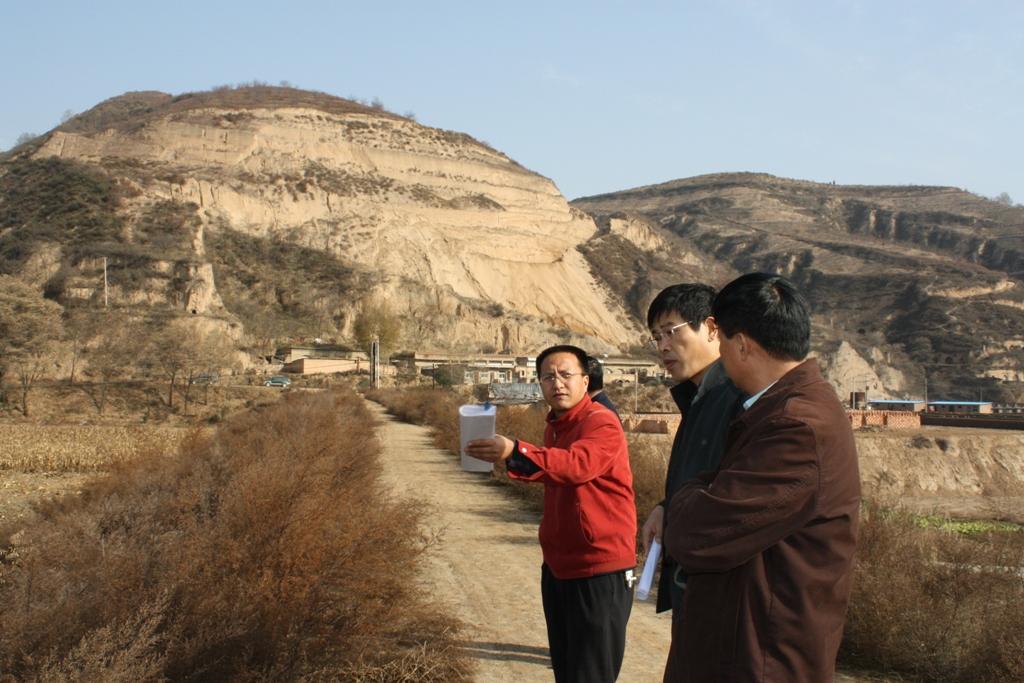
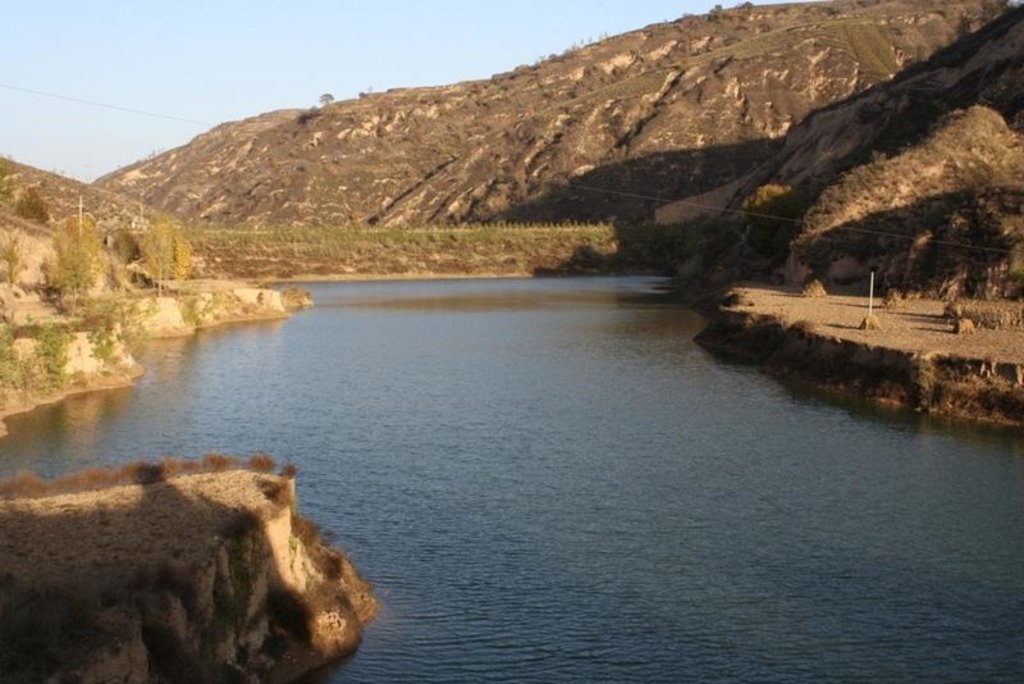
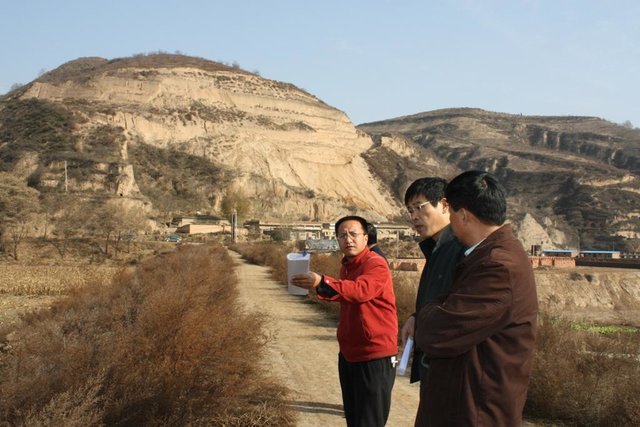
Check dam for land [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Fei WANG
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
淤地坝,谷坊
technologies_1455 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Mu Xingming
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
中国
SLM专业人员:
Wen Zhongmin
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
中国
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Chen Yun-ming
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
中国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Project of check-dam for land [中国]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- 编制者: Fei WANG
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Check dam for land is a structural SLM practice that is constructed in the valley of a watershed in order to slow down the runoff and increase sedimentation. After this, the land quality of the controlling area will increase because soil and water conditions in this place are improved.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The check dam is a small dam designed to reduce flow velocity, control soil erosion, and allow to settle on the bed of the valley. The whole system includes main body of dam, spillway, overflow and supporting measures. The check dam for land is a small dam mainly for land after it is filled up by the sediment from upstream area, from several years to 20 years in common, it could be flat land in the valley, not mainly for water collection (different from reservior).
