Agroforestry and Reforestation for Improved Livelihoods and Ecosystem Services [印度尼西亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Siti Indriani
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Tree Planting or Agroforestry
technologies_7142 - 印度尼西亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Land Use Based Mitigation for Resilient Climate Pathways (LANDMARC)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Sustainability & Resilience company (su-re.co) - 印度尼西亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
It can be declared a sustainable land management technology
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
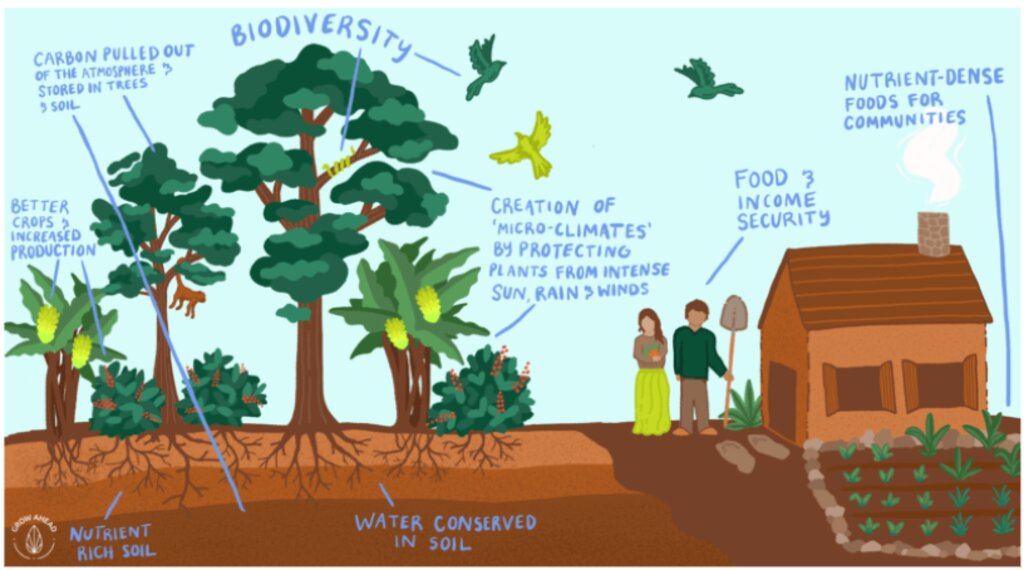
Approximately 20,000 hectares of degraded land is being rehabilitated land using assisted natural regeneration, enrichment planting and agroforestry. The resultant secondary forests and agroforests will have high values for ecotourism, sequester substantial amounts of carbon, produce a range of in-demand commodities (e.g., coffee, spices), generate bioenergy, and offer improved ecosystem services.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A partnership of local communities and governments is, in collaboration with international and national development organizations, donors and investors, rehabilitating approximately 20,000 hectares of degraded forest and agricultural land using assisted natural regeneration, enrichment planting and agroforestry. The resultant secondary forests and agroforests will have high values for ecotourism, sequester substantial amounts of carbon, produce a range of in-demand commodities (e.g., coffee, spices), and generate bioenergy. They will also offer improved ecosystem services to Bali as a whole, which will be very valuable for the tourism industry, representing an opportunity for investment and payment for ecosystem services (PES).
In the first 20 hectares, around 1,600 trees were planted per hectare, consisting of Coffee Arabica Katimor and Local Avocado trees. In between, shrubs such as local cassava and root species already existed. The spacing followed recommendations from ICCRI (Indonesian Coffee and Cacao Research Institute) whereby 2-3 meters distance are placed in between coffee trees, with much further distances for the shade trees. For fertilization, local goat manure is primarily used and filled in the planting holes the size of 30cm x 30cm x 30cm.
Northeast Bali, Indonesia — which includes the Batur UNESCO Global Geopark — features approximately 135,000 ha of degraded land in the Government’s Forest Estate (‘Kawasan Hutan’), which is managed by the provincial government’s Forestry and Environment Agency (Dinas Kehutanan Dan Lingkungan Hidup Provinsi Bali/DKLH).
