Cover crops [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
- 编辑者: Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma, Noel Templer
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Yeshifan Sebil (in Amharic)
technologies_6628 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Falaha Fanaye
Farmer
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
With good management, a legume known as desmodium is a very good cover crop that can be integrated into perennial and annual crops. It improves soil fertility, repels insects and caters feed to the livestock.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Cover crops are crops grown on bare, fallow farmland or under a main crop to cover and conserve the soil by protecting it from exposure to the sun, wind, and direct impact of rain. It fixes nitrogen (if a legume), improves soil fertility, supplies livestock fodder, and helps manage both pests and weeds.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
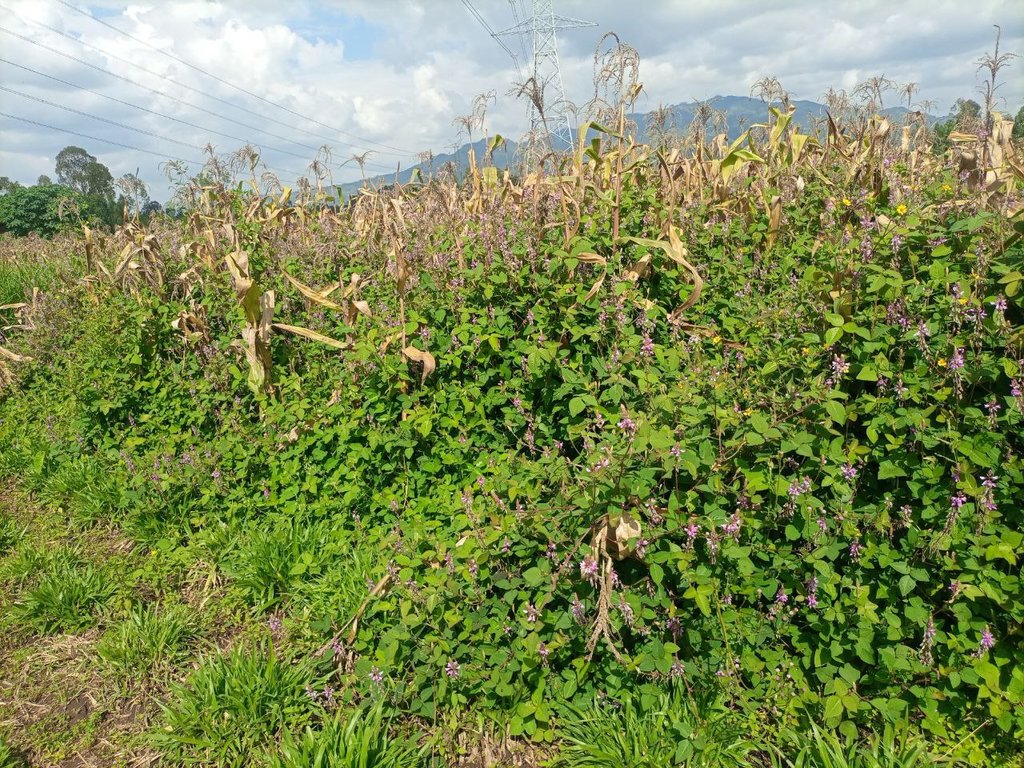
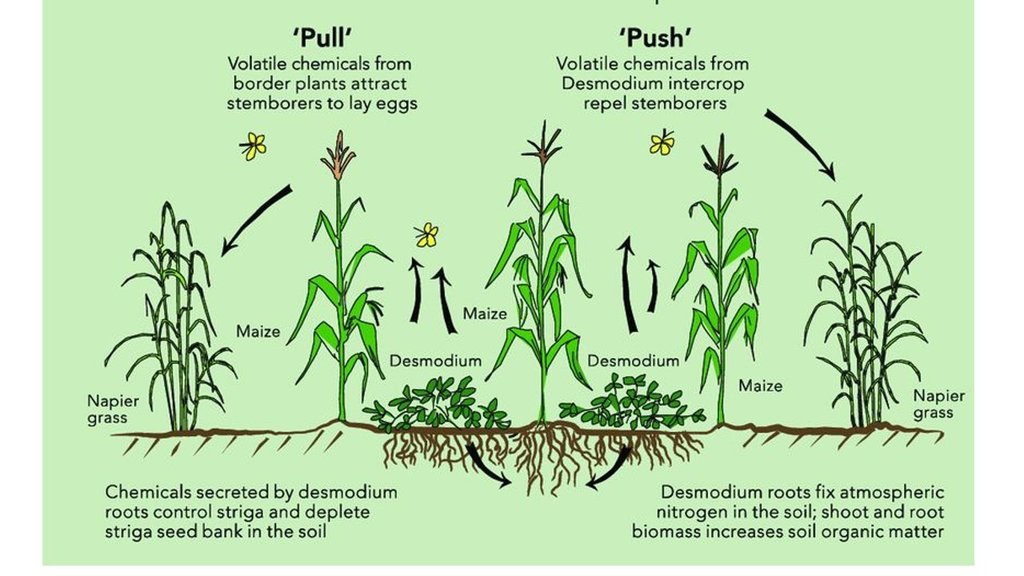
Cover crops are planted to conserve the soil on bare, fallow farmland or under a main crop. They can be grown on their own or between rows of annual and perennial crops such as maize, coffee, and fruits. The main purposes of growing cover crops are to cover the soil with low-growing vegetation, protect the soil from exposure to sun and rain, suppress weeds, improve soil fertility, supply livestock feed, and manage insect pests. Cover crops may be nitrogen fixing (if legumes), and they make productive use of spaces between crop rows, as well as controlling wind and water erosion. They also have the potential to restore soil fertility and help in climate change adaptation, as well as sequestration of atmospheric carbon above and below soil surface. Furthermore, cover crops can be fed to livestock, helping to bridge periods of shortage of feed when grazing lands are not available – which is an increasing problem because of growing population pressure and expansion of croplands. Land users give huge credit for its role as a pesticide by deterring armyworm and stalk borer when used as a border, and stopping their advance into the maize crop.
Desmodium is an example of a leguminous cover crop, improving soil fertility via fixing atmospheric nitrogen, increasing infiltration and productive use of soil moisture, and catering for livestock via a “cut-and-carry” fodder system. Desmodium is planted between rows of maize crops as well as between grass hedgerows around the farm. For its establishment, access to desmodium seed is essential. Once established, it remains to serve as a permanent source of planting material. Nevertheless, there are some disadvantages of desmodium: seed collection is difficult, it may trap honey bees and it can compete with the crop for light and space if allowed to grow too tall. Thus, efficient management of desmodium is essential. Nevertheless, as part of an agro-ecological intervention, cover crops like desmodium deliver multiple benefits to resource-poor farmers and can be viewed as an investment in improving soil fertility as well as soil health. Overall, cover crops improve productivity, and help ensure yield stability and contribute to a healthier ecosystem.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
The photo portrays the location where desmodium and other grass species mutually play distinct but complementary push-pull roles of attracting and repelling insect pests from infesting the main crop past the visible hedgerows.
