Rangeland Rehabilitation [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Franci Petra Jordaan
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Grazing land (vegetative) combined with management education
technologies_1379 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Van Rooyen Jaco
Department of Agriculture, North West Province
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Dept of Agriculture North West Province (Dept of Agriculture North West Province) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Rangeland rehabilitation where we use perennial grasses to rehabilitate the footslopes in a semi-arid region on a clay loam soil
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
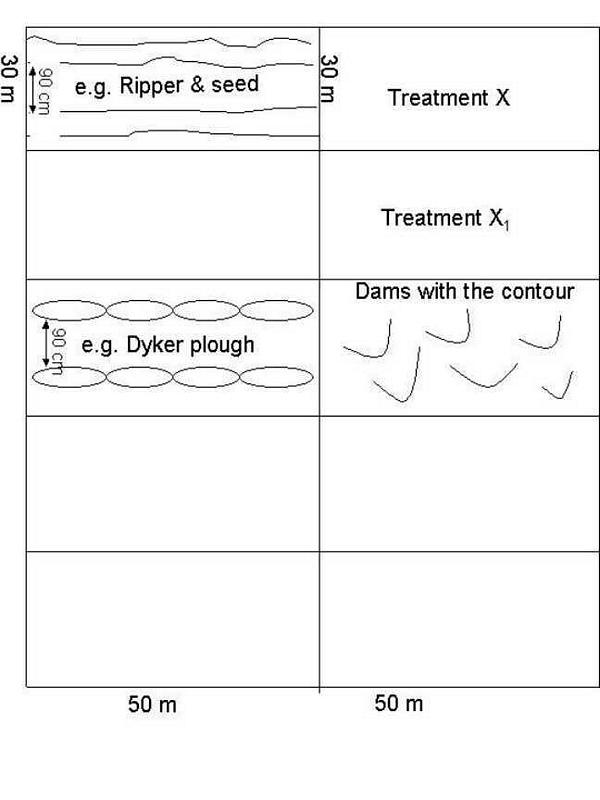
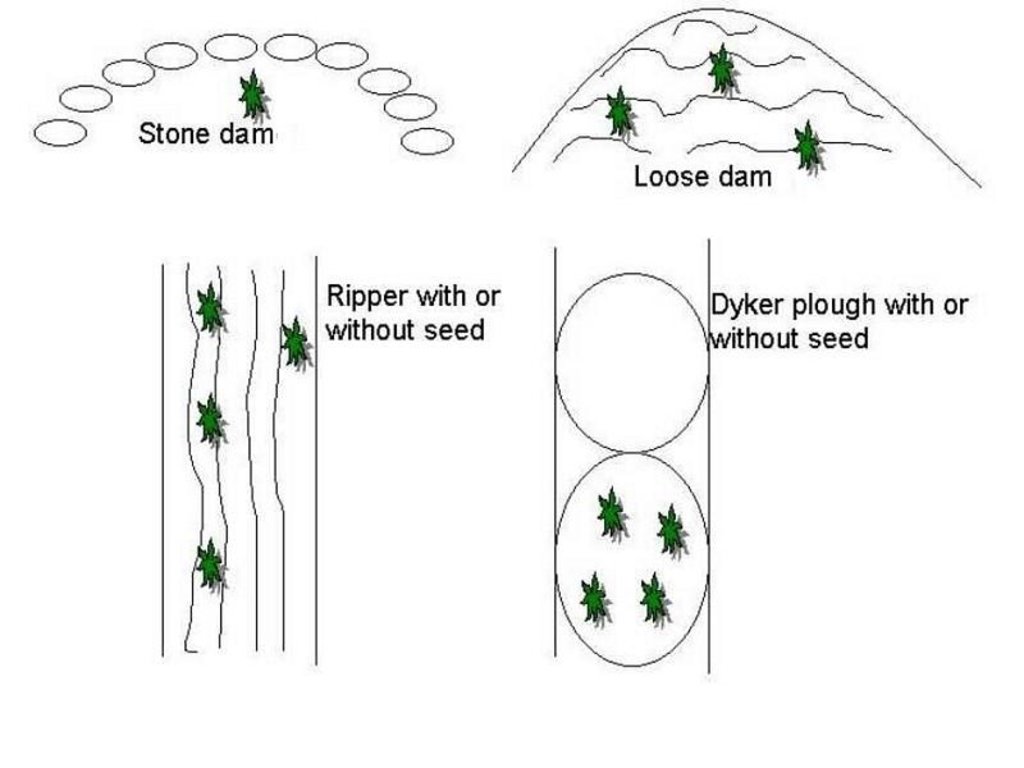
Different techniques (mechanical: e.g. ripper, dyker plough) as well as biological (stone dams, loose dams) are used to rehabilitate a totally degraded area. Different combinations are also used: e.g., ripper with seed and ripper without seed, to see if there is a natural seed bank left. The research is being done in a semi-arid area and on a footslope (medium depth and clay loam soil). The purpose is to get palatable vegetation back in the area for animal consumption. In the process, erosion is stopped and water run-off decreased. At the same time, the community is also trained and educated regarding management, grazing capacity, etc.
Researchers and technicians of the Provincial Department of Agriculture planted the experiment. The community is always present when any treatment is applied. The area is fenced off and maintained by the Department. The community will take full responsibility of the trial at a later stage. They are very eager to take over and their participation is very good.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
RSA32
有关地点的进一步说明:
Leharatshe
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.4 km2.
At Driefontein we do only rangeland rehabilitation. At Middelrand we do a combination of bush control and rangeland rehabilitation. The Driefontein area is representative for more or less the whole province. Small village 1.5 - 2km away from Driefontein. Former homeland (Bophuthatswana)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
From the researchers of the Department of Agriculture
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
动物类型:
- 山羊
- 骡子和驴
- cattle
产品和服务:
- 交通工具/役畜
注释:
Main animal species and products: Cattle & goats, donkey
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Too many animals for the specific area. No camps - so no form of rotation possible; no management plans - animals can walk and graze where they want to.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Need more land so that the animals have a larger area to move in.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Cattle & goats, donkey (transport)
