Humic acid application [荷兰]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jason Stuka
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Toepassing van humuszuur (Dutch)
technologies_1254 - 荷兰
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Smit Annemieke
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra)
荷兰
SLM专业人员:
Rienks Willem
Rom3D
荷兰
SLM专业人员:
Leever Henk
HOEDuurzaam
荷兰
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ROM3D - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Hoe Duurzaam - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Wageningen Environmental Research (Alterra) - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Provincie Gelderland - 荷兰有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Vitens - Laat Water Voor Je Werken - 荷兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Regional process, social innovation [荷兰]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- 编制者: Simone Verzandvoort
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Humic acid application is a technology that allows the farmer to supply organic matter to the soil, without supplying additional nitrogen and phosphorus.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The application of humic acids to the soil is a way to supply organic matter, without supplying additional nitrogen and phosphorus, which is disadvantageous for farmers under the current manure legislation, since this imposes a threshold for the entry of nitrogen and phosphorus.
Humic acids stimulate the binding of K, Mg, Na, Ca and trace elements to the soil complex, causing the soil to supply more nutrients to the plant roots. umic acids fix iron and calcium particles, preventing these to fix phosphorus. This enables the release of phosphorus for take up by plant roots.
Purpose of the Technology: Increasing grass yield and nutritional value of grass.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Solution is applied with a tractor sprayer approximately 33 metres apart. Only small strips are applied as this is a test by farmers. Strips are shifted and rotated each year. They spray with a density of 60 L/ha. Width of strip is only the width of the sprayer.
Natural / human environment: Humic acid is a by-product of the water company's treatment of drinking water.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
荷兰
区域/州/省:
Gelderland
有关地点的进一步说明:
Haarlo - Oude Eibergen
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Humic acid is applied on grassland fields in small strips. There are 344 ha of grasslands in the area spread amongst 44 farmers. Only 4 farmers applied this technology.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
- Introduced by water company
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Decrease of soil organic matter content. Nutrient losses to ground water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The group of farmers in the area experience decreasing organic matter content in soils, soil moisture deficits and declining yields of grass and maize cultures.
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 250 Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Hq:地下水水质下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Hq: decline of groundwater quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Ploughing intensive grassland renewal)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (rotation with more corn and less grassland)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
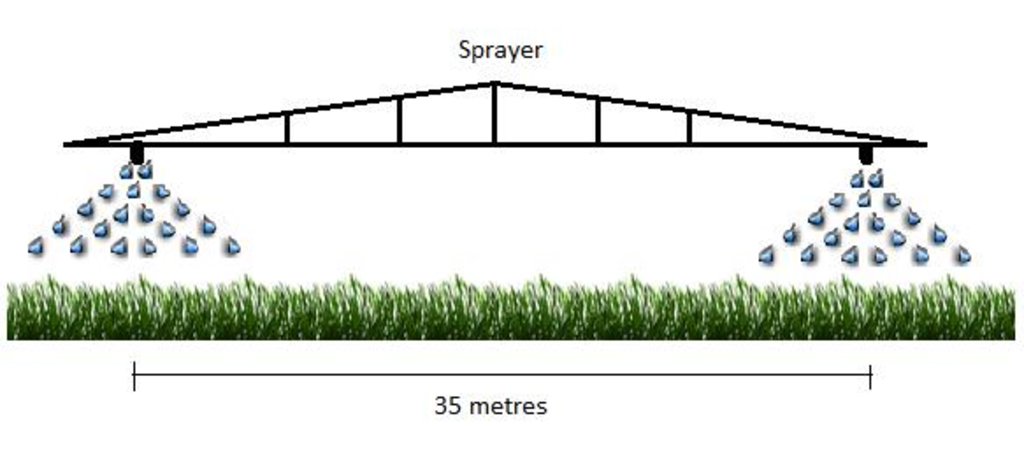
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Sprayer on a tractor applies humic acid in short strips 35 metres appart.
Location: Wageningen. Gelderland
Date: March 20, 2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Quantity to apply is important.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Easy to apply.)
Main technical functions: increase in organic matter
Secondary technical functions: increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: Humic acid
Quantity/ density: 60 L/ha
Remarks: strips 35 metres apart.
作者:
Jason Stuka, Wageningen University
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.94
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
255.70
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Spray humic acid on grasslands | Once per year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 36.17 | 36.17 | 50.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Humic acid | ha | 1.0 | 140.43 | 140.43 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 176.6 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 187.87 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor, sprayer.
