Usage of Gher boundary for cropping [孟加拉国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jalal Uddin Md. Shoaib
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Gherer bunder upar nana prokar shakshabjee uthpadon
technologies_1171 - 孟加拉国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Shaha Tapan Kuma
SRDI
孟加拉国
SLM专业人员:
Bhander Bidhan Kumar
SRDI
孟加拉国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI) (Soil Resource Development Institute (SRDI)) - 孟加拉国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Gher (shrimp cultivation) boundary usage for multiple cropping.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
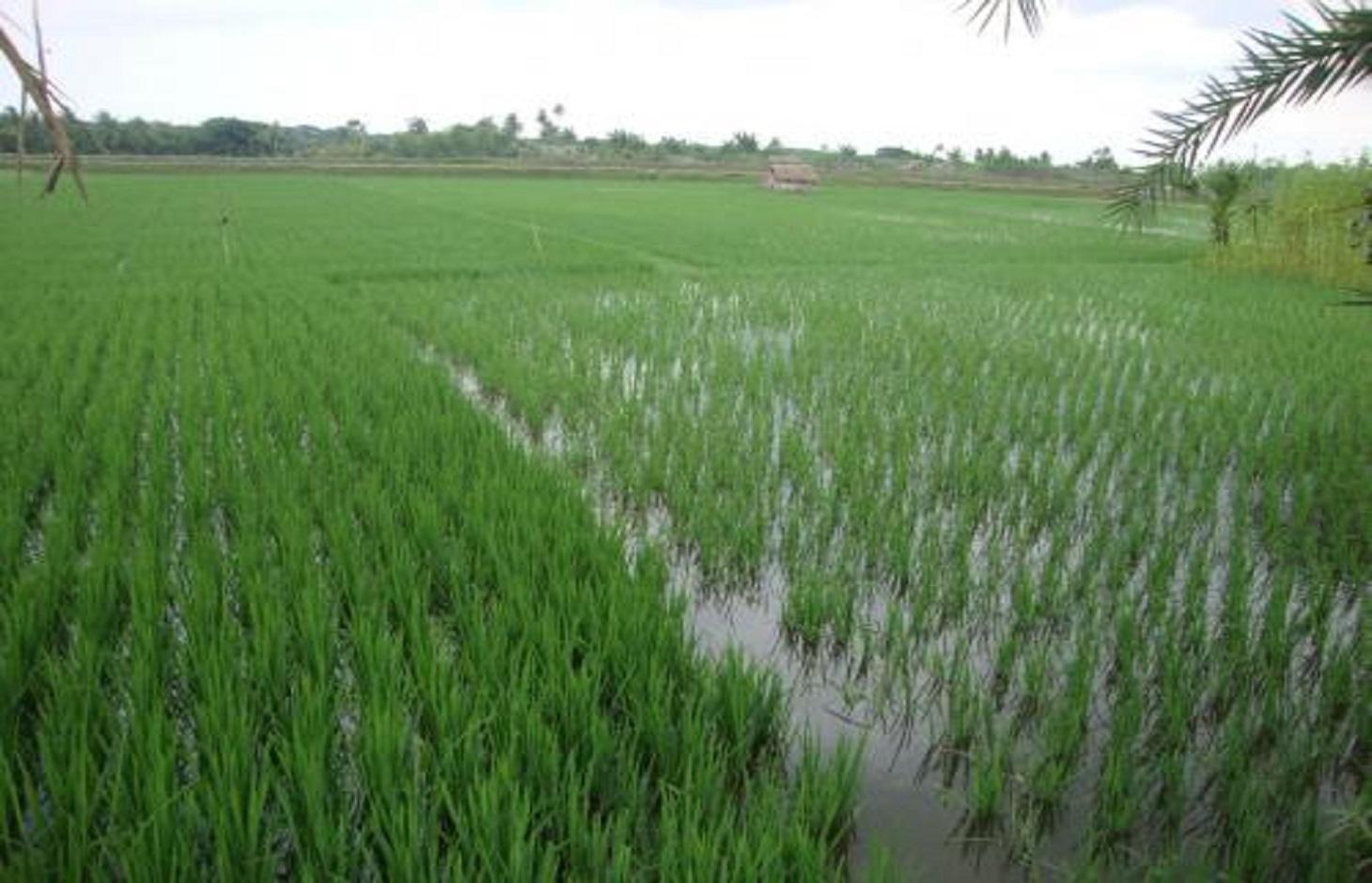
Gher is a local word used for shrimp cultivation plot. The boundaries of these ghers are nowadays raised and maintained to grow vegetables, fruits and also some tree species. In this case the boundary of the plot is raised at least 3 feet with grest width 1 feet plus depending on the height of the boundary (Bund/dyke). Within the gher the land is used for both sweet water prawn (Golda) or saline water prawn (Bagda) with other different types of fishes (locally called Sada Mach) if suitable depending on the salinity of water. Some of the gher lands are used for transplanted Aman with shrimp/fishes.
