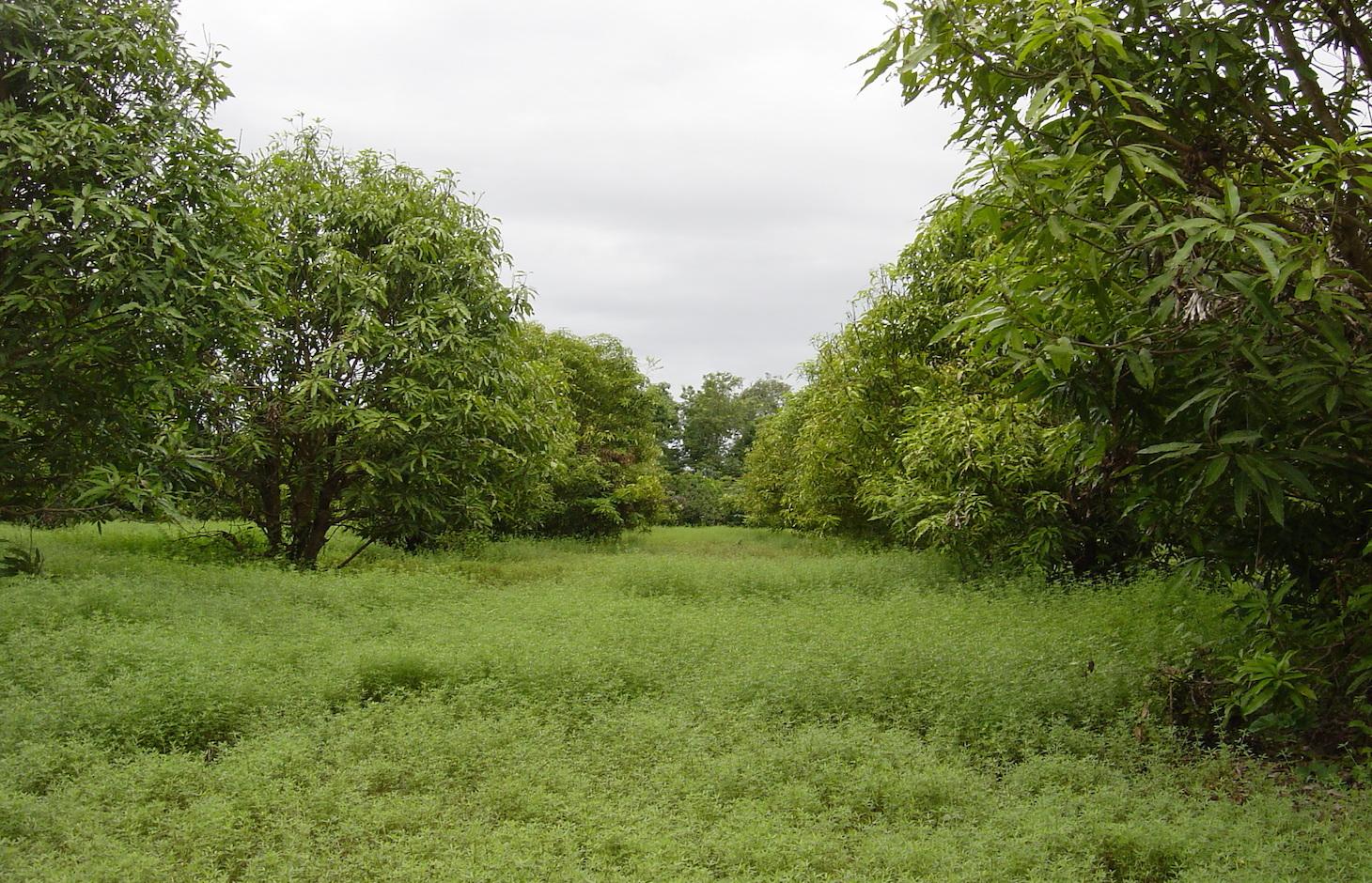
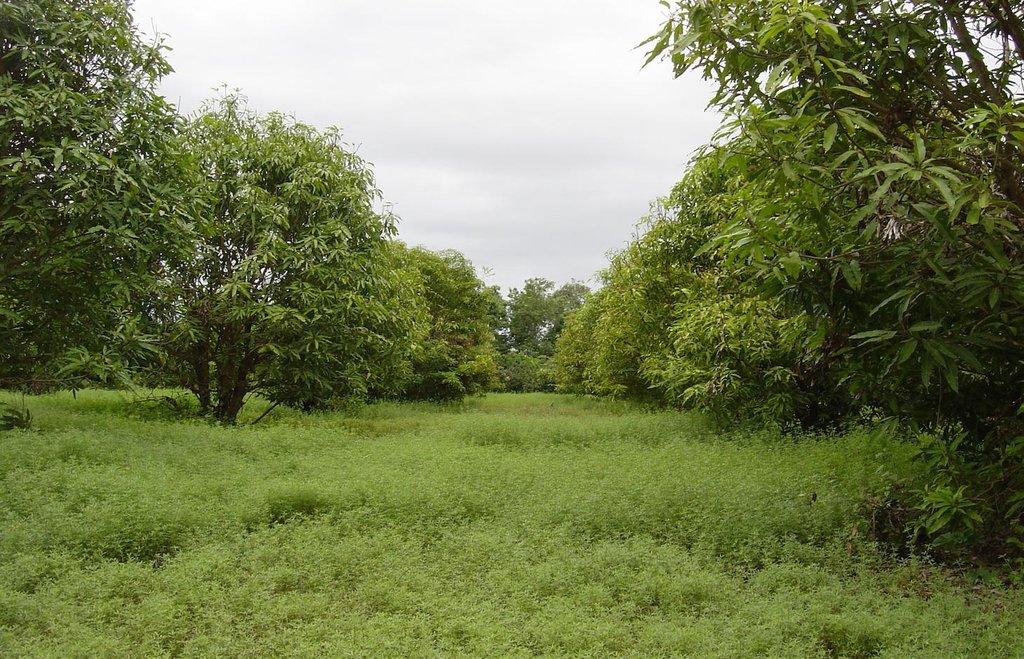
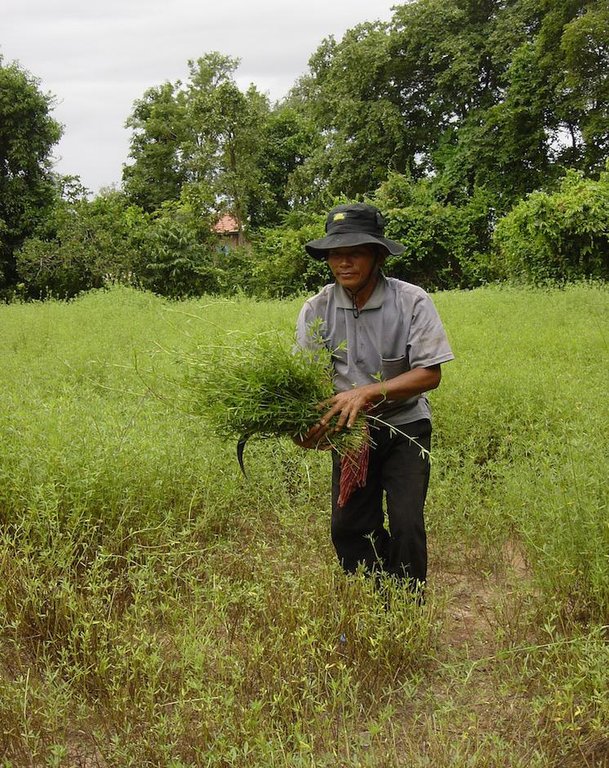
Growing stylo grass (Stylosanthes guianensis) as cattle fodder between and under mango trees. [柬埔寨]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Christoph Kaufmann
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
ការដាំស្មៅជាចំណីសត្វ (Stylosanthes guianensis) ទៅតាមចន្លោះដើមស្វាយ (Khmer)
technologies_1642 - 柬埔寨
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Stylo grass (Stylosanthes guianensis) is grown under and between mango trees to be used as fodder for cattle.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
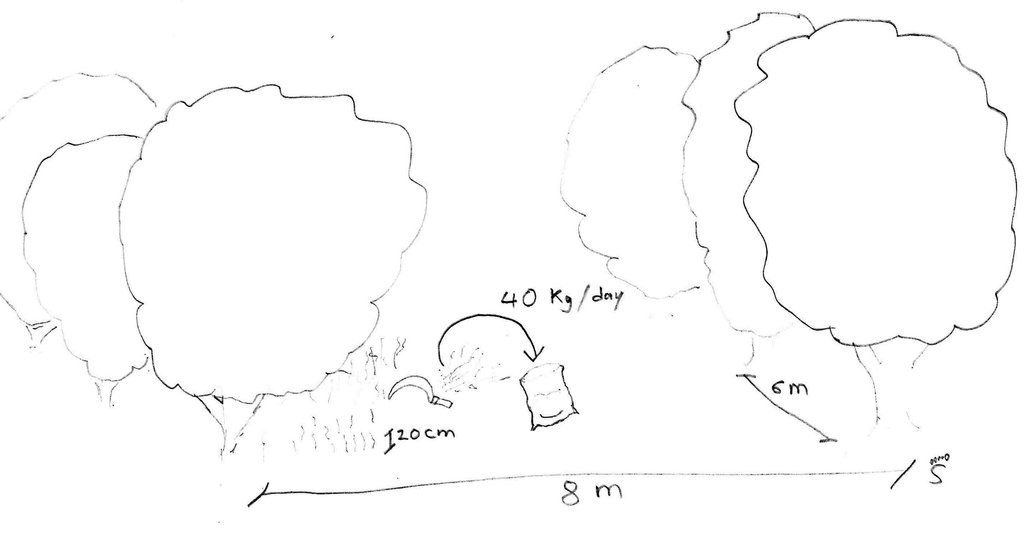
Stylo grass (Stylosanthes guianensis, CV. Stylo 184) is a leguminous shrub which is used in pastures and as fodder crop. It is drought tolerant and can be harvested during the whole year, though it grows only when sufficient water is available. Mangos (Mangifera indica) are grown mainly from seeds in the area, either as single trees in home gardens or as orchards. The farmer of this case study has a mango orchard of 0.6 ha with trees spaced 6 by 8 meters, and grows stylo grass as a cover crop under and between the trees. Each day a patch of stylo grass is harvested by hand, and around 40 kg of this fodder is fed to the cattle together with rice straw. This allows the farmer to keep more cattle than before, 11 heads instead of 5. The mangos are mainly sold on the market, and some are dried. This agroforestry system reduces erosion by wind and water, as the soil is covered the whole year and the trees slow down the wind. The cattle can be kept near the house, which is good for making compost and biogas.
