Afforestation /Tree planting [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Okubyara emiti ahiyabire etari (Runyankore)
technologies_1577 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Mpiirwe Emmy
Dept. of Agriculture, Mbarara District Local Government
乌干达
SLM专业人员:
Mazimakwo Kukundakwe
Kabale District
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - 意大利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of agriculture, animal industry and fisheries (MAAIF) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Afforestation/Tree planting [乌干达]
Tree planting carried out by individual land users on hilly slopes to improve soil cover ,reduce wind strength , provide wood fuel & household income.
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
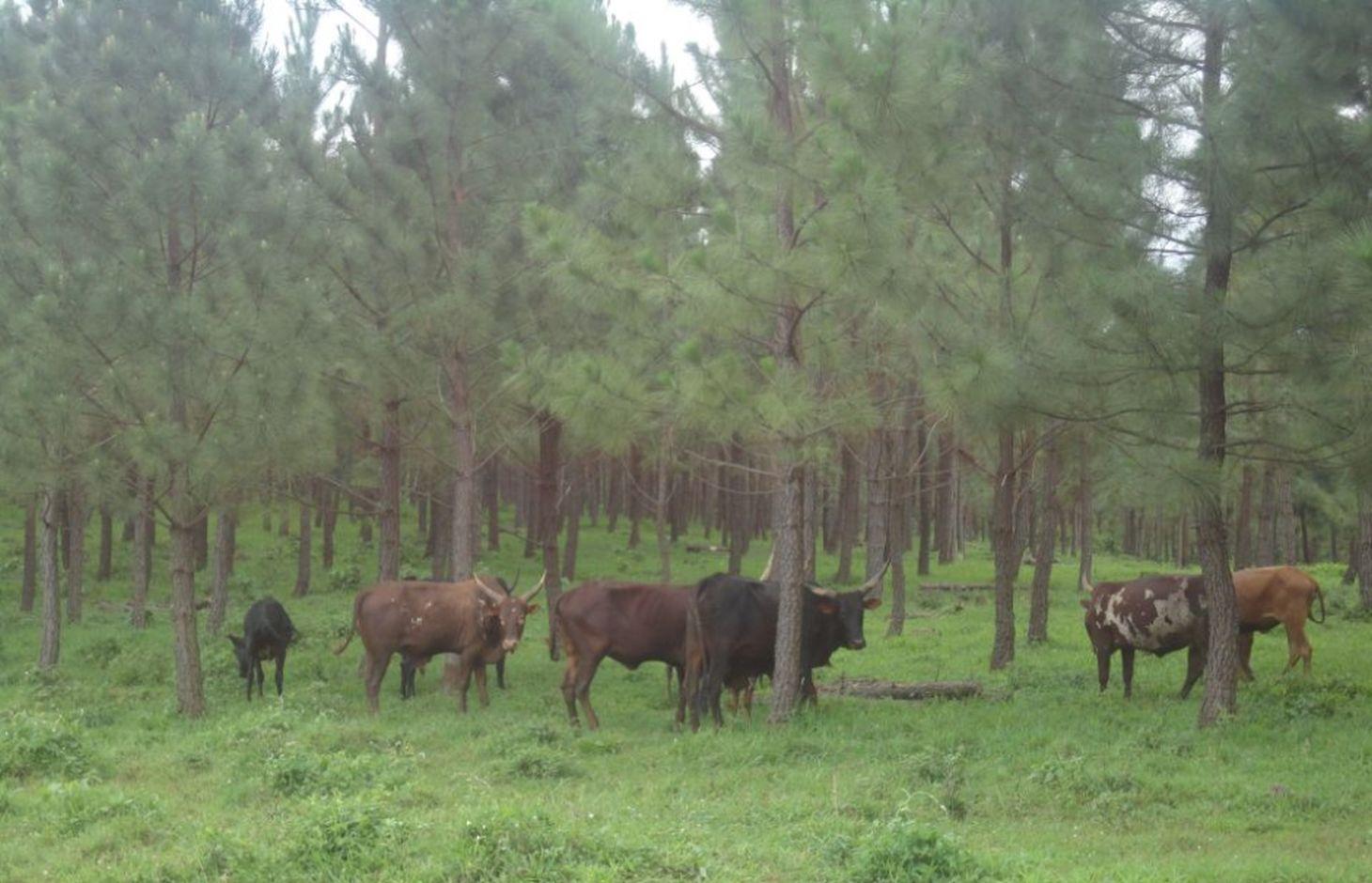
Pine tree forests have been strategically planted on previously bare ridges and slopes to mitigate mass soil movement.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The technology has mitigated soil erosion and damage on road infrastructure by fast flowing runoff, and rejuvenated biodiversity in the area. Much forest cover in Mwizi has been decimated as the need for fuel wood, charcoal and land for agriculture has increased. Coupled with changing weather patterns, human and livestock pressure, many ridges and hilly slopes have been left bare. With annual rainfall of over 1200 mm, runoff often causes extensive damage to cropland and road infrastructure.
