Terrace [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Meili WEN
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Terrace
technologies_1367 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
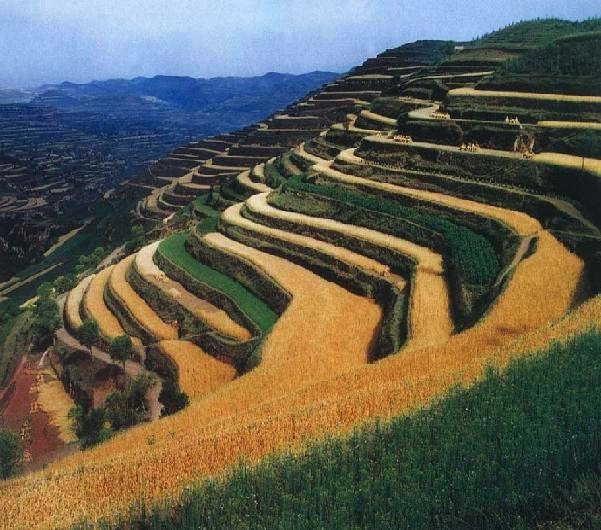
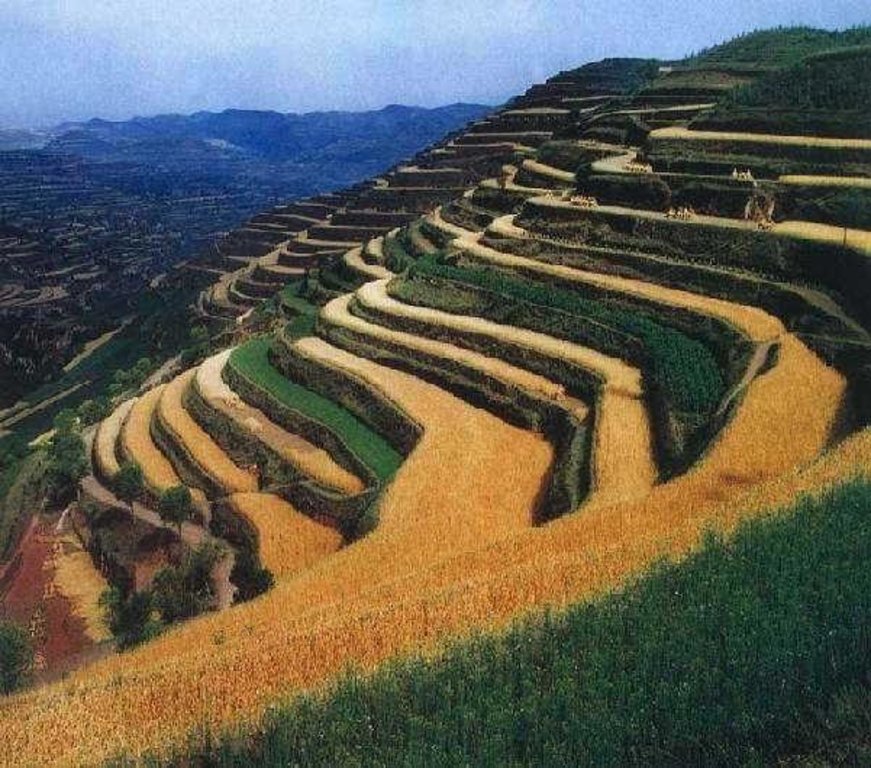
A terrace is a kind of measure to change the slope, which has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A terrace has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top. It can reduce slope angle and length, retain runoff, increase infiltration and reduce the soil loss. Crops can grow well because water increases in soils. Meanwhile, ground cover is improved. Terrace can be constructed by manual labor or machine. Firstly, determining the width of the field according to the slope angle and soil texture. Secondly, putting the topsoil aside. Thirdly, leveling up the slope and constructing banks. At last, putting the topsoil to the top of the flat surface.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Shaanxi, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Henan, Gansu
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
26666.7
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- > 10,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 26666.7 km2.