Farmers dug a ditch along the boundary or in any corner of the field or at the center of the plot to preserve water and fishes during the dry season. In some of the cases the farmers used shallow tube well water to sustain the fishes. In non-to slightly saline areas they used it even for boro (winter rice).
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of this technology is a boundary which is used for various types of crops, including year round vegetables and land for rice and fishes including shrimps.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The boundary is constructed above flood level (2-3 feet), the width is approx. 2-3 feet, the ditches are 2-3 feet deep along the boundary or at the corner or at the center.
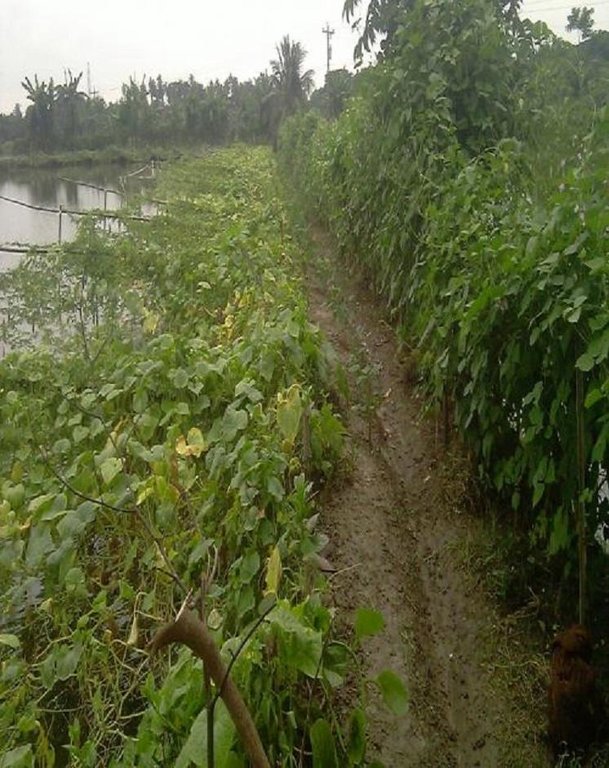
To grow vegetables farmers used nylon nets for creeping supported by the bamboo or Dhaincha or strings.
Top soils kept on top of the bunds to avoid relatively less fertile soil on the bunds.
Main inputs are seeds of vegetables, nets, bamboo, strings, fingerlings of fish etc.
