Calliandra contour hedges [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Orugo rwa Calliandra (Rukiga)
technologies_1178 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - 意大利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kabale District Local Government (Kabale District Local Government) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
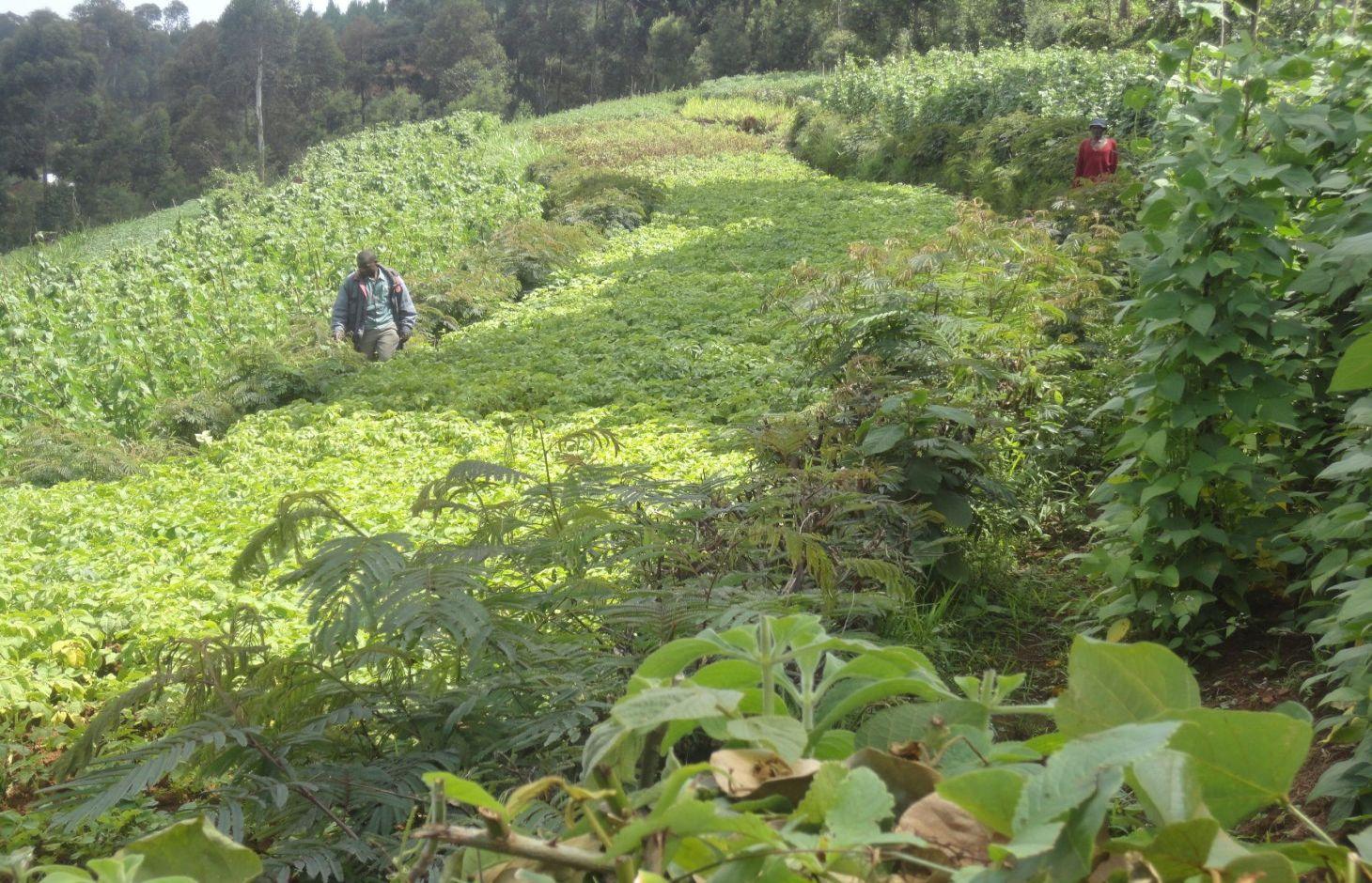
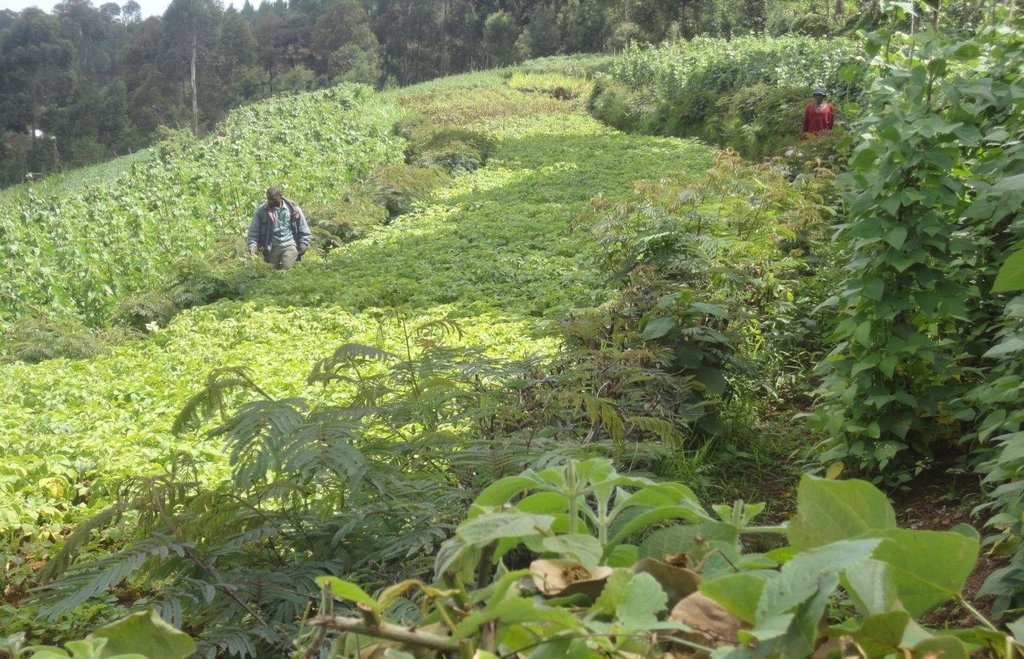
Contour hedges of Calliandra planted on very steep slopes to combat soil erosion by decreasing surface runoff and increasing infiltration.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Calliandra Calothyrsus trees are closely planted along the contours on hilly and steep slopes to create natural and effective barriers for reduction of the surface runoff and retention of eroded sediment. Calliandra hedge barriers are a fairly cheap, effective, and sustainable way of controlling soil erosion and landslides on vulnerable steep slopes, especially where trash lines and Napier grass strips were inadequate to mitigate dispersed and concentrated soil and water runoff. Once established, the living barrier is durable with minimal additional maintenance cost to the farmer apart from pruning. The average length of a hedgerow is 50 to 70 m, corresponding to the width of a single terrace. The height varies according to intended use of the mature shoots. To use the stems as stakes, the hedgerow is allowed to reach a height of 4 to 6 m at maturity while a height of 1 to 2 m is sufficient for harvesting foliage as livestock fodder. The hedge barrier reaches its mature, maintenance level after 12 to 18 months.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the Calliandra hedge barrier is to reduce soil and water runoff.Calliandra is a leguminous shrub with deep roots that provids additional benefits such as soil stabilization and soil fertility improvement through nitrogen fixing. Calliandra is a source of fodder and its flowers attract bees.
