Climate Resilient Irrigation Scheme [不丹]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Tshering Yangzom
- 编辑者: chenga Tshering
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Nam Shi Thub Pai Zhing Chhu Yu Wa (གནམ་གཤིས་ཐུབ་པའི་ཞིང་ཆུ་གཡུར་བ།)
technologies_6849 - 不丹
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Dorji Sonam
NA
不丹
土地使用者:
Chedup Tenzin
NA
不丹
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Strengthening national-level institutional and professional capacities of country Parties towards enhanced UNCCD monitoring and reporting – GEF 7 EA Umbrella II (GEF 7 UNCCD Enabling Activities_Umbrella II)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric (National Soil Services Center, Department of Agric) - 不丹1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A climate-resilient irrigation scheme is one that aims to successfully cope with and manage the impacts of climate change while preventing those impacts on the scheme from growing worse. The pipes are retrofitted with new and climate-resilient technology. Such a climate-proof irrigation system is designed to better withstand extreme weather conditions.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
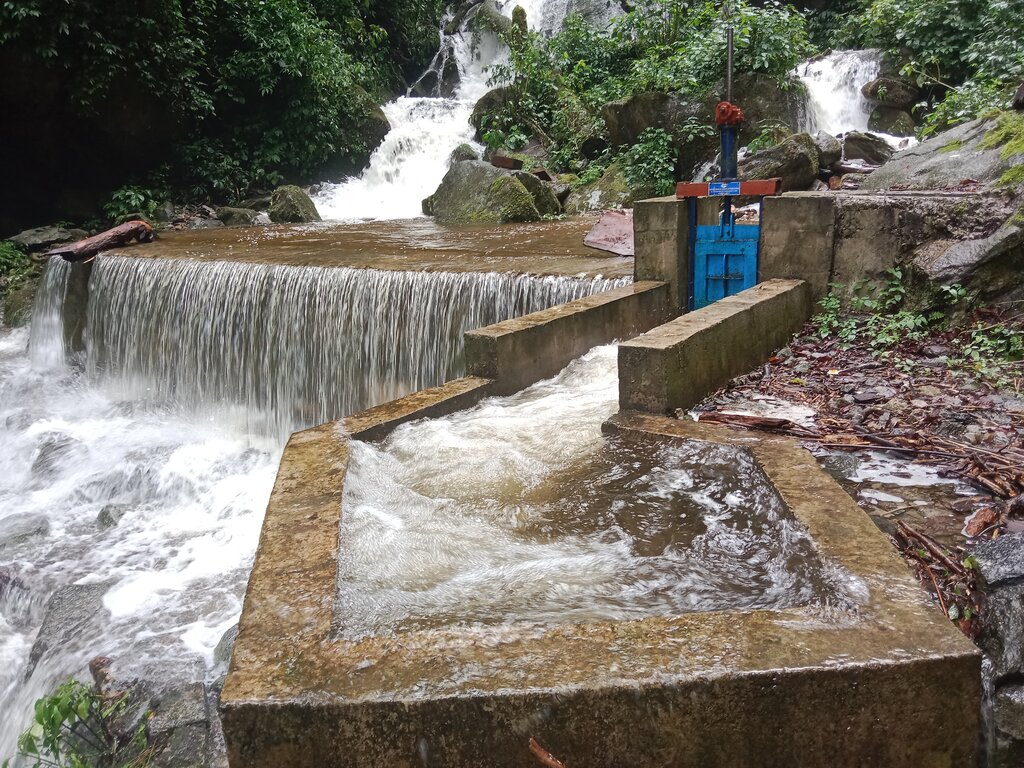
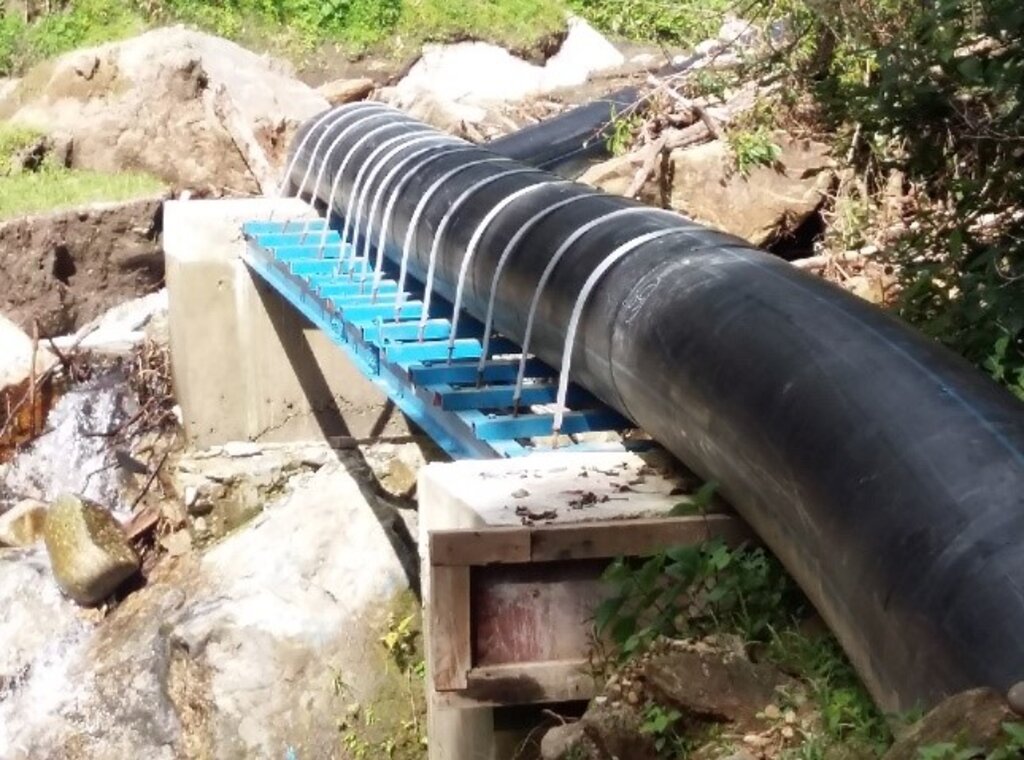
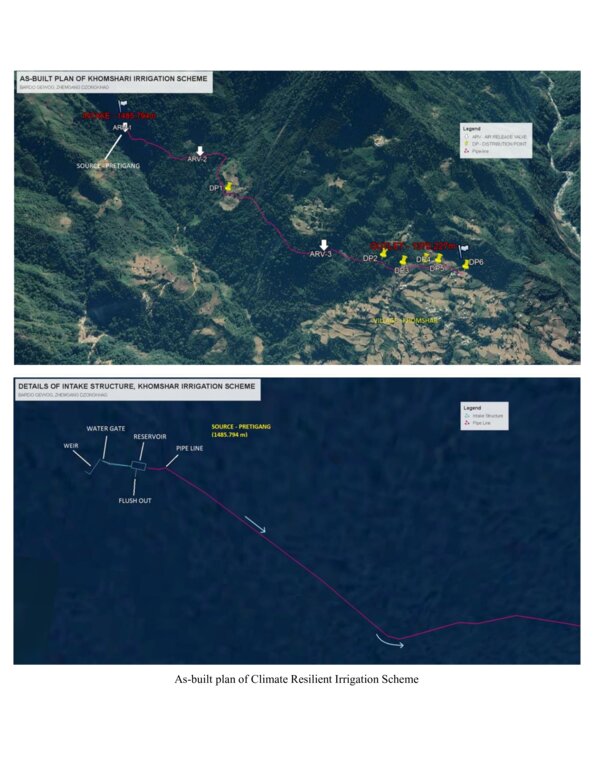
The climate-resilient irrigation scheme in Khomshar Chiwog under Bardho Gewog (Block), Zhemgang Dzongkhag (District), was funded by the Green Climate Fund (GCF), UNDP-Bhutan. The 3.9 km irrigation system was designed with a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) pipe system benefiting 150 households with a command area of 955 acres (approx. 386 ha). The total irrigation cost incurred was Nu. 18,055,180 (approx. USD 225,700) and was completed in 11 months (7 December 2020 - 7 November 2021). The irrigation scheme was officially handed over to the community on 27 August 2021, upon the formation of a water-user group (WUG).