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Videos of this technology is not taken.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
SNNPR
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kuto Sorfela kebele, Sodo Zuria
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The land user is a member of the the ISFM+ implementing farmers group and recently evolved to the Agro ecology since the kebele is an agroecology site.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The cover cropping practice has introduced via ISFM+ farmers group.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- Desmodium
年作制度:
玉米/高粱/谷子与豆类间作
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Belg (short rain) when maize is planted and Meher (long rain) when other crops are planted.
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Desmodium/haricot beans is intercropped with maize.
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Cereal crops such as maize/tef is rotated with root crops such as sweet potatoes/taro or the legume crops such as haricot beans.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Desmodium and the grass (Brachiaria species) serving as push-pull technology to the pest. Adopted from https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/desmodium-legume-cover-crop-solution-food-insecurity-africa-ndiritu/. In this particular case, Brachiaria play the "pull" function on the periphery of the maize farm.
作者:
Africa Sustainable Agriculture Biweekly Newsletter, ICIPE Push Pull Project
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
Timad = 0.25 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha = 4 Timad
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
ETB
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
53.6283
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
250
4.3 技术建立活动
注释:
We believed to address only the maintenance costs of desmodium as it demands only seeds, skills, and knowledge as compared to the other SLM technologies.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
We jumped to the following session as maintenance cost is rather decisive for the cover crops.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation and planting | Before and at planting |
| 2. | Cutting desmodium to use as feed for cattle | During the growing season |
| 3. | Harvesting desmodium biomass and /or seed | At harvest maturity |
| 4. | Access to planting materials, if newly started | Anytime in the offseason |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation | PDs | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cutting for use as feed | PDs | 8.0 | 250.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting total biomass and /or seed | PDs | 5.0 | 250.0 | 1250.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Desmodium seed | kg | 3.0 | 120.0 | 360.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 5610.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 104.61 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Agroecology/ Integrated Soil Fertility Management Project (ISFM+)
注释:
Prices of agricultural inputs are frequently changing in Ethiopia.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The prevailing economic crisis and rising of inflation in the country contributes to inputs and other services price uncertainty.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainfall distribution is uniform except in El Nino cases or recurrent drought experienced in the country and the region.