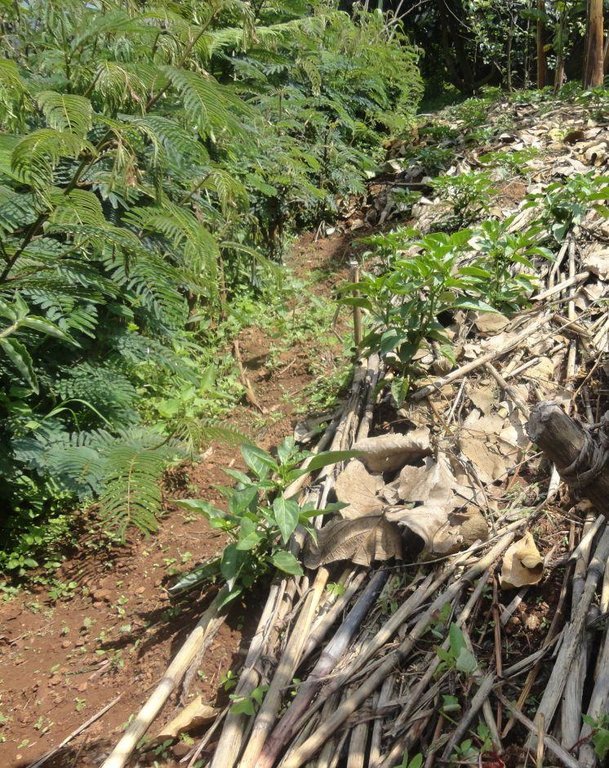
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: At the beginning of the rainy season, calliandra seedlings are transplanted from the nursery (0.2m to 0.3m height) and planted in a row (0.3m spacing). In the early stages, gap-filling with more seedlings may be necessary as some fail to get established. A mixture of top soil and manure is applied in the spaces between the seedlings and watering is done to improve the seedling survival rate. The distance between rows is 10 to 15 m and depends on the gradient of the slope. Establishment of hedges starts with construction of an earth banked terrace, creating a trench at the lower end of the terrace. Calliandra seedlings are planted on the higher side of the trench. Measuring off 10 m lengths upwards into the terrace, other rows of Calliandra seedlings are planted along the contour in order to achieve the inter-row spacing. Establishment is manual labor intensive and therefore the community, organized as Farmer Field Schools, participates in the planting, one field at a time. Simple tools such as hand hoes, sokajembe (pick-axe) and shovels are used. Maintenance is achieved by weeding, mulching and cutting back. For it to establish well, Calliandra needs to be weeded to minimize competition with weeds for water and nutrients . The weeds also harbour pests. It may also be necessary to mulch the area around each seedling during the dry season. Where mulching is done, the mulch is placed at least 0.05m away from the plant to reduce pest attacks. Calliandra calothyrsus trees are cut back at a height of 2m to between 0.15m and 1m to improve foliage which is used as fodder for livestock. The hedge is then maintained at a height of 1 to 6 m depending on the intended additional uses. The branches removed can be used as fuel wood or stakes, while leaves can be used as fodder.
