Range Pitting and Reseeding [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Fahim Ghassali
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Nakr al mara
technologies_1410 - 阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Bathika Nabil
ICARDA
阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
SLM专业人员:
Gintzburger Gustave
Institut de Botanique -Univ. Louis Pasteur
法国
SLM专业人员:
Hill Stephen
Australian Revegetation Corporation Ltd.
澳大利亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - 黎巴嫩有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Université de Strasbourg (UNISTRA) - 法国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Australian Revegetation Corporation Ltd - 澳大利亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Government assisted rangeland rehabilitation [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
The rehabilitation of overgrazed and denuded rangeland with government intervention
- 编制者: Unknown User
2. SLM技术的说明
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
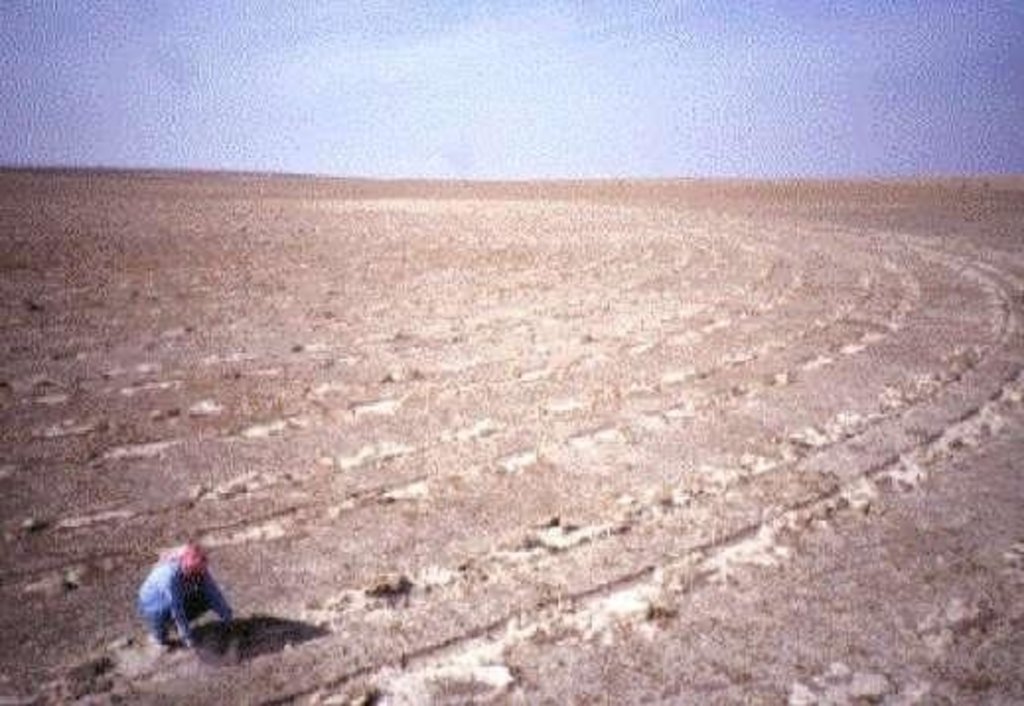
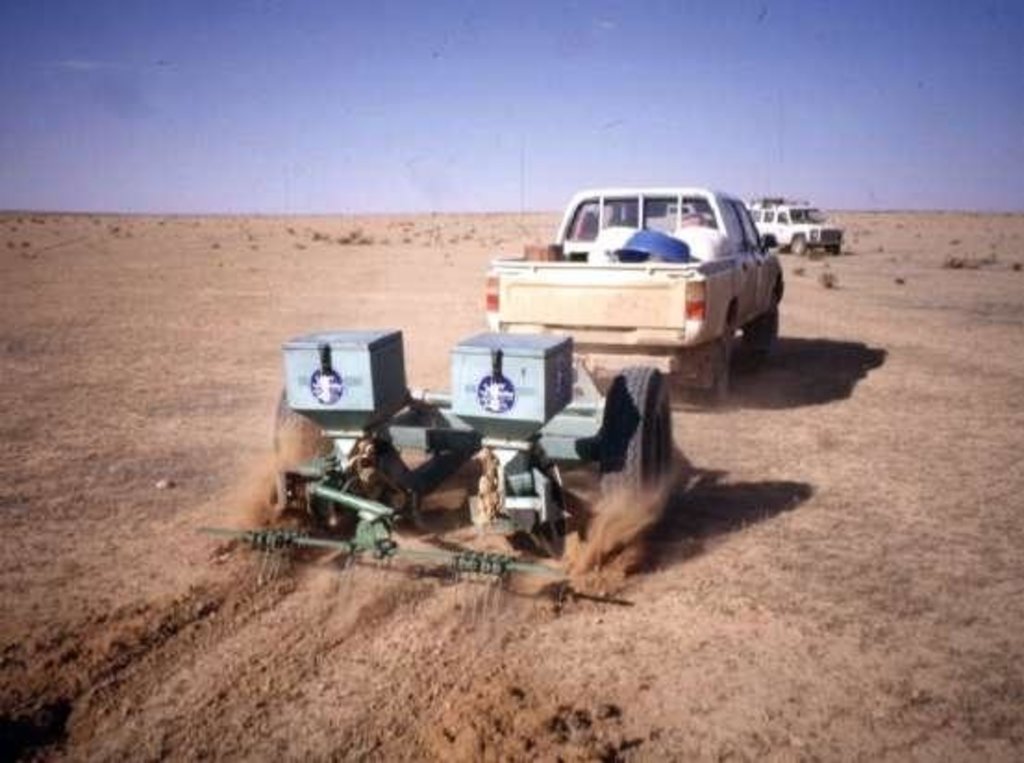
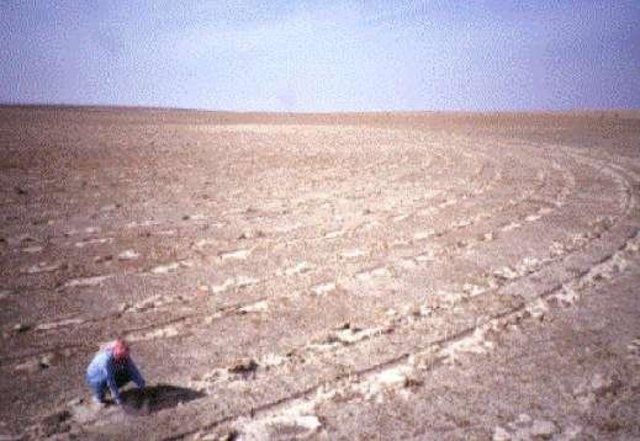
This technique is used to restore degraded rangelands (steppe areas) in the 150-200 mm rainfall zone in Syria. The technique is based on the pitting technique developed in Australia using the 'Camel Pitter' implement. The implement an be towed by an ordinary 2-wheel-drive pickup. Small ahallow 'pits' are scooped out by the action of inclined metal disks (similar to the disks of a disk plough). A seed hopper mounted on the top of the implement releases small quantities of range-plant seeds into the pits and an attached light harrow coveres the seeds with a thin layer of loose topsoil. The implement can also be used without the seeding device. The pits are usually made at the beginning ot just before the rainy season. In the soops made by the implement, rainwater collects and increases the soil moisture storage in and around the pits. On extremely shallow soils, pitting is not recommended because it removes the very top layer of soil and organic surface material and may expose the infertile subsoil. Seeds which emerge in the pits find favourable conditions for emergence and growth. During the early growth stages, the young plants are also sheltered by the pits from wind. The pitting machine should be pulled along the contour to optimize the capture of rainfall. Experience has shown that treating just 10-20 % of the area is sufficient to reestablish a 'starter vegetation' on completely denuded rangeland. In Syria, ARTEMISIA and SALSOLA species have been used successfully for rangeland reseeding. If used without the seeder, the pits will assist the reestablishment of the natural vegetation by providing sheltered and moist sites for seed emergence. To assure optimum reestablishment of vegetation, grazing should be controlled during the initial establishment phase.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿拉伯叙利亚共和国
区域/州/省:
Aleppo Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Obisan, Dalbouh
注释:
Comments:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 110 km2.
The main collaborator was the Ministry of Agriculture (Steppe Directorate)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Western Australia
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing and cutting of woody shrubs for firewood. Large-scale cultivation of fodder barley (for grazing) completely removes the natural vegetation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land tenure system. Rangeland is 'public land' and control over its use is difficult to implement.
