Livestock Urine Collection and Use [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
- 编辑者: Kidist Yilma, Julia Doldt, Noel Templer
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Yeshint Madaberya
technologies_6623 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Shone Wachara
Farmer
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology replaces the chemical fertilizer, urea, to restore soil fertility and improve vegetative growth and crop production. Also, it serves as a pesticide to manage insect pests.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- 编制者: GERBA LETA

Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) is a grass root level platform aims to bridge gaps on agricultural technology transfer between research and extension linkage and provide a platform of 20-30 members from research, extension and farmer for their joint learning and active participatory role in agricultural technology evaluation and dessimination.
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Collection of livestock urine allows resource-poor farmers to capture nutrient-rich livestock waste and use it to substitute urea fertilizer. It is a liquid organic product that restores soil fertility and pest management.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
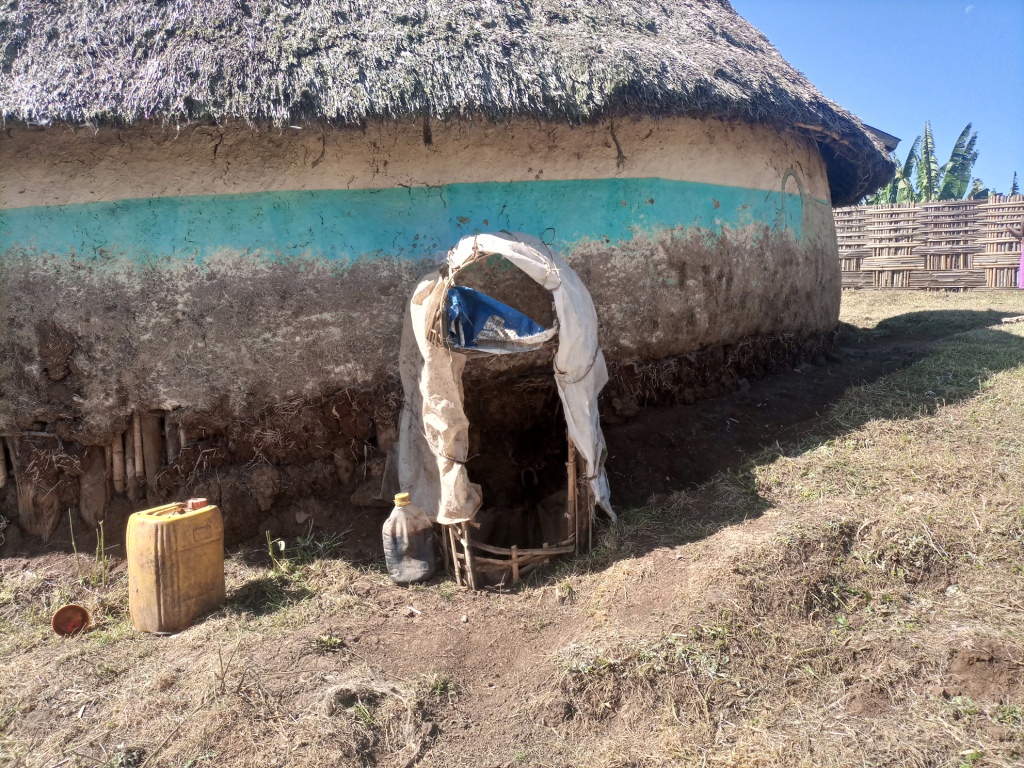
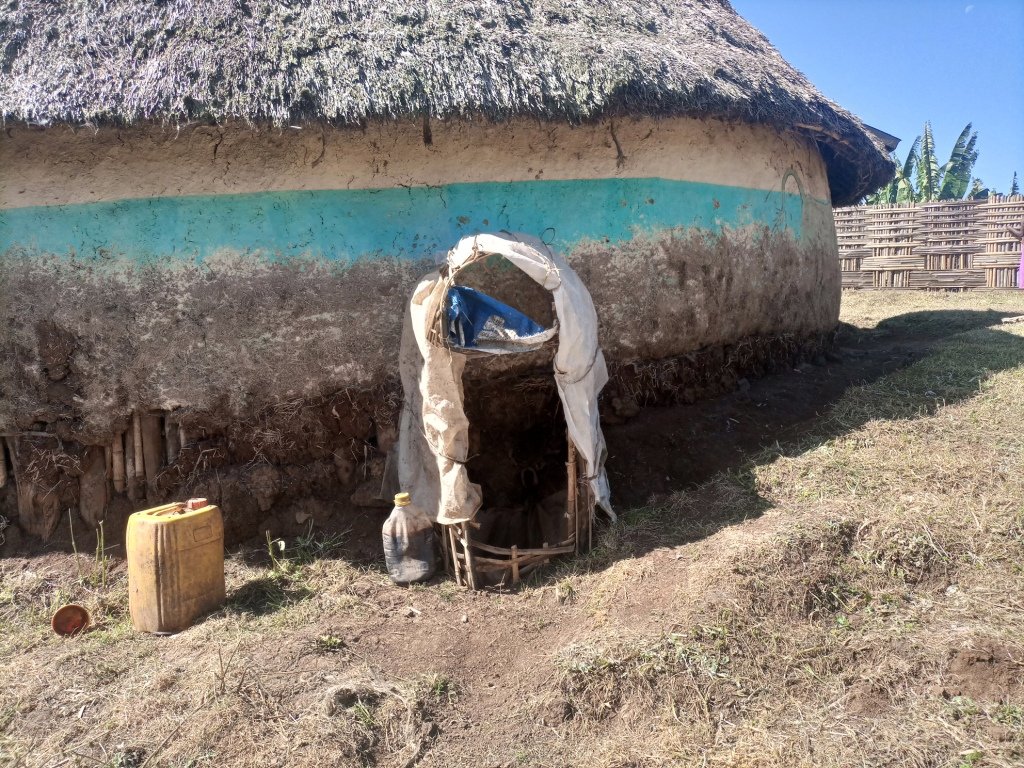
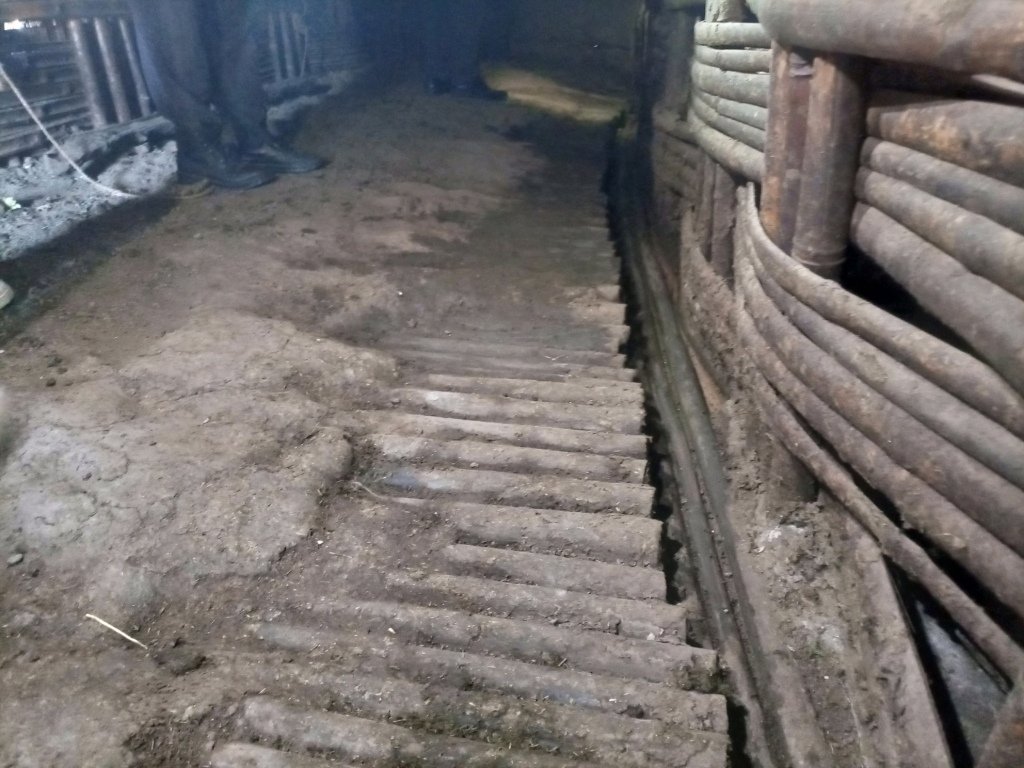
