Treating acid soils with lime [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
- 编辑者: Noel Templer, Julia Doldt, Kidist Yilma
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Biyyoo dhangagaa'e nooratiin haakiimu
technologies_6641 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Benti Mohammed
Farmer
埃塞俄比亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Lime ameliorates the degraded soil due to growing soil acidity.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
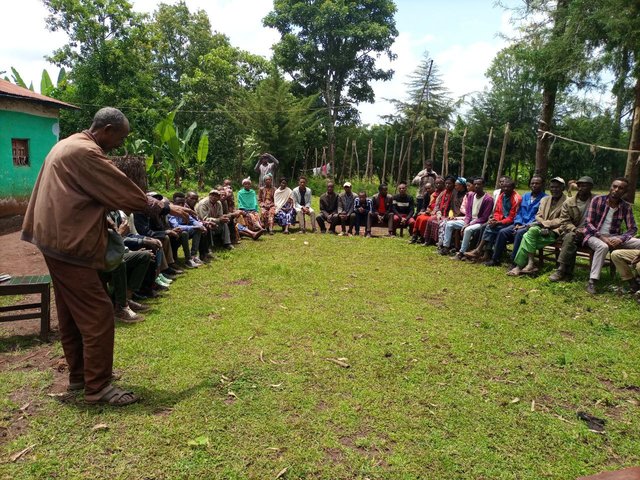

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Acidic soils deprive crops of their full nutrient absorption capacity. Lime application to these soil makes them less acidic. It breaks the barrier that fixes nutrients and ensures crops access to vital soil nutrients that unleash their productivity potential.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
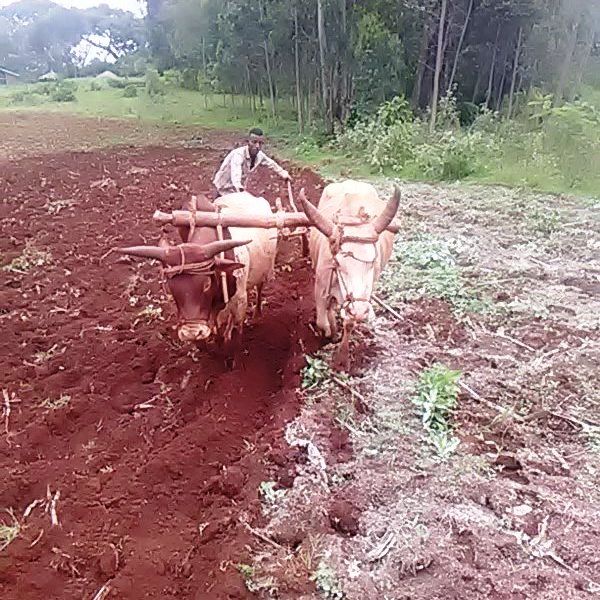
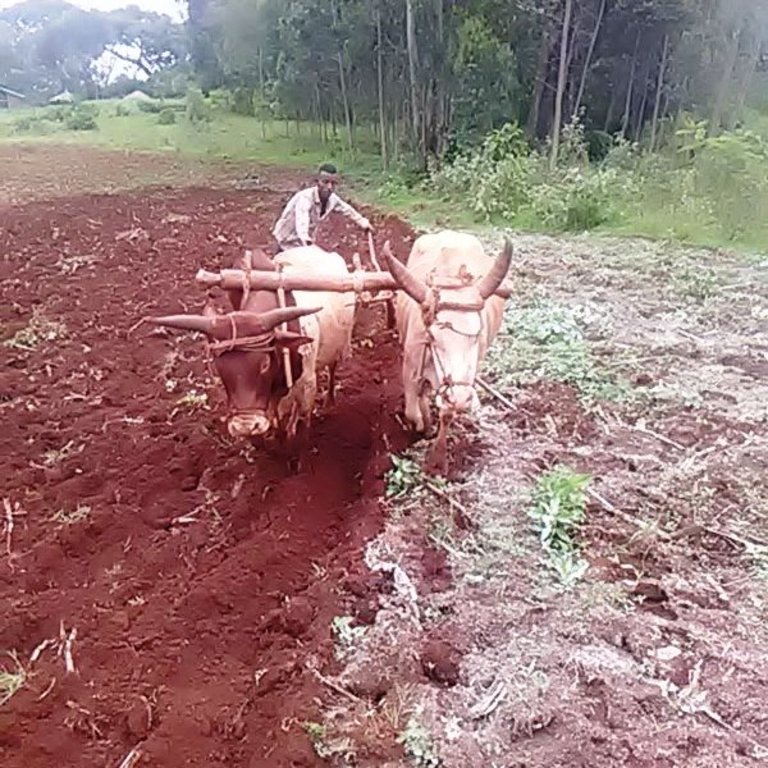
Acidic soils deprive crops of their full nutrient absorption capacity. The farm under the assessment has soil with a pH below 5.0. Lime application to these soil (liming) makes them less acidic. It breaks the barrier that fixes nutrients and ensures crops access to vital soil nutrients that unleash their productivity potential. Soil amendment with lime needs to be at least a month in advance of planting the intended crop. It requires thoroughly mixing the lime powder into the soil. The crop response from the treated soil is gradually visible, particularly during the second cropping season. Lime application takes place after the soil is pulverized very well. Most small cereals (for example “tef”, Eragrostis tef, wheat and barley) need tillage at least four times to create a good environment for the small seeds to emerge and quickly compete effectively with the weeds.