The vegetation, soils and water resources are designated as ‘potentially’ to ‘very severely’ degraded on 463,500 hectares. This is steadily increasing owing to unsustainable forestry and farming practices. Local communities within and surrounding the Kawasan Hutan — among the poorest in Bali — are affected by droughts, flash floods, landslides and poor water quality.
The Geopark in Northeast Bali was established in 2012 on the active volcanic landscape of Mt Batur, which features not only unique and dramatic geological formations, protected forests and endemic flora and fauna but also 15 villages. Approximately 90% of the Geopark is classified as severely degraded owing to a lack of post-eruption rehabilitation and unsustainable farming practices. The Geopark received almost one million visitors in 2019.
The ten-year project will be implemented by a consortium consisting of Sustainability and Resilience Co. (a local NGO), Indonesian government (through DKLH), local university (Udayana), international research-in-development organization (CIFOR-ICRAF), specialist national research organizations, intergovernmental organization, larger private sector and investment partners, each bringing a specific set of skills and expertise.
The work will be carried out through four major components.
1. Establishment of a coordinated enabling environment through a multistakeholder forum of local governments, national and provincial government agencies, communities, larger private sector and project consortium members.
2. Co-designing and co-implementing models of integrated ecosystem and livelihoods restoration that suit local socio-economic and environmental conditions with staged expansion over the ten years.
3. Training communities, local small businesses and Government staff in co-design, establishment and management of restored, productive ecosystems and value chains.
4. Strengthening and further introducing partnerships between the community, public and private sectors in all aspects of the landscape, including co-developing and co-implementing an enabling investment environment for continuing financial flows.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
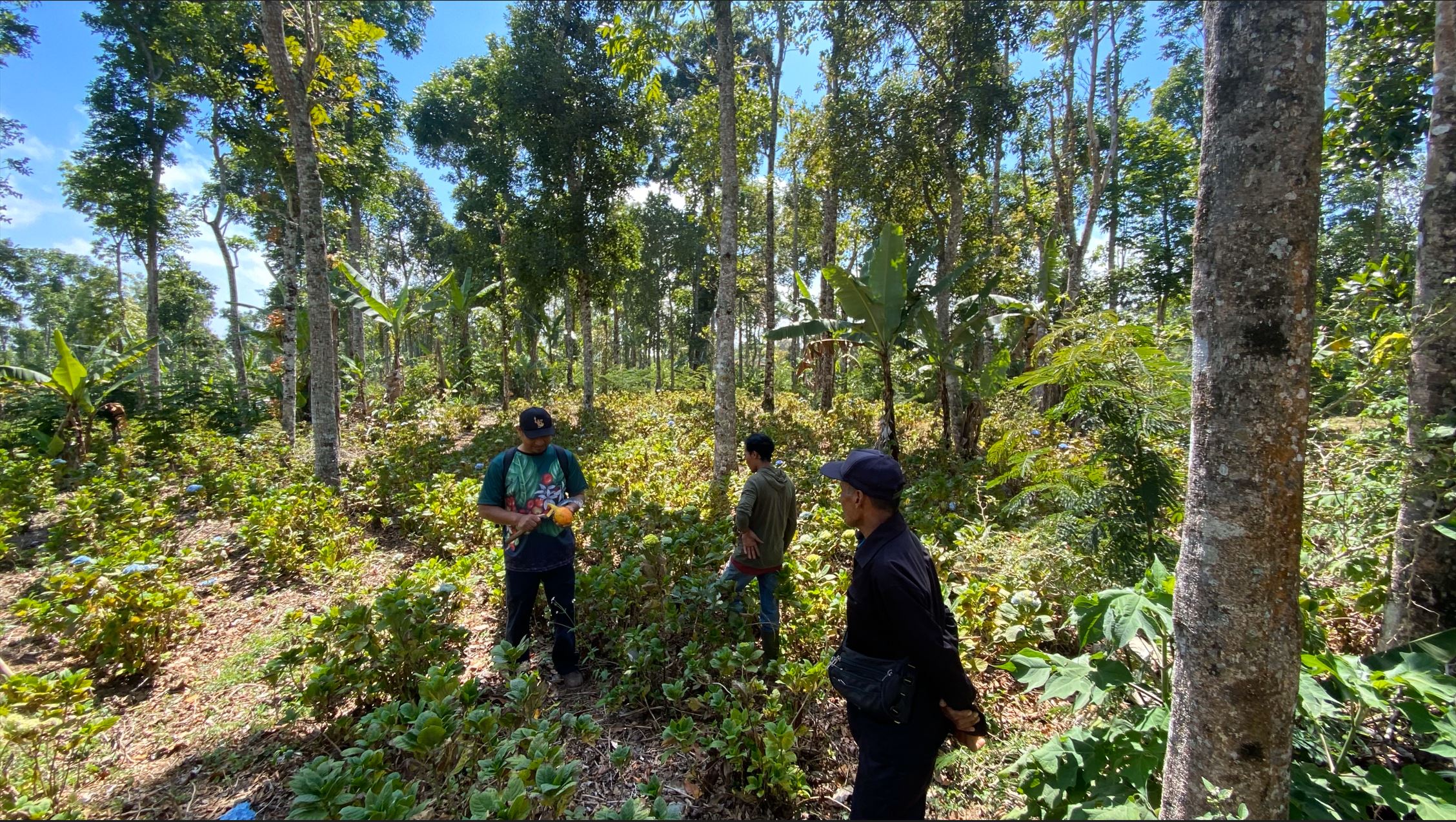
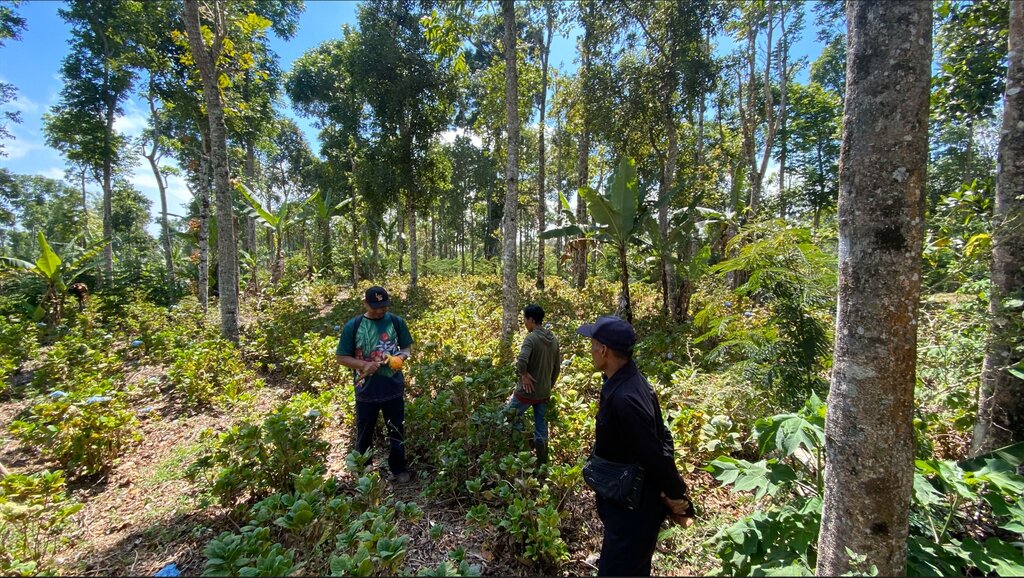
Degraded area in Wanagiri, Bali, as a pilot location
日期:
04/06/2024
位置:
Wanagiri, Bali, Indonesia
摄影师的名字:
Fabian Wiropranoto
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度尼西亚
区域/州/省:
Bali
有关地点的进一步说明:
Wanagiri, Northeast Bali
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
Batur UNESCO Global Geopark
注释:
Batur UNESCO Global Geopark
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2024