In 2004, the farmer cleared a forest and planted mango seedling. Between the mangos, he grew pumpkins, watermelons and cucumbers, but even though he used compost the soil fertility deteriorated fast and the cucurbits did not produce anymore. A local NGO, LAREC (Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre), was looking for farmers with enough cattle and land in the area to try stylo grass, which was unknown in the area. The farmer, first reluctant because his other crops were not producing, started to plant stylo grass seeds he got from the NGO in July 2013 (information for this documentation was collected one year after the start).To do so, he plouwed and harrowed the fields with the hand tractor, and broadcasted the seeds by hand. After the first 3 months, during which he needed to weed, he started harvesting the fodder, and he cut 40 kg a day, one patch after another, 20 cm from the soil. This allows the reproduction of this cover crop.
The land user wants to expand his stylo grass to his other mango orchard, and is collecting seeds for this. Other farmers in the area are also interested in this technology; and the land user of this case-study starts to sell them stylo grass seeds but does not produce enough for all yet.
The analysed area is mostly flat (slope < 2%), tropic (dry and wet season), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soils contain little organic matter (low soil fertility, acidification, small amount of cattle, area has been deforested) and the groundwater table is rather high (3 m below soil level during the dry season, on the surface during the wet season).
Due to climate change, the rainfalls are more erratic, temperatures rise and droughts are more recurrent. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Rice is often grown in monocultures and harvested once a year. Once the rice is harvested (dry season), some farmer release cattle to the paddy fields to eat the straw and weeds.
As an addition to rice, most land users grow vegetable and fruits in small home gardens (subsistence) and complement their income by producing handicrafts or through off farm income / remittances from family members working in other places. The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge which different NGOs try to re-establish.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
柬埔寨
区域/州/省:
Kampong Chhnang
有关地点的进一步说明:
Sre Ouk Samlor Sap/Taing Krasaing/Rolear Pha,er
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.006
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
0.6 ha
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
It started in July 2013 when SOFDEC gave stylo grass seeds to farmers with enough cattle and land
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 草
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210 Longest growing period from month to month: June-December
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of organic matter, lack of water retention in soil, irregularity of rainfall, low soil fertility (sandy soil), monocultures, bare soil during dry season.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low soil fertility, lack of water, soil erosion by water on the slope.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Soil left bare during the dry season.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation in 2004)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (.New areas are deforested, and are degraded after a few years.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Lack of irrigation.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Stylo grass is harvested daily between the mango trees, one patch after another. This allows different stages of growth.