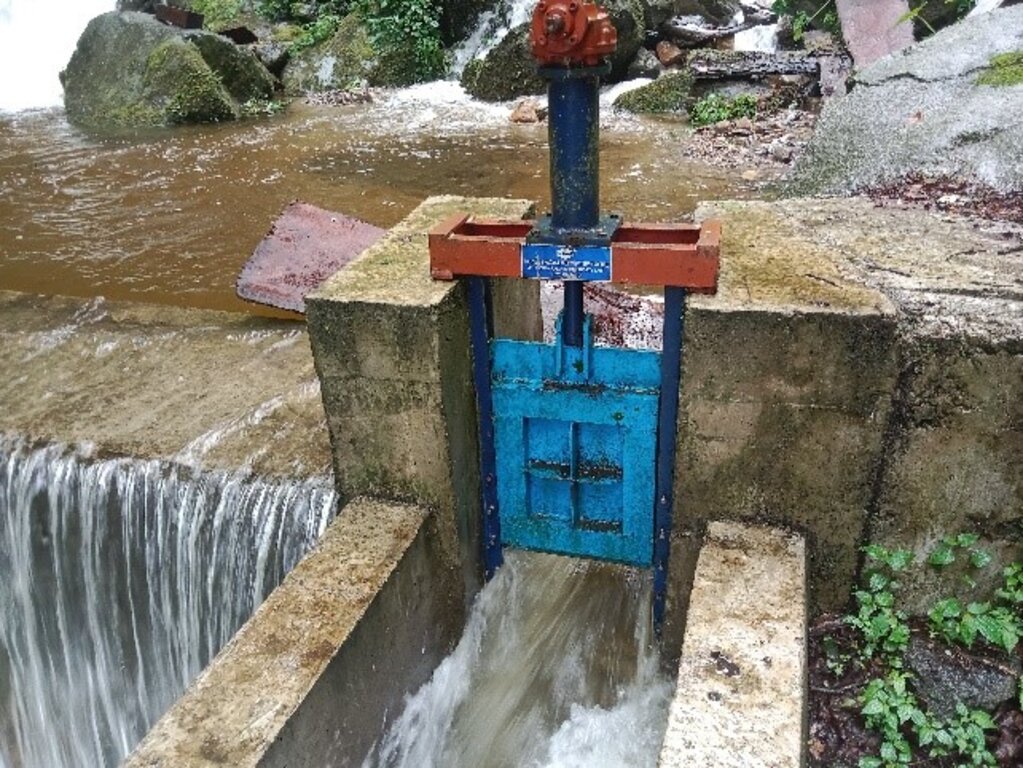
The smart irrigation system consists of key components, viz. intake, sluice gate, silt-cum-inlet tank, flush-out valves, air release valve, water distribution points, and tail point. The intake collects and diverts the water from the source to the sluice gate. The land users were taught to maintain the intake by regularly clearing it from bushes and removing debris. The sluice gate controls the flow of the water into the tank based on the water requirement. The silt-cum-inlet tank holds the water to settle out sediments and debris before clean water flows through the pipe at a constant rate. Flush out valves clear the sediment and debris from the tank. The air release valve vents out the air trapped in the pipe and water distribution points. Water distribution points deliver water to the users, as required, up to the tail point where water is discharged.
The irrigation scheme fulfils the need for a continuous water supply for both drinking and irrigation purposes. To ensure sustainability, a WUG headed by a chairman, a secretary, and a treasurer was instituted. The WUG ensures operations, maintenance, and harmonious distribution of water. The group is also responsible for the safety of the irrigation system.