Enset, the “false banana”, is a perennial that grows well under the supply of organic fertilizers (farmyard manure, urine, compost and other household refuse). In the enset farming system, farmers traditionally shelter their livestock behind a partition within the main house. They construct a sloping floor in the livestock stall to allow the urine to drain into a narrow channel that leads to nearby enset and vegetable plots. However, construction of a collection chamber on the outlet side is an innovative approach which allows for better use of the urine. The collected urine fertilizes annual crops such as barley, maize, and vegetables - notably kale, carrots, and onions, via foliar and basal applications. Land users collect and preserve the urine for about 15 days before applying it to the target crops for the intended purposes. The urine is also used for pest management such as aphids and cutworms. According to the land user interviewed about 20 litres a day can be collected from six cattle. This implies the potential to collect about 7 cubic metres a year by a farmer: a considerable resource that should not be lost when there is an urgent need to restore soil fertility given ongoing and severe problems with land degradation. Therefore, urine collection and storage can be a way of reducing substantial investment in chemical fertilizers. To learn and showcase the benefits of urine as a replacement for urea fertilizer, a farmer sprayed 80 litres of urine twice onto 600 m2 of a ISFM+ barley demonstration plot. The sprayed amount replaced the equivalent of 6 kg urea that currently costs about 300 ETB.
