Ked Forest Park: : a Prototype for Community Indigenous Plant Management [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Areerat Wangkaew
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7254 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
co-compiler:
Yamclee Pramote
Land Development Department
泰国
土地使用者:
Trirat Prempree
-
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Jintaridth Bunjirtluk
Land Development Department
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - 泰国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Centre of Excellence for Soil Research in Asia (CESRA)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
An urban community forestry park – the “Ked Forest Park” - has been established by a group of people who wanted to conserve and develop resources and the environment in Phra Pradaeng District. Planting and maintenance of indigenous, edible and medicinal plants are carried out.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
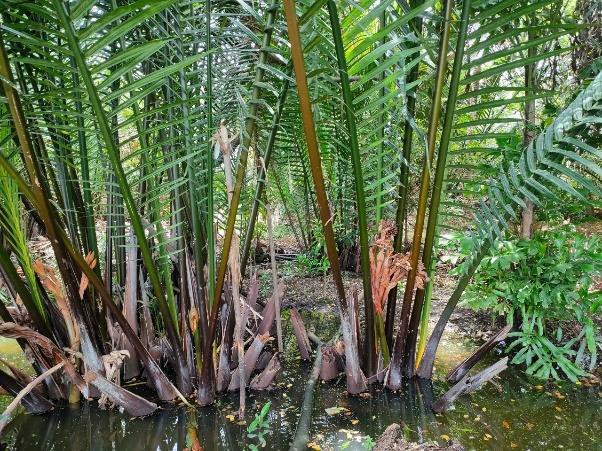
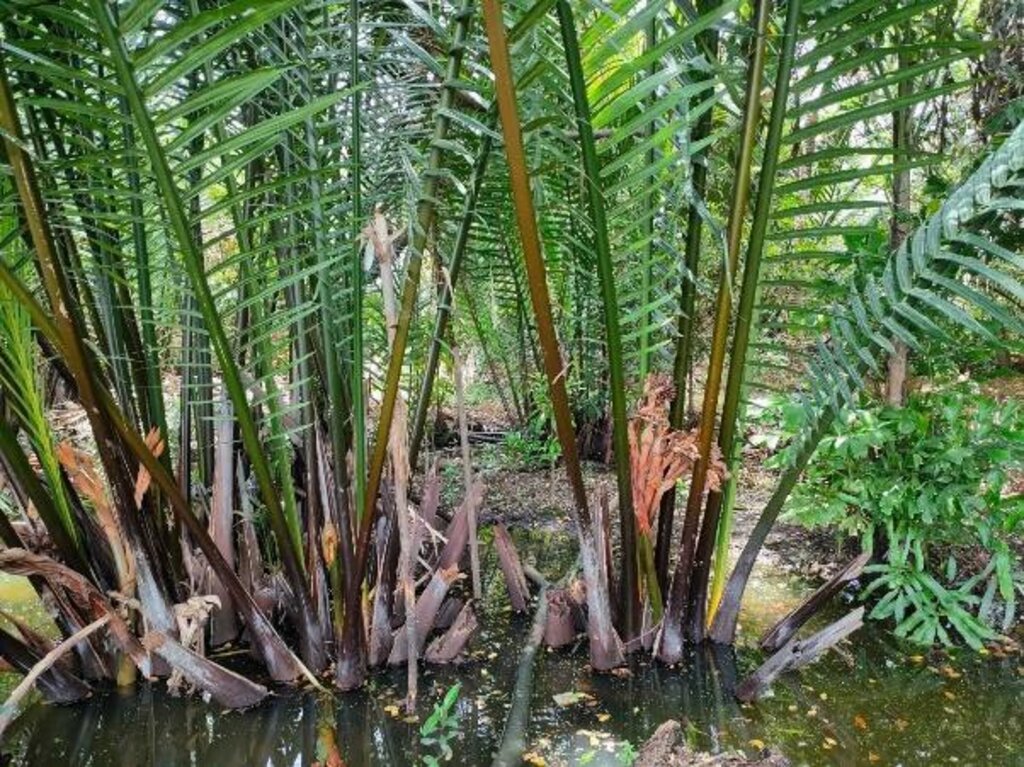
The story started with a small group of people in the area of Khung Bang Krachao. These people wanted to conserve the environment and develop resources in Phra Pradaeng District in Samut Prakan Province under an urban community forest park – the “Ked Forest Park”. It is state property land within the Metropolis. The community leader gathered people to conduct activities on the basis of natural resources and environment conservation. Many activities take place. For example, garden beds are cleaned and weeds removed. Planting and maintenance are conducted for indigenous edible and medicinal plants. This also includes collecting seeds of indigenous plants for propagation. Then, these seedlings are transferred to be planted in the forest park of urban communities.
