Lime application to acid soils [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: William Akwanyi
- 编辑者: JUSTINE OTSYULA, Innocent Faith, Noel Templer
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6702 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Wekesa Maryann Nanjala
Lukina Women Group - Welthungerhilfe farmer group
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil protection and rehabilitation for food security (ProSo(i)l)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Alliance Bioversity and International Center for Tropical Agriculture (Alliance Bioversity-CIAT) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
There have been no adverse effects on the environment in the area since lime was applied to the demo site in 2022.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Lime application is a rapid way to treat soil acidity and improve productivity.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Liming is the application of soil conditioners, including marl, chalk, limestone, burnt lime, or hydrated lime to the soil to raise its pH; thus, reduce its acidity. Calcium (Ca) and magnesium (Mg)-rich materials are the most used – the Ca or Mg increase the base saturation in the soil hence neutralizing soil acidity that is often caused by the effects of acids from nitrogen (N) fertilizer, slurry, and high rainfall. Liming improves soil fertility by increasing the activity of beneficial earthworms and improving soil structure. It is a source of Ca, and by raising the pH of soils it increases uptake of plant nutrients.
The soil must be tested to determine its pH level. Lime should be applied to soils with pH levels below 5.0, but especially to soils with pH below 4.0 which are very acidic. High concentrations of acids decrease the availability of plant nutrients, especially phosphorous (P) and molybdenum (Mo) and increase the toxic effect of aluminium (Al) and manganese (Mn). In addition, acidity causes some plant nutrients to be leached below the plant rooting zone.
A farmer must wear protective clothing, including face masks, goggles, gumboots, gloves, and an apron before working with lime. The best time to apply agricultural lime to any piece of land is during the dry season. The lime must be covered with soil immediately after application to prevent loss through evaporation, since it is highly volatile. If lime has to be applied during the rainy season, the farmer must apply the lime just before it starts to rain so that the rainwater can leach the lime into the soil. Agricultural lime can be applied in three ways:
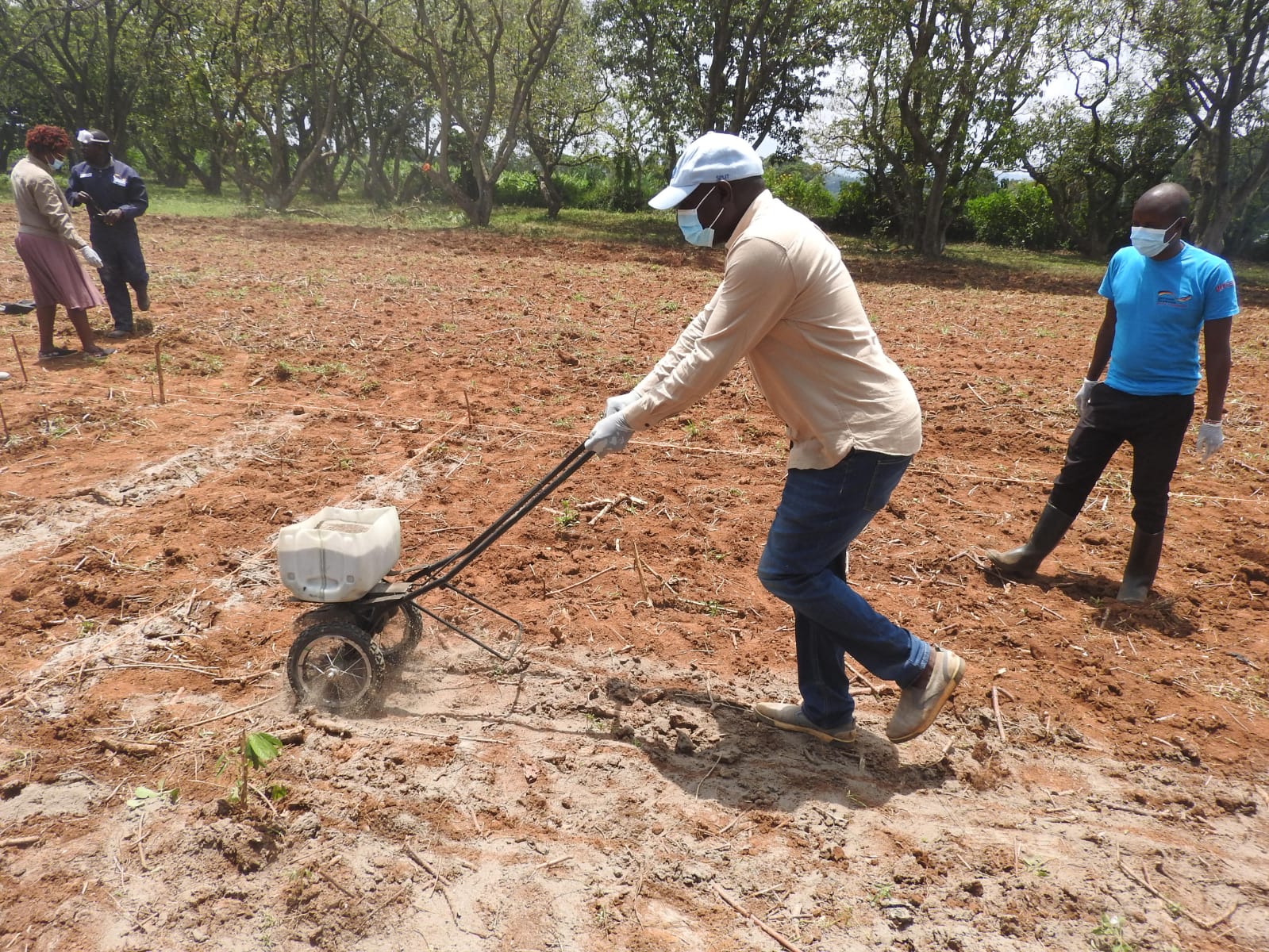
a) Broadcasting with a spreader. The land must be ploughed immediately to cover the lime and to prevent loss through evaporation.
