Vermi compost technology [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1236 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Pandey Anagha
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Shrestha Prasanna
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Maharjan Sanu
Kathmandu, metropolitan Teku
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Technology for converting biodegradable waste into organic manure with the help of earthworms
2.2 技术的详细说明
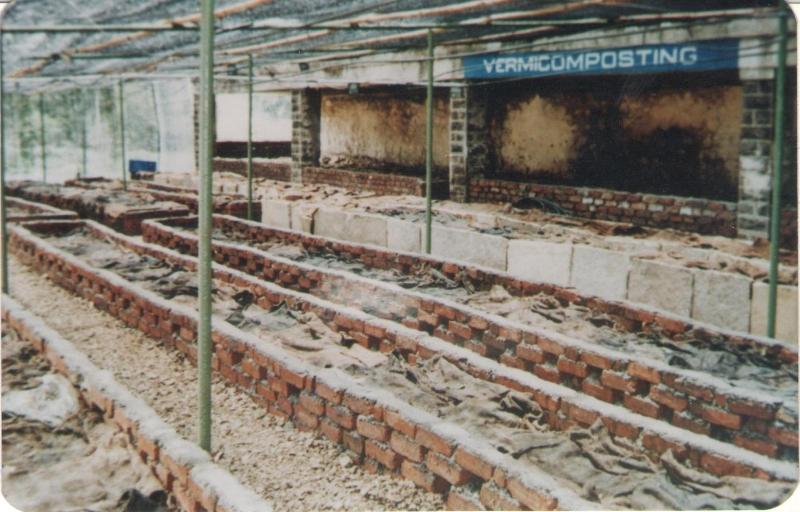
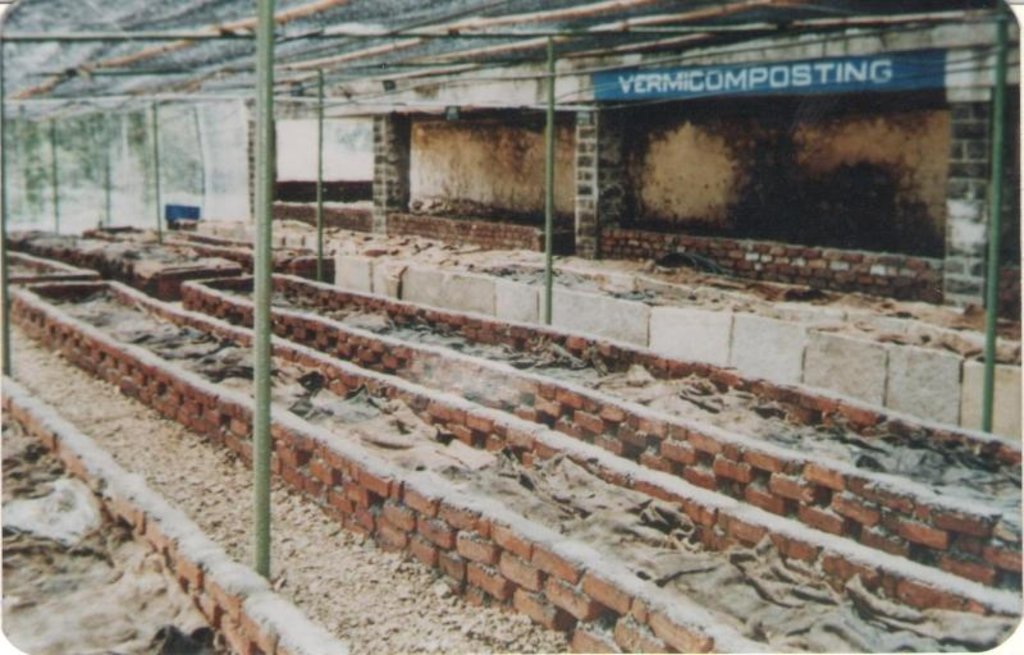
说明:
Vermicomposting or worm composting is a simple technique that is used to convert the biodegradable waste into organic manure with the help of earthworms or other worms. Great care should be given in the process, since it is prepared by earthworm and are very sensitive to the external environment. The compost prepared after vermicomposting may be much beneficial as a fertilizer. It has low capital cost and operating cost. It provides excellent employment, beside the best technology it is eco friendly.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is mainly focused on management of 64% of organic waste produced everyday. It has contributed in vegetative waste management.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of this technology was taken into consideration after many researches a decade ago. Once the set up is made to perform a vermi culture the maintenance in 3-4 months in necessary. But the maintenance is not difficult as it can be done in a very small space.
Natural / human environment: For this culture to go on smoothly there exists some natural conditions. The moisture contents should be maintained in the vessel in addition to temperature not more than 28-32°C.
In addition the vermi composting should also be given adequate safety by human. The domestic animals and other should be kept far away from the area of composing because they would harm earthworm which plays te most important role in composting. The vessel shouldn't be more than 2 ft in height.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Nepal
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kathmandu, Lalitpur, Biratnagar, etc
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
No actual data has been recorded till date related to SLM approach area. It can be practised in small area to large area. There is not any commercial background in Nepal so its indefinite. It's wide spread all over.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- access to fertilizer
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- rice
注释:
major cash crop: Rice and potato
major food crop: Maize and cauliflower
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): - mixed household waste
- difficulty in separation of organic and inorganic waste.