Purpose of the Technology: Check dams in the Loess Plateau are very common. There are many advantages. The check dam could not only reduce the erosion of the gullies, furthermore it retain the sediment in the flow and this decreases the sediment of the Yellow River. The check dam is good quality land for the soils because of the sedimentation of organic matter and other nutrients from topsoil . In this region soils are deep and very fertile because most soil is from the top soil upstream. The soil moisture of check dam is also much better than in any other places in the watershed because the flood should go away from its surface and the water inflitration is great in raining seasons.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment needs enough money because it has to be safe enough, and the maintenance cost is not so high. The catchment with great soil erosion is better when we considered the formation time of land.
Natural / human environment: The controlling area of check dam for land varies greatly from 30 square km or more. Since the "Grain for Green" Project of China in 1999, the soil erosion on the slope decreased. The time from reservoir to land need more time because there is less and less sediment from upstream and the sedimentation changed slowly.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Shaanxi Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Yanhe River Basin
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Only one check-dam for land is listed here.
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 19.4 km2.
The total area with different measures is almost 2000 km2 . Yanhe River is a first class branch of Yellow River, China. The average channel slope is 3.26‰, and the area of whole basin is 7,687 km2. It is situated in the semi-arid North Temperate Zone with an average annual precipitation varying from 500 to 550 mm, and an average annual air temperature ranging from 8.5 to 11.4℃. It is in hilly gully area of the Loess Plateau covered by loess. The landform is broken seriously. The gully density (the length of channel in one km2) is amount to 2.1 to 4.6 km•km-2. The soil loss is severe all along.