b) Band method: Lime is applied between crops if it was not applied before land preparation. The lime must also be covered with soil immediately.
c) Spot method: Lime is applied at the base of the crop (similar to top dressing). Similarly, the lime must also be covered with soil immediately.
Farmers like agricultural lime because it improves soil structure and larger particles are formed in a process called flocculation. In addition, lime binds the larger particles of humus producing a good crumb structure. This improves soil drainage by creating more air spaces. Thus, the soil become easier to cultivate and plant root growth is facilitated. One acre (0.4 ha) of land with a pH of below 4.0 requires 300-350 kgs of lime; a pH of between 4.0 and 5.0, requires 200–250 kgs.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Bungoma County in Western Kenya
有关地点的进一步说明:
Luuya Bwake Ward, Kabuchai Sub-county
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
There are not protected areas in the area where the technology is implemented.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Introduced by the ProSoil Project under a Soil Health Programme.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- legumes and pulses - lentils
- 油料作物 - 花生
- 根/块茎作物 - 红薯、山药、芋头/椰子,其他
年作制度:
玉米/高粱/谷子与豆类间作
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- 饲料作物 - 草
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 水果、其他
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- 木瓜
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Crops are grown during the long and short rain seasons.
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Maize/ millet and legumes (beans) or groundnuts.
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Part of the land is left fallow during the short rains.

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- 家禽
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Manure from livestock is applied to the crop field.
产品和服务:
- economic security, investment prestige
- 蛋类
- manure as fertilizer/ energy production
- 肉类
- 奶类
品种:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
计数:
3
品种:
家禽
计数:
10
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
There is drip irrigation using plastic bottle for bananas.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理

管理措施
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
- M7:其它
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化
- Cp:土壤污染

物理性土壤退化
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降

生物性退化
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.4 ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
KES
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
124.21352
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil testing | In preparation for liming |
| 2. | Lime acquisition | In preparation for liming |
| 3. | Acquisition of personal protective equipment clothing (PPE) | In preparation for liming |
| 4. | Lime application | Before soil disturbance through ploughing/ before rains |
| 5. | Ploughing/ covering lime | After lime application |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Lime application | Man-days | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Ploughing/ covering lime | Man-days | 15.0 | 300.0 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | PPE | Set | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Lime | 50 kgs bag | 20.0 | 300.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Soil testing | Sample | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 14900.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 119.95 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Regular testing | Every 3 years, after 6 months if all required lime was not applied |
| 2. | Lime acquisition | In preparation for liming |
| 3. | Reapplication | Dependent on soil test results |
| 4. | Ploughing/ covering lime | After lime application |
注释:
No maintenance has been done so far.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Lime application | Man- days | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Ploughing/ covering lime | Man- days | 15.0 | 300.0 | 4500.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | PPE | Set | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Lime | 50 Kg bags | 3.0 | 300.0 | 900.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Soil testing | Sample | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 9800.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 78.9 | |||||
注释:
No maintenance has been done so far. The indicated costs are for information purposes. Reapplication is dependent on recommendations of soil testing. It is assumed that reapplication will require a smaller amount of lime than the initial application.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Rate of man-days and costs vary from one place to another, farmer to farmer, and with type of work. Costs for maintenance are subject to change with time.