Housing animals enables the collection of a reasonable quantity of urine to restore the soil fertility at the homestead and on the farm. Locally available bamboo helps to construct partitions and stall floors for the livestock as well as serving as a pipeline to drain the urine into a collection chamber. The benefits of applying urine goes beyond simply urea replacement, and its potential is merely limited by land users knowledge, skills, and motivation. These can be acquired via training, demonstration, exchange visit, and social learning. Land users like the role of urine in restoring soil fertility and boosting production. Furthermore, urine serves as integrated pest management via targeted application, deterring insects. However, the smell of the urine is unpleasant and may deter farmers from its use as they do not have safety clothes or masks to use when spraying the crop.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
The photo portrays the floor orientation and the livestock partition/ stall drainage canal that leads urine to the collection chamber outside the house.
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Video for this technology was not captured.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Sidama
有关地点的进一步说明:
Tuticha Kebele 01
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Purely collecting and using urine for target application to the crop as a replacement for urea fertilizer was introduced by ISFM+ of the GIZ. However, land users used to drain slurry of manure and urine from livestock stall to the nearby enset farm. Land users forge spraying vessels and collection pits lined with plastic materials and temporary shade to urine collection points.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 饲料作物 - 草
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- False banana (enset)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Belg (short rain) and Meher (long rain).
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Cereals, like barley, rotate with legumes (such as field peas or faba beans).
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Bimodal rainfall is received twice yearly (short rain Mid-February to Mid-April, and prolonged rain from June to September).
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Crop protection: it plays the role of Integrated Pest Management (IPM).
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
The nitrogen in urine stimulates the growth of various crops and non-crop wild species and restores degraded and potentially degradable lands.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
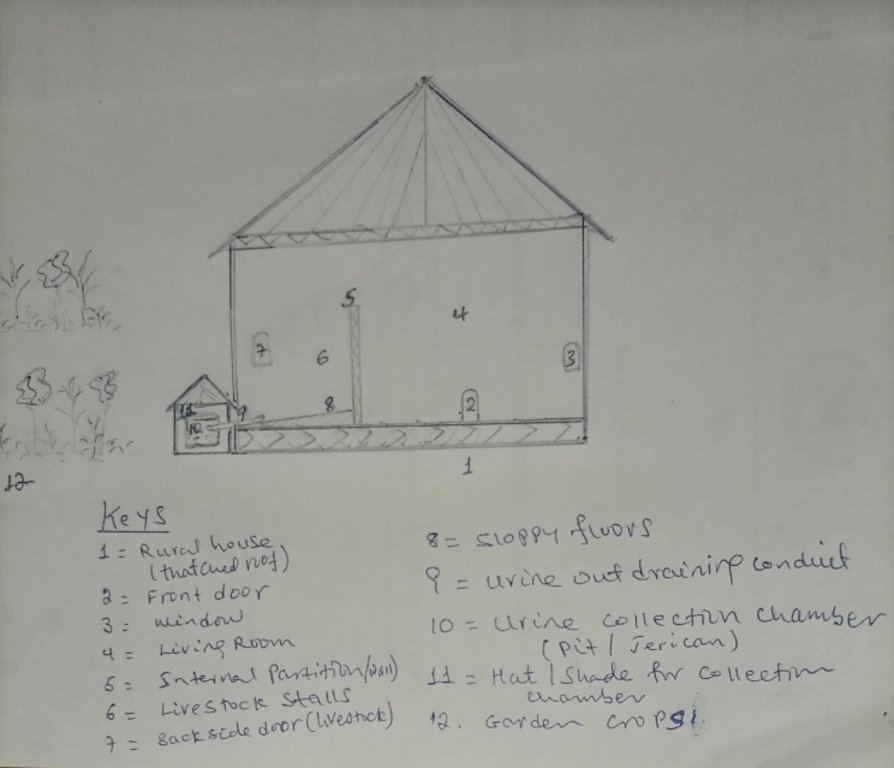
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The urine collection chamber is set up adjacent to the rural house on the side of livestock stalls. It receives urine that drains out of the sloping floor intentionally constructed using stone or bamboo to drain the liquid wastes through conduit directly to the collection chambers. A ditch that is placed adjacent to the outlet also takes the slurry to the nearby farm/garden. The dimension of the collection chamber and the types of materials used to establish the technology varies depending on resource availability or the number of livestock held by the land user. Other materials such as concrete pits or pits lined by google membranes can be used. Furthermore, jerrican or clay pots are the other alternative tools to collect urine. The different local materials replace the use of expensive materials. Small protective caps over the chamber is recommendable to protect the collected urine from rain and the heat of the sun that triggers the volatilization loss of urea. It is also possible to note additional information from the associated keys to describe the sketch.