The main purpose of this best practice is to conserve and propagate indigenous plant varieties, to have green areas available in the form of urban community forests for environmental restoration, to prevent and treat soil and water pollution and to make land use sustainable in a brackish water ecosystem. Products are cooked for tourists in the name of "indigenous vegetables, and local food". Apart from being responsible for taking care of conserving soil and water resources and increasing green areas, people in this community also transfer experiences and knowledge. Therefore, Ked Forest Park is considered to be a prototype of developing green-areas by communities. Currently, Suan Pa Ked (Ked Forest Park) is under the supervision of the Royal Initiative and Special Project Bureau, The Royal Forest Department in the form of a green area conservation network. This is promoting the public to participate in managing Khung Bang Krachao green areas in line with the concept of the Royal Initiatives of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn. There is cooperation between government agencies, the private sector and educational institutes. The participation of communities is most important because ultimately, the trees which everyone plants, will benefit them.
This area has the capacity to absorb a huge amount of carbon dioxide as reported by the Royal Forest Department. Due to these exceptional ecological benefits, it was recognized as "The Best Urban Oasis of Asia" by the Time Asia magazine in 2006.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
KED FOREST PARK
位置:
Samut Prakan Province
摄影师的名字:
Pramote Yamclee
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Samut Prakan Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Suan Pa Ked Nom Klao, Moo 2, Soi Petch Hueng 16, Song Kanong sub-district (Soi Wat Pa Ked), Phra Pradaeng District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
natural resources and environment conservation area
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2007
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology arises from land users’ innovation and is supported by external interventions and government agencies that acknowledge the value of technology to the community by providing resources, funding and supporting research and development.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

森林/林地
- 植树造林

水道、水体、湿地
- 沼泽、湿地
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地

水道、水体、湿地
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
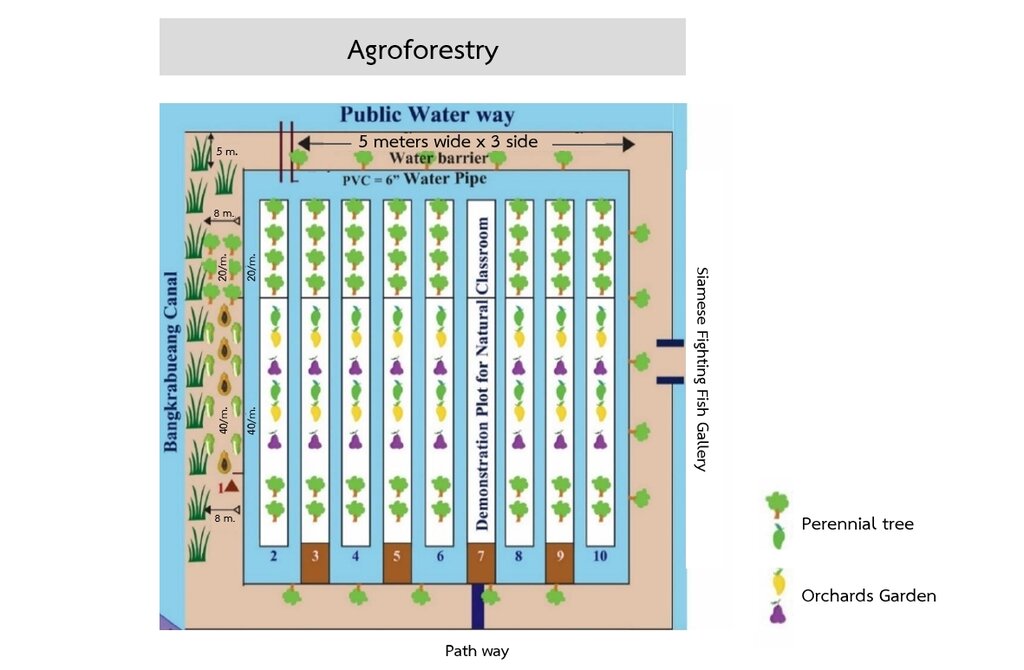
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Tree planting in the brackish forest area is carried out in three levels:
Primary trees: These are native species in the area, primarily mangrove trees, which are highly tolerant to brackish and saline water conditions that persist for over six months of the year. Examples of planted species include Tin Pet Nam (Cerbera odollam Gaertn.) and Indian Tulip Tree (Thespesia populnea).
