Cut-off drain [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Unknown User
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Rong rabai nam (Thai)
technologies_1405 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Tiparat Sutep
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Outarasak Vorachai
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Suksom Prasong
Highland Flower Growing Promotion Project
泰国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Doi Tung Highland Agricultural Extension Center - 泰国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Highland Flower Growing Promotion Project - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Cut-off drain [泰国]
This approach is the 'way' or 'how' the cut-off drain has been implemented on steepland in northern Thailand.
- 编制者: Samran Sombatpanit
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
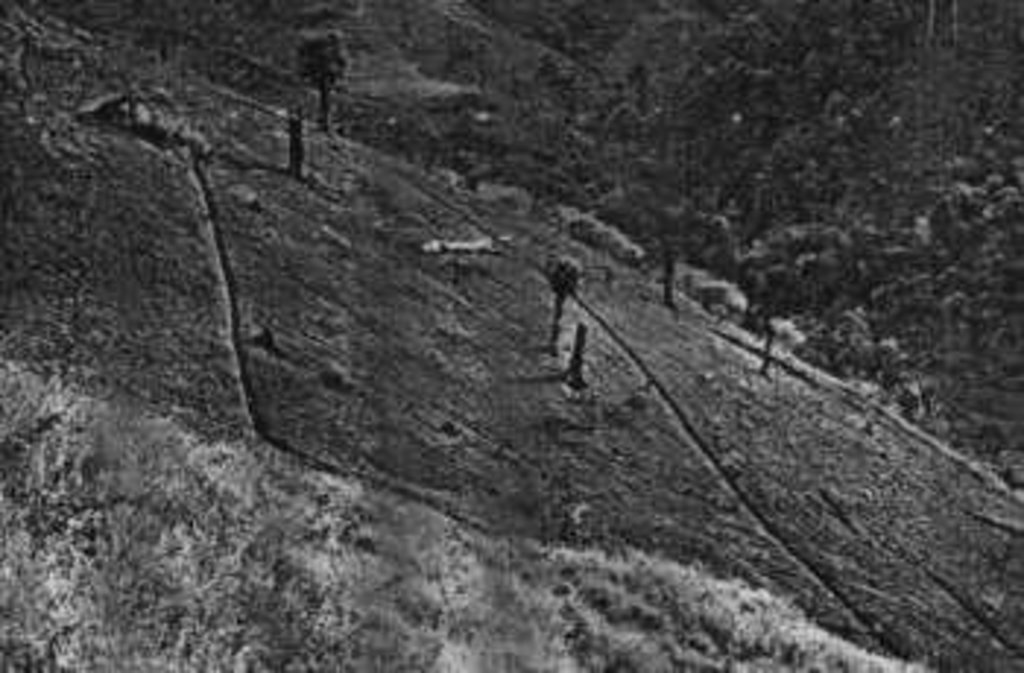
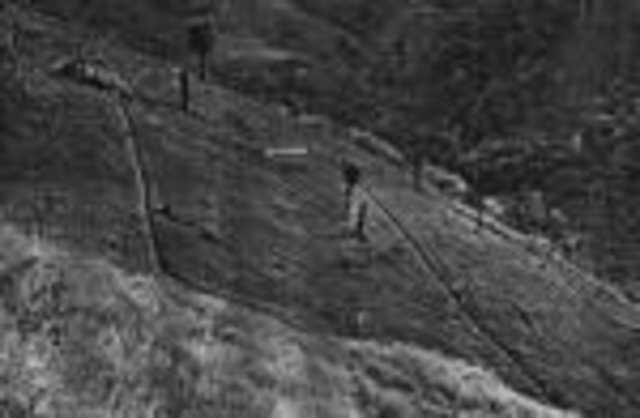
Cut-off drain is a drainage ditch dug to quickly drain water out of sloping agricultural land.