The main reason for considering such irrigation scheme as being “climate resilient” is that unlike open earthen channels, this type of irrigation scheme results in zero loss of water through evaporation and leakage, as it is a closed channel. Furthermore, being closed, it is not prone to blockages caused by landslides triggered by rainfall. There is also complete end-to-end management, i.e., management at source including the watershed, and management at tail-end.
The irrigation scheme was constructed by a private company through a contract award: community members were not involved. The irrigation scheme was also accompanied by a land development programme (bench terracing) by a separate contractor, with the prospect of transitioning to irrigated paddy cultivation in the future after adequate soil stabilization. More than 90 acres (36 ha) of fallow lands were revived. This blended approach was applied to ensure the food self-security/sufficiency of the beneficiaries.
Though at a very initial stage, the construction and operation of the irrigation scheme have brought happiness to the beneficiaries. They expressed their hope and expectation of improved crop production, stable and reliable water availability, and major fallow land reversion.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
不丹
区域/州/省:
Khomshar Chiwog, Bardho Gewog, Zhemgang Dzongkhag
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2021
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The climate-resilient irrigation scheme in the community was supported by a GCF Project, which is a six-year project from 2019-2025. The project promotes climate resilient agricultural practices, integrates climate change risk data into water and land management to support smallholders, and reduce the risk and impact of climate change-induced landslides during extreme events that disrupt market access.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 水稻(湿地)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
- herbs, chili, capsicum
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Maize double cropping
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 选伐
- 非木材森林的利用
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 混合落叶或常绿
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 放牧/啃牧
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

其它
具体说明:
Shrubland
注释:
The land use system has changed due to the technology introduction. About 90 acres of shrubland were converted to terraces with the use of an excavator machine, to transition to wetland cultivation in the coming years. Currently, these terraces are in the stabilization stage with the production of dryland crops.
注释:
The land use system has changed due to the technology introduction. About 90 acres of shrubland were converted to terraces with the use of an excavator machine, to transition to wetland cultivation in the coming years. Currently, these terraces are in the stabilization stage with the production of dryland crops.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
The land users depend both on the irrigation system and the rain for farming.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Source: https://www.bhutangcf.gov.bt/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Khomshar-WUA_Training-Report.pdf
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Irrigation line
指定单位面积(如相关):
Irrigation line: 3.9 km
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Nu.
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
80.0
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
18055180.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Green Climate Fund
注释:
The cost breakdown is not possible as the activity was carried out through a contract award. However, with the total cost of the establishment being Nu. 18,055,180 (approximately USD 225,700) with a command area of approximately 386 hectares, the amount incurred per ha of irrigable land is around USD 585.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replacement of pipe | One time (just after the completion) |
注释:
The irrigation scheme was handed over to the community on 14 May 2022. As of now, no major maintenance activities were required except for a portion of pipe replacement (the break down occurred due to a falling boulder), and a few occasional sediment clearing.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
48000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Royal Government of Bhutan (Gewog budget)
注释:
The exclusive pipe replacement expenditure was borne by the Gewog Office. The work was allocated to the same contractor.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Annual rainfall: 1200-1800 mm
The rain estimate has been derived based on the agro-ecological zone (AEZ) the area falls under. Bhutan is divided into six AEZs (source: https://www.fao.org/3/ad103e/AD103E02.htm).
Bhutan has six AEZs. The wet sub-tropical zone is from 150 to 600 m, followed by the humid sub-tropical zone from 600 to 1,200 m. The dry sub-tropical zone starts at 1,200 m and extends to 1,800 m, followed by the warm temperate zone, which reaches 2,600 m. The cool temperate zone lies between 2,600 and 3,600 m and, finally, the alpine zone between 3,600 m and 4,600 m.