作者:
Gerba Leta
日期:
30/03/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
ETB
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
53.6283
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
500
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct collection chamber | Dry season |
| 2. | Construct hats or covering lid for the chamber/collection pit | Dry season |
| 3. | Lining drainage line heading to the pit with concrete | Dry season |
| 4. | Storage vessels/barrel | Anytime |
| 5. | Supplying safety clothes (wear, boots, gloves and mask) | In advance |
注释:
Urine collection chambers, lids or roofs, storage vessels, safety wears, and spraying tools are essential for collecting, storing, and further treating urine before use.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Casual labor | no. | 4.0 | 250.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Carpentering | no. | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 50.0 |
| 设备 | Safety wears (shirt & trousers, gloves, mask, boots) | Lump sum | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | |
| 设备 | Watering cane | no. | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Effective Micro Organism | Litre | 2.0 | 100.0 | 200.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Cement | kg | 100.0 | 20.0 | 2000.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | m3 | 1.0 | 2000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Corrugated iron | pcs | 2.0 | 1000.0 | 2000.0 | 50.0 |
| 施工材料 | Posts and nails | Lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 50.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 13200.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 246.14 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
ISFM+ of the GIZ
注释:
For the model farmer who pilots livestock urine collection for soil amendment and management of pests, supporting the construction of a standard collection chamber and supplying associated kits helps to train and facilitate scaling of the technology in the best way. Effective Microorganisms (EMO) is an input being tested to investigate whether it has the property of changing the stink of the urine collected for storage and use on the farm.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Effective Microorganisms | Throughout collection and application |
注释:
The use of EMO to change the bad smell of urine, particularly during storage and application needs to be further investigated to prove and use it to reduce the abhorred side of collecting and applying urine for soil amendment and pest management.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | EMO | Litre | 6.0 | 100.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Family labor | no. | 52.0 | 100.0 | 5200.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 5800.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 108.15 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
NA
注释:
With the assumption that the land user can collect, treat and use about 140 liters of urine per week for different crops, family labor can be used at a lower rate as it is not a full-day operation. Despite our estimation, material and labour costs change in Ethiopia persistently because of market instability and economic crisis that is not uncommon since the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Economic crisis, spiking inflation, and overall labour and material market cost instability.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Receive bimodal rainfall with a summer maximum.
农业气候带
- 半湿润
The rainfall distribution is nearly consistent. The temperature is cold typical of highland weather conditions.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The topography is unremitting ups and downs.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Not available
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Surface and groundwater quality in the highland areas of Sidama region was not suggested as an issue. Rather, surface water can be polluted by soil erosion before the crops cover the ground.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The technology is piloted around the homestead. Agriculture is highly intensified in the area. Hence, only plantation forest or peripheral plants such as Eucalyptus species are the common tree species. This signals medium to lower species diversity that similarly applicable to habitat diversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The land user doesn't have off-farm income. He generates his livelihood from 2 hectares of land and a few livestock.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Farming is operationalized by hoes (hand-dug) to grow cereal crops. Otherwise, enset culture demands hand digging.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The land was inherited from the family line. However, the adopted national constitution declared land belongs to the state and the users. Thus, usufructs issued by the government to the land user.
注释:
In Ethiopia, the 1995 constitution declared the land as state property but the farmer has usufructs right. As a result, the certificate was issued except in the pastoralist areas of the country. Of course, most people inherited specific plots of land from their lineage, though there was frequent land redistribution during the Derg and early years of the EPRDF regime.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
Although they mentioned the quality of both ground and surface water is good in the preceding section, the level of sanitation is not significant as the resident use water from the springs for drink and other household activities.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
70 kg from 0.12 hectare of land.
SLM之后的数量:
400 kg from the same land.