Treating exhausted acidic soils enhances the availability of nutrients that otherwise remain fixed by non-leaching mineral elements in the soil. Application of lime along with organic fertilizers improves soil structure, soil pore space, and soil infiltration capacity. Treating acid soil increases crop production and productivity of the soil. It reduces labour costs relative to output, since it leads to a relatively high yield from a small area. The practice helps to stop land being converted from cropping to grazing. Even when this conversion occurs, the grazing land itself is poor because of the acidity and may be abandoned and simply become unproductive degraded land.
However, availability and accessibility of lime, transportation, and manual application to the farmland are challenging. Based on the degree of soil acidity, the amount of lime required can be high. Apart from the large quantity required (4 or more tonnes per ha), the price per unit is discouraging to smallholder farmers. The high price, poor supply, and delays in delivery are the main challenges to effectively address the prevailing issues of soil acidity.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
The photos portray liming improves the vigor of crops by improving the productivity of soil that was once plagued by soil acidity that fixes the nutrients in the soil.
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Videos of this technology is not documented.
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Oromia
有关地点的进一步说明:
Gechi district, Gito kebele
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The technology applied on the farmland that is located closer to the homestead.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2017
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
- Bureau/office of agriculture
注释(项目类型等):
The project is an Integrated Soil Fertility Management (ISFM+) with a focus on acid soil management in the highland and high rainfall regions of Ethiopia through the application of integrated practices, and by adopting a participatory.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Rotate large cereals with small cereals, or the legume crops.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 农畜综合管理
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A7:其它

其它措施
具体说明:
It is a topsoil treatment or management by incorporating lime into the soil.
注释:
The agronomic measures also involve the application of lime and mixing up with the soil weeks before planting the main crop.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
注释:
The technology improves biomass production and the biodiversity of the farmland.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
The technology reduces soil acidity, improves soil productivity, and increases crop production.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
Sanga 4
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha = 8 Sanga
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
ETB
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
53.12
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
400
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | In advance of the main planting season. |
| 2. | Lime transportation to the farm | One month in advance |
| 3. | Lime application | 1 month before planting. |
注释:
The wage is inclusive to a pair of oxen.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation | PDs | 8.0 | 400.0 | 3200.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Lime transportation | PDs | 10.0 | 100.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Lime application | PDs | 4.0 | 400.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Lime | ton | 2.0 | 5000.0 | 10000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 15800.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 297.44 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
ISFM+ of the GIZ covers input costs at the beginning of introducing the technology. Of course, the project covered input costs for 600m2 of the farmland just to demonstrate the technology.
注释:
Uniformity of cost is the estimation for a hectare of land just to standardize and simplify understanding of the cost of technology. Otherwise, farmers apply lime on areas of land below a hectare, which could be on a quarter or one-eighth of a hectare. That is why the term local units such as "sanga" is introduced in subchapter 4.2 above. Essentially, as the availability of lime and affordability to access and transport to the farm is another issue, land users lime their farm on an incremental basis year and again.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation | 2-3 times before lime application |
| 2. | Lime application | A month before planting the crop. |
注释:
Other subsequent activities post planting such as weeding, harvesting, etc., are the regular jobs of the land users that are not computed as cost for adopting this technology.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land preparation | PDs | 8.0 | 400.0 | 3200.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Lime application | PDs | 4.0 | 400.0 | 1600.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Lime | ton | 2.0 | 5000.0 | 10000.0 | 50.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 14800.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 278.61 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Cost sharing of the land users is expected with the ISFM+ project to sustain independent uses of the inputs and avoidance of dependency on external actors. However, for the demonstration plots, the cost is covered by the project.