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Training communities, local small businesses, and Government staff in the co-design, establishment, and management of restored, productive ecosystems and value chains.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 轮垦
(半)天然林类型:
- 热带山地系统自然植被
树木类型:
- 金合欢树种
- 银合欢
- 大叶桃花心木
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 常绿
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 水果和坚果
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
注释:
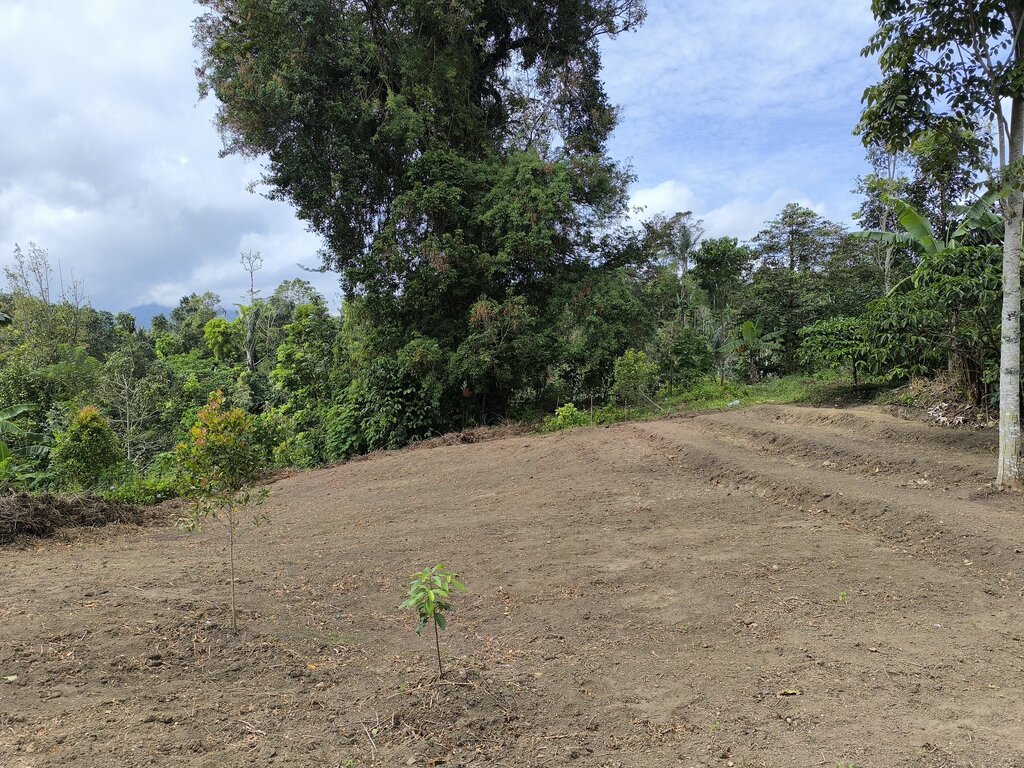
Degraded or unproductive land in Wanagiri, Bali, Indonesia
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

不毛之地
具体说明:
Underutilized forest land
注释:
Agroforestry
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A5:种子管理,改良品种

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V3:植被的清理
- V5:其它

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
- S9:动植物庇护所

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Agroforestry practices
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
In the first 20 hectares, around 1,600 trees were planted per hectare, consisting of coffee arabica Katimor and local avocado trees. In between, shrubs such as local cassava and root species already existed. The spacing followed recommendations from ICCRI (Indonesian Coffee and Cacao Research Institute) whereby 2-3 meters distance are placed in between coffee trees, with much further distances for the shade trees. For fertilization, local goat manure is primarily used and filled in the planting holes the size of 30cm x 30cm x 30cm
20 ha is the pilot area
Spacing between plants [m]
Avocado: 5x5
Coffee: 3x3
Vertical vegetative measures [m]
Avocado:
Coffee:
Lateral gradient of structures
Density of plants per ha
Avocado: 20
Coffee: 50
作者:
Bruno Bordoni
日期:
30/05/2024
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
20 ha as the pilot case
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha = 2.47 acres
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
600.0
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey | Month 1-2 |
| 2. | Stakeholders Engagement | Month 3-4 |
| 3. | Climate Field School | Month 4 |
| 4. | Nursing Establishment | Month 5-7 |
| 5. | Initial Tree Plantation | Month 8 |
| 6. | Fertilizing and Biocides | Month 8 |
| 7. | Maintenance | Month 9-12 |
| 8. | Tree Planting | Month 13 |
| 9. | Fertilizing and Biocides | Month 13 |
| 10. | Maintenance | Month 14-17 |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Workers and Researchers | 1000 | 20.0 | 1000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | 500 | 40.0 | 500.0 | 20000.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic fertilizer | 60 | 100.0 | 60.0 | 6000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Nursery | 1000 | 14.0 | 1000.0 | 14000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 60000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 100.0 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
