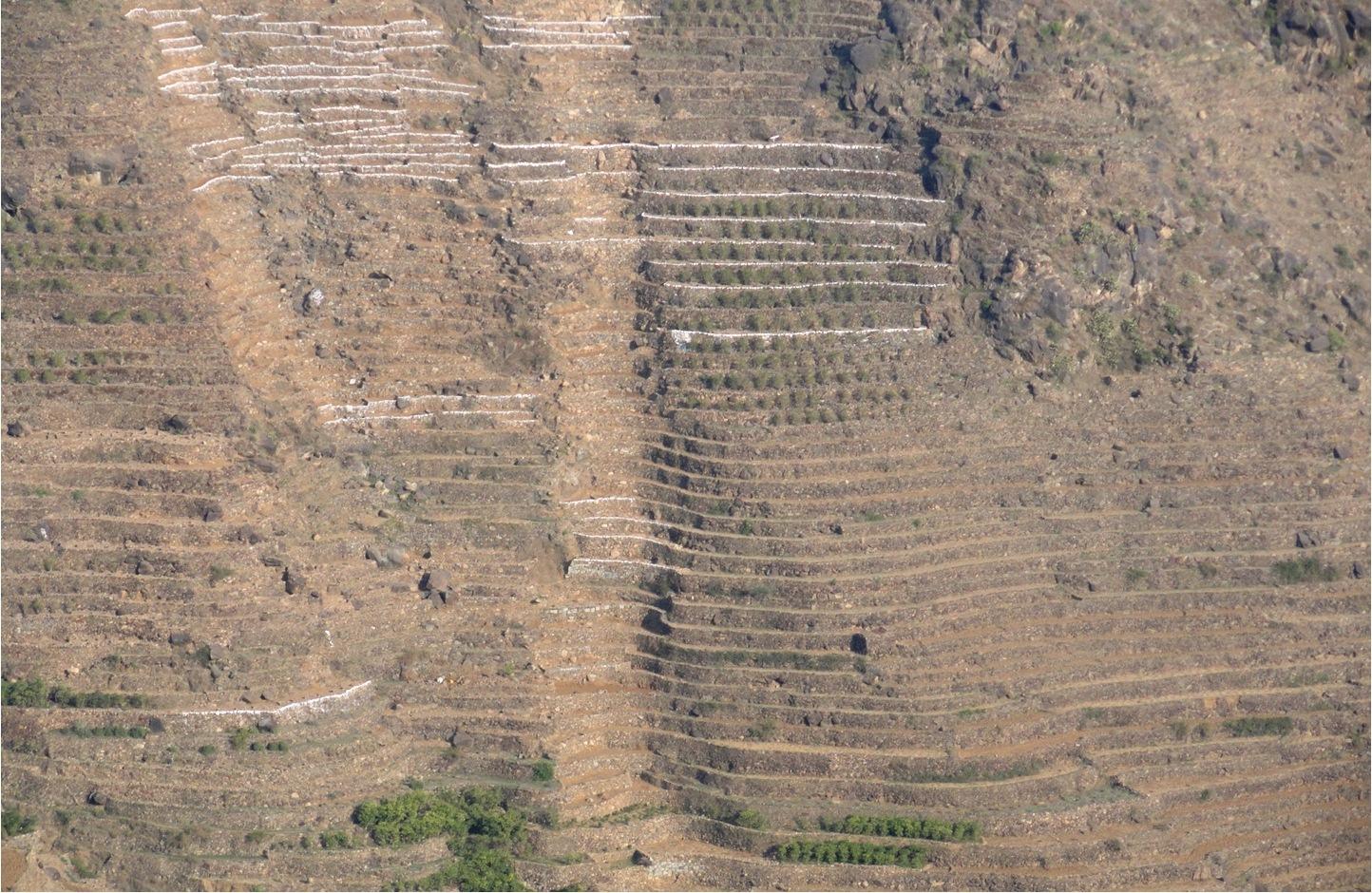
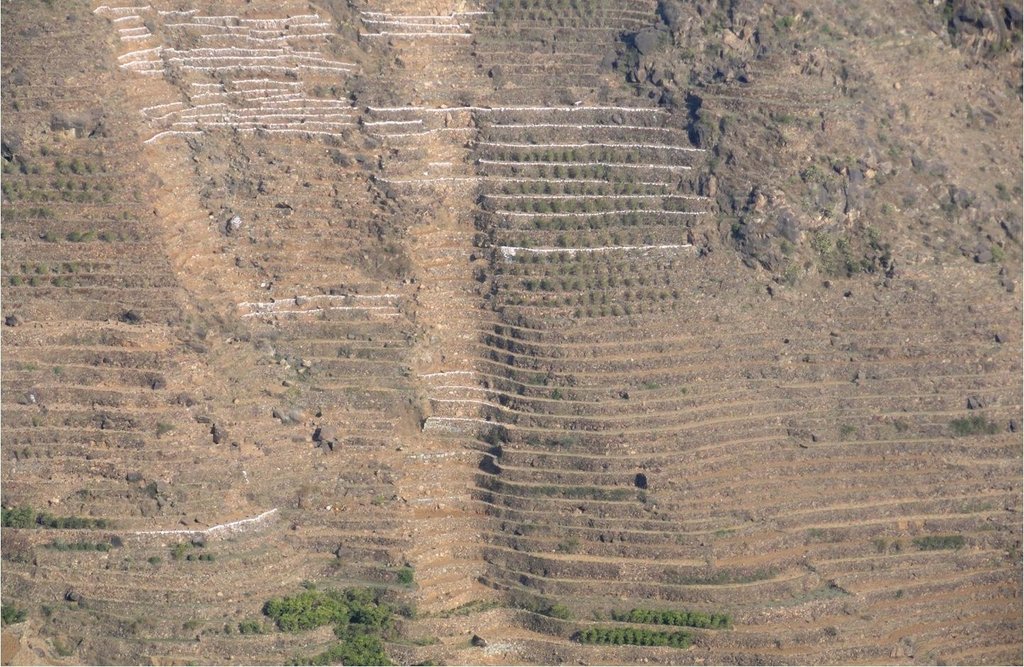
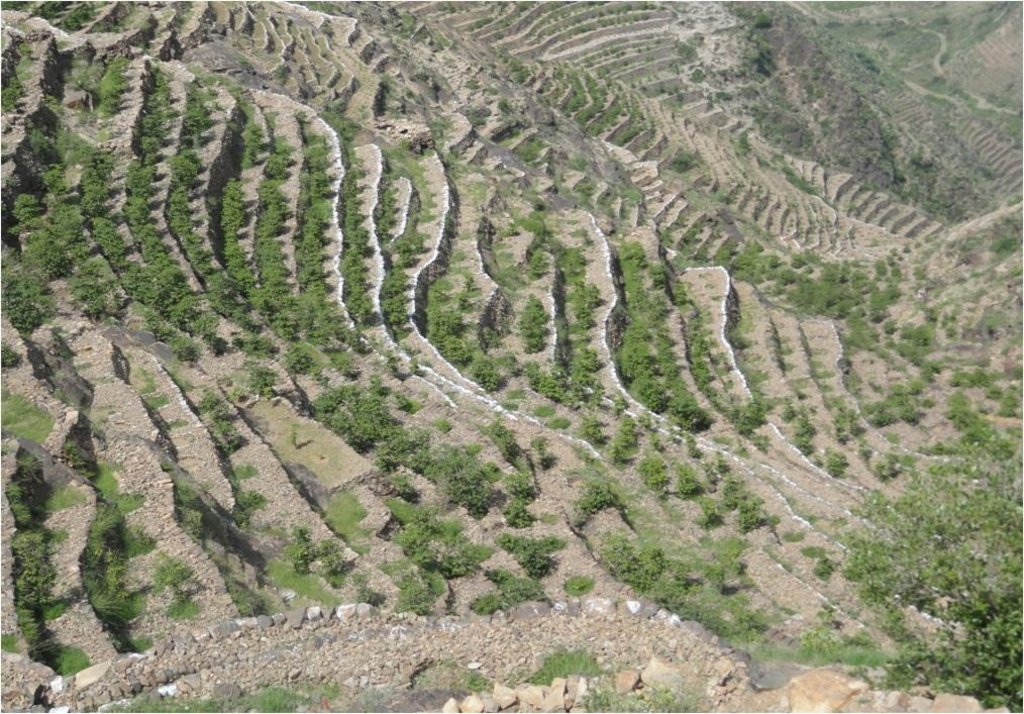
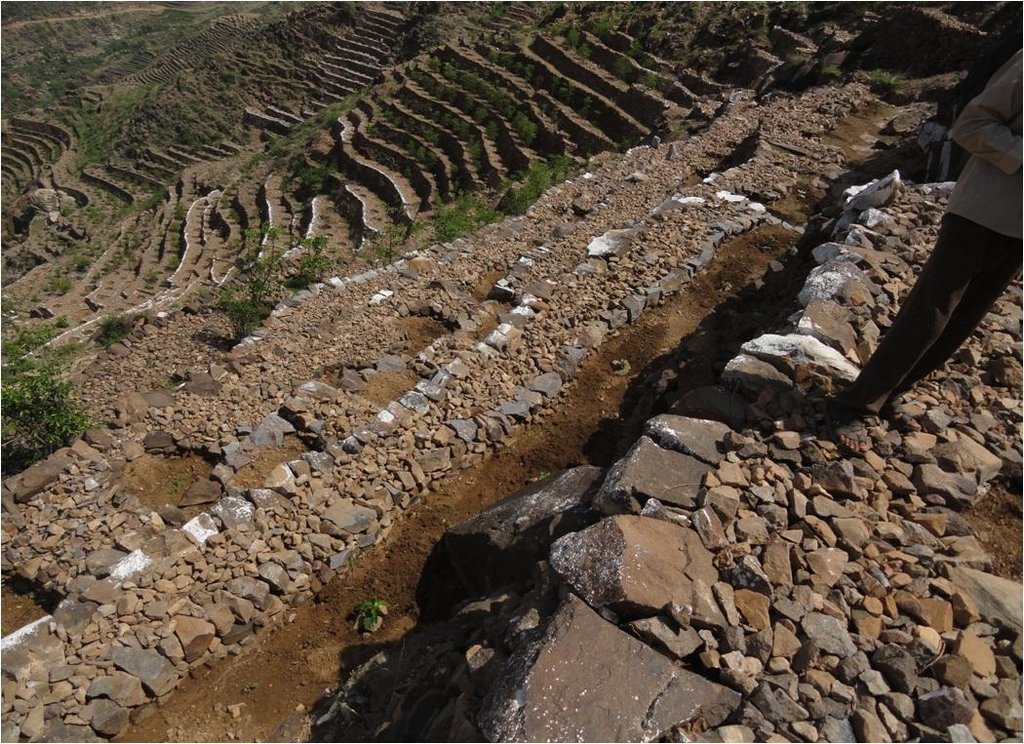
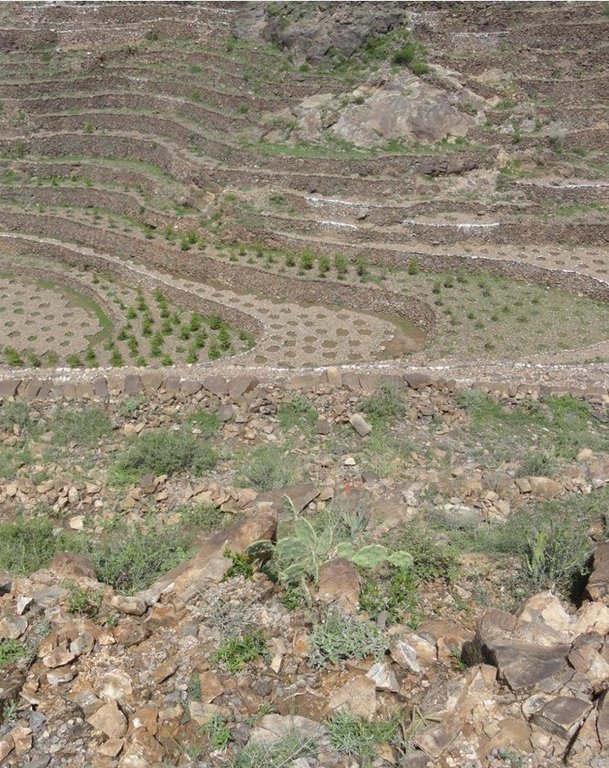
Bench terraces covered with small stones [也门]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: ahmed algalal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
المدرجات المغطاه بالأحجار
technologies_1560 - 也门
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Agricultural Research and Extension Authority (AREA) - 也门1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Building and rehabilitation of agricultural terraces. [也门]
Pay incentives for farmers rehabilitate degraded terraces in order to face the crisis of increasing food prices.