注释:
Once applied, the lime believed to serve its purpose for about consecutive five years.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Global increment of Fuel prices influences the corresponding increase in the price of inputs and other services costs in addition to the prevailing economic crisis and persistently rising inflation.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
The type of soil is Nitisol with acidity of pH 4.94.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The prevailing soil acidity strongly affected the diversity of flora and fauna.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
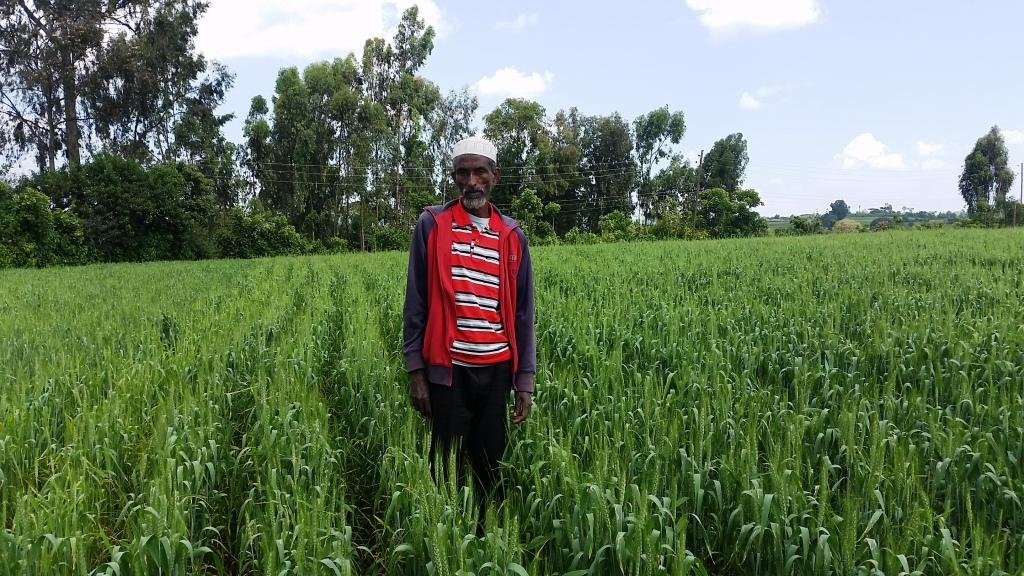
The 73 year old land user is convinced by the effects of lime on treating soil acidity. The abandoned land regained its productive potential and favours the regeneration of the lost species.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The land is inherited but administered by the state based on the existing constitution.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
0.4 ton
SLM之后的数量:
4 tons
注释/具体说明:
Highly increased. With proper application of lime to acid soil crop production increased from about 0.4 to 4 tons on a hectare of land.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Significantly increases as compared to crop production without liming the farm.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
As liming increases biomass production, it contributes to fodder production through the supply of surplus crop residue.
饲料质量
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
The attributes converge with the availability of quality fodder.
生产故障风险
产品多样性
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Land management is simplified as liming promotes high biomass production in combination with the use of organic and inorganic fertilizers.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
As it improves crops absorption of the available nutrients by releasing the nutrients that are otherwise fixed in the soil, it reduces the investment in more inputs/fertilizers.
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Lime transporting and application demands a large number of labor.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
It converges with good harvest and access to nutritious food.
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Improved through evidence based practical learning.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
No facts supporting this particular claim.
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Liming unfix the available nutrients in the soil system and newly applied ones.
酸度
注释/具体说明:
Soil acidity highly reduced by the application of appropriate amount of lime.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
As the intervention is a recent one, this estimation is more conceptual than the actual one.
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
As the intervention is a recent one, this estimation is more conceptual than the actual one.
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
The growth of dense biomass reduces soil movement which causes pollution.
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 适度 |
注释:
This part may not be directly related questions to the technology. However, liming acid soils improve the resilience of crops to decrease in rainfall as the technology gradually improves soil properties including water retention capacities.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Few individuals did by their own.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Fix problem of soil acidity. |
| Increases crop production from a given land unit. |
| Increase biomass production and improve soil structure. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improve land users understanding of SLM. |
| Motivate farmers to share cost for accessing the inputs or purchase it by their own. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Demands a relatively higher amount to effectively treat a given land unit. | The land users need to treat their land on a gradual basis. |
| Difficult to transport large size of lime to the farm. | Need to mainstream well the cost-benefit of using lime to the land users. |
| Cost per 100 kg is high (about 500 ETB) | More subsidy is demanded from the government. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Low amount, and untimely supply of the inputs. | Serving providing organizations/governments need to increase the quantity of supply in time wanted by the land users. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/02/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil Acidity and its Management Options in Ethiopia: A Review. Golla, A. S. 2019. DOI:10.18535/ijsrm/v7i11.em01
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.ijsrm.in › index.php › ijsrm
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Leta, G., Schulz, S., Alemu, G. 2020. Agricultural extension approach: evidence from an Integrated Soil Fertility Management project in Ethiopia. Frontiers of Agricultural Science and Engineering, 7(4): 1-13. DOI: 10.15302/J-FASE-2020331
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://journal.hep.com.cn/fase
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
SUSTAINABLE LAND MANAGEMENT PROGRAM (SLMP) TRAINING SERIES: FIELD GUIDE TECHNICAL IMPLEMENTATION INTEGRATED SOIL FERTILITY MANAGEMENT
URL:
www.slmethiopia.info.et
7.4 一般注释
Page 13 crop rotation and intercropping interpolated, or the computer-based one does not matched with a paper-based questionnaire.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) [埃塞俄比亚]
A Farmers Research and Extension Group (FREG) engages about 50 or more farmers in a kebele (lower administrative unit), with three sub groups of 17-20 each who live in a homogenous landscape. It is a local institution established for joint learning, piloting, and evaluating soil improvement technologies across the intervention …
- 编制者: GERBA LETA
模块
无模块