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The visited farmland lay on gentle slope and less vulnerable to the effects of erosion.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Not available.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Seldom, when heavy rainfall is intercepted, there is a flood event.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The farming system in the area features the best agroecology practices with diverse agrobiodiversity. The type of crops grown in the area ranges from root crops (such as sweet potato, cassava, and yam), cereals (teff and maize), to perennial crops: coffee, fruits and enset.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
In addition to crop production, the land user engaged in off-farm activities such as making local liquor to support her family's livelihoods. Furthermore, the land user adopted diverse ISFM technologies such as biogas/bio slurry and vermicomposting.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
注释:
As compared to the local people, the adoption and implementation of diverse agricultural activities and the size of the farm put the land user on a relatively larger scale.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The farmland was inherited from the predecessors.
注释:
Parts of the land used by the user are leased in from the other land owners.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
The land user accessed electricity in rural areas. She also used biogas for energy production.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Increase with proper management of the companion crops on a gradual basis.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Simultaneously increase with good harvest per unit of land as the integration allows to combat against pests.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Desmodium gives high biomass production. So it supplies more fodder if timely trimmed and supplied to the livestock.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Believed to increase with the application of appropriate management practices.
畜牧生产
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Desmodium fixes atmospheric nitrogen that improves the fertility of the soil in addition to the production of large biomass that supplies organic matter to the soil.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Slightly decrease as desmodium fix atmospheric nitrogen in the long run and partly complements urea fertilizer.
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
It demands follow-up and frequently monitors and manages the growth of desmodium to reduce its competition with the main crops.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
As it creates evidence-based learning, it improves land user's SLM knowledge.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
High biomass production and the ground covering traits of desmodium assist to slow down surface runoff and promote infiltration deep into the soil.
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
As the companion crop fixes atmospheric nitrogen, it improves nutrient cycling.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Land users suggested the pesticidal role of desmodium as compared to the hidden contribution to the improvement of soil fertility through its natural traits of fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
It increases biomass production that absorbs carbon above and below the surface of the soil.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Contributes to groundwater recharge by reducing surface runoff.
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
Facts are not available to complement this allegation since the implementation is on smaller areas of farmland.
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
It breaks the speed of flood that overflow and damage neighboring areas.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 非常好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The benefit from desmodium can be made in the short term. Its high biomass production to enrich grass fodder and suppression of weeds and pests are promptly seen as compared to some other SLM technologies.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology improves soil fertility. |
| It manages insect pests and stops their advance and negative consequence they might causes on the main crops. |
| Supply protein-rich feed to the animals. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Cover crops provide multiple benefits to the family farmers such as the best uses of land between the rows of maize crops. |
| It smothers weeds and improves soil fertility and crop productivity which have a positive contribution to the livelihoods of family farmers. |
| Cover crops and the practice itself have a beneficial role in agroecology intervention and improvement of the ecosystem functioning. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Fast growing and overwhelming the main crops (competition for space). | Applying intensive management such as cutting and feeding to the animals. |
| Feeding the animals with fresh harvest is not friendly to the livestock. | As it is a protein-rich fodder crop the harvest must be slightly dry and mixed with grass fodder that reduces the adverse effects of either bloating or diarrhea. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Difficulty to manage and harvesting desmodium seeds. |
1. Intensify the management of desmodium and reduce harvesting inconvenience on main crop. 2. Replace desmodium with other farmer's friendly legume species such as Dolichos lablab...as cover crops. |
| Hooky nature of the seed that sticks to the clothes. |
-Wear nylon wears/clothes that reduces the effects of hooky seeds. - Produce seeds on separate plots. |
| Quick growth and climbing traits that dominate the main crops. | - Apply intensive management and use the above-ground parts as fodder for the livestock by adopting cut-and-carry feeding system. Also, needs to keep the green parts under frequent management practices. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
4 people
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
3
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Cover Crops for Sustainable Crop Rotations. Clark, Andy. 2015
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.sare.org/resources/cover-crops/
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Greenleaf desmodium. A Fact sheet index describing about the cover crop
URL:
https://keys.lucidcentral.org/keys/v3/pastures/Html/Greenleaf_desmodium.htm
7.4 一般注释
The questionnaire is wide. Also, it requires many data sources including the sketching of the technical application of the technology, video graphic description, etc., which seems ambitious to be addressed by an expert.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
模块
无模块