注释/具体说明:
With the application of ISFM+ approach and urine as a replacement for Urea, a substantial yield increment was achieved.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
As the technology is at its early stage of implementation where documentation is not well organized, it was impossible to quantify the harvest and quality of the crop.
土地管理
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
As urine complement urea fertilizer, other nutrients from Sulfur, Phosphorus and other micro nutrients remain important.
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
文化机会
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Crop response to urine application is an evidence based for adoption of the SLM technology.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Not practically measured and documented. Besides, the technology is at earlier phase to judge the real impacts.
酸度
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
It has tangible impacts on managing pests.
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
As a foliar application of urine to the target crops might be subjected to evaporation, if not good hours of the day are not identified, there is a likelihood of emission. However, its amount is very insignificant as the little amount used for foliar feeding.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
The on-site assessment is made based on conceptual knowledge of the beneficial effects of collecting and applying livestock urine as a replacement to urea fertilizer and the farmer and experts' knowledge on the fertilizer and pesticidal effects of liquid urine. Otherwise, careful documentation of various types of data is commendable to quantify and properly address such comprehensive questions included in the questionnaire.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
The impact has not yet measured.
温室气体的影响
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
As an optimum application of urine substitute urea fertilizer, it favors the growth of diverse plant species, positively contributing to the overall ecosystem services and reducing degradations. However, it has not been empirically measured.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 适度 |
注释:
The technology has no direct influence on climate change/climate variability in the short term.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Post-establishment, the maintenance costs are believed to be very low. This shows the technology is cost-effective to resource-poor farmers.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Forty-four (44) farmers are currently piloting this technology. Of these, 30 farmers are innovative and adopted the technology on their own using locally available materials to collect and spray urine as a complement to urea fertilizer to the target crops.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
注释:
Thirty farmers represent the most significant portion who spontaneously took up the technology.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
Unavailability of the right kits/materials
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Land users use locally available materials to collect, store and spray the urine on the target crops. Meaning the concept is introduced in a way it matches or complements conventional uses of livestock wastes to improve the fertility of soil on which Enset, a perennial crop is growing. Otherwise, standard designs or types of materials and safety precautions kits have not been associated with the technology. Despite the unavailability of the necessary kits for the establishment of the technology, farmers forge their mechanisms to collect and use urine. This indicates the innovativeness of the land/technology users.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduce costs spent on chemical fertilizer. |
| Increase yield per unit of land and land users' income in general. Furthermore, it increases the number of tillers per plant and overall biomass yield. |
| Manage insect pests such as cutworms and aphids. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It seems a good substitute for chemical fertilizer, urea. It improves farmers' access to wasted resources without being used. |
| It restores the fertility of the soil and improves production and productivity, and species diversity which improves ecological benefits on top of the high return from the most minor investment in fertilizer. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Bad smell of the urine when sprayed on the target crops. | By ensuring access to necessary tools. Otherwise, they will not give up on using it since the benefit outweighs the loss. |
| Lack of spraying materials. | If not accessed spraying tools, the farmer committed to using locally forged ones. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Stinking of the urine while applying to the crop. | Try to test whether using Effective Micro Organism (EMO) can improve urine smell before using it in the field. |
| Lack of safety wear and associated necessary kits. | Improving access to the necessary materials, knowledge, and skills to use the available resources or materials effectively. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Four (4) persons, including a land user.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
A farmer
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
Three (3) persons (district expert, regional SLM specialist, and ISFM+ regional advisor).
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/01/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Use of Cow Urine in the Field of Agriculture. Singh, R. 2022
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.pashudhanpraharee.com/use-of-cow-urine-in-the-field-of-agriculture/
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Utilization of urine waste to produce quality cauliflower. Khanal, A., Shakya , S. M., Shah, S. C., Sharma, M. D. 2011.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.nepjol.info (Free access)
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Nitrogen concentration in the urine of cattle, sheep and deer grazing a common ryegrass/cocksfoot/white clover pasture. Doi.org/10.1080/00288233.2010.499899
URL:
https://www.tandfonline.com
7.4 一般注释
Not every question in the questionnaire is relevant to the Livestock urine collection for soil amendment and integrated pest management practices. Urine collection and use does not address every kind of land degradation stated in the questionnaire. However, it directly or indirectly addresses some of the SLM-related issues.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- 编制者: GERBA LETA

Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
Farmer-Research-Extension Group (FREG) is a grass root level platform aims to bridge gaps on agricultural technology transfer between research and extension linkage and provide a platform of 20-30 members from research, extension and farmer for their joint learning and active participatory role in agricultural technology evaluation and dessimination.
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
模块
无模块