The Ganguyi Hydrology Station (109°48′E, 36°42′N) located in the Ganguyi Town, Baota Country, Yan’an City, Shaanxi Province. The area up Ganguyi Hydrology Station is 5,891 km2, including of Jingbian County(256km2), Zhidan County(708km2), Ansai County(2,699km2) and Baota County(2,228km2). The average annual runoff is 0.22 billion m3, and the runoff modulus accounting for 4,776.36 m3•km-2•yr-1. The average annual sediment flow is 4.776 million tons, and the sediment flow modulus accounting for 8,100 t•km-2•yr-1. The coarse sediment (sediment particle diameter not less than 0.05 mm) flow modulus is 2,430 t•km-2•yr-1 on the Ganguyi Hydrology Station.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
It is an old methodology in the Loess Plateau. Since 2003, the check dam had been determined as "Highlight Project " of the Ministry of Water Resources in order to expand in the whole area of the Yellow River Basin.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小米
- 花卉作物
- 饲料作物 - 苜蓿
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- buckwheat
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 枣子
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: March to NovemberSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: April to October

水道、水体、湿地
- 池塘、大坝
注释:
major crop: beans, sunflower, apple, Chinese date, alfalfa, potato, millets, maize, buckwheat
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Normally, the bed of valley is V-shaped and is covered by grass and trees. For the seasonal torrent or flash, it is very difficult to plant crops. The gully also cuts down by runoff and extends because of erosion's gravity .
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): It can not be used as agricultural purpose, especially to get more food.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S11:其它
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It is the reason of erosion that influence the valley.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
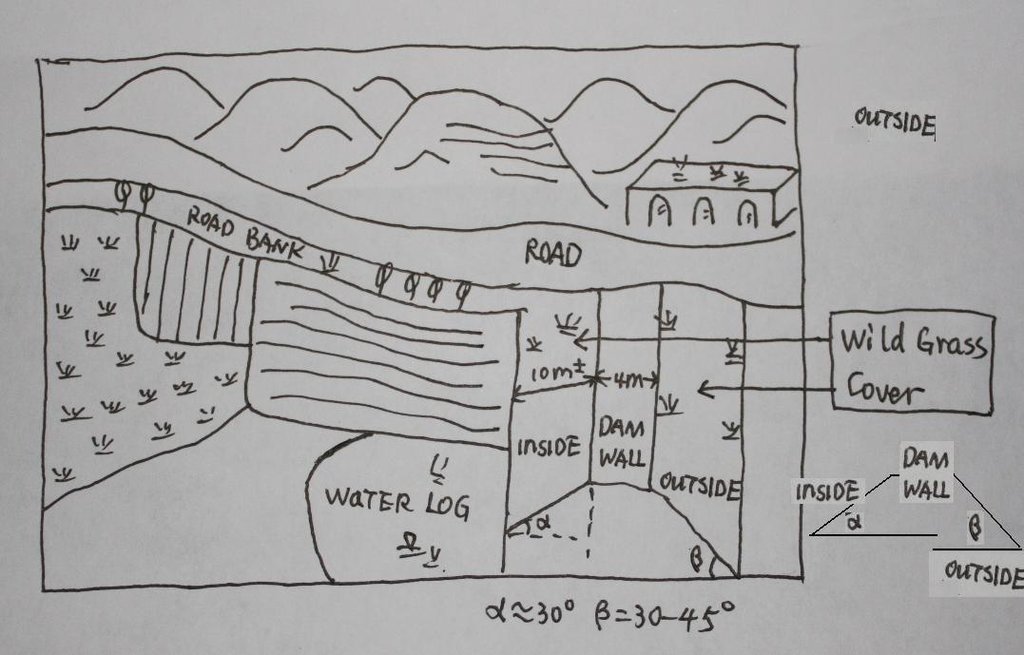
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The check dam land.
Location: Mazhuang Watershed. Baota County, Yan'an City, Shaanxi China
Date: 2008-10-20
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The design and construction need professional knowledge.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (it is easy to use, like alluvial land or wide terrace.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap
Spillway
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 6
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 6
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 10
Spacing between structures (m): 100
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50-100
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300-1000
Construction material (earth): The earth-bank dam is built in Yanhe River Basin.
Construction material (stone): to build the spillways
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2-5%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 180000m3
Catchment area: 58.3km2m2
Slope of dam wall inside: 30%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 60%
Dimensions of spillways: 3m
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
作者:
Wang Fei, Yangling, Shaanxi Province, China
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
-2.17
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
8.80
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field survey and location selection | Before design |
| 2. | Design | before construction |
| 3. | Build the dam wall | |
| 4. | Check and accept | After the construction |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Building the wall/ field survey and planning | Person/day | 180.0 | 8.8 | 1584.0 | 90.0 |
| 劳动力 | Building the wall/ field survey | Machine/hrs | 75.0 | 43.8 | 3285.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stone | m^3 | 40.0 | 26.35 | 1054.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5923.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | -2729.49 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | check the dam wall | annually |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | check annualy the dam wall | Person/day | 15.0 | 8.8 | 132.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 132.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | -60.83 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: crawler type bulldozer, giant jet, tractor, traditional tools, ruler,
The grass on both sides of check wall is natural grass.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The wide of dam wall affects the cost greatly, the wider, more expensive.The labour cost and the distance of rock quarry are also important.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm, up
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours
It is based on the classification sysytem only based on the rainfall.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: All check dam and check dam liand here is in such altitudinal zonation.
