Plastic-lined conservation pond to store irrigation water [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Madhav Dhakal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Plastic bichchhayeko Samrakshan pokhari - Nepali
technologies_1462 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A plastic-lined dugout pond to store runoff and household wastewater for irrigation purposes during dry periods
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
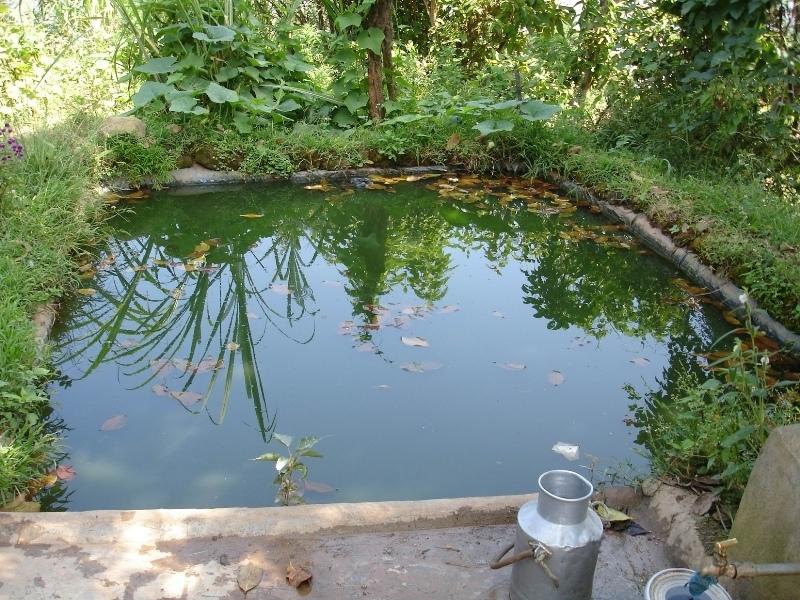
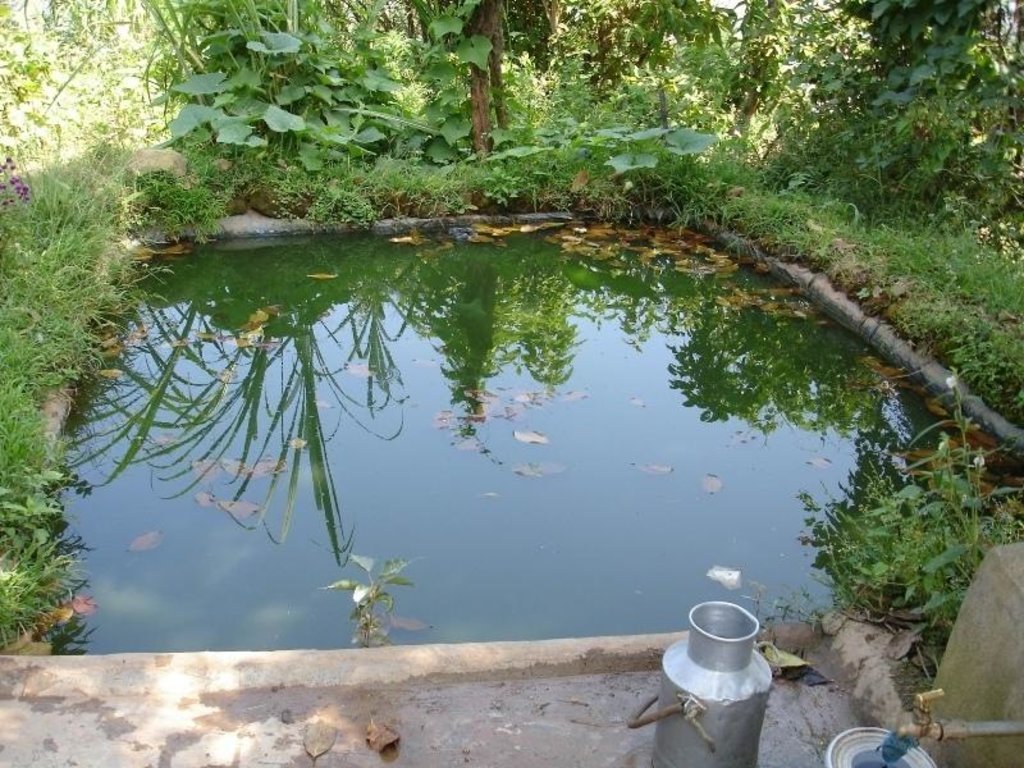
Water harvesting technology is very useful in areas where there is limited rainfall for long periods of the year. These dry periods severely limit the growing of crops across Nepal’s middle mountains especially on steep slopes where conventional irrigation can be difficult to arrange. Plastic-lined conservation ponds store water for irrigation more efficiently than the traditional earthen ponds which lose much water to seepage.
