Farmer managed natural regeneration in smallholdings [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Grace Koech
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
FMNR
technologies_6600 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Sabina Atieno
lead farmer
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Reversing land degradation in Africa by scaling-up Evergreen Agriculture (Regreening Africa)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Centre for Research in Agroforestry (ICRAF) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
FMNR has been embraced by the local community as they consider it low cost and products from FMNR are utilized for various livelihood activities such as woodfuel for household use and surplus for sale, beekeeping is practiced within the plots: passion fruits are integrated also - climbing on frameworks of prunings.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Farmer managed natural regeneration (FMNR) has been embraced by the local community as they consider it a low cost method of establishing agroforestry, and products are utilized for various livelihood activities such as woodfuel for household use and surplus for sale, beekeeping is practiced within the plots: passion fruits are integrated also - climbing on frameworks of prunings.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
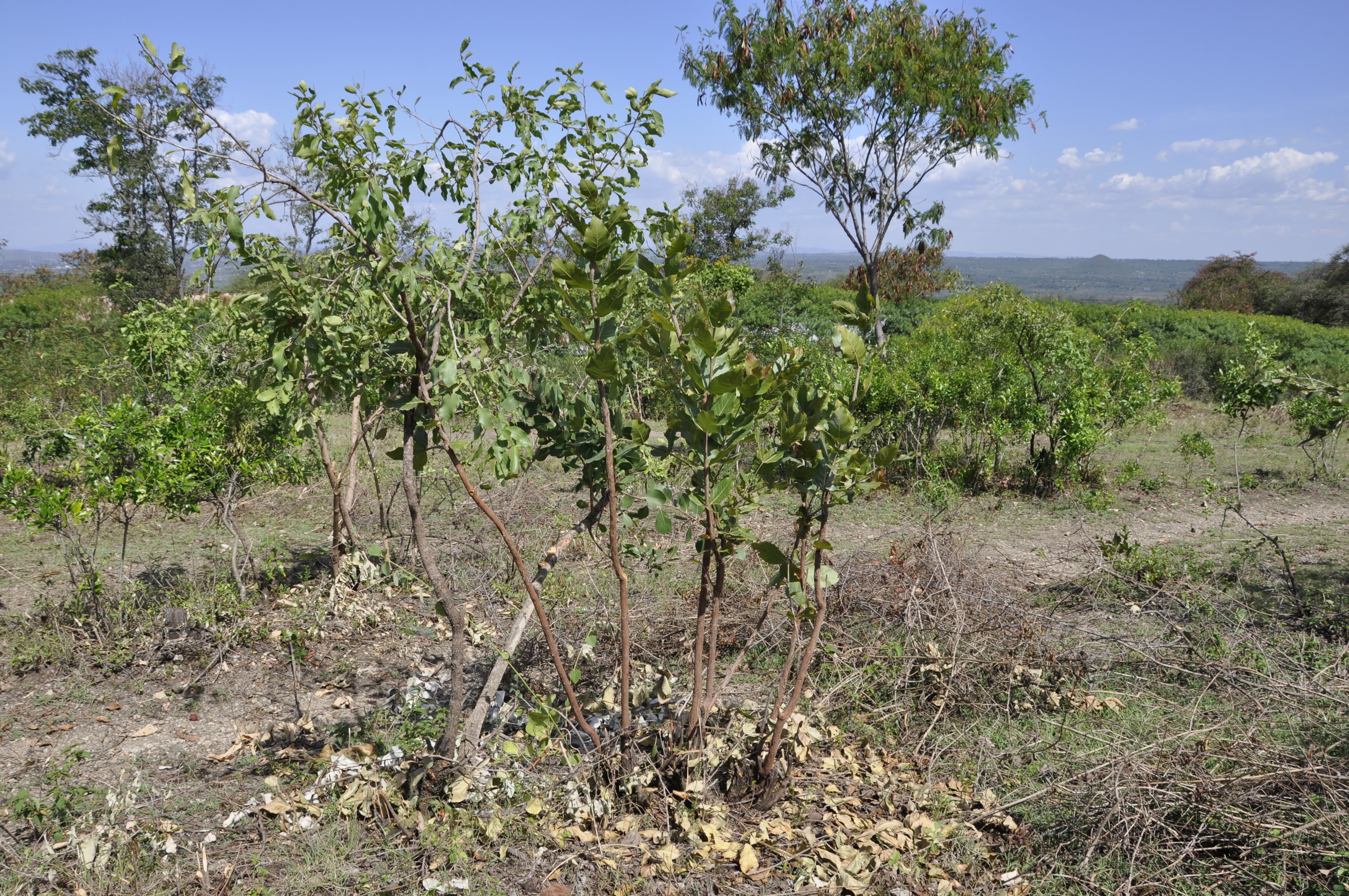
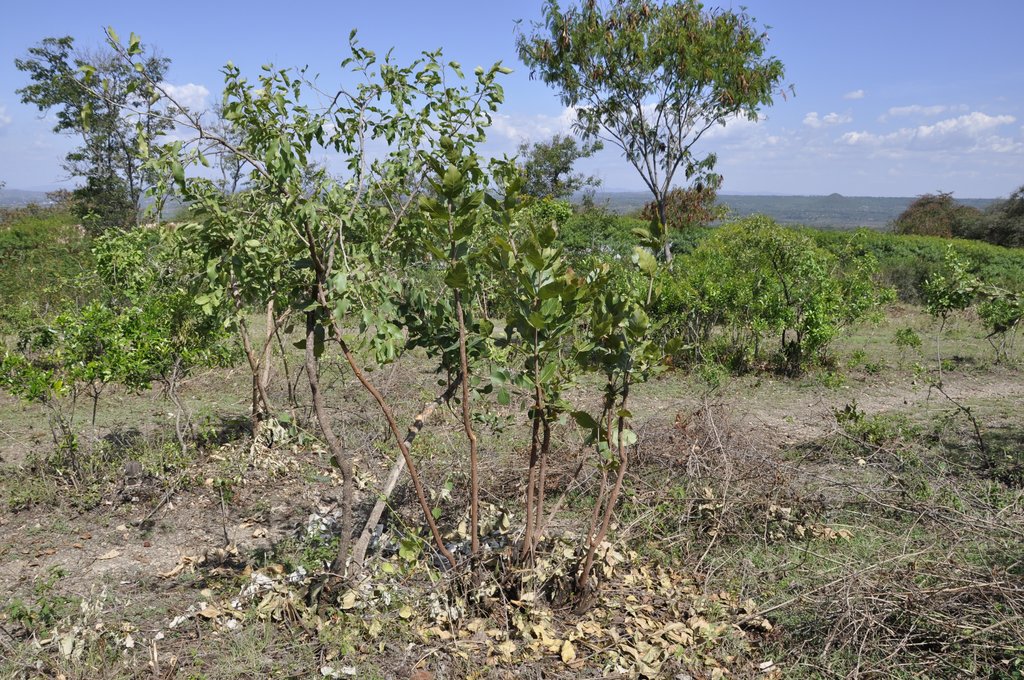
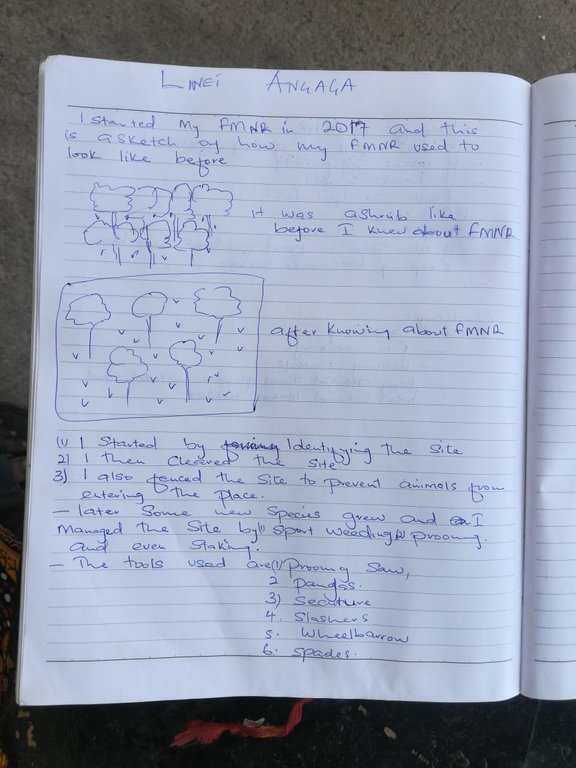
Farmer managed natural regeneration (FMNR) involves helping naturally regenerating trees to grow at the homestead - in cropland or within enclosure. FMNR begins with assessment of the land to ascertain the potential to practice the technology. Plots that have shrubs or stumps are selected. Management by thinning is practiced to provide a suitable density to allow prolific growth. The offcuts and twigs from clearing the shrub can be used as mulch, stakes for beans or passion fruits, or as wood fuel. Other techniques used includes propping to support weak stems and protection of site to avoid interference by human and livestock. In Homabay county, Western