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 8
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vegetative measure: Covering the soil
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Mangoes, Mangifera indica. Planted.
Grass species: Stylo grass, Stylosanthes guianensis. Seeded.
作者:
Stefan Graf
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plow the field, dig holes and plant mango seedlings. | Once at the beginning of the wet season (May-June) |
| 2. | Sow stylo grass. | Once in July. |
| 3. | Weeding | first 3 months |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 21.25 | 21.25 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | machine use | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 8.0 | 8.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 357.25 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 357.25 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvest 40 kg of stylo grass. | 1h/d |
| 2. | Harvest mangoes | April-May |
| 3. | Maintain the stylo grass, sowing bare spots | 2 person days per month |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 590.0 | 590.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 590.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 590.0 | |||||
注释:
The costs were calculated in 2014 for an area of 0.6 ha. The farmer got 100’000 riel (25US$) for the 800 – 1000 kg mangoes produced, and a bag of fodder (40 kg, that he harvests each day on 0.6 ha) can be sold for around 5000 riel (1.25) on the market.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The costs were calculated as if he hired someone, and bought mango seedlings. As he did all of the work by himself, it was much cheaper. The most expensive is the harvesting of the fodder, but it should be taken into account that it is less labour intensive than harvesting wild grasses and cheaper than buying them.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
1486.45 mm 2013 in Kampong Chhnang
农业气候带
- 半湿润
27° to 35°C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
availability of surface water poor durin dry seasons
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Only one man is applying the technology, his wife works in the garment industry.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: His wife works in a factory.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Land ownership is very complex. Most of the land belongs officially to the government, yet many land users hold a paper confirming they applied for a land title – but de iure, this paper is worthless.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产区域
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
Contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Less time needs to be invested in harvesting wild grasses.
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
No wind erosion because of the soil cover, less water erosion.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Stylo gras is a leguminous, thus fixes nitrogen.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
The mango leaves fall to the soil and increase the organic content.
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
注释/具体说明:
The mango trees slow down the wind
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
Fields need to be fenced because of the neighbour's cattle
注释/具体说明:
The living fence was already planted before.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The maintenance costs consist mainly of harvesting, which is very positive.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
100% or 1 land user family
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Other farmers in this village want to grow stylo grass, but cannot get seeds. This farmer starts to sell seeds to other farmers.
Other farmers in this village want to grow stylo grass, but cannot get seeds. This farmer starts to sell seeds to other farmers.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Other farmers in the village showed strong interest to start applying this technology. The farmer of this case study started to sell seeds to 3 of them, and 7 others in the area showed interest as well but there were not enough seeds available.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| As a leguminous, stylo grass could be plowed into the soil to improve the soil fertility. |
| Less time is needed to harvest fodder for the cattle, as he does not need to collect it from the wild anymore. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| As a leguminous, stylo grass has a high protein content, which makes it valuable as fodder. |
| The soil is covered, trees slow down the wind, inducing a good micro-climate and stopping wind erosion. |
| Water erosion on slopes is reduced as the stylo grass covers the soil. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The land has to be fenced off, as neighbours cattle otherwise graze in his fodder. | Living fence (currently used by the land users), needs only little maintenance. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Productivity of the mangoes is mostly low as seedlings were used. | Learn how to graft, with improved varieties or selected individuals from the farm. The use of seedlings allows a selection of new varieties; the grafting can take place at any tree size. |
| The cultivar Stylo 184 has only a single-gene resistance to anthracnose (tropicalforage.info). In case of breakdown all the fodder is lost. | Mixed cropping with another fodder, or mixed cropping of different cultivars of Stylosanthes guianensis |
| Stylo grass is not considered shade tolerant (tropicalforages.info), when the mangoes will grow higher could become unproductive. | Use dwarf rootstocks for the mangoes, space them further apart, or use different species of fodder. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/07/2014
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Tropical forage info website. Stylosanthes guianensis
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.tropicalforages.info/key/Forages/Media/Html/Stylosanthes_guianensis_var._guianensis.htm
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Feedipedia Website. Stylo (Stylosanthes guianensis)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.feedipedia.org/node/251
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块