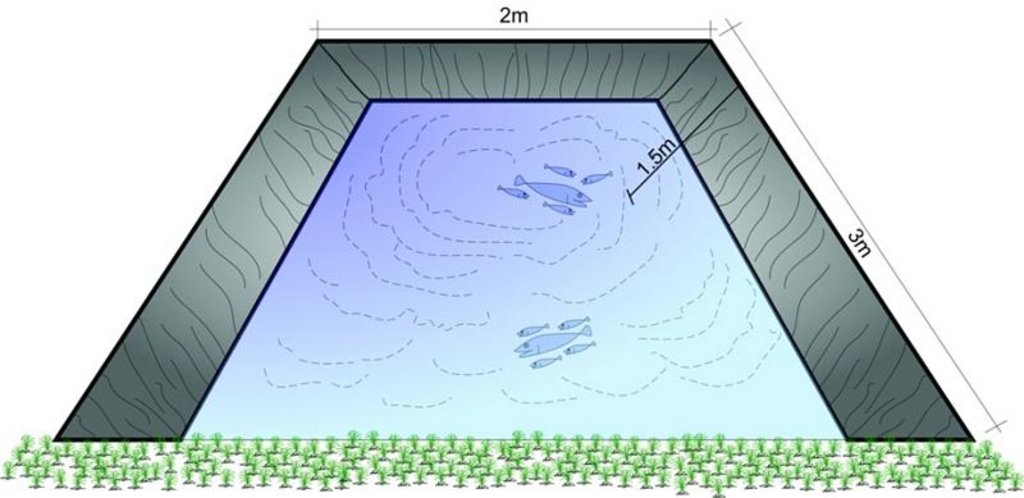
The ponds are dug out and the earthen walls lined with high density polyethylene (HDPE) sheet or SILPAULIN (multi-layered, cross laminated, UV stabilised) heavy duty plastic sheeting. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available and the soil characteristics. The PARDYP project tested and demonstrated plastic-lined ponds with a capacity of 8,000-10,000 litres. These ponds were about 3m long, 2m wide and 1.5m deep and were located at shady sites to minimise evaporation losses. The conservation ponds tested and demonstrated by the PARDYP project were used for irrigating high value off-season horticultural crops (vegetables, fruit, and spices). These crops were irrigated with drip irrigation and micro sprinklers (see sheets QT NEP6 and QT NEP21). The ponds were fed from rainwater, upland springs and taps, and household wastewater. The ponds were established during the dry season in three days. They were prepared by selecting a suitable site with a sufficient catchment; mapping out the area and depth of the pond; digging out the soil; removing protruding stones and roots; and compacting and smoothing the sides and bottom of the pond. Then the sides and bottom of the pond were lined with sieved soil followed by plastic sheet, which was anchored by stones and soil.
The main maintenance activity is to prevent livestock and people from entering the pond to avoid damaging the sheet. The pond should not be allowed to dry up as this would let rats damage the sheet. The sediment that accumulates in the pond should be removed once a year carefully by hand only as the use of agricultural tools could puncture the sheet.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kavrepalanchowk district/ Lamdihi, Patalekhet, Chiuribot, villages of Jhikhu Khola watershed
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
It is an ancient water management technique, later adapted according to the local condition.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- Improve water availability
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 其他
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- 种子作物 - 芝麻、罂粟、芥末、其他
- rice, wheat, tomato
每年的生长季节数:
- 3
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
注释:
major cash crop: Tomato and potato
major food crop: Rice and wheat
other: Mustard and legumes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): 1. Small landholdings which are mostly rainfed for cropping.
