Oyster Mushroom [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Parale Chyau
technologies_1194 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Dahal Dikshya
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Karki Nabina
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Budhathoki Karuna
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Ghimire Kishor
Agricultural Office, Sindhuli
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Singh Yubraj
Agricultural Office, Sindhuli
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Neupane Shankar
Management Post Institution Lalitpur, Hattiban
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
District Agriculture Development Office, Sindhuli (DADO) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
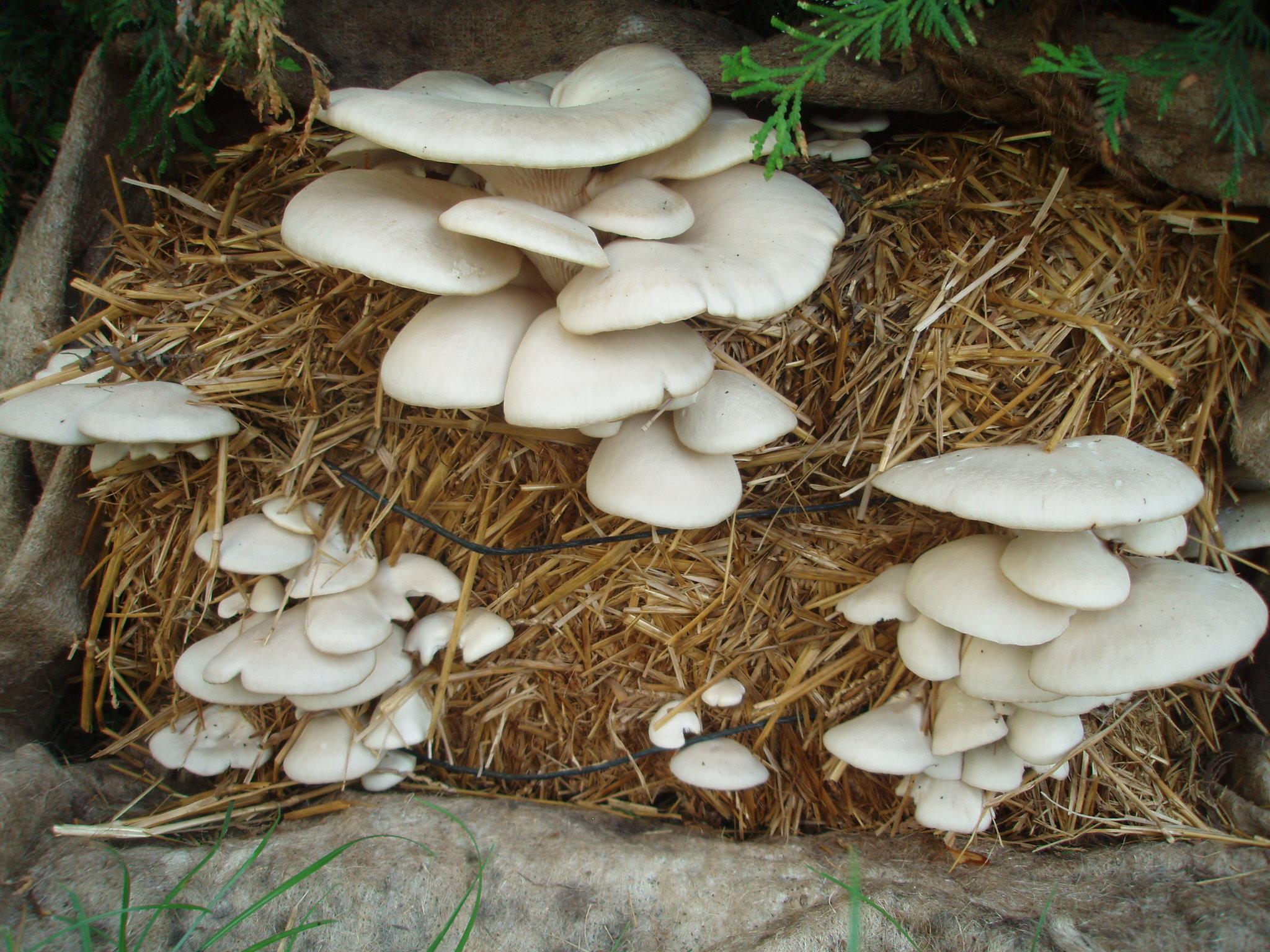
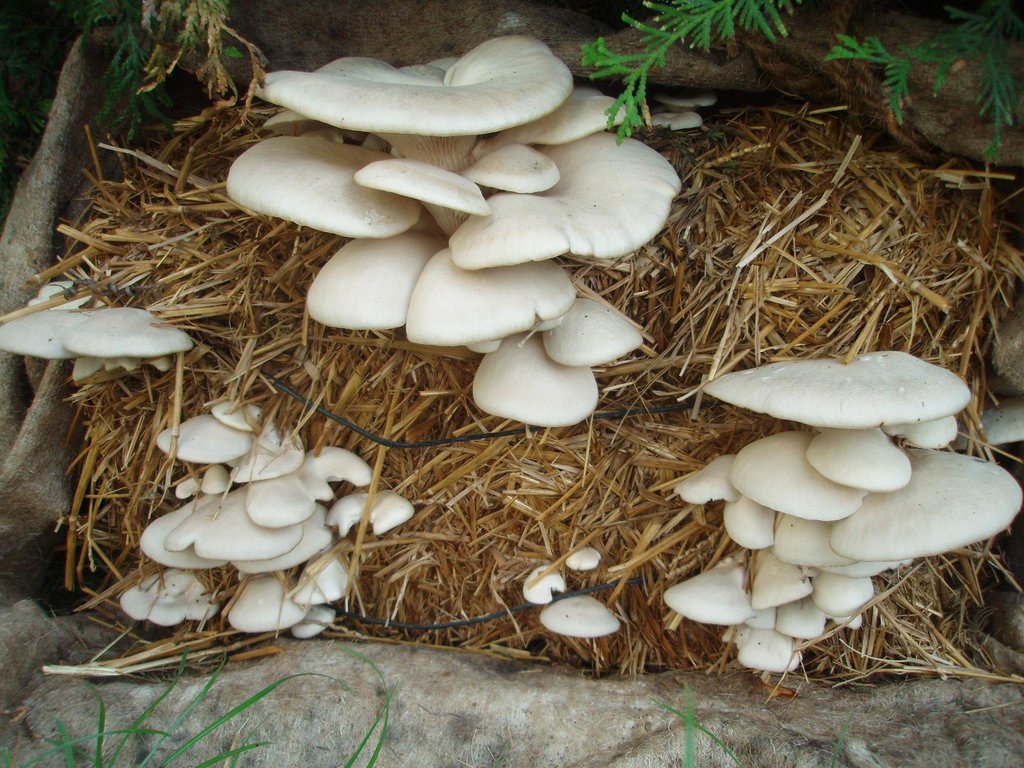
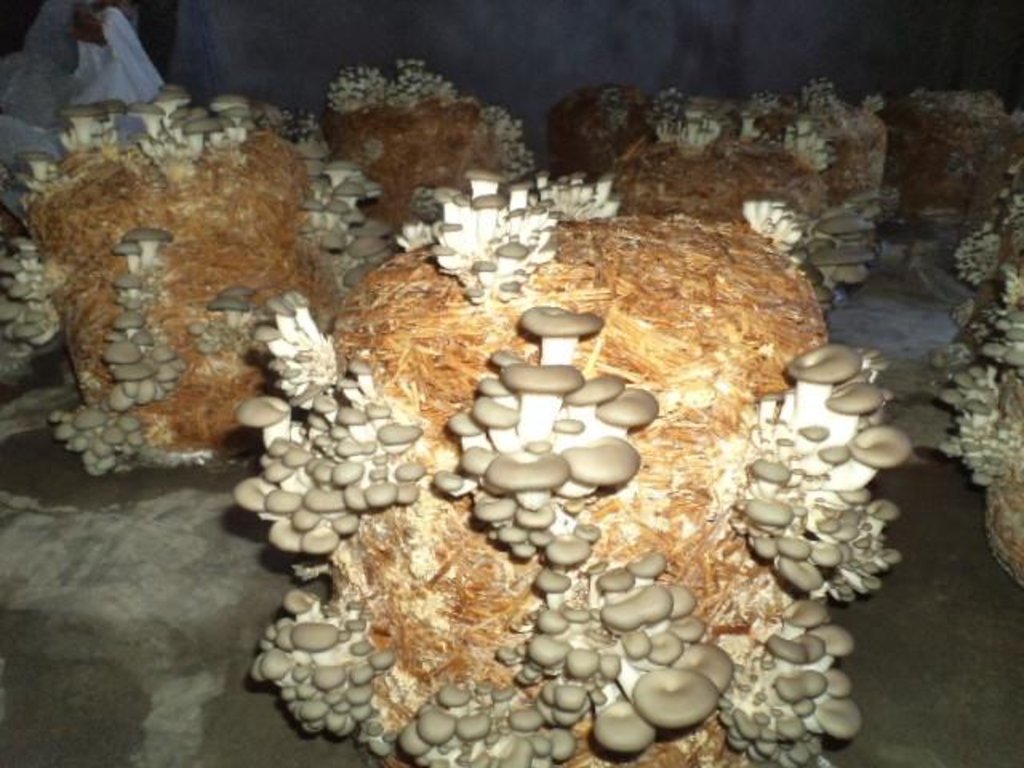
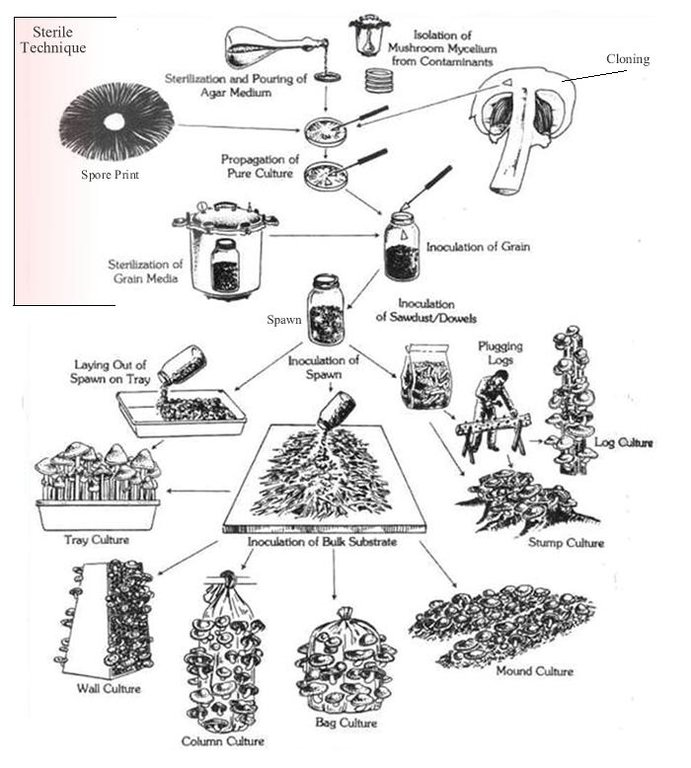