-pollution created due to waste (vegetative and agricultural)
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): -crop productivity is limited by poor soil fertility
-intense cropping, and a scarcity of irrigation water
-decrease in the health of their crops and degraded soil conditions when chemical fertilizers are overused
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 养蜂、养殖业、家禽业、养兔业、养蚕业等
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M4:活动时间安排的重大变化
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cp:土壤污染

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
Main causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (it cause erosion of top soil), population pressure
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), change in temperature (denaturation of nutrients), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …), governance / institutional
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
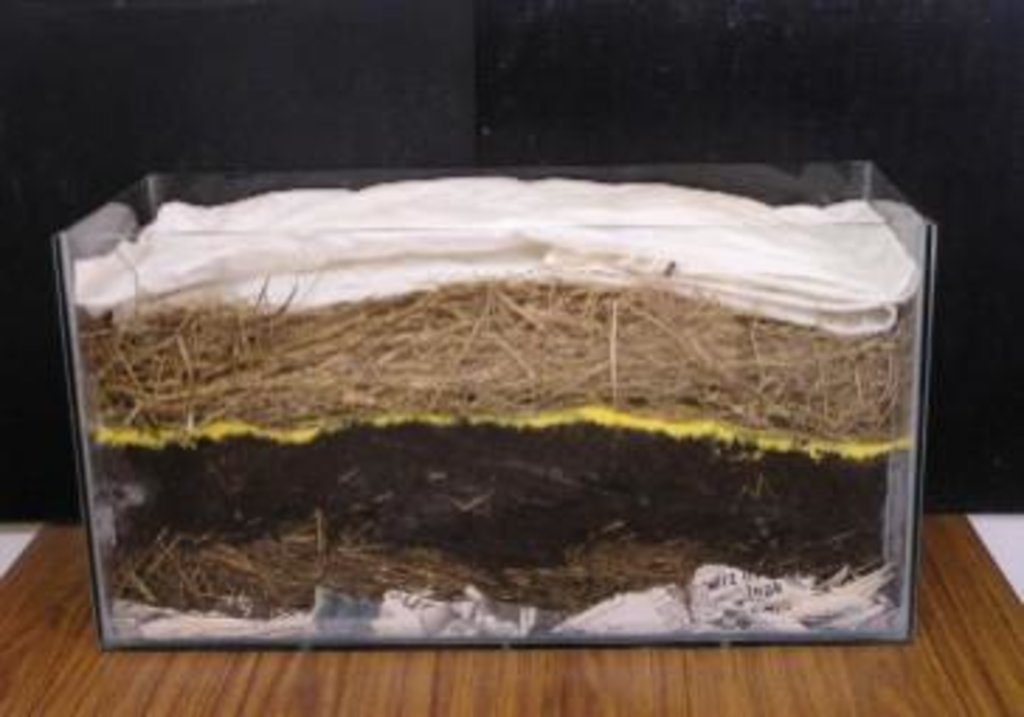
Firstly, the wastes are segregated and is arranged in a container. the base of the container i.e the bedding may be done using straw or paper. The layer above it is the soil layer. Next, the earthworm layer followed by the organic waste. the container is closed with a lid with holes in it. After certain time interval the manure prepared is arranged .
Later, the earthworms are separated from the compost formed.
Kathmandu
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (indigenous knowledge)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 4.3 tonnes/ha
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Structural measure: container
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6096
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.4384
Construction material (earth): mud can be used as base or it is also used in the container made of other materials.
Construction material (concrete): a container is necessary
作者:
Teku
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | container with lid | |
| 2. | earthworm | |
| 3. | straw, paper or cloth |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Container with lid | pieces | 1.0 | 62.5 | 62.5 | |
| 设备 | Earthworm | worms | 625.0 | 0.02 | 12.5 | |
| 设备 | Straw, paper or cloth | kg | 2.0 | 0.9 | 1.8 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 76.8 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 76.8 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | moisture maintenance | once a day |
| 2. | hatching | once in 3-4 months |
| 3. | vegetative waste | added everyday for 1-2 months |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Moisture maintenance | persons/month | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 劳动力 | Hatching | persons/3 month | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 设备 | Vegetative waste | kg | 2.0 | |||
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 3.0 | |||||
注释:
Costs calculated on the basis of earthworms used and some of the tools used.
The container used in Kathmandu metropolitan, Teku is of measurement 2.4384 m in length and 0.6096 m in width which gives about 500 kg of compost after few months.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The number of earthworm used for composting affect the cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
10% of the land users are rich.
60% of the land users are average wealthy.
30% of the land users are poor.
Level of mechanization: Tractor use.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
- 个人,未命名
- government
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
land and water resources are used fro communal property
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
产品多样性
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Time consuming
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It has taught people to manage 64% of the household waste. - the product from this technology is much efficient in the agriculture. - this can be taken into commercial level. - the solid waste management problem is reduced to minimum on adoption of this technology.
Production of smell
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
注释:
- more variety of earthworm.
- new design for the base formation.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
The vermi composting has many benefits compared to harms and is very economical in any way.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Management of solid waste, reduces cost of waste management. |
| utilization of organic waste. |
| helps to generate income. |
| very economical and gives best manure for food crops. |
| no much labour. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Vermi culture is not wide spread even within a community. | Awareness to a high priority is required. |
| No segregation from household level. | Governmental efforts should be given priority. |
| No sufficient market. | Priority from all the sectors is important. |
| Process can be quicker only in the presence of more labour. | Different technical support can help to make it quicker. |
| Vulnerable to environment pressure such as temp, drought, etc. | Regular maintenance is required. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Technical manuals:Community mobilization unitKathmandu Metropolitan
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Teku, Kathmandu
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块