Exchange rate for February 2023, source: European Commission/ InfoEuro online at https://commission.europa.eu/funding-tenders/procedures-guidelines-tenders/information-contractors-and-beneficiaries/exchange-rate-inforeuro_en
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1200.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Monthly rainfall variability is high with some months such as January recording less than 5 mm of total rainfall.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Bungoma Meteorological Station
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
The climate in the area favours most agricultural activities.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The farm is located at an area that is higher in altitude compared to other areas in the larger area. The farmer's field lies at an elevation of 1,505 m above sea level.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
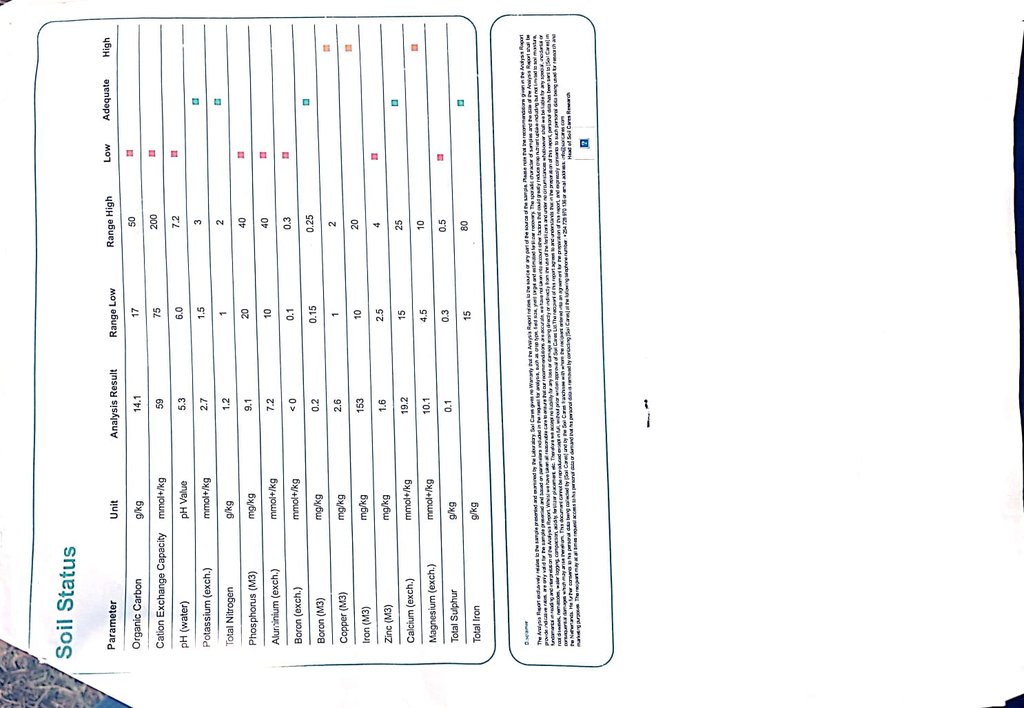
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
pH = 5.3, Cation Exchange Capacity = 59 mmol+/kg, nitogen = 9 g/kg, SOC = 14.1 g/kg
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
There are several boreholes in the area and according to interviews with some borehole owners, the depths are not more than 50 metres.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Most farms are under crops and trees; hence, the area has high agrobiodiversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
The above rating varies from one village to the other.
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
3
SLM之后的数量:
9
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the number of 90 Kg bags of maize produced per acre.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Not easy for the farmers to quantify.
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
6
SLM之后的数量:
10
注释/具体说明:
Quality refers to the number of bunches/ loads of harvested napier grass.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Not easy for the farmers to quantify.
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
40
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the percentage probability of the crop failing to do well.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Not easy for the farmers to quantify but the farmer says that it is easier to work on the soil since lime was applied.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
3,500
SLM之后的数量:
6,000
注释/具体说明:
The farmer used to buy 1 bag of 50 Kg DAP for the 1 acre. The test results recommended that she applies 2.5 bags of 50 Kg NPK. This increased the expenditure on fertilizer.
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
6,000
SLM之后的数量:
15,000
注释/具体说明:
She used to sell 2 bags of 50Kgs of maize at KES 3,000/- but after improved production she was able to sell 5 bags at the same price.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Not easy to quantify but the work has slightly increased due to the need to apply lime.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
2
SLM之后的数量:
1
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the number of months in a year when there is total lack of food in the house, and the farmer has to buy all the food required in the house.
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
30
SLM之后的数量:
70
注释/具体说明:
Quantity refers to the estimated percentage of knowledge in SLM/ land management.
生态影响
土壤
酸度
SLM之前的数量:
5.3
SLM之后的数量:
Not known
注释/具体说明:
The has not done a confirmatory test but it is clear that the pH has reduced due to the improved production.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
None noted
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
About 30 households
注释:
Still in demonstration stage.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improves crop yields. |
| Efficiency in use of fertilizers. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Makes it easier to work on land. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High cost of PPE. | The farmer should budget for and plan to buy the PPE early before time of application. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Limitation in accessing soil testing facilities/ services. | Create awareness about and link farmers to existing soil testing facilities/ services. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Visit to demo farms.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Interview with members of Lukina Women Group. Follow-up questions on phone with the contact person, Maryann Wekesa.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
ProSoil team and project implementers from WHH consulted.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/02/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Liming effects on soil pH and crop yield depend on lime material type, application method and rate, and crop species: a global meta-analysis
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Free download at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327188728_Liming_effects_on_soil_pH_and_crop_yield_depend_on_lime_material_type_application_method_and_rate_and_crop_species_a_global_meta-analysis
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Soil Acidity and Liming
URL:
https://www.ctahr.hawaii.edu/oc/freepubs/pdf/pnm10.pdf
标题/说明:
Bungoma County Integrated Development Plan, 2018-2022
URL:
Free download at https://www.devolution.go.ke/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/Bungoma-CIDP-2018-2022.pdf
7.4 一般注释
1. Provide a function to be able to link the documented SLM to similar work that has been documented in other databases e.g., LandPortal, etc.
2. Some of the impacts (section 6) cannot be quantified.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块