Secondary trees: These include edible trees, both fruit-bearing and leafy vegetables, which are resistant to brackish and saline conditions. Examples are Tamarind (Tamarindus indica) and Neem (Azadirachta indica).
Herbal plants: These are various herbs that grow well under the shade of larger trees. Examples include Betel Leaves (Piper sarmentosum), Nightshade (Solanum indicum) and Pandan Leaves (Pandanus amaryllifolius).
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
2.56 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
6.25 rai
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
8.82 USD
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Main plants refer to local plants in the area, namely plants in mangrove forests which are tolerant to being brackish and salinity of natural water resources for more than 6 months per year. The plants grown are Cerbera odollam, Indian laurel, Bruguiera sexangul, Intsia bijuga, Thespesia populnea, cork tree and Copper pod. | |
| 2. | Secondary plants refer to edible plants for fruit trees and plants with edible leaves. These plants are tolerant to brackish conditions and salinity such as tamarind, neem, Cassod tree, Great morinda, Luna nut, Ardisia polycephala | |
| 3. | Medicinal plants thriving well under shade of big trees such as Piper Samentosum, Solanum incanum, Pandanus leaf, Cordyline fruticosa, Sea holly |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Deepen the garden ditch in the area of 2.56 ha | Bed | 50.0 | 17.6 | 880.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Water pump | Machine | 2.0 | 147.0 | 294.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Compost | Tonne | 30.0 | 29.4 | 882.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | 15-15-15 chemical fertilizer | Sack | 20.0 | 29.4 | 588.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Lime | Tonne | 10.0 | 88.2 | 882.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | 500 liter plastic bucked | BucKed | 5.0 | 58.8 | 294.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Water salinity meter | Machine | 2.0 | 29.4 | 58.8 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | 8 inch PVC with the length of 3 meters | Piece | 3.0 | 29.4 | 88.2 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Plant varieties including planting labor costs in the area of 2.56 ha | Tree | 10000.0 | 0.15 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Materials used in building the nursery including labor costs | Square meters | 20.0 | 29.4 | 588.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 6055.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 6055.0 | |||||
注释:
External organizations and government agencies contribute by offering essential financial and technical support to local communities.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | weed removal | |
| 2. | fertilizer application | |
| 3. | tillage | |
| 4. | planting for repairing and maintaining trees in the cultivation plot |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Management during planting and maintenance (1 year) | Force | 1.0 | 352.8 | 352.8 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Electricity costs | USD | 12.0 | 14.7 | 176.4 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 529.2 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 529.2 | |||||
注释:
External organizations and government agencies contribute by offering essential financial and technical support to local communities.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1. Labour cost
2. Agricultural materials costs
3. Construction materials costs
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1545.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
The soil is Samutprakarn soil series (Sm), soil series group 3. The parent material of soil is derived from marine sediments mixing with alluvial sediments. Soil reaction is moderately acidic to moderately alkaline (pH 6.6-8.0). The limitation factor of land-use is saline soil and be flooded by sea water.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
具体说明:
land-use is flooded by sea water
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
The area features a unique geography and environment, located within a horseshoe-shaped bend of the Chao Phraya River, which forms a natural buffer between urban Bangkok and its surroundings. This distinctive setting fosters a diverse range of aquatic, riparian, and terrestrial ecosystems, supporting a rich array of plant and animal life. Additionally, the region encompasses various habitats, including mangroves and wetlands that serve as vital refuges for numerous bird species, fish, and amphibians. The forested areas, with their abundance of native tree species, provide essential shelter and food for many wildlife species.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Planting trees in the ecosystem of brackish-water forests and aquatic animal culture have brought about a variety of plant varieties and animal species such as egret.
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Plants can lower groundwater levels, reducing salinity and waste water problems.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 减少 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| This technology contributes to environmental preservation and mitigates the burden of annual land ownership taxes, thereby promoting sustainable land use. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology aids in preserving soil and water fertility, restoring the environment, and sustainably expanding forested areas within urban communities. |
| Incorporating native plants and maintaining natural habitats can enhance biodiversity. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology has a relatively low economic return. | Developing land use practices in agriculture, fisheries, livestock, and other sectors is crucial. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology significantly impacts the environment, however, its importance is not fully recognized by the community. | It is essential to develop more diverse land use patterns in agriculture, environmental management, and the tourism industry to generate income and ensure sustainable land use. |
| Low adoption of people around the project plot. | Increase local engagement and interest by host workshops or information sessions to introduce the project, explain benefits, and address any concerns from locals. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
8
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
5
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Sustainable soil management practices in Asia
URL:
https://e-library.ldd.go.th/library/Ebook/bib10906.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块