locally adapted rareseedinspecies, e.g., Atriplex halimus, Salsola vermiculata, Artemisia herba-alba
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Too many animals. Grazing pressure is too high), Over-exploitation of vegetation (Too many animals. Grazing pressure is too high), Land subdivision (Land parcels for communities are limited in size)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting
Vegetative measure: pitting: scooping out very shallow pits
Vegetative material: O : other, O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other, O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other, O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other, O : other
Other species: locally adapted rareseedinspecies, e.g., Atriplex halimus, Salsola vermiculata, Artemisia herba-alba
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Syrian Pound
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
4.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | pitting | beginning of the rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 960.0 | 960.0 | 10.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 270.0 | 270.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Sand | ha | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1351.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 27.02 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | pitting | beginning of the rainy season /annually where plants have not come up |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 96.0 | 96.0 | 10.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 3.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 117.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 2.34 | |||||
注释:
per ha of treated area
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour, slope, soil depth
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Dryland area with 150-180 mm rain
农业气候带
- 干旱
Area not suitable for arable farming
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Flat (flat areas prone to wind erosion)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: migrant work
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
45
SLM之后的数量:
5
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
4
SLM之后的数量:
1
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Improvement of wildlife
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
Natural seed multiplication and supply
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
50 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The land belongs to the state and not to the land users
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Better vegetation growth How can they be sustained / enhanced? More involvement of the local community. Pay attention to land-use rights and land ownership |
|
Better feed resource How can they be sustained / enhanced? More involvement of the local community. Pay attention to land-use rights and land ownership |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
cost-effective way to revegetate denuded rangeland How can they be sustained / enhanced? Protection from grazing for the first 3 years |
|
Increased range productivity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Better regulated grazing of the vegetation. Preventing overgrazing |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The pitting machine removes the top 5 cm of soil and the vegetation over the area of the pit | Method should not be used on extremely shallow soils |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Government assisted rangeland rehabilitation [阿拉伯叙利亚共和国]
The rehabilitation of overgrazed and denuded rangeland with government intervention
- 编制者: Unknown User
模块
无模块