Use of Panchhagavya for Plant Protection [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Panchhagavya
technologies_1145 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Maskey Sunwi
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
K.C Rabi
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Shrestha Archana
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Dahal Sabitri
SADP
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Sustainable Agriculture Development Program Nepal (SADP) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
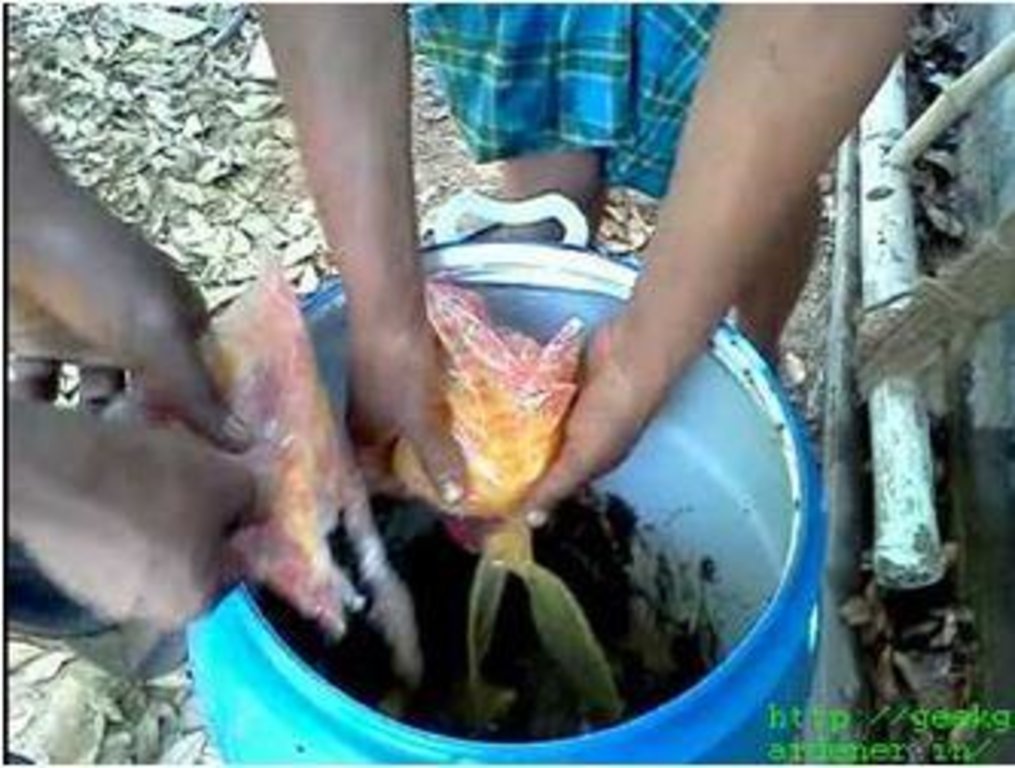
Making the use of cow dung, cow urine, cow ghee, cow milk and honey with other materials, in order to make a fertilizer for plant production.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Panchhagavya was in practice from Neolithic period but recently has become a common interest. It has been used by Hindu Society and has also been mentioned in Vedas. In 1950, James F. Martin made a liquid by lactating cow milk, using dung, sea water and yeast. It was claimed that it was capable of greening degrading land.
It is an organic product that has the potential to play the role of promoting growth and providing immunity in plant system. It consists of nine products i.e. cow dung, cow urine, milk, curd, jaggery, ghee, ripened banana, tender coconut and water.
This technology most importantly focuses on agronomic measures and conserves the manuring and composting. It does not lead to changes in slope profile of the land. Organic matter is used for soil surface treatment which increases the fertility of the soil. This agronomic measure is also combined with management measures where change in management of soil results in giving improved vegetable cover.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of Panchhagavya is to deal with major land problems such as soil infertility, less production of crops and water pollution due to use of fertilizers. It focuses on cropland where annual cropping is done. Annual crops are usually harvested within one or maximally within two years. Chemical and physical soil deterioration and biological degradation are the types of land degradation addresses by the technology.
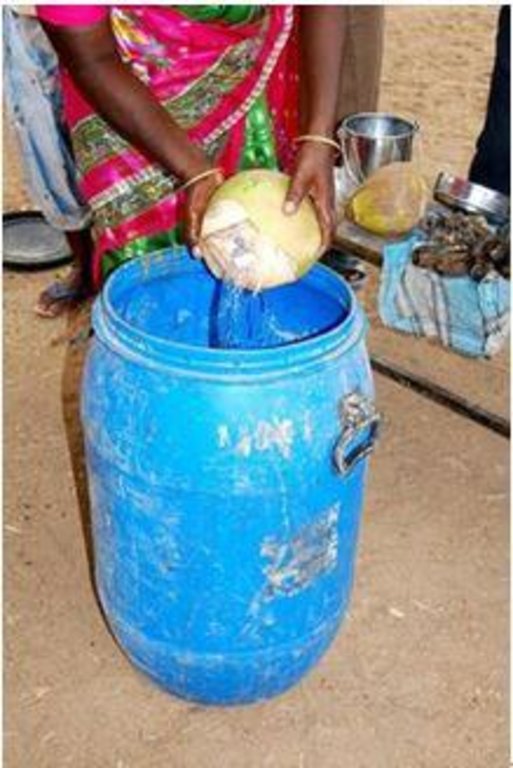
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In a container, mix 5kg of cow dung and 1/2kg of ghee. This mixture is stored in a shade for 4 days.On 5th day, the mixture is poured in a new container and cow milk, curd and cow urine is added to it. Then Jaggery is added by dissolving it in water. Ripened bananas are mashed and added to the above mixture with coconut water. This is stored for 30 days. Now, the mixture is stirred and mixed daily. This mixture is then sprayed to the crops. If the mixture is sprayed with hand sprayer then the nozzel must have greater pores. The preparation of Panchhagavya requires lot of products and takes around 30 days which makes it a bit costly.
Natural / human environment: The Panchhagavya thus produced is then sprayed in the agriculture fields. So, this can be used as a substitute for fertilizers as a type of organic manure. It can help promote greenery. Panchhagavya is prepared indoors in huge quantities and may be used overtime as required.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
The use of Panchhagavya is specially seen in different sates of India and Nepal. The area isn't uniformly distributed.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
It was in practice from neolithic period (7500-6500) but recently has become a common interest.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Improve soil fertility
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- rice
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 柑橘属
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: July-December; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: February-March