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 210; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Apr
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
注释:
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Ripper and dyker ploughing with or without seed
Location: Driefontein. North West Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 6kg seed
Grass species: Panicum maxium, Chloris gayana, Digitaria eriatha, Chenchrus ciliaris
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
作者:
Franci Jordaan
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
6.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fencing of area | 1week (end of growing season) |
| 2. | Application of different techniques (treatments) | 2 weeks (beginning of growing season) |
| 3. | Planting of grass | 2 days (beginning of growing season) |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Keep fence in tact | /Regularly |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labours didn't want any money - they feel that they will reap the benefit in the end.
The implements must come from Potchefstroom which is 300km from the area.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is lo because organic material is gone due to overgrazing & water erosion
Topsoil organic matter: No organic matter
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor and there is a very high water runoff
Soil water storage capacity is very low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
100% of the land users are poor and own 100% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Sunflowers and maize for self subsistence
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
NA
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
From no grass to fodder for the animals
饲料质量
收入和成本
工作量
其它社会经济效应
input constraints
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
90
SLM之后的数量:
50
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
4
SLM之后的数量:
1
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
其它生态影响
soil fertility
biodiversity
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Quickly done |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Quickest way to get more palatable grass, a more economical way |
| Very effective |
| Biological methods |
| Manpower to do it |
| Community was not paid, more sustainable |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Expensive | |
| It is difficult to get the seed | |
| Seed itself is expensive |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Community do not have implements | Maybe landcare |
| Lack of knowledge (a lot is needed) | Come and see, learnt a lot by implementing |
| On a bigger scale - fence off more or less impossible - at this stage (can not afford) | Maybe branch packing (enough black thorn bush encroachment) |
| Do not understand the system |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块