Kenya, farmer manage their plots by thinning, supporting stems and pruning. Species are regenerated using protection of naturally seeded trees, including Acacia spp, Grewia bicolor, Balanities aegyptiaca, Psidium guajava, Combretum collinum, Markamia lutea, Thevetia peruviana, Albizia coriara and Rhus spp. FMNR has been embraced by the local community as they consider it a low cost way of establishing agroforestry and products are utilized for various livelihood activities such as woodfuel for household use and surplus for sale, beekeeping is practiced within the plots: passion fruits are integrated also - climbing on frameworks of prunings.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
we can only get the youtube link to the video
https://youtube.com/clip/Ugkxk1nImuwSZVktgpAkvKwotlFKDo7s6_-8
日期:
14/12/2022
位置:
Migori
摄影师的名字:
@manathaproductions
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Homabay and Migori counties
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2018
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Regreening project or project on restoration of degraded landscape combined with traditional agroforestry.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 药用/芳香/杀虫植物和草药
年作制度:
木薯/土豆/树薯 - 玉米/高粱/小米
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- fodder crops - legumes, clover
- natural grasses
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 柑橘属
- 饲料树木(朱缨花属、银合欢、前庭草等)
- 水果、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
March to May, October to December
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Maize and beans
sweet potatoes and vegetables
groundnuts, indigenous vegetables and cassava
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- beekeeping, apiculture
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- fish
- 山羊
- 家禽
- 绵羊
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Farmers utilize animal manure for soil amendment, the systems provide a buffer incase of crop failure
产品和服务:
- economic security, investment prestige
- 蛋类
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- 肉类
- 奶类
品种:
beekeeping, apiculture
计数:
5
品种:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