Slopes on average: Based on 1:100 thousand scale landform map
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: The depth of Loess varies from nearly 30 m to more than 100 m in Yanhe River Basin. The depth of soil is less than this but it could be nearly 10 meters in commom.
Soil texture: There are more than 50% soil particle which are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM
Topsoil organic matter: <0.5%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration in Loess is very fast, but it prones to sealing when flashing
Soil water storage capacity low: Evaporation and drainage are easy
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Availability of surface water also poor/ none and: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal rivers
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region
Water quality (untreated): Good quality for there are few pollution sources
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
It is very stable in this region
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
(The Check dam for land are build together in some villages for all the people funded by national sub).
Level of mechanization also manual work: The harvesting and other management are by hand
Level of mechanization animal traction: Tillage with animal power mostly
Level of mechanization mechanized/motorized: Tillage with machine in large area check-dam land.
Market orientation of production system mixed: Some production for themselves, but most of production is exchanged on the market.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
According to 0.054 ha per capita
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Like other rural areas in China
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
600
SLM之后的数量:
6000
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
4500kg/ha
SLM之后的数量:
2500kg/ha
注释/具体说明:
In extreme year with great rainfall, low yield of check dam land
产品多样性
生产区域
SLM之前的数量:
950
SLM之后的数量:
59
社会文化影响
国家机构
社会经济弱势群体的情况
SLM之前的数量:
200 kg
SLM之后的数量:
350 kg
Livelihoods and human well-being
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
SLM之前的数量:
8 m
SLM之后的数量:
4-6m
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
12-16%
SLM之后的数量:
16-22%
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
60t/ha/yr
SLM之后的数量:
5t/ha/yr
其它生态影响
long time period to form land
注释/具体说明:
Sediment from slope decelerate the process of building arable land. In other words the economic function can not appear soon.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
SLM之前的数量:
2events/yr
SLM之后的数量:
nearly no
地下水/河流污染
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
The better condition of soil and water of check dam land improves the capacity of land tp cope with the changing climate.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
In the first stage, there is no economic output but the check dam is going to fill up with sediments. Afterwards the check dam forms land and with it benefit which would keep up a long time.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
675 households in an area of 19.4 km^2 (11 percent of the area)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
675 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: All the lands (cropland on the slope or check dam land and forest et al, ) are shared evenly by people. Of course, the work like to build check dam should be finished by all the families.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No single farmer or family can finish this work because the land right and great investment.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more local farmers want to get more check dam land for its long-term benefits.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The yield of check dam land is much higher than that on the slope land. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the local people to do more work without payment because they would get more benefits from this land as such. |
|
The yield is stable because the soil moisture is good even in dry year How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use the land efficient and mainten it. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It could reduce the soil erosion originated from the gully. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The local people know this benefit that make them try to find chance to build check dam. |
|
The dam can retain the flow and sediment and reduces the sediment delivery of the downstream. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ask the people or government of the lower reaches to combat soil erosion through the building of check dams. |
|
The check dam land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
|
Land is fertile and productive How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the awareness of local people to use this technology. |
|
The ceck dam can be used as rural road. How can they be sustained / enhanced? When we make the plan or design the construction, we should better take this into account. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It is too expensive to build the check dam. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams.The local people can work together without payment. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The land in a check dam with less and less soil erosion on the slope, needs longer time to form | It is difficult to overcome this because the control of erosion on slope has higher priority. We can find how to use the water or the temporary wetland. |
| The input of check dam is quite high. | Ask the government or other organization and person to invest in check dams. The local people can work together without payment. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Library of ISWC, CAS
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Project of check-dam for land [中国]
Approach of check dam for land is a kind of soil and water conservation activity to reduce the sediment discharge and improve the agricultural condition through building a dam across the valley in order to silt the sediment from upstream untill it convert to land with few soil erosion and …
- 编制者: Fei WANG
模块
无模块