Hand-dug trenches [尼日尔 ]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dieter Nill
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Tranchées manuelles (French)
technologies_1625 - 尼日尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
德国
SLM专业人员:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP)
尼日尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (GIZ / PROMAP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - 德国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Misereor - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Hand-dug trenches contribute to the restoration of tree cover and prevention of water erosion on slopes.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
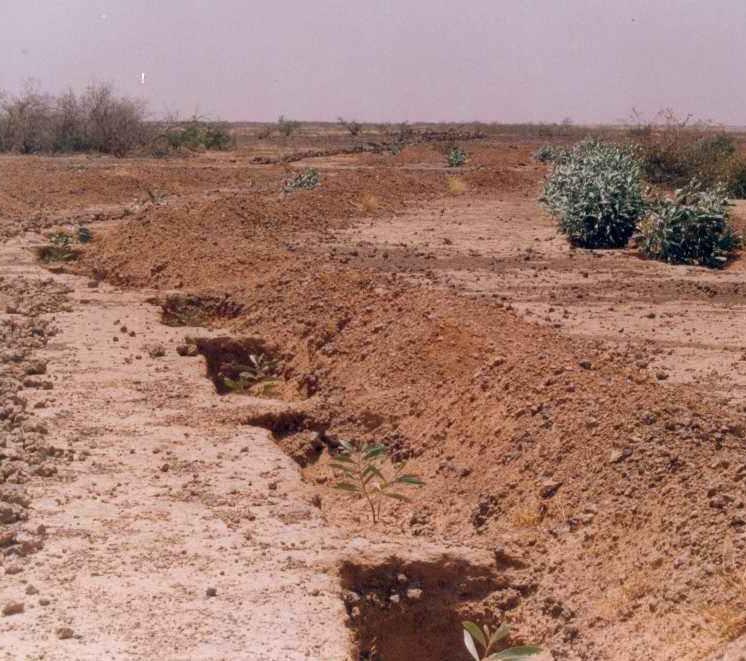
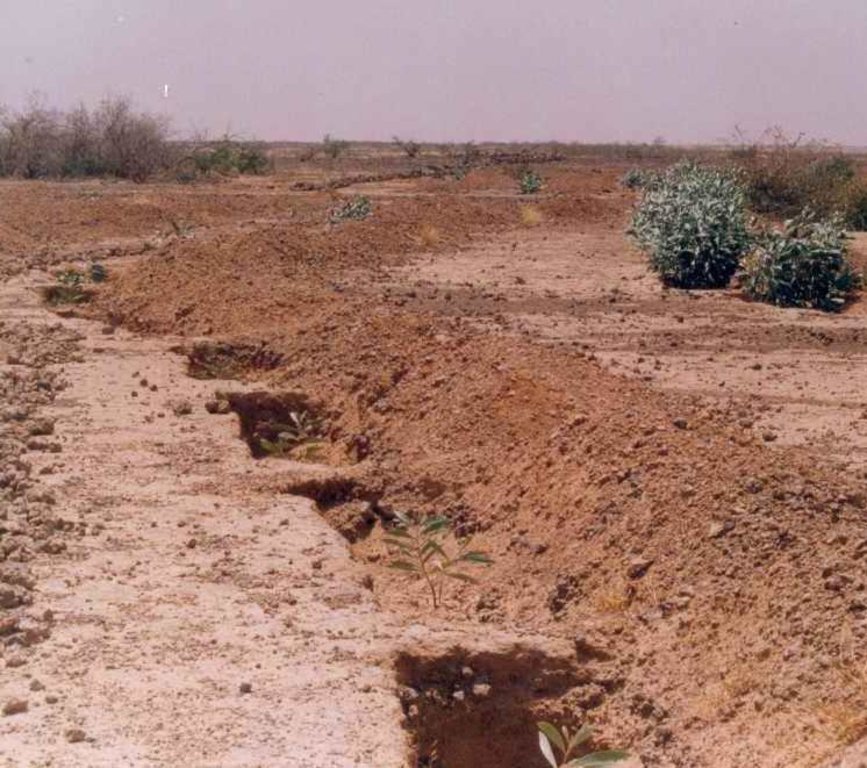
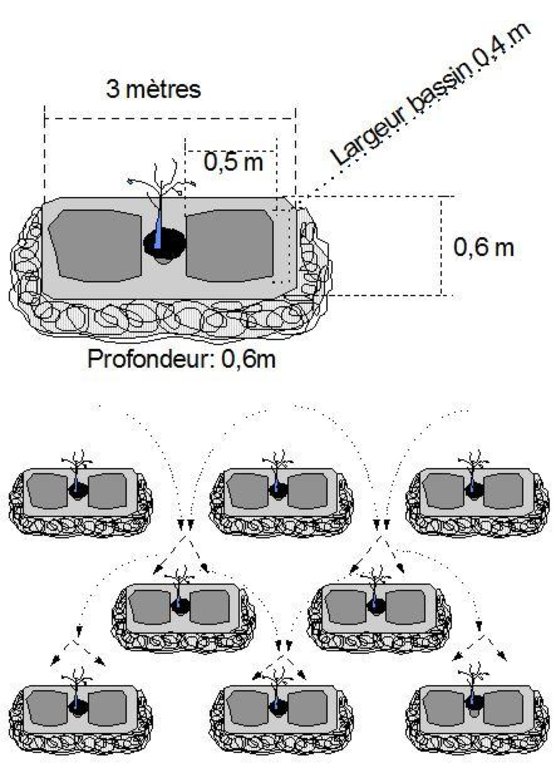
This technique is designed to restore communal land on slopes and highland pediments. It involves manually excavating trenches 3 to 3.5 m long and 0.6 m deep, spaced 4 m apart in staggered rows. This results in around 625 trenches per hectare. The excavated earth is piled downhill of the trenches, which are aligned perpendicular to the slope. In the middle of each trench, a 0.40 m high step is left on which the tree seedling is planted. The tree receives the water it needs from the trench where it collects.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this technique is to restore tree cover on degraded, unfertile land and prevent water erosion on slopes by reducing the flow of water that threatens land downstream. The trenches reduce gully erosion and pedimentation of areas with a fragile soil structure. Like all afforestation measures, in the medium term, this technique is effective in protecting the land against water and wind erosion. The shade provided by the trees also lowers the temperature of the soil and the infiltration of water in the hand-dug trenches contributes to groundwater recharge.