2.2 技术的详细说明
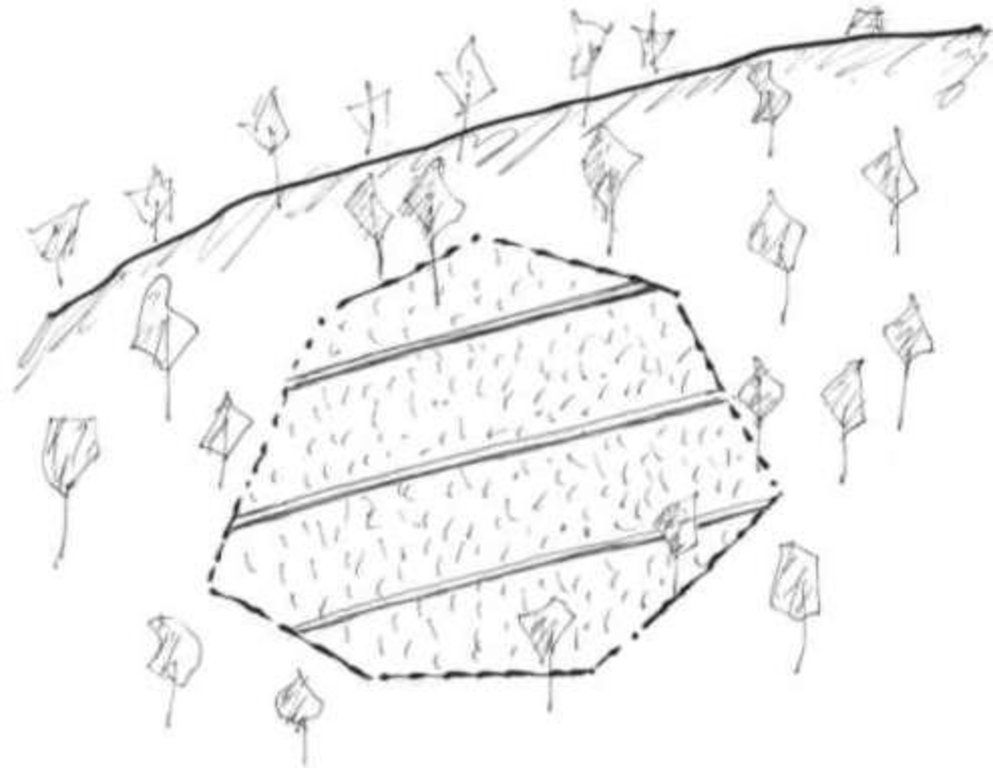
说明:
The cut-off drain is the same thing described as 'diversion' or 'diversion ditch'. It is dug by hand-hoe, only one hoe wide in the first year and may expand wider in the second and third year. It is dug with gradient from 15-50% to facilitate drainaing of runoff, not to scour the soil. Note: 1. The width of one hoe is approx. 21 cm , 2. The dimension of the ditch may become 30-40 cm wide and deep after 3 years.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Chiang Rai
有关地点的进一步说明:
Amphur Mae Fa Luang
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 15 km2.
E-kaw, Lahu, Lisu, Mien, Khin, Thai Yai, Haw Chinese, H'mong. They have been doing this practice for a long time. The technology transfers from generation to generation.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
It is an original idea. No one knows how/when it was originated.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 水稻(旱地)
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 水果、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: May - Aug Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Nov

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
- 半游牧畜牧业
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. There is soil erosion problem because of high terrain, 2. Lacking of land ownership (The whole land area is reserved forest), 3. Low price of agricultural produce,
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): 1. Lacking of land ownership, 2. Land users do not have Thai citizenship; less than 20 % have ID cards (not citizenship).
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), Lack of enforcement of legislation or authority
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural activities), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
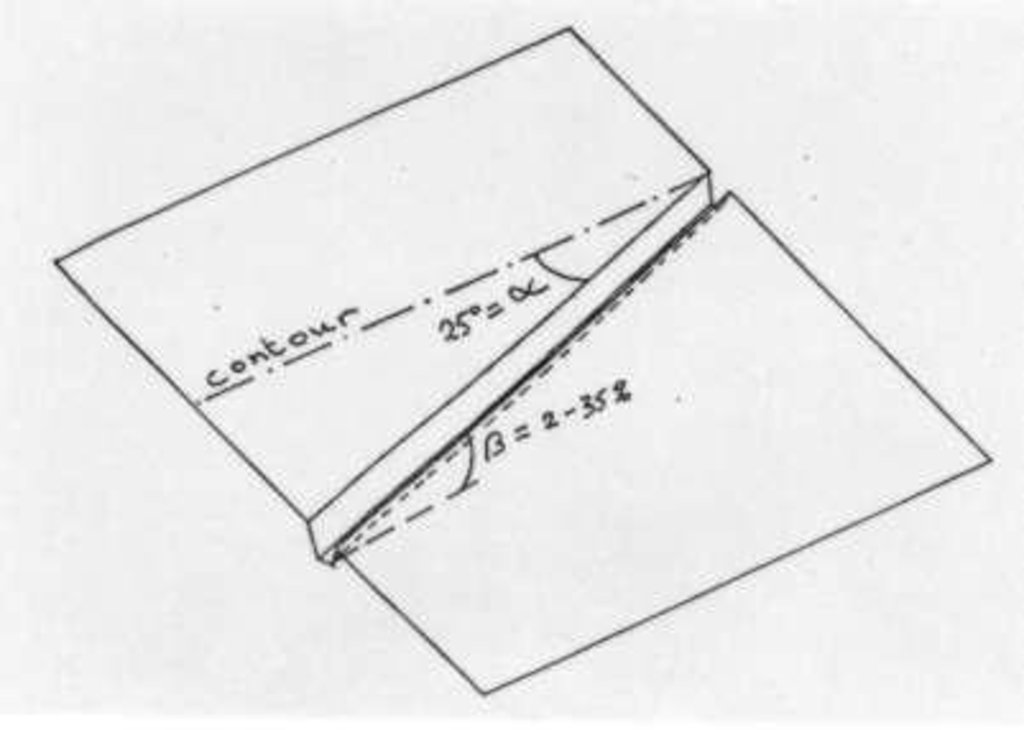
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Average slope properties of a cut-off drain.