60000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Project donors and grants will cover all costs
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fertilizer | Once per year |
| 2. | Transportation, accommodation for fertilizing and stakeholders engagement | Once per year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Transportation, accommodation in the 1st year | Package | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Transportation, accommodation in the 2nd year | Package | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Transportation, accommodation in the 2nd year | Package | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Goat manure in the 1st year | kg | 400.0 | 0.2 | 80.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Chicken manure in the 1st year | kg | 400.0 | 0.1 | 40.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Goat manure in the 2nd year | kg | 400.0 | 0.2 | 80.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Chicken manure in the 2nd year | kg | 400.0 | 0.1 | 40.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Goat manure in the 3rd year | kg | 400.0 | 0.2 | 80.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Chicken manure in the 3rd year | kg | 400.0 | 0.1 | 40.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1110.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1.85 | |||||
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
1110.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The project donors and grants will cover all the cost
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Climate or seasonal change will affect the fertilizing time and will affect the annual cost for fertilizer
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Staklim Bali
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Lenght of Growing Period > 270
Tropical
Oct-March: wet season
April-Sept: dry season
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Andosols (volcanic soil)
Rich organic matter
Highly porous
Dark coloured
Developed from parent material of volcanic origin
Low pH
High porosity
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Wanagiri forest
67 plant species
Agroforestry systems involve growing crops and trees together, which can increase the overall biodiversity of the area.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
注释:
52.64% primary education
35.51% lower secondary and upper secondary
11.85% undergraduate and graduate school