Natural / human environment: The hedge barrier may be attacked by pests. Scales are white, powdery insects that attack Calliandra stems. Scales can be controlled using washing detergents such as ‘Omo’ dissolved in water and sprinkled on affected plants using leafy branches or a knapsack sprayer. Black ants can seriously damage trees. They can be controlled by spraying. Other likely pests are crickets and grass hoppers which affect seedlings in nurseries, and Armillaria mellea, a fungus that attacks roots of Calliandra plant causing root rot and eventual death. Affected plants are uprooted and burnt. In addition, calliandra is affected by hot, dry weather. During the hot, dry weather, the hedge barrier becomes weak. However during the wet season it sprouts again, and, if well managed, becomes healthy again. A well-maintained hedge barriers can last well over 20 years.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kabale District
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.29294, 29.96006
-1.29336, 29.96027
-1.29327, 29.96084
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.03 km2.
The documented case study area is around 3ha
-1.29371, 29.96095
-1.29345, 29.96091
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was introduced by ICRAF in 2006 and scaled-up Kagera TAMP project 2 years ago.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 其他
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 饲料树木(朱缨花属、银合欢、前庭草等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: February to MaySecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
- Livestock is grazing on crop residues
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
1-10 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The slopes are steep >30% to very steep >60%), with very high precipitation (>1440 mm). Severe surface erosion and landslides may occur at the beginning of the rains, before sufficient vegetation covers the soil. Continuous cultivation with little external inputs and nutrient transfer affects negatively soil fertility and in results reduces crops growth/vegetation cover, leading to erosion on steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Floods are common in the valleys over the past ten years.
Improved pasture: Diary hiefers,pigs(largewhite and layers)pasture include calliandra,stellia and elephant grass.
Constraints of settlement / urban: floods invade houses
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): transport problem
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor vegetative cover/no trees to bind soil particles.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Rainfall intensifying in september and April.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (steep slopes (extreme topography)), population pressure (Population increase/no of people increased per sq km), poverty / wealth (lack of resources to implement known natural resources degradation mitigation measures)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
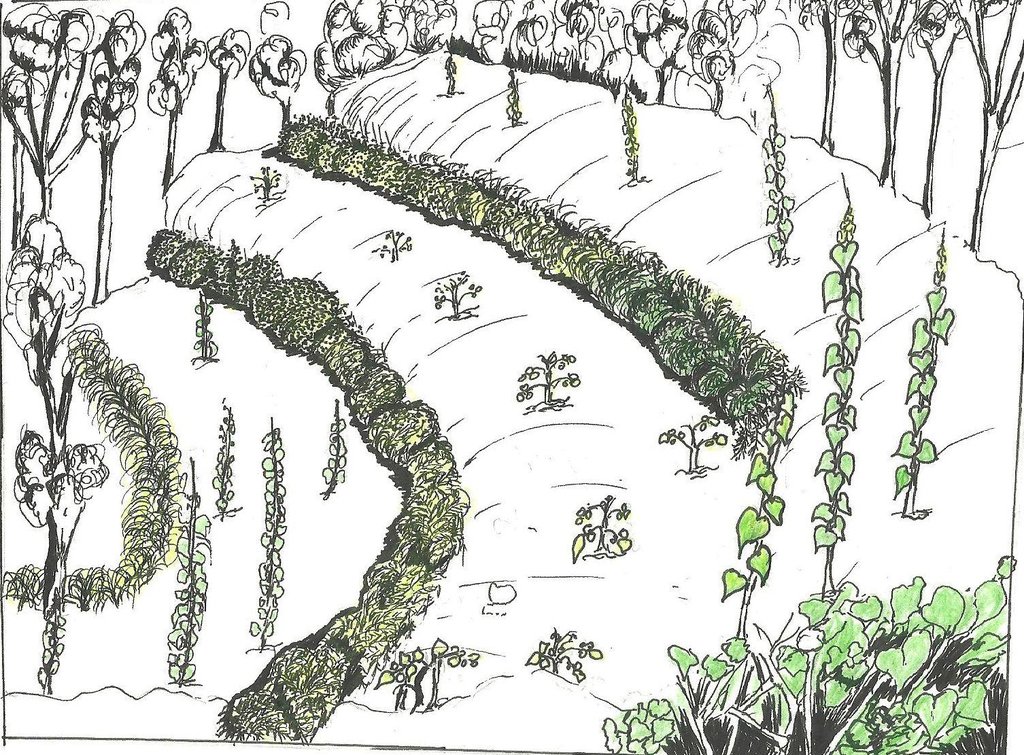
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Calliandra trees are planted in rows along the contour. Cutting back is done between 12 and 18 months to a height of 0.5 m. The trees are allowed to grow to between 1 and 6 m and the hedge is maintained at that height. Gap-filling, weeding and trimming are critical for a productive hedge.