计数:
4
品种:
fish
计数:
10
品种:
山羊
计数:
4
品种:
家禽
计数:
10
注释:
FMNR is practiced on cropping field where farmers encourage naturally growing trees of high value to regenerate alongside the crops. within the grazing field, pruning and thinning of naturally regenerating trees is done to allow grass to grow. in some cases the grazing field are enclosed and farmers can only cut and carry the grasses especially when the trees/ seedlings are young.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Maize, beans
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
注释:
The land is used in the same way before and after the technology, the difference is the productivity of the land that has improved as a result of implementation of the technology. for example with increased availability of forage, farmers have witnessed milk production that translate to more food for the household and surplus for market that also support other livelihoods such as access to quality seedlings.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Most farmers do not irrigate the trees that regenerate naturally, they are mainly rain-fed systems.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V4:更换或清除外来/入侵物种

结构措施
- S1:阶地
- S2:堤、岸
- S10:节能措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
注释:
The choice of the measure depends on the level of degradation. in severely degraded areas a combination of measures are integrated.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Another form of degradation managed using the technology is invasive species management by thinning out unwanted species or uprooting.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
- 适应土地退化
注释:
The technology is promoted to reverse effects of land degradation and adapt to changing patterns as a result of the degradation. for example the area enclosure is able to regenerate within the prevailing environmental conditions.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The height of the seedlings to be regenerated ranges from as low as ground level to fully grown trees, the spacing between the trees is 10m apart in crop land and 5m in grazing field. .