Natural / human environment: The salinity of the soils from the bunds is washed away by rainwater, which facilitates vegetable production: Rain water desolves salt and moves to the bottom of the bund, and soil becomes non-saline or slightly saline where vegetable could be grown.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
孟加拉国
区域/州/省:
Bangladesh Southern region
有关地点的进一步说明:
Khulna
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- Cropland and aquaculture
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water salinity during dry season; tidal surge; cyclones
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Water salinity; tidal surge; sidre (name of a cyclone)
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mo: Other
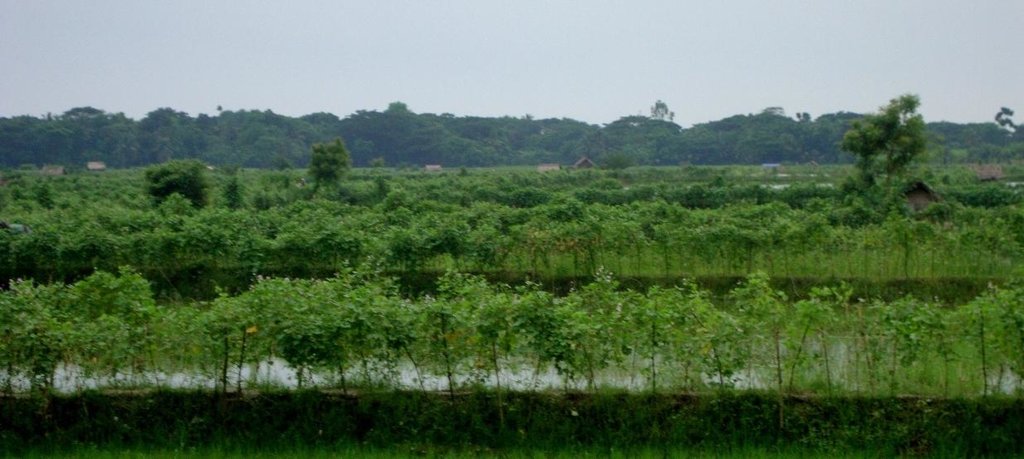
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Gher use is very much variable. The main issue of using land is to adapt soil and water salinity. Some ghers are used for only shrimp, some are mixed with other fishes, some are mixed with transplanted Aman. But the boundary/bunds are used for year round vegetables, Banana, fruits (Kul, Guava, Mango) etc.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Mixed: Mo: Other
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 160; Longest growing period from month to month: July to Sept
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 养蜂、养殖业、家禽业、养兔业、养蚕业等
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Gher (Shrimp cultivation) boundary used for multiple crops; vegetables, fruits, tree etc in southern coastal region of Bangladesh.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Salinization: salination of top soil is due to saline ground water coming in shallow depth), Salinization (The area under this issue is in coastal zone. Conflict of land use is prominent. The lands became saline as other stakeholders keep saline water for other uses (salt production, shrimp))
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
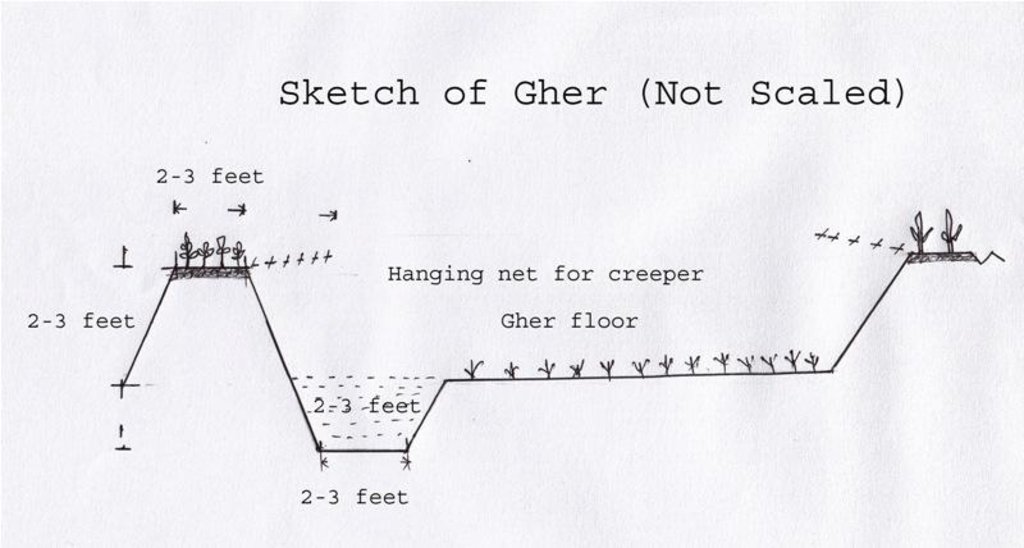
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The gher boundary is raised approximately 2-3 feet with a crest of 2-3 feet. A ditch also dug to store water and fish during dry season.