In Rubagano, the Forest Department of the Government of Uganda set aside over 20 km2 of degraded ridges and hilly slopes for tree planting. The department planted the first part as a demonstration. The other part is being planted by individuals. Projects such as ULAMP (5 to 10 years ago) and Kagera TAMP (since 2011) have worked with the communities in the area, encouraging the technology by supplying Pinus spp seedlings, training farmers to start their own tree nurseries and forming Farmer Field Schools as vehicles for generation of community consensus on sustainable land management interventions.
Purpose of the Technology: The objectives of afforestation are to provide protection of the land against soil erosion, to return productivity to degraded hilly slopes, to reduce crop (banana) devastation caused by strong winds during rainy season, to grow the capacity of available fuel wood in the area, to diversify future households incomes and protect public infrastructure, especially the road network during the rainy season.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Most of the older trees, 3 years and over, were planted from seedlings bought from established tree growers. Currently, the Farmer Field Schools are planting seedlings from their own nurseries. In the nursery, plastic sleeves called poly-pots are packed with top-soil mixed with animal manure to provide a growing medium. A calculated amount of sand is added to enhance drainage. Sowing, watering and root pruning are carried out manually.
Out on the hilly slopes, the land user establishes the woodlot and maintains the trees using his own resources. Field trainers facilitated by Kagera TAMP provide technical guidance to farmers regularly.
Natural / human environment: Woodlots are established on degraded hilly slopes or any other land use type that is not under crop production. The trees need to be protected against destruction by wild fires and livestock.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mbarara
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.85203 30.62232; -0.85792 30.62021; -0.85850 30.62204
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 3.5 km2.
Tree planting is continuous over a 20 km2 area.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
2 years for concerted project initiative but more than 10 years for land user initiative.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

牧场

森林/林地
树木类型:
- 松属物种(松)
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 自然灾害防护
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion on hilly slopes denuded by livestock overgrazing.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Continuous loss of soil and livestock pasture due to lack of, or inadequate vegetation cover
Plantation forestry: It takes long to harvest.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The adoption is slow because trees take long period to mature and it is expensive in establishment stage.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting of short savannah trees for fuel & agricuture land .), overgrazing (Communal and with large herds (over 150 per household)), droughts (Extended droughts over several years in the past decade)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Thatch, mulch, etc.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara District. Uganda
Date: 5-DEC-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (A good grounding in planted forest management including best practices and what could go wrong.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (Needs technical knowledge on seedling, planting, thinning weeding and spacing; maintenance including protection from fires and disease)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Trees/ shrubs species: Trees (pine spp.) planted from seedlings
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15-25%
作者:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabale
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
2600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.85
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging holes | Beginning of rainy season |
| 2. | Buying tree seedlings | Beginning of rainy season |
| 3. | Transporting seedlings to the site | Beginning of rainy season |
| 4. | Planting tree seedlings | Beginning of rainy season |
| 5. | Fencing | Any time before the beginning of relevant rainy season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 18.63 | 18.63 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 6.8 | 6.8 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 28.43 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.01 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
US $ per unit and US$ per hectare is not quantified because labour was contracted yearly at a cost of Shs 3,000,000.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | Once every rainy season |
| 2. | Pruning |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.7 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 12.7 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: pangas, hand hoes
Planting 900 pine tree seedlings per hectare (on average), at 3m by 3m spacing.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Availability and cost of labour are the most determinate factors affecting establishment and maintenance of the technology.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
September to December and March to May rains. Altit
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. Average annual temperature 18°C to 24°C, very close to the equator.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: The plantation area ranges between 1650 and 1850 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (it is easy to reach the underground rock)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (rocky and coarse)
