Non-inversion tillage in UK arable cropping; Loddington [英国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
minimum tillage (English), conservation tillage (English)
technologies_986 - 英国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Soil and water protection (EU-SOWAP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Game & Wildlife Conservation Trust - 英国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/11/2004
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Participatory on-farm demonstration in UK arable cropping: Loddington [英国]
Provision of expert knowledge in appropriating equipment and setting up small scale on farm trials in collaboration with the land manager
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Surface cultivation of the top 10cm of soil but not complete inversion
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
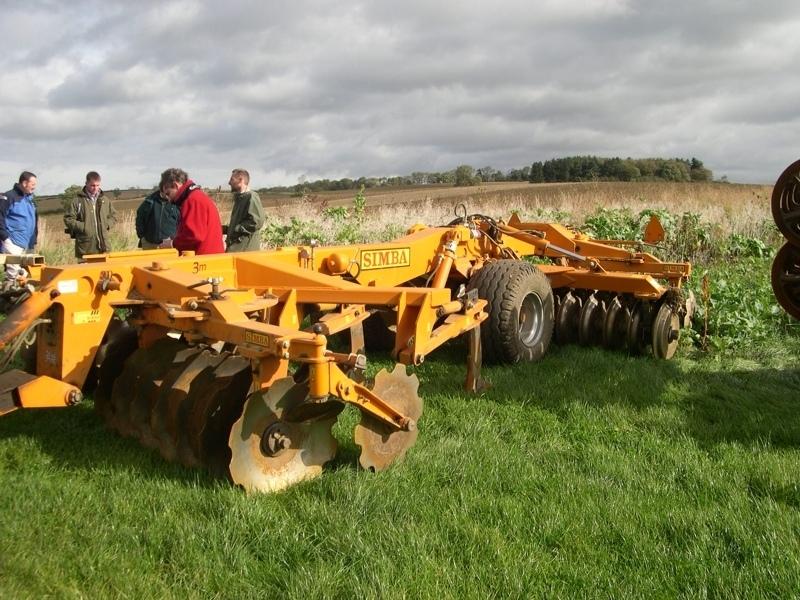
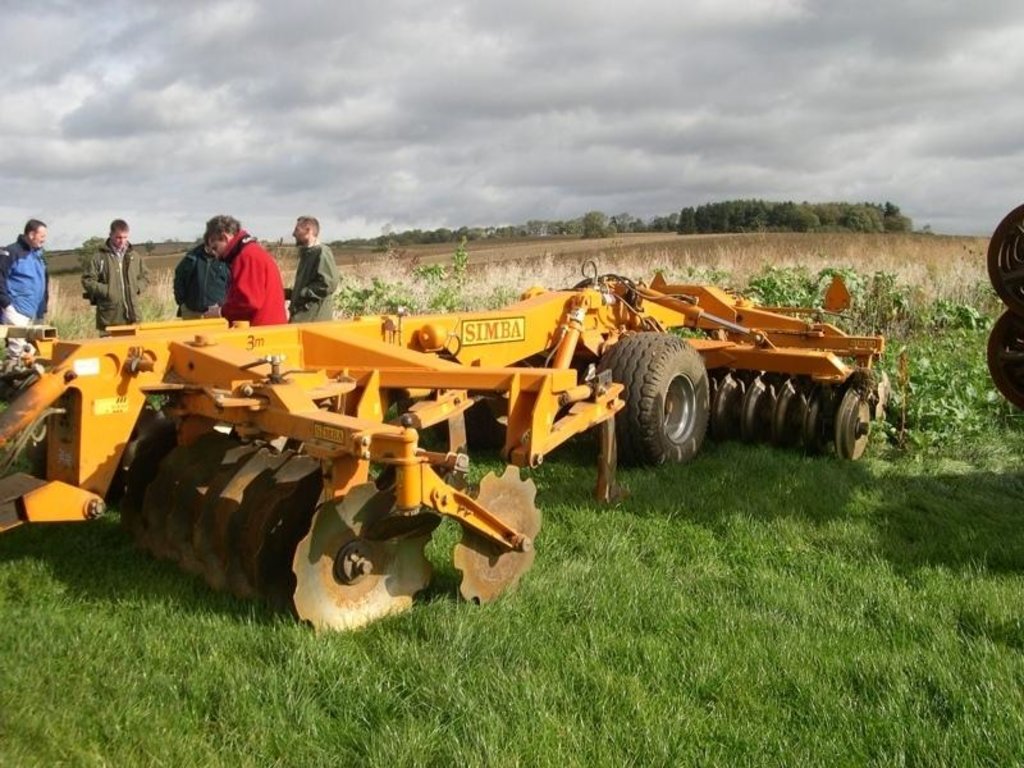
machinery with discs or tines replace the plough.
Purpose of the Technology: (i) improved crop establishment particularly by speeding up of operations (ii) improved soil structure.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: appropriate machinery, soil condition and following crop all determine establishment.
Maintenance: on an annual basis.
Natural / human environment: farmer working to protect environment and maintain rural employment
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
英国
区域/州/省:
Leicestershire
有关地点的进一步说明:
Loddington
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
注释(项目类型等):
From the USA where in te 1930's the 'dust-bowls' necessitated the development of soil conservation in intensive agriculture
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Wheat
Other crops: Oilseed rape, beans
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water turbidity, compaction, erosion
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Compaction
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: wheat - oilseed rape - wheat - beans. Typically these will be winter-sown (Sept) crops rather than spring sown (March)
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 330Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Aug
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 1.46 m2.