作者:
William Gumbo, farmer Homabay county
日期:
03/04/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 acre
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
0.4 ha
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
$3
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey land | dry season |
| 2. | Take an inventory of available species and their priority uses | dry season |
| 3. | generate a priority use list for the farm | dry season |
| 4. | generate a preferred species list | dry season |
| 5. | Mark and remove the unwanted species | dry season |
| 6. | select species and stumps to be regenerated | dry season |
| 7. | manage the stumps/stems by removing unwated stumps,thinning to remain with manageable density | dry season |
| 8. | keep three to five stems on each of the selected species and stumps | onset of the rain season |
| 9. | Manage the selected by pruning ofside branches, protection by fencing, utilize the prunning and coppices as firewood, make biochar, stakes for vegetable farming, compost making, construction work etc | raining season |
| 10. | allow the trees to grow for preferred use, periodically pruning is required | 2-6 months |
注释:
Where the trees regenerated has low density or diversity or the high value/preferred species are not available consider enrichment planting. in areas where FMNR is not feasible resort to enrichment planting. other technologies such as grass reseeding, soil water conservation could be implemented alongside FMNR.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land survey and inventory of species | person day | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | marking and removing unwanted species | person day | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | marking and regenerating the preferred species | person day | 3.0 | 3.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | managing regenerated trees | person day | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | machete | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | axe | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | file | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | fork hoe | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | hoe | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | wheelbarrow | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | rake | 100.0 | ||||
| 设备 | pruning saw | 100.0 | ||||
| 施工材料 | use locally available, dead fence | |||||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 18.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 18.0 | |||||
注释:
Where the farmer decide to do enrichment planting, permanent fencing, grass reseeding the cost is higher that what is projected here. the cost for the first year is high, subsequent years the cost is low. The household use available equipment to manage and regenerate the trees.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | pruning and removal of emerging species | twice per year |
注释:
Maintenance depend on the availability of rainfall that determine how faster the trees establishes.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | pruning and removing unwanted | 1 | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 3.0 | |||||
注释:
Maintenance cost is lower since it is done periodically and trees establishes at different growth rates.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1) density of the species
2) frequency and intensity of the rains
3) level of degradation
4) management objectives
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
FMNR is mainly a dry land practice but can also be practiced on humid areas where existing trees are managed by pruning and thinning to manage density.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Topography has no effect on FMNR
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil information is not available
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
FMNR rely on natural environmental conditions
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Agrobiodiversity increases with FMNR/ Agroforestry
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
木材生产
森林/林地质量
非木材林业生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
well managed FMNR farms in Migori and Homabay increase availability of timber and non timber products on farms.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
effect of FMNR on water resources indicated increase as shown within the nyatike mirema hills where over time rivers that had disappeared are restore and water access increased in the area. similarly Homabay has received increased rainfall as compared to previous years due to increased tree cover with trees of varying growth heights.
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Business such as beekeeping and firewood bulking is practised within the FMNR plots generating additional income for the homestead.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
increased, FMNR based enterprises developed for example beekeeping, firewood
经济差异
注释/具体说明:
data not documented
工作量
注释/具体说明:
time to access firewood which is the main economic activity in the area due to reliance of it for cooking is saved as pruning from the plot serve this purpose and surplus sold hence more time for other livelihood activities.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
some plots are managed communally, this bring people together to exchange ideas and conversation as they working together on the plots building the social cohesion within the community, additionally, community receive more people visiting their sites to learn more about the practice which comes with some prestige for the community.
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
improved due to access to more products and income increasing purchasing power of the community.