Soil fertility: Very low (ranked 1, soil fertility was poor) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (the land was bare with rocky soil)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (water infiltrates slowly/easily)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (the soil drains easily)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: >50m (It is very hard to reach ground water table)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (while the rainfall is good, permanent wells are scarce. Runoff dams behind natural rock formations or concrete walls on a rock base, but quickly drys up after the rainy season)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, while it looks a muddy brown, it has been used for drinking and other domestic purposes without observable harm to the users)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Slowly rejuvenating since the establishment of the technology.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: In Rubagano, the women are mostly involved in ensuring food security of the household and are not normally involved in aforestation. However, the Farmer Field School methodology has brought many women on board and, helped by the understanding that fuel wood collection is a women's role, women are developing interest in the technology.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 40% of the land.
40% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The technology is new and apart from providing grazing land in the short to medium term, it will yield dividends in 20 to 25 years. Meanwhile, those who are keen on the technology continue to depend on their usual income generating activities, on-farm or off-farm.
Market orientation: Mixed (Land user wanted to reduce soil erosion , increase fuel wood , diversify future income of households)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Most households have less than 1 ha. Few land users have 5-15 ha.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
注释:
The land users own land individually inherited or bought by the holders. Water harvesting and storage in underground tanks is slowly introducing individual water rights and household water security.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Quantification of benefits is difficult at the moment because there is no harvest from the planted trees now.
产品多样性
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
注释/具体说明:
The costs of maintainance.
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The land was bare before, land slides were destroying infrastructure like roads. Problem well mitigated.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Not yet to reap the economic benefits of tree planting because trees have not matured.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
With dense forest come the risk of fire. this is common in a neighboring district (Kiruhura) but is not yet a problem in Rubagano.
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
注释:
Once established, the pine trees can tolerate all kinds of weather extremes. However, before the initial 12 or so months of establishment, the seedlings are very sensitive to drought and dry spells and will likely dry up because irrigation is not an option in Rubagano, water sources being quite scarce. Mulching helps in preserving soil moisture but the mulch should be at least 30cm away from the plant to avoid destruction by pests.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The land users expect to benefit from the technology when fully established.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
125
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
125 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: While the external material contribution was by way of tree seedlings and contributed probably just 5%, all seedlings were supplied by the project.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Land users have committed their own resources (over 95% of total establishment costs) but all received the seedlings, at least initially, form the project. The incentive was a wake-up call and the farmers have adopted the technology with enthusiasm.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The trend is slow due to high cost of initial investment and limited land for tree planting.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Protection of soil cover. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fencing off the woodlots from livestock and other land users. |
|
Provision of fuel woodl. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular pruning and thinning. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology has improved soil cover and reduced soil erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? More effort should be put into mobilization of land users in order to scale up best practices onto other areas with bare hills and slopes. |
|
The technology provides an easier alternative source of fuel wood from the remaining pockets of natural woodland. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular thinning should provide even more fuel wood and convince land users, especially women, of the advantages accruing from adopting the technology. |
|
Diversification of future household income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular monitoring of the growth of trees to check for pests & diseases. |
|
improvement of micro climate conditions. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting trees that have little negative effects on other crops in other land use types. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Loss of biodiversity due to trees suppressing under growth of other species. | Copicing to raise the canopy and experimenting with multistory cropping could improve sunlight penetration and improve the emergence of undergrowth. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Afforestation/Tree planting [乌干达]
Tree planting carried out by individual land users on hilly slopes to improve soil cover ,reduce wind strength , provide wood fuel & household income.
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
模块
无模块