March 20, 2015 - No new equiptment is needed for this technology.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Price of product - humic acid.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
182 days of precipitation annually.
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C (LGP 240-269 days, mean monthly temperatures vary between 2-17 °C)
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitidunal zone: 0-100 m a.s.l. (up to 45 metres a.s.l.)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm), deep (A and B horizons up to 40 cm in Gleyic Podzols and Umbric Gleysols (ca 75% of the area). Hardly any soil organic matter below 15 cm depth. Rooting depth is up to 80 cm depth), shallow and very deep (deep topsoils rich in organic matter in the Fimic Anthrosols (12% of the area))
Soil texture: Coarse/light (All sandy soils)
Soil fertility is medium
Topsoil organic matter (The purpose of the pilot project is to increase soil organic matter)
Soil drainage/infiltration is good (deep ground water. Sandy soils.) and medium (some shallow groundwater)
Soil water storage capacity is medium (Dependent on soil organic matter content)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (Contaminated. Requires treatment by water company (Vitens).)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Most outdoor farm opersations are completed by men.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Market orientation is subsistence (Grazing and fodder for dairy cows)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
Average grassland is 7.8 ha per household.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
All agriculture land is owned by individual farmers. Some farmers lease their land to other farmers. There are some regulations on land uses set by communities.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Estimated. Not measured or proven.
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Estimated. Not measured or proven.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Humic acids are provided by the company Triferto. In the future this will be on commercial basis.
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Created farmer's foundation
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Farmers understanding ecological impacts of farming practices, dairy farmers have learned more about soil health.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
Farmers collaborating with water company.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
土壤
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Expected. Not proven yet.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
Slightly positive benefits are mentioned based on a test by Triferto (the company selling the humic acid) in 2014 in one cut of grassland. The yield was 8% higher and the grass contained higher concentrations of trace elements.
However, there is no evidence from farmers about improvement of their yields as a result of the application of humic cid. Increase in weight of grass production has not been measured and value has not been compared to application costs. The few farmers that are applying humic acid have only done so for two years and results are not measured yet. But farmers are subsidized for humic acid application until 2024.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
4
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: It is too early to state this, since the technology is still in the test phase. Humic acid is applied on 29 ha of the 130 ha total surface on which measures to increase soil organic matter are applied in the pilot Gezond Zand. Results on the effects are only sparsely available, Farmers are being subsidized to apply the measure until 2024.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology is likely to increase soil organic matter, to improve nutrient uptake by the crop and to improve the soil moisture retention capacity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Test the expected impacts in field implementations of the technology by farmers. Continue subsidy or payment for the humic acid until positive effects have been demonstrated. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology is likely to increase soil organic matter, to improve nutrient uptake by the crop and to improve the soil moisture retention capacity. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Test the expected impacts in field implementations of the technology by farmers. Continue subsidy or payment for the humic acid until positive effects have been demonstrated. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farners are unlikely to pay for the application of humic acids until impacts are proven, but they know that the application of humic acid does no harm to their soils or crops, and ae therefore not reluctant to apply the humic acid as long as it is paid for by the subsidy arrangement or the drinking water company. | Continued financial support for applying the humic acid and proof of impact. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The drinking water company (supplier of the source material for the humic acid) and the company selling the humic acid raise big expectations about the technology, but thus far there is no scientifically based proof of impact on maize or grass yield. | Continued tests in real farm implementations. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Gezond Zand: Met een verbeterde bodemkwaliteit naar een betere waterkwaliteit Haarloseveld en Olden Eibergen By Willem Rienks and Henk Leever 2014Unravelling changes in soil fertility of agricultural land in The Netherlands Arjan Reijneveld 2013RECARE_WP3 Report: CS_11_Ouden-Eibergen_v2 Annemieke Smit and Simone Verzandvoort 2014
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Free http://www.hoeduurzaam.nl/images/gallery/nieuws/Brochure/BrochureHoeduurzaam%20Definitief.pdfWageningen University Library http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/wda/2044057Free annemieke.smit@wur.nl
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Regional process, social innovation [荷兰]
Social innovation for sustained soil organic matter, clean drinking water and sustainable crop production
- 编制者: Simone Verzandvoort
模块
无模块