Technical assistance
Employment
Markets
Energy
Road and transport
Drinking water and sanitation
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
0 ha
SLM之后的数量:
20 ha
注释/具体说明:
This is calculated per 20 ha of the pilot area.
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
1 income source
SLM之后的数量:
2 income sources
注释/具体说明:
Per 20 ha
社会文化影响
文化机会
SLM之前的数量:
0 activity
SLM之后的数量:
3 activities
注释/具体说明:
Traditional rituals in 20 ha of the pilot area
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
SLM之前的数量:
30%
SLM之后的数量:
75%
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
5 types
SLM之后的数量:
10 types
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
Organisational Support
SLM之前的数量:
0 organisation
SLM之后的数量:
10 organisations
注释/具体说明:
Per 20 ha
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 适度 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Enabling environment for investment in tree-product supply chains
Readily investable business plans and economically viable restoration models targeting profitable species, such as Pongamia, Bamboo, Coffee
Carbon credits
A landscape of integrated restoration, bioenergy, and payment for ecosystem services.
At least 10,000 male and female farmers trained in assisted natural regeneration, enrichment planting, climate-smart agroforestry, bioenergy and other productive practices.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
Yes, they voluntarily did the tree planting
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
By applying intercropping, farmers will have more products variants, e.g. potatoes, chillies
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Quality germplasm from commercially viable nurseries (coffee, avocado, cassava, jackfruit, lamtoro) |
| Landscape restoration |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Community engagement |
| Carbon credits |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Reduced crops production due to lack of capacity and resources to maintain | Monitoring, evaluation, and maintenance |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Natural Disaster | Risk Mitigation |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
30
- 与土地使用者的访谈
20
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
10
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
21/10/2024
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
N/A
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Let's restore 43,000 ha of Bali
URL:
https://www.su-re.co/tree-planting
7.4 一般注释
Envision a revitalized Bali where degraded lands bloom once more, fostering sustainable farming, robust ecotourism, and enhanced ecosystem services.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块