Oyster Mushroom Farming Technology is the cultivation of oyster mushrooms as a food source, economic source, and as primary compost, to increase the quality of soil and help upgrade living standards of local farmers.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The technology is carried out in Kamalamai Municipality, Sindhuli District, Janakpur, Nepal. The Pennsylvania Department Of Environmental Protection (DEP), other regulator agencies and the community are at charge. Oyster were identified as being both economically viable and suited for local cultivation. Nepal Agriculture Research Council (NARC) and a few private organizations are the major resources centers for supplying the quality spawn to the farmer/growers.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this document is to provide uniform instructions and operating procedures for the use or disposal of mushroom compost (as soil amendment or conditioner). Another basic purpose is use of mushroom as food and income source for local farmers.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Best Practices for Environmental Protection in the Mushroom Farm
Community (1997) was developed as a result of realization among authorities of Pennsylvania DEP, to help people to understand that farms are operating according to the highest environmental standards, and will help improve coexistence with nearby residents, through environmental regulation. This implemented a mushroom farm development for specific operations with the natural resource conservation. The member co-ordination, knowledge, and experiences are critical in establishing the practices as workable and rational means to meet the goal of environmental protection and agricultural operation.
Natural / human environment: Mushroom Farm Environmental Management Plan (MFEMP) is designed to prevent pollution or danger of ground or surface water on common health, by helping in maintaining/improving the condition of soil, and prevent the pollution of surface water, groundwater and air, as well, at little or no cost. This technology helps local farmers to increase soil fertility and act as a good income source in small scale.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Janakpur
有关地点的进一步说明:
Sindhuli
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 12*18 inch.