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
- 半游牧畜牧业
- 经营牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
- cows

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
- 植树造林
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 选伐
- 皆伐
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 其它森林产品
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护
注释:
Main crops (cash and food crops): (CA) Rice, (CP) potato and (CT) orange
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil infertility, less yield or production of crops, water pollution due to use of fertilizers.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Less yield of crops
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Ranching: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: Yes
Plantation forestry: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism, protection against natural hazards
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Constraints of mines and extractive industries
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation and post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V3:植被的清理

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: improves water holding capacity of soil
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, green manure, manure / compost / residues, soil conditioners (lime, gypsum)
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cp:土壤污染
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Ps:有机土壤沉降,土壤沉降
- Pu:由于其他活动而导致生物生产功能的丧失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Cp: soil pollution, Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ps: subsidence of organic soils, settling of soil, Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Panchagavya, an organic product has the potential to play the role of promoting growth and providing immunity in plant system. Panchagavya consists of nine products viz. cow dung, cow urine, milk, curd, jaggery, ghee, banana, Tender coconut and water.
Location: Bakhundol. Kathmandu
Date: 18-01-2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, control of fires, reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Structural measure: soil management
Structural measure: increase crop yield
Structural measure: increase crops immunity
Other type of management: storage of the mixture should managed
作者:
Saurav Lohala
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | mix 7 kg cow dung and 1 kg cow ghee | store in shade for 4 days |
| 2. | on 5th day pour milk, curd and cow urine | 1 day |
| 3. | dissolve jaggery in water, add ripened banana and tender coconut water | store for 30 days |
| 4. | stir and mix mixture daily | for 30 days |
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mix 5 kg of cow dung and 1/2 kg of ghee | 4 days |
| 2. | On 5th day pour milk, curd and cow urine | 5th day |
| 3. | Dissolve jaggery in water and add ripened banana and tender coconut water | 30 days |
| 4. | Stir and mix mixture daily | Everyday |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Fertilizers are found everywhere and is cheap but the properties of Panchhagavya requires a lot of products and takes around 30 days which makes it costly.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
- 半干旱
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: tropics
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
Thermal climate class: polar/arctic
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Species diversity: Also medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 5-15 ha and 15-50 ha for use of wood.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 社区/村庄
注释:
Land ownership: Also group
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业收入
经济差异
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
文化机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
其它生态影响
hazards towards adverse events
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
Prefer drainage system and better plant diversity
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Can improve the lifestyle because it helps to increase the economic status. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Land users also should be active and motivates other to use. |
| Fresh vegetables without chemical fertilizers can be sold in market and gain more profit. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increase the productivity of crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Awareness program, training should be done in local level in each and every part of the country. |
|
Sustain drought condition because roots are grown into deeper layers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Different research based project should carried out. |
|
Reduces the use of chemical fertilizers because Panchhagavya itself is a fertilizer. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Research study initiation based on Panchhagavya should be established. |
| Improve the quality of the soil which ultimately improves the yield also. |
| Increase the immunity of the plant. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Preparation of Panchhagavya is lengthy process so farmer use chemical fertilizer rather than Panchhagavya. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The preparation of Panchhagavya is a lengthy process so people are not ready to use instead of chemical fertilizers. | Awareness training program within the people. |
| The use of Panchhagavya should be done in specific quantity. If not then it has negative impact on plants. | Use of Panchhagavya in specific quantity as referred by the SLM specialists. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块