Location: Bukoora, Kabale. Kabale/Uganda
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Such knowledge as is required to manage the Calliandra nursery, transplant and maintain the plants especially until the first coppice.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The land user is responsible for maintaining the technology on his or her land and a good hedge requires diligence)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 670 to 720
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: Calliandra was planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: n/a
Perennial crops species: n/a
Grass species: n/a
Other species: n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 40%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): n/a%
Gradient along the rows / strips: <3%
作者:
Byonabye, Prossy, Kagera TAMP, Kabale, Uganda
日期:
2013-11-29
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
2602.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.80
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of Calliandra nursery | Dry season |
| 2. | Plantation of Calliandra seedling on the higher side of the trench | Wet season |
| 3. | Weeding |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | 1.0 | 44.6 | 44.6 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | tools | 1.0 | 16.2 | 16.2 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | 1.0 | 30.4 | 30.4 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seeds | 1.0 | 9.6 | 9.6 | 100.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 100.8 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.04 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 18 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prunning and triming the hedge barriers | wet/dry season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | 1.0 | 20.8 | 20.8 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | tools | 1.0 | 16.2 | 16.2 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 100.0 | |
| 其它 | 100.0 | |||||
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 38.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.01 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: I panga,1 watering can, 1hoe.
The cost assesment above refers to steep slopes.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost of seedlings (0.20 US$ each) and their transport up along steep slopes are the key factors affecting costs and hindering spontaneous adoption of the technology. Otherwise, the technology is acceptable to farmers as benefits are easily visible in the short run.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. at the Equator
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Maintenance such as pruning trimming is mostly done by the men, but the other activities are done by both men and women.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (meets basic needs/necesities).
45% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Crop and animal production greatly increased for land users implementing conservation measures , compared to those who do not implement.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
注释:
The land belongs to an individual with no title but has all the rights over it.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
n/an/an/an/a:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
150
SLM之后的数量:
700
饲料质量
SLM之前的数量:
-
SLM之后的数量:
-
畜牧生产
SLM之前的数量:
-
SLM之后的数量:
25
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
1.5 million
SLM之后的数量:
3.5million
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
-
SLM之后的数量:
-
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
其它生态影响
increased pests
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
对邻近农田的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
-
SLM之后的数量:
-
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
-
SLM之后的数量:
-
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
| n/a |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Benefits are high compared to establishment and maintenance cost
6.5 技术采用
注释:
88% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
45 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is appreciated by most farmers but adoption is limited by cost of seedlings and transportation up steep slopes
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Calliandra binds the soil, thus reduces landslides. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It should be maintained through proper management |
|
Adds scenic beauty on a plot How can they be sustained / enhanced? By regular trimming |
|
Calliandra is good and attractive to bees How can they be sustained / enhanced? Leave every second or third row to flower |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It is easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote education campaign and spread information |
|
It has helped to increase crop and animal production How can they be sustained / enhanced? By proper management and not overgrazing animals |
|
Stabilize the soil and strenghtening resistance to intensive rainfall and fast runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology through increased community mobilization |
|
Very effective to reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other practicies e.g. mulching |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The hedge barrier is ineffective before 12 months | Combine with trash lines before establishment |
| Technology harbors nesting birds | Ensure regular trimming of Calliandra to reasonable height and use scarecrows |
| Needs at least 2 seasons to establish | Apply manure and water to the seedlings to ensure accelerated growth |
| May reduce the amount of sunlight available to young crops if left untrimmed | Trim regularly |
| Extra cost in protecting from damage by livestock | Inter-crop with other fodder species to act as alternative fodder for livestock |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kagera TAMP Project website
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块