The cut-off drain is the same as 'diversion'. It is dug by hand hoe, only one hoe wide in the firs yer and may expand wider in the second year and third year. It is dug with gradient in order to facilitate draining of runoff, not to scour the soil. The gradient may vary from 3:20 (15%) to 1:2 (50%).
Note: The land may be cropped for 3 years and left for shrubs to grow for some years. Then farmers return to clear the land to grow crop again.
Location: Average slope properties of a cut-off drain.. Chiang Rai Province
Date: 1999
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope length
Structural measure: Cut-off drain
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 40
Construction material (earth): It is the earth dug in situ.
Lateral gradient along the structure: 20%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
作者:
Turkelboom
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Baht
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
37.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.16
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging of the ditch after land preparation | Before rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4.32 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.12 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dredging up the earth that fell down when preparing for next crop | Before rainy season/Annually |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 4.32 | 4.32 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4.32 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.12 | |||||
注释:
Cost per ha of land protected
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Steep slope will require larger number of the cut-off drains, thus affecting the cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average = 1600-1800 mm
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Also shallow (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: High (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (good drainage though being clayey soil)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium and low (both ranked 1)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
6% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
24% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (Large proportion are poor).
10% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers spend much time doing wage earning labour jobs.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Ranked 1: 1-2 ha. Farmers may farm at 2-4 plots far apart from each other
Ranked 2: 2-5 ha
Ranked 3: 0.5-1 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Production is not decreased.
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Farmers don't mind
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
经济差异
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Drainage can function as a farm path
其它社会经济效应
Input constraints
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
20
SLM之后的数量:
15
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
10
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
中性/平衡
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
800. 13% of the area covered
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
800 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: When farmers understand the use of it they will do it.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It can drain excess water from the field quickly, not to cause scouring of the field. |
| This T is cheap and simple to install in any field. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It can drain excess water from the field quickly, not to cause scouring of the field. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When farmers get the idea, this T will be sustained/enhanced. |
|
This T is cheap and simple to install in any field. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cheapness and simplicity will make it sustained. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land users do not see any disadvantages |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| This T may cause erosion of its own structure at the beginning. | Government agencies should help design the size and gradient of this T toi be properly used. |
| This T may cause erosion off-site especially when the drained water is allowed to flow directly to open land | Design and build waterway to receive the disposed water. |
| This T does not enhance soil fertility improvement | Try to use it along with other measures which improve soil fertility or change it to something else. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Pongsapich, A. Indigenous Technical Knowledge for Land Management in Asia. 152 pp.. 1998.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
IBSRAM, Bangkok
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Turkelboom, F. On-farm diagnosis of steepland erosion in Northern Thailand, PhD thesis. 309 pp.. 1999.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Laboratorium Voor Bodemvrucktbaarheid en Bodembiologie, Katholieke Universiteit Leuven,Kardinal Mercierlaan 92, B-3001 Heverlee,Belgium
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Cut-off drain [泰国]
This approach is the 'way' or 'how' the cut-off drain has been implemented on steepland in northern Thailand.
- 编制者: Samran Sombatpanit
模块
无模块