Location: Dumuria. Khulna
Date: 03-09-13
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (It is only land manipulation.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Previously farmer did not put the top soil on the top of the bunds. That impedes crop production on bunds.)
Main technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, Decrease of soil salinity, Increase of options for growing more crops
Agronomic measure: Top soil kept on top
Structural measure: Bunds
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5-1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10-50
Construction material (earth): Bunds are raised by piling earth
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Bunds are used for year round cropping
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Taka
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
79.0
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | 结构性的 | Nov-Dec |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Farmers cut the earth from adjacent lands | ha | 10.0 | 65.0 | 650.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 2.0 | 300.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Watch and ward | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Seeds, nets etc | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1605.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | 农业学的 | July/Nov |
| 2. | Cultural practices | 农业学的 | Aug-Oct/Dec-March |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Transplanting seedlings/seeds | persons/day/ha | 2.0 | 10.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 20.0 | |||||
注释:
Piling earth to construct gher bunds
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Availability of labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Most of the rainfall experienced in rainy season
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Coastal plain, narrow ridge with broad flat basin
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is very low - low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women casually worked during harvesting vegetables
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
70% of the land users are poor.
Level of mechanization: Power triller on hire.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
15-50 ha: Mainly owner of lands of this area
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 租赁
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Desalinized soil of the bund
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
Cash from vegetables
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Conflicts to use water resource
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Growing and marketing of year round vegetables help the farmer to get cash money throughout the year. That improves their livelihood and access to health care, education etc.
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Ghers are ponded and no water can be drained
土壤
盐度
注释/具体说明:
+ Soil salinity reduced as washed by rainwater -> found in soils of Gher bunds
- Due to ground water abstraction -> found in coastal regions, increasing trend
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
注释:
Salinity is washed out from the bund by rainwater. Consequently year round vegetable can be grown on bunds of the gher besides fish in the main land or transplanted rice (depending on the salinity of soil and water and choice of farmers).
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
Long term benefit is yet to be observed
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Leased land users are not capable to adopt the technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Growing more crops will benefit the farmer with more return. As of now marketing of the goods are facilitated by local small entrepreneurs. Most of them have poor linkage with broader markets. How can they be sustained / enhanced? These entrepreneurs could be appropriately linked with bigger one at regional levels (Upazila/ Districts). At the same time road net works are to be alleviated to facilitate access of transport to carry farmers good with all securities. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Land could be used as farmers are managing themselves How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain production and produce such as vegetables and fishes deserve uninterrupted marketing linkage essential. |
|
Changes in land management by the farmer to grow multiple crops indeed scale up their economy than before. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To sustain the farming system good variety and quality seeds supply will enhance the scenario. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Water management of the areas became critical, specially sweet water | Good water management system is to be introduced through local and regional planning. |
| Conflicts of land uses are prominent. | Social awareness and concept of land zoning seems to be essentials at all levels. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Due to construction or rearrangement of field bunds (Dykes) almost all drainages ways blocked. Consequently the whole area became water logged. This situation will definitely aggravate soil quality, environment and ultimate ecosystem | Community approach to manage the landscape will be effective. In this regard local administration and community leaders can play a vital role. |
| Soils of Gher boundaries (Dykes) are subject to erosion when exposed to rain water. | Good cover crops and management are necessary to protect soils from erosion. At same time farmers may be trained on this issue. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块