- 编制者: ahmed algalal
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Building terraces in steep areas for the purpose of reducing the slope, water harvesting and soil moisture conservation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
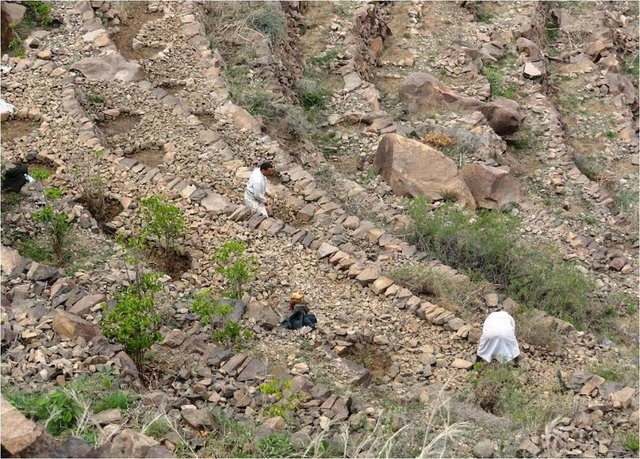
Cutting and collecting stones for the construction of terraces on steep slopes of the mountains, structural measure to reduce the length and angle of the slope and the speed of runoff. This makes it easier to harvest water and reserving deposits. A wall terraces is built of stones where the height of a wall should be increased height of 1.8 - 3 m, a width of 1.5 - 4.3 m and the length from 8 - 14 m to keep the accumulated deposits. The cutting stones are brought from distant places for the purpose of building the walls. These terraces are similar to mountain terraces but the top soil surface can be covered with stones to protect it from heavy rain storms and prevent sheet erosion that results from raindrops hitting the bare top soil surface. The stone layer, also prevents evaporation and maintains soil moisture. The stones are arranged in a layer of about 0.25 – 0.7 m thickness over the entire surface of the soil except where to put the coffee trees with an average diameter of 1 m. It is difficult to use equipment in the process of building the terraces due to severe slopes. Therefore it is a labor intensive process of manually building terraces. Due to the slow process of construction it requires a lot of time. However, building terraces on steep slopes can lead to increased erosion in the absence of well maintaining outlets that allow draining the excess water from one terrace to another, avoiding breaking of terraces' walls. In any case, terraces need regular maintenance to ensure the sustainability of this technology. The landscape of the region is mountainous, bench terraces which are used for crop production exist in slopes exceeding 60%. The texture of the soil is silty loam and the depth of the terraces is moderate to deep. Due to small holdings and steepness of the terraces, the local implements are used for land preparation. The climate in the region is arid to semi-arid and annual precipitation ranges between 200 and 450 mm. The major crop in this area is coffee, which is cultivated because of its high economic value on the market.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
也门
区域/州/省:
Sanaa governorate
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bani Ismail- Manakha District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Bani Ismail's Uzlah is situated in west part of the capital Sana'a
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.75 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
It is very ancient technology but was rehabilitated in 2011 by the users of the land by getting a fund from the Social Fund for Development
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 咖啡,露天种植
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water erosion in the form of Gullies, large stones loss (landslides) due to the sever steepness in addition to low soil moisture.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
注释:
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 集水
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S1:阶地
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Severe rainstorm), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Severe slopes and fall of large rock masses), land tenure (Fragmentation of holdings), Immigration and search for other income sources
