Treadle Pump [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Laxmi Dhiki Pump (Main Contributor: Purusottam Gupta, IDE-Nepal)
technologies_1690 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Gupta Purusottam
IDE-Nepal
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
iDE Nepal (iDE Nepal) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
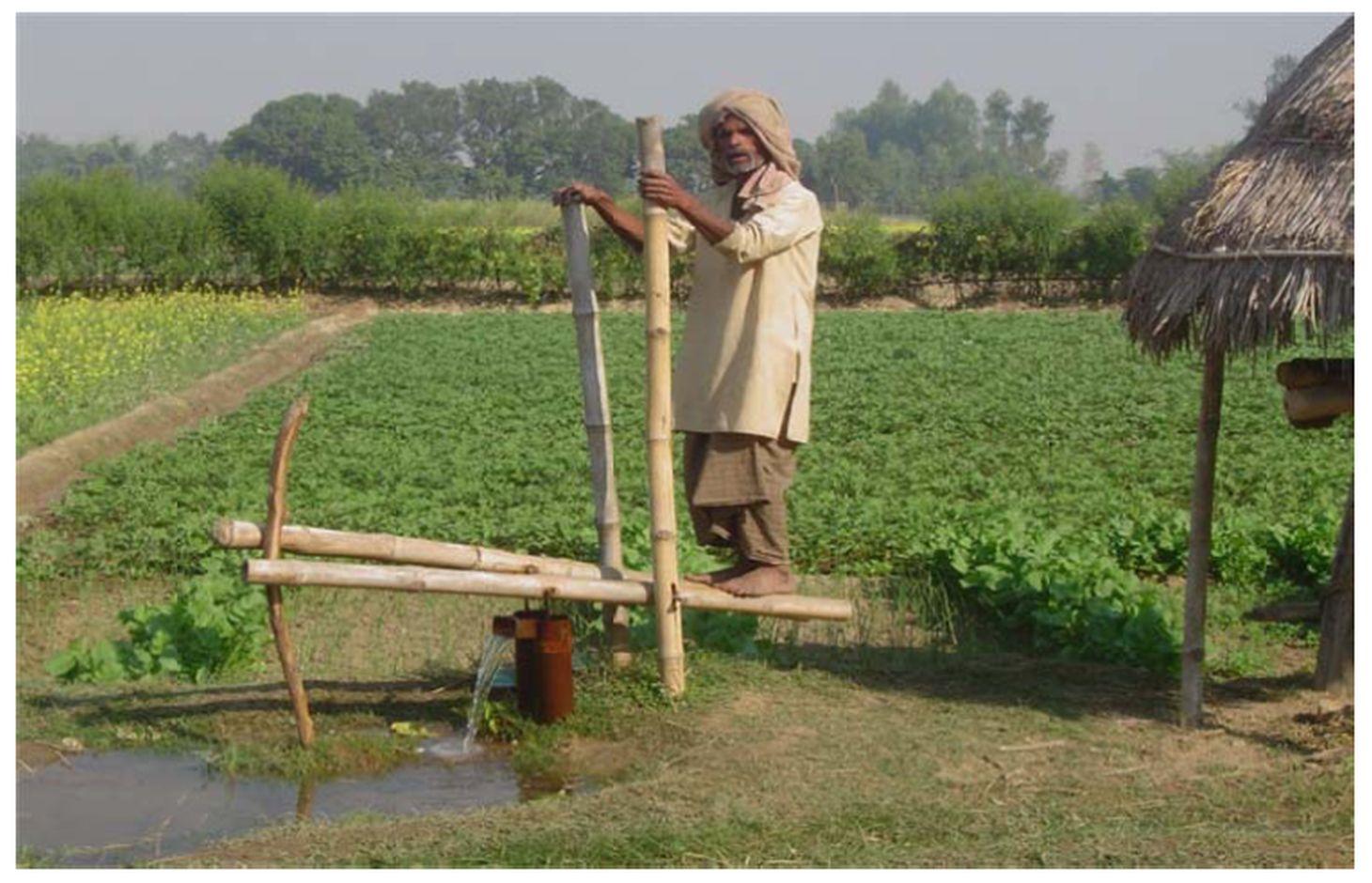