农业气候带
Dry Sub-tropical Zone in Bhutan
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitude: 1319 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Moisture content-5.41%
Organic matter-5.48 %
Organic carbon-3.18%
pH-6.25
Electrical conductivity-368.97 µs/cm
Nitrogen-0.16
Phosphorus-0.33
Potassium-80.10 mg/100ml
Soil texture-Sand Clay Loam
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
The source of the water serve for both drinking and irrigation purposes.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The rich periphery environment, higher vegetation coverage, and evident agroforestry indicate high species and habitat diversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
The average land holding area of the community ranges from 5 to 6 acres, falling under large-scale based on the local context.
In general, the average household land holding in Bhutan is 3 acres.
In the local context:
3 acres (1.2 ha) = medium scale
> 3 acres = large-scale
<3 acres = small-scale
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
- Family land
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
The land use rights in Bhutan is based on a traditional legal system guided by formal land act and land rules and regulations.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
250-300 Drey from one acre paddy land
SLM之后的数量:
600-700 Drey from one acre
注释/具体说明:
The old conventional irrigation channel used to suffer multiple breakdowns quite often. Due to this most of the paddy fields were left fallow (30%) because of insufficient irrigation water. Currently, all the wetlands (100%) are brought under cultivation. Hence, the production has been enhanced.
Note: Drey is a traditional grain measuring container. One Drey is about 1.5 kg.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
The paddy harvest appears to be of better quality when there is enough irrigation. Otherwise, the growths are hampered, resulting in higher vegetative growths only.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
The higher hay production (by-product) has been beneficial for farmers to feed livestock.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Safe and readily available water to feed the livestock, facilitated by the irrigation scheme has enhanced animal production. Earlier, the farmers used to depend on the far-flung streams/ponds.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Better access to irrigation water has motivated farmers to adopt land development. Hence, about 90 acres of fallow lands in the community have been revived through new terrace constructions.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
The irrigation water is being used for drinking purposes too. The drinking water quantity has been enhanced. Earlier, the drinking water source was not enough to meet the requirements due to higher households, especially in winter.
饮用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
The drinking water tapped from this irrigation is clean and hygienic, unlike before.
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Due to new terrace construction, the demand for irrigation water has increased.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
One acre of paddy cultivation used to take 4-5 days. Now, one acre takes 1 day. Mechanization is enhanced.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Currently, the impact is at the initial stage (1 year). The income could quantified in the later years.
社会文化影响
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation and land development interventions have beautified the community (aesthetic). The external visitors are astonished.
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Community dispute over water demand and mid night water guarding during paddy cultivation due to water scarcity used to be rampant before.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
土壤
土壤水分
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
The conventional irrigation channel used to result in water seepage and accumulation of groundwater, leading to flooding of underneath fields. Now, this pipe irrigation has been solved and flooding is not evident.
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
Due to improper irrigation source management before, the water outflow was used to wash away a huge portion of lands and roads below. Due to enhanced source protection, this issue is solved.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 非常好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 非常好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
| 局地雷暴 | 非常好 |
| 局地风暴 | 非常好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 极端冬季条件 | 非常好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 滑坡 | 非常好 |
注释:
The respondents pointed out that the current rainfall pattern has changed compared to the past 10 - 15 years. Before, there used to be steady and enough rain. Now, the dry days continue for quite a long time and when rain comes, it's sudden and very heavy.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
150
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Enough irrigation and drinking water compared to earlier conventional system. |
| Fallow land reversion is being enhanced. |
| Cleanliness (social hygiene) due to better water availability. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Fallow land reversion is being enhanced. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Risk of source destruction due to landslide. | Shifting the current source tank to a different location. |
| No proper filtration at the source. Currently, a locally fabricated filter is being used. | Permanent filter is required. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The road leading to source, constructed exclusively to monitor the irrigation line is not being maintained well. | Timely road maintenance by the beneficiaries. |
| The source tank premise needs proper fencing to avoid casualties. | Fencing the irrigation source premises. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Two
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Two
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
12/07/2023
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Formation and Training Report on Khomshar Water-User Group and the Bylaws for the Khomshar Irrigation Scheme in Bardo Gewog under Zhemgang Dzongkhag
URL:
https://www.bhutangcf.gov.bt/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Khomshar-WUA_Training-Report.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块