The straw and spawn (mushroom) should be packed in plastic bags. Two or three inches of straw are packed into the plastic bag and the spawn is lightly sprinkled on top. This should be repeated until the bag is almost filled, the top of the plastic should be closed and holes should be poked in the bag.
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
注释(项目类型等):
This practice was performed by American mushroom institutions in 1997 and earlier 1984.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

其它
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Low productivity of land, soil erosion, water scarcity, cultivation of land slopes, tillage resulting in soil loss.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Infertility of land, having to use fertilizers and pesticides, scarcity of water for irrigation, having to plow farm seasonally and repeatedly.
Constraints of recreation: Dark and moist environment is necessary.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 75; Longest growing period from month to month: January-March
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, mulching, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (soil erosion, low productivity of land, tillage), overgrazing (Fodder for domestic animals such as cow, buffalo, goat etc.), change in temperature (Uneven rainfall, long dry or cold seasons)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (terrace farming problems), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Use of timber for burning), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Only required vegetation was used), poverty / wealth (Medium to large scale production costly for local farmers)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
It is kept in a room with temperature 22-28 degree.
Location: Room. Sindhuli
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Knowledge on preparing substrate, incubation period and harvesting of mushroom and proper use of mushroom compost.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Since land usage is very less.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Mulching
Material/ species: straw and spawn
Quantity/ density: 2:1
Construction material (earth): mud in cement
Construction material (stone): stone
Construction material (wood): wood plants
作者:
Nabina Karki, Karuna Budhathoki
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rupees
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
90.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 施工材料 | Straw | unit | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Container | unit | 1.0 | 990.0 | 990.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Fuel | unit | 1.0 | 125.0 | 125.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stove | unit | 1.0 | 770.0 | 770.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Plastic | unit | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Cutting Machine | unit | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2210.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 24.56 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Method of cutting straw | dry season |
| 2. | Warming the straw | dry season |
| 3. | Harvesting the mushroom | dry season |
| 4. | Maintainance of mushroom | dry season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Method of cutting straw | persons/day | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 150.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 1.67 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: plastic bag,water storage tank.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour should be managed properly.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
DADO Sindhuli, 2010
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Mostly mushroom grow in about 24 degree Celsius.
Mostly mushroom grow in about 24 degree Celsius.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Flat surface is needed.
5.3 土壤
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil water storage capacity is medium: Mushroom need water daily two times.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water: May face scarcity of drinking water in dry seasons.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Found mostly in eastern region, and almost in the western parts as well.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There is no difference in involvement of men and women in this technology, both can be involved.
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
注释:
It is found that this technique is used even by people with little amount of land.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Mushroom Compost usage
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Leftover straw
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Richer in nutrients than dry hay
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Little to no cost required
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Mushrooms sold widely as food source
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Recreational method, provides options for farmers
经济差异
工作量
注释/具体说明:
1 or 2 individuals are enough.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Cheap and easy way for earning money
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Mushroom compost used instead of chemical fertilizers
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Good way to utilize time, gain profits
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It has helped to increase knowledge
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Provide nutrients to plants
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Composting
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Composting
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Mushroom: edible fungi
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Alternative mushroom composts
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
The technology could be made more tolerant by keeping the room dark and warm (22-28 degrees), and carry out cultivation in almost all seasons (except winter).
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Yes, this technology can give both short-term returns and long-term returns.Positive result because it is the best type of production for the environment and economic resources.
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
3 households covering 32 percent of stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
2 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
By government point of view almost all members of a village and city, both can cultivate this technology. 1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support. Comments on spontaneous adoption: Without external support also this technology can be carried out.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Best Practices for Environmental Protection in the Mushroom Farm Community
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It is used as vegetable. |
| Waste water management |
| It is used as manure |
| Good income source |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Erosion and sedimentation control |
| Surface water and stormwater management |
| Economic purpose |
| Nutrient management for substrate utilization |
| Integrated pest management |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Place for growing | All locals do not have spare rooms or sheds for mushroom cultivation. This proves to be a huge disadvantage as they require dark room and moist conditions. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Less theoritical knowledge | Locals should be made aware about growing technologies that can help increase their quality of life. |
| Place for growing | Rooms or shed may not always be available. Providing darkness during can be a problem. |
| Seasonal problem | Room temperature required is 20-30 degree Celsius. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块