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (For domestic use due to lack of gas as a fuel source), poverty / wealth (Poverty), education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
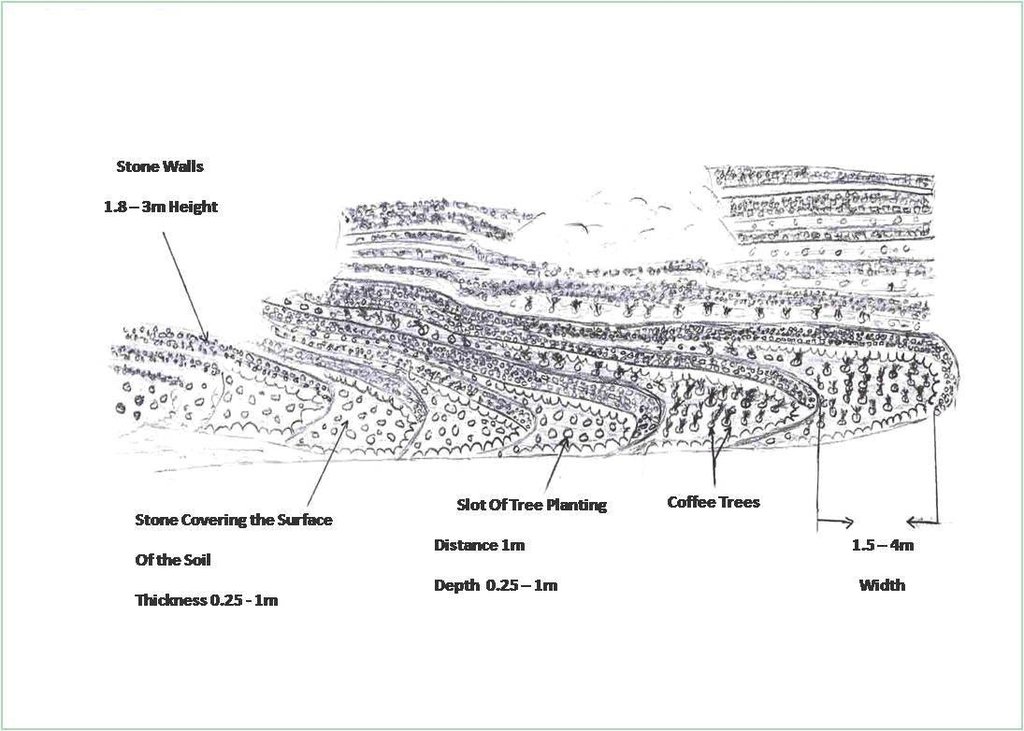
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Flat agricultural terraces covered with stones on the soil surface
Location: Bani Ismail. Sana'a governorate - Manakha district
Date: 5/3/2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Construction process needs skill and experience)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Has experience)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, Reduce speed of runoff
Secondary technical functions: sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.8 -3
Spacing between structures (m): 1.5 – 4.3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.8 -3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5– 4.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 8 - 14
Structural measure: The Coverage with stones
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5– 4.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 8 - 14
Construction material (earth): Remove residuals of water erosion and refill the soil-eroded with soil
Construction material (stone): Construction of walls from the existing stones in the region
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 66.7%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:1
作者:
AL Galal
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6.30
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Remove the spate deposits and filing the gullies with soil, then the top soil surface has to be leveled | Before the rain season |
| 2. | Collecting and transporting stones | Before the rain season |
| 3. | Building the walls of the terraces | Before the rain season |
| 4. | Cover the top soil surface of the earth with stones | Before the rain season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Building terraces | ha | 1.0 | 42430.0 | 42430.0 | 11.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 42530.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 42530.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 7 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair walls that were destroyed | annually after the rain season |
| 2. | Inverse the soil covered with stones |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Repair walls that were destroyed | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Inverse the soil covered with stones | ha | 1.0 | 186.0 | 186.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 236.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 236.0 | |||||
注释:
It is important to note that the implemented works to achieved is about 6 hectare, the project which support money against work, contributed with 231720.54$ to cover most of works such as collecting and transfer stones, and constructing the wall of terraces at 16639.16 m, and covering soil surface with stones for an area estimated of 53560.08 m2. While the land users performed cleaning waste of constructions, filling the target area with soil and leveling it. The total cost of constructing per hectare for building walls terraces at 3273.2 m long and 1.8-3 m height and covering soil surface with stones for an area of 8926.68 m2, and 0.25-0.7 m thick, this cost including other works which already have discussion before.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1- Collecting and transporting stones and arable soil manually as a result of the bad road accessibility.