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
land and water rights applies to all community members
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
FMNR practice bring people together that present many opportunities to interact and promote collective action.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
increased as people are visiting the demo farms
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
strengthened communities formed groups to enable them work together to better their community, access financial support and market their products jointly
国家机构
注释/具体说明:
FMNR practises links different actors together during trainings, field days and demonstration on practise. This approach has contributed to increased knowledge and skills and interaction between the local and national institutions.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
knowledge products on FMNR practice in Kenya developed, training materials prepared, several trainings conducted on FMNR.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
N/A
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
N/A
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
restoration of water sources due increased ground water as a result of restoration
水质
注释/具体说明:
N/A
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
more water accessed due to increased volumes of water due to more rains
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
increased vegetation cover reduce surface flow in the intervention areas
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
N/A
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
see above
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
higher water conservation
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
more water infiltrate to soil and stored at the root zone
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
more cover crops, foliage from leaf fall increases soil cover
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
soil is not exposed for ease of erosion
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
N/A
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
N/A
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
N/A
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
with increased water availability, reduced soil temperature nutrient cycling increased
盐度
注释/具体说明:
N/A
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
N/A
酸度
注释/具体说明:
N/A
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
N/A
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
注释/具体说明:
N/A
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
N/A
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
N/A
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
N/A
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
N/A
干旱影响
飓风、暴雨的影响
注释/具体说明:
N/A
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
N/A
火灾风险
风速
微气候
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
FMNR increases diversity on-site. Issues of water, carbon, soil were not assessed in the study.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
Offsite benefits of FMNR were not assessed.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 |
注释:
land users are conversant to temperature and rainfall as the main climate related issues.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| user friendly and complementary to other land use activities |
| cost effective after the first investment |
| high potential for scaling |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| preserve biological diversity |
| start with the knowledge that farmers posses |
| build on the local knowledge of the farmers |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| high cost of initial investment | form farmer cooperatives to access credit |
| limited available natural regenerants | compliment with enrichment planting |
| sometimes available stumps are not the preferred species | compliment with enrichment planting |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| FMNR policy missing | Support policy reforms to include FMNR |
| practiced mainly in the rangeland where land tenure is communal | Strengthening existing community structures |
| slow growing of the indigenous species making it less preferred by the farmers | compliment with fast growing high value trees |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
9
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
13/12/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
10.Wanjira, E.O., Muriuki, J. & Ojuok, I. (2020). Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration for Kenya: A primer for development practitioners. Nairobi, Kenya: World Agroforestry (ICRAF), pg133. Erick Wanjira 1:02 PM 2.Muriuki J, Wanjira EO, Ojuok I. 2022.Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration in Kenya: A trainer’s guide for farmers, pastoralists and other land users. Nairobi: World Agroforestry (ICRAF), 56. 3.Obwocha E, Muriuki J, Wanjira EO, Mohamed A, Muse IM.2022. Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration in Somali context: Practitioners’ manual. Nairobi: World Agroforestry (ICRAF), p84 Erick Wanjira 1:03 PM Rinaudo, T., Muller, A. & Morris, M. (2019). Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR) Manual. A resource for project managers, practitioners and all who are interested in better understanding and supporting the FMNR movement. World Vision Australia.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
open access
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
10.Wanjira, E.O., Muriuki, J. & Ojuok, I. (2020). Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration for Kenya: A primer for development practitioners. Nairobi, Kenya: World Agroforestry (ICRAF), pg133. Erick Wanjira 1:02 PM 2.Muriuki J, Wanjira EO, Ojuok I. 2022.Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration in Kenya: A trainer’s guide for farmers, pastoralists and other land users. Nairobi: World Agroforestry (ICRAF), 56. 3.Obwocha E, Muriuki J, Wanjira EO, Mohamed A, Muse IM.2022. Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration in Somali context: Practitioners’ manual. Nairobi: World Agroforestry (ICRAF), p84 Erick Wanjira 1:03 PM Rinaudo, T., Muller, A. & Morris, M. (2019). Farmer Managed Natural Regeneration (FMNR) Manual. A resource for project managers, practitioners and all who are interested in better understanding and supporting the FMNR movement. World Vision Australia.
7.4 一般注释
The team is available to provide additional information
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块