Terrace is one of the most outstanding achievements in SWC in China. It can prevent soil and water loss so that slope land can be sustainable development. There are about 26.7 million ha of terrace in China, of which more than 13.3
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
Summary from farmers' long term experience in SWC, later being innovated.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: May-Sep
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water lose seriously, soil degrades, soil fertility decreases and crop yield declines.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): crop yield declines, weak ability of resisting drought
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
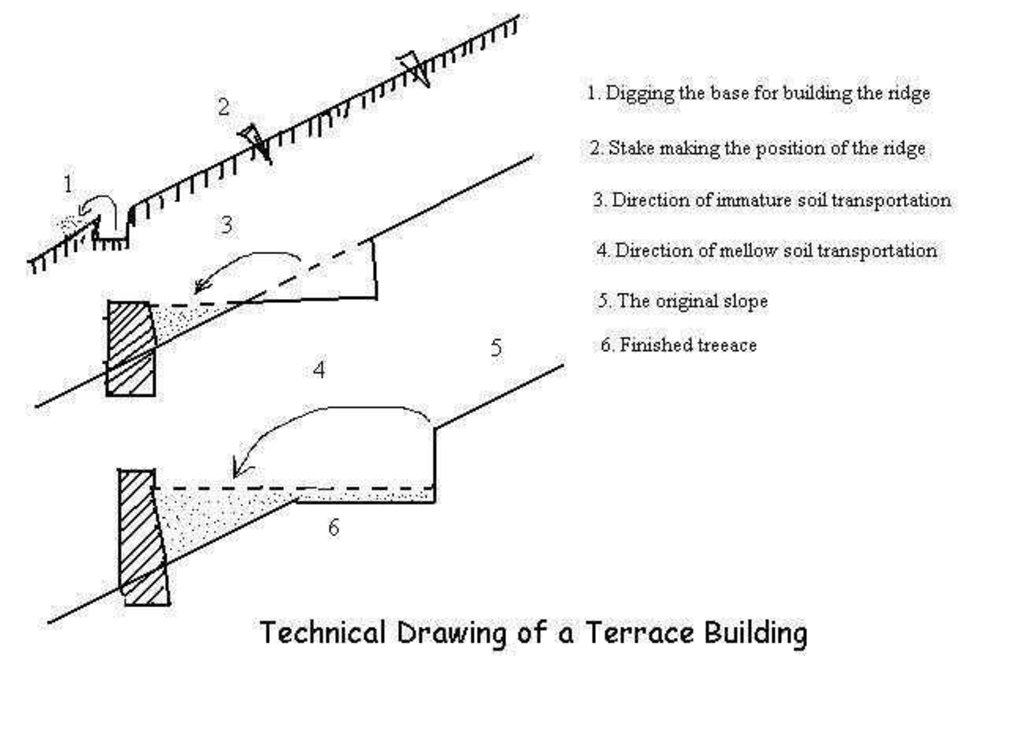
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Drawings of a terrace building in the Loess Plateau
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, Gansu, Inner Mongolia
Date: 2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Construction material (earth): Construct ridge of terrace
Construction material (stone): Construct ridge of terrace
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 80%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:6
作者:
BAI Zhanguo, Beijing China
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | survey | After harvesting crop |
| 2. | constructing terrace: determine the excavation line which should make the excavation and the filling equal and the least workload | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 3. | constructing terrace: pilling mellow soil up to the middle of a bench | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 4. | constructing terrace: moving the immature soil of lower part to fill the upper part or moving the soil from inside to fill up outside | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 5. | constructing terrace: building the ridge | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 6. | constructing terrace: spreading the mellow soil on the surface | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | periodically inspecting | After a storm/About 1 year |
| 2. | repairing where terrace is collapsed | Whenever finding it is destroyed/timely |
| 3. | level up the field | after harvesting crops/timely |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Terrace section, building by bulldozer.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The factors are topography, soil texture, means of construction. The section of terrace is the most important factor.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
449.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average also rolling
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Relative level of wealth: all selected
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, average, poor, very poor
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: estimate
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 社区/村庄
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
10
SLM之后的数量:
4
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
180
SLM之后的数量:
58
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If they have enough money, they would like to do, because they have known the benefits from terraces.
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
(inner resources) Suide Water and Soil Conservation examination station of Yellow River Water Resources Committee.. 1981.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
orpus of Test Research of Water and Soil Conservation (the second volume), p130~185.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
(inner resources) Water and Soil Conservation Department of Yellow River Water Resources Committee of Ministry of Water Resources and Electric Power.. 1987.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Corpus of economic benefits of water and soil measures, p77~102 ,510~514
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Dongyinglin,Changpiguang ,Wangzhihua. Discussion on the several questions on increasing production of the terrace with two banks.. 1990.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.1, p36~37
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Jiangdingsheng. Discussion on section design of the terrace on the Loess Plateau.. 1987.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ACTA CONSERVATIONIS SOLI ET AQUAE SINICA, Vol.1, No.2,p28~35.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Liangqichun, Changfushuang , Liming. A study on drawing up budgetary estimate quota of terraced field.. 2001.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, Vol.21,No.5, p41~44.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Liumingquan, Zhangaiqin, Liyouhua. Pattern engineering of reconstruction the slope cropland.. 1992.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p18~21.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Lixuelian,Qiaojiping. Synthetic technology of fertilizing and improving production on the new terrace.. 1998.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p13~14.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ministry of Water Resources of China. Terraces in China.. 1989.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
The press of Jilin science & technology.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Wangxilong,Caiqiangguo,Wangzhongke. The consolidating function and economic benefit analysis of the terrace hedgerows in the hilly loess region of northwest Hebei Province.. 2000.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Journal of Natural Resources,Vol.15, No.1, p74~79.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Xuyuanxu.The surveying report of the terrace benefits in yanbian autonomous prefecture. 1995.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Water and Soil Conservation,No.4, p50~52.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Zhujianqiang,Lijing. Experimental study on soil compact characteristics and its shearing strength in changing slope field into terrace on south shaanxi province.. 2000.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ransaction of the CSAE,Vol.16, No.2, p36~40.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块