2- Severe steep slopes
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1400 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: 150 cm
Soil texture: Flood deposits
Topsoil organic matter: Soil covered with stones except where the tree plantation
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium - good
Soil water storage capacity is medium - high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Men have more experience and more power for work than the women.
Women carried out the weeding in the field in addition to food preparation at home.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
90% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
其它社会经济效应
Growth of weeds competing for water
注释/具体说明:
Due to coverage of the top surface of soil with stones
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
As a result of not repair the damage occurring in some of the terraces and that lead to the damage of other terraces.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
其它生态影响
soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
120 households covering 100 percent of the stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
120 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is one of the old folk traditions, but due to the deterioration of the living conditions of families and high maintenance costs the terraces left abandoned and when support is available by the government to help farmers rehabilitate and terraces rundown Reclamation. As for the adoption of the technique is essentially the traditional techniques of farmers and they have knowledge of their importance, but in the event of major damage farmers are unable to repair where it needs to expensive costs. Consequently, farmers have to leave and search for another source of income through internal migration. Such as these damages do not happen like this only in the event of a heavy rainstorms and it is very rare, which leads to washed and destroyed many of the terraces. Consequently, the farmer cannot repair the damage by himself. As previously stated it was targeting a group of land users who do not applied to the project to ask for help.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
This ancient technology is original and appropriate to the local situation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Raise awareness among land users of the importance of maintaining the technology. |
|
The sustainable cropping of the soil terraces on steep slopes prevent soil loss and degradation How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue maintenance and appropriate land management |
|
Increase soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Periodic maintenance |
|
Reducing runoff and increasing water harvesting How can they be sustained / enhanced? Periodic maintenance |
|
Improve soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue to add organic matter to increase soil fertility and conservation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The high cost of rehabilitation and maintenance of the terraces by an individual user | Strengthening cooperation and assistance in the rehabilitation and maintenance collectively by land users |
| High runoff may lead to the erosion of terraces | Planting the upper part of higher slopes with trees or water breakers (controls) for water runoff to reduce the flow velocity, as well as periodic maintenance of watercourses and water outlets in the terraces |
| Cover the surface of the soil with stones may lead to soil compaction | To avoid compaction due to covering soil with stones reduce the thickness of this layer |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Technical study for construction and reclamation for terraces in some villages, Bani Ismail's uzlah, Manakhah district.2- Mid-monthly reports for implanting terraces construction in Bani Ismail's uzlah, Manakhah district.3- General Census of Population, Housing and Establishment (Census, 2004).4- Guide of agricultural climate in Yemen (Al Khorasani, 2005).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Social Fund for Development, Sana'a 976714496722- Social Fund for Development, Sana'a 97671449672 3-Central Bureau of Statistics4-Agricultural Research and Extension Authority, AREA
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Building and rehabilitation of agricultural terraces. [也门]
Pay incentives for farmers rehabilitate degraded terraces in order to face the crisis of increasing food prices.
- 编制者: ahmed algalal
模块
无模块