This represents 60% of the total arable area on the farm
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pc: compaction
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure, increase in soil fertility
Mulching
Material/ species: crop residue
Quantity/ density: 5 t/ha
Remarks: dispersed over soil surface
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: NPK
Quantity/ density: 0.14 t/ha
Remarks: broadcast
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: cereals/ broad-leaved crops
Remarks: alternate years
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: localised
Minimum tillage
Remarks: using discs and tines
Breaking compacted subsoil
Remarks: localised
Deep tillage / double digging
Remarks: localised
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UK pounds (£)
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.56
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
155.00
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Year1: chop straw as low to the ground as possible | 农业学的 | at harvest (usually August) / annual |
| 2. | Year1: incorporate straw to 10cm depth, though this is dependent on density of straw | 农业学的 | September / per crop |
| 3. | Year1: additional cultivation | 农业学的 | early October / per crop |
| 4. | Year1:drilling (4cm depth) | 农业学的 | early October / once per crop |
| 5. | Year1: consolidation (more in Annex 3) | 农业学的 | early October / once per crop |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 204.0 | 204.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine hours (year 2) | ha | 1.0 | 184.0 | 184.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine hours (year 3) | ha | 1.0 | 236.0 | 236.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 624.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Simba Solo, Cambridge rollers, Vaderstad drill
Per hectare of land where technology applied. The costs represent the total crop establishment costs (machinery + labour) for this technology. Other costs eg seeds, fertiliser, are not included as these are identical to those incurred by other technologies (UNK1b) at this farm. These costs are related to the prevailing conditions - crop type, state of the soil, climate etc. Crop establishment costs by ploughing were: 224 (year1), 204 (year2), 263 (year3)
Additional info: - Year2: chop straw as low to the ground as possible: after harvest / annual - Year2:incorporate straw to 10cm depth, though this is dependent on density of straw: September / per crop - Year2: additional cultivation: March / per crop - Year2: drilling (2.5-4cm depth): March / once per crop - Year3:chop straw as low to the ground as possible: after harvest / annual - Year3: incorporate straw and relieve compaction of soil: October / per crop - Year3: additional cultivation: October / per crop - Year3: drill (2.5-4cm depth): October / once per crop - Year3: consolidation: October / once per crop
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Equipment costs, slope (higher horse power required for steeper slopes), presence of weeds (higher herbicide costs),
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
660.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Hill slopes (some slopes < 8%)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
50% of the land users are rich and own 60% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The time saved by practising non-inversion tillage (52 minutes/ha) allows the land manager to undertake contracted work on other farms
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
250 ha of cultivated arable land
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
- Trust
- Trust
- Trust
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
In good (weather) conditions, yields from ploughed fields often better
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
timeliness of operations
注释/具体说明:
Speed of working allows larger acreage to be managed
Input constraints
注释/具体说明:
herbicide resistance is increasing in a number of weed species therefore a better range of herbicide options required
Window of operation
注释/具体说明:
Can be more narrow than when ploughing
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Better infiltration of water
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Better germination in dry years
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Crop residue
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
0.01
SLM之后的数量:
0
注释/具体说明:
Better soil structure
其它生态影响
Maintenance of rural employment
注释/具体说明:
enabled the farm to just about support the land manager and farm worker
Soil fertility
注释/具体说明:
Higher organic matter levels
Biodiversity enhancement
注释/具体说明:
Higher bird and invertebrate numbers
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Fertilisers and pesticides not transported with eroded soil, better soil structure + biodiversity slow + improve metabolism of chemicals in the soil
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Currently 40% of UK farmers practice non-inversion tillage mainly for economic reasons
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Timely crop establishment + good work rate How can they be sustained / enhanced? good planning |
|
Lower costs How can they be sustained / enhanced? Increased acreage to spread costs |
|
Increased contractor income How can they be sustained / enhanced? as above |
|
improved soil structure - higher organic matter and provision of a better seed bed to drill into How can they be sustained / enhanced? continue with practice |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
cost effectiveness How can they be sustained / enhanced? increase ares under cultivation (economy of scale) |
| increased work rate |
|
improved soil quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? continuation of current soil management principles |
|
increased biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? price premium for biodiversity-friendly products |
|
improved water quality How can they be sustained / enhanced? no option. The EU Water Framework Directive requires watercourses to be of good status by 2015 |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| narrow weather window | drill non-inversion tillage fields first |
| grass weeds | crop rotation; new herbicide modes of action |
| slug management | monitoring slug populations |
| large acreage required to justify cost of machinery | consider not cropping headlands |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Grass weed control | New herbicide modes of action, more integrated management options |
| Untidy appearance of field (due to crop residue) | Familiarity with the technology |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Guide to managing crop establishment, SMI
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.smi.org.uk
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Improved soil management for agronomic and environmental gain, SMI
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.smi.org.uk
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ECAF website
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
www.sowap.org
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Participatory on-farm demonstration in UK arable cropping: Loddington [英国]
Provision of expert knowledge in appropriating equipment and setting up small scale on farm trials in collaboration with the land manager
- 编制者: Ceris A. Jones
模块
无模块