Areas restored using hand-dug trenches can subsequently be exploited to a limited extent in accordance with strict controls.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The technique is very labour intensive. Work must begin immediately after harvesting when the soil is still moist and workable. A protection and monitoring system is required to ensure that grazing animals do not damage the young trees. The mortality of trees after planting is relatively high (survival rate is about 60%), and dead trees must be replaced systematically during the first three years. Good community organisation is required.
Natural / human environment: Hand-dug trenches are particularly useful when rainfall is low, as they retain water and make it available to the trees growing in them. In years when rainfall is abundant or there are violent downpours, the young trees are protected, as they are planted on a raised step within the trench, although there is a risk of flooding in the event of very heavy rain.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼日尔
区域/州/省:
Niger
有关地点的进一步说明:
Regions of Tillabéri, Filingué, Ouallam, Téra and Tahuoa
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by German Development Cooperation (BMZ, GIZ, KfW) in Niger by projects e.g. PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 油料作物 - 花生
- 谷类 - 小米
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豌豆
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 选伐
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 其它森林产品
- 放牧/啃牧
注释:
major cash crop: Ground nut
major food crop: Millet
other: Sorghum, cow peas and mangoes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): water erosion (gully, sheet), wind erosion, degraded and infertile land
Nomadism: Yes
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Yes
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Improved pasture: Yes
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): Yes
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.)
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: armers are mainly agropastoralists with some communities specialised on pure pastoralism
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
Livestock density: 1-10 LU /km2
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated and post-flooding
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted land use methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rains), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Trenches are manually excavated 3 to 3.5 m long and 0.6 m deep, spaced 4 m apart in staggered rows. This results in around 625 trenches per hectare. The excavated earth is piled downhill of the trenches, which are aligned perpendicular to the slope. In the middle of each trench, a 0.40 m high step is left on which the tree seedling is planted. The tree benefits from the water collected in the trench.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Vegetative measure: planted in trench
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Spacing between structures (m): 4
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.5
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
作者:
MDR, Niger: Reports
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | marking out the contour line | |
| 2. | laying out the trenches in staggered rows | |
| 3. | digging two rectangular microcatchments separated horizontally by a flat surface | |
| 4. | making a hole in the central area | |
| 5. | planting the seedlings | |
| 6. | sowing grass on the ridges |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | All the Labour | unit | 1.0 | 220.76 | 220.76 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | unit | 1.0 | 41.55 | 41.55 | |
| 其它 | Transport of seedlings | unit | 1.0 | 1.93 | 1.93 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 264.24 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 264.24 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A protection and monitoring system is required to ensure that grazing animals do not damage the young trees | |
| 2. | dead trees must be replaced systematically during the first three years |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Other costs
• equipment, such as jumper bars, shovels and axes
• 625 tree seedlings
• 15 kg of grass seed
• cost of transporting 2 cartloads of seedlings
• 120 seedlings to replace dead trees.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 200 m a.s.l.
Landforms: Also footslopes and valley floors
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor - medium
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: > 10m
Availability of surface water: Surface runoff generated by limited but intense rainfalls
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
(mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
Market orientation of production system: Most households crop for subsistence , but surplus is sold on the market. Some vegetable growing is just for commercial/ market.
Level of mechanization: Oxes and donkeys used for animal traction.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 1-2 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 社区/村庄
- not titled
土地使用权:
- 个人
注释:
Traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
木材生产
生产区域
收入和成本
工作量
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
This technique permits the reintroduction of trees on degraded, unfertile land. Areas restored using hand-dug trenches can subsequently be exploited to a limited extent in accordance with strict controls.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
注释:
Establishment of the trenches involves considerable labour and growth of trees takes a couple of years.
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology has been applied by PDRT on common land using food/cash for work in order to inject money and food into the local communities.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There was no spontaneous adoption. The technology is designed for common lands and takes considerable labour that only very well organised communities are able to mobilise.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The young trees are protected of flooding, as they are planted on a raised step within the trench |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Hand-dug trenches retain water and make it available to the trees growing in them. Although the trenches are progressively filled with sediment, which reduces their capacity to retain water, at the same time, the trees develop and become less dependent on stored water. |
| This technique has proved effective in restoring forest/rangeland sites. The progressive development of grass and tree cover continues on the improved sites, where the tree population is up to 20 years old. After around ten years, the average annual production of wood is 1.3 steres per hectare. |
| The shade provided by the trees also lowers the temperature of the soil. |
|
In the medium term, this technique is effective in protecting the land against water and wind erosion. |
| Areas restored using hand-dug trenches can subsequently be exploited to a limited extent in accordance with strict controls. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technique is very labour intensive. Work must begin immediately after harvesting when the soil is still moist and workable. | Good community organisation is required. |
| A protection and monitoring system is required to ensure that grazing animals do not damage the young trees. The mortality of trees after planting is relatively high (survival rate is about 60%), and dead trees must be replaced systematically during the first three years. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块