety of densities. Electric fences have installed for protection and will be removed once the trees are large enough to withstand browsing. Additionally, field trees are being planted and protected with "cactus tree guards" (tubular sleeves of wire mesh with outer spikes).
3. Lower slopes - 3 ha area. Old pasture which has been grazed exceptionally lightly for a number of years. Allowing native trees, mostly birch, willow and hazel to naturally regenerate. Bracken and bramble have been controlled by pigs with the aim of rehabilitating towards a silvopastoral system. Some thinning of trees will be undertaken in places to achieve that end.
4. Riparian woodland - 1 ha area. Occasionally grazed by cattle on an "as needed" (ad hoc) basis.
The system aims to produce high quality nutrient-dense food, with the highest animal welfare, whilst simultaneously providing maximum biodiversity benefits.
New tree planting is protected by electric fencing comprising chestnut posts with ring insulators and poly wire, with cactus tree guards for individual trees.
The benefits include shelter and shade for animals, with increased diversity of forage. In time there will be a harvest of edible products for human consumption (fruits and nuts etc). And the system provides a variety of biodiversity benefits as well as a visual - aesthetic - improvement to the landscape.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
英国
区域/州/省:
Wales
有关地点的进一步说明:
Machynlleth
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
Cefn Coch, Glaspwll, Machynlleth, SY20 8UA
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2018
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- Improve animal welfare
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
否
产品和服务:
- 肉类
品种:
牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
计数:
15
品种:
生猪
计数:
5

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
植树造林类型:
- 温带大陆林人工林
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 落叶植物
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 林牧业

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
否
产品和服务:
- 肉类
品种:
牛 - 非奶牛牛肉
计数:
15
品种:
生猪
计数:
5

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
植树造林类型:
- 温带大陆林人工林
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 落叶植物
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 防风林/防护林带
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
40 hectares
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha = 2.47 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
£GBP
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
£150
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ground preparation – marking out planting lines | Winter |
| 2. | Planting trees | Winter |
| 3. | Erecting electric fencing | Winter |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
8000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
100%
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Checking trees visually | Ongoing - monthly |
| 2. | Vegetation maintaince via mowing | Once a year in late summer |
| 3. | Management of rotational mob grazing | Ongoing during grazing season - daily |
| 4. | Checking electric fences | Ongoing - weekly |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Checking trees & electric fences | Hours | 24.0 | 10.0 | 240.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Vegetation maintance | Hours | 30.0 | 10.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Management of rotational grazing pastures | Hours | 100.0 | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Flail mower attachment to tractor / strimmer | unit | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1540.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1811.76 | |||||
注释:
Flail mower attachment to tractor / strimmer already owned as part of farm management
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost of trees, establishment (i.e. planting & replacing trees) and fencing
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Increased diversity with new tree forage available
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Improved welfare for cattle as trees provide shelter.
森林/林地质量
注释/具体说明:
Increased forest areas, diversity and connectivity
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Trees provide wood fuel, fruit and nuts, alongside possible future option for recreation and tourism opportunities
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Trees provide wood fuel, fruit and nuts, alongside possible future option for recreation and tourism opportunities
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Time for installation and management is higher than previous
社会文化影响
Aesthetic appeal of landscape - i.e. landscape looks better
注释/具体说明:
More trees in the fields and flowering hedgerows etc
生态影响
土壤
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Trees as stores of carbon and improved soil health
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Addition of above ground biomass in trees and hedgerows
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
More diversity of productive and native trees and hedges
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
More space for biodiversity
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Offers the opportunity to radically increase the biodiversity potential of the farm |
| Shelter belts improve animal welfare |
| Productivity increases with diversification of products and co-benefits. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| A whole system approach promotes co-benefits of the farm improving animal welfare, biodiversity and diversification and thus resilience of the farm business. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High set up costs | Careful choice of tree protection mechanism and seeking grant assistance |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The system can be expensive to implement for little return in short-term | Grant assistance |
| Approach takes time to implement (i.e. trees to grow) before full benefits are seen, and management during this time in particular is higher than traditional methods | Long-term farm planning and seek guidance for the most effective implementation techniques to ensure best chance of success |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Multiple farm visits by SLM specialist in support of implementation
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Formal interview with farmer to gather required information and experiences to share learnings
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/11/2021
7.4 一般注释
The implementation of this silvopastoral agroforestry system is still in its relatively early stages as the trees and hedges have not yet reached maturity and thus the land user has not seen the full benefits of the work undertaken. However, in this whole-system approach to long term regeneration of the farm the land user has been able to plan well and utilise expertise and experience to make it a success.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块