2. Low soil fertility status and high susceptibility to erosion.
3. Limited supplies of irrigation water and poor irrigation infrastructure.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The farmers experience serious constraints in terms of adopting better farming options, e.g., cash crops due to soil fertility and soil moisture problems.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Maize- wheat/ vegetables
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Plastic- linined conservation pond
Location: Patalekhet, Lamdihi and Chiurobot.. Kavrepalanchowk
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap
Structural measure: pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Construction material (earth): It is a earth excavated pit with earthen side walls
Construction material (other): plasitc sheet - Lining of a HDPE sheet or SILPAULIN (Multi-layered, cross laminated, UV stabilized p
作者:
A.K. Thaku, Madhav Dhakal
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Pond
指定单位面积(如相关):
3m long, 2m wide and 1.5m deep
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.10
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Select a preferably fl at site with a suffi cient catchment area | dry months |
| 2. | Measure the area to be irrigated and estimate the size of the pond | dry months |
| 3. | Measure and mark out the pond | 1st day |
| 4. | Dig out the soil to the pre-determined depth | 1st day |
| 5. | Remove protruding stones and roots | 2nd day |
| 6. | Compacting and smooting the sides and bottom of the pond. | 2nd day |
| 7. | Line the sides and bottom of the pond with sieved soil (preferably a clay | 2nd day |
| 8. | Lay out the plastic sheets without any folds over the pond with | 3rd day |
| 9. | Overlay thick fine soil on the plastic sheet | 3rd day |
| 10. | Anchor the edges of the sheet at the rim of the pond with stones and soil. | 3rd day |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Dig out pond | persons/unit | 3.0 | 2.1 | 6.3 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Plastic | unit | 1.0 | 29.2 | 29.2 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 35.5 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 35.5 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 3 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prevent livestock and humans from entering the pond | daily/regularly |
| 2. | Ensure that the pond is not allowed to dry out completely as this could | dry months./regularly, |
| 3. | Removing accumulated sediment once a year carefully by hand (using | dry months./once in a year. |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Clean and maitaining the pond | persons/unit | 3.0 | 2.1 | 6.3 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 6.3 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 6.3 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: measuring tape, spade, shovel, knife, hoe, hammer, trowel, and pan
The cost given above is for unit technology having 9000 litre capacity as in 2006.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of plastic, members of a household contributed as labour in all sites.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1070.00
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality (untreated): Also good. More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: spring
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 90% of the land (ranked by land users).
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and
increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries, whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are
working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia, and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
Market orientation of production system: Vegetables- commercial
Level of mechanization: Manual labour consists of planting, irrigation , harvesting, while field field preparation is carried out by animals, also machines but just in valley bottom.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
due to availability of more water for irrigation
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
due to informal network of farmers with ponds
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
farmers discuss and share experiences
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
increased vegetable production, more income from vegetables.
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
fallow land is turned into cropped land
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
due to trapped runoff
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Perception of land users who accepted the technology by getting
incentives from the PARDYP project. If incentives are not available the short-term costs and benefits would be equal.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
5 households in an area of 10 ha
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: because of the expense of the plastic sheet and it not being locally available
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Water is sufficient to irrigate 2-3 ropani( 1 ropani = 508 sq.m.)land in one season. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Advantages of the technology should be shared with large number of people. |
| Plastic pond lasted more than 5 years and it is leak proof. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Good income from sales of vegetables in the dry season can be achieved even from a small piece of land How can they be sustained / enhanced? Advantages of the technology should be more widely shared |
|
The source of water for these ponds was not only rainwater but also other sources like springs and taps, These ponds are fed with rainwater and household wastewater and from springs and taps. The ponded water was mainly used for micro irrigation including drip irrigation and micro-sprinklers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the use of other water conserving techniques like mulching when using the harvested water |
|
Reduced the dependence on large scale water supply schemes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Harvest all possible sources of water |
|
No seepage loss observed fi ve years after building the ponds meaning that the plastic lasts at least five years How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue trials |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Plastic pond is expensive for poor farmers. | subsidised cost for poors |
| unsafe for small childrens | Protection structures should be constructed. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| SILPAULIN (multi-layered, cross laminated, UV stabilized) heavy duty plastic is not available in local markets and is expensive for poor farmers | Make it available in the local market at a subsidised cost for poor farmers. |
| The ponds attract insects, mainly mosquitoes, that cause disease; and the ponds are unsafe for small children | Regularly clean the pond and fence them in |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
ICIMOD (2007) Good Practices in Watershed Management, Lessons Learned in the Mid Hills of Nepal. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SCWMC (2004) Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Measures and Low Cost Techniques. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Soil Conservation and Watershed Management Component - Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
DSCWM, Kathmandu
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Shafi q, M.; Ikram, M.Z.; Nasir, A. (1995) Water Harvesting Techniques for Sustainable Agriculture in Dry and Cold Mountain Areas. Paperpresented at the Workshop on Sustainable Agriculture in Dry and Cold Mountain Areas, Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, 25-27 September1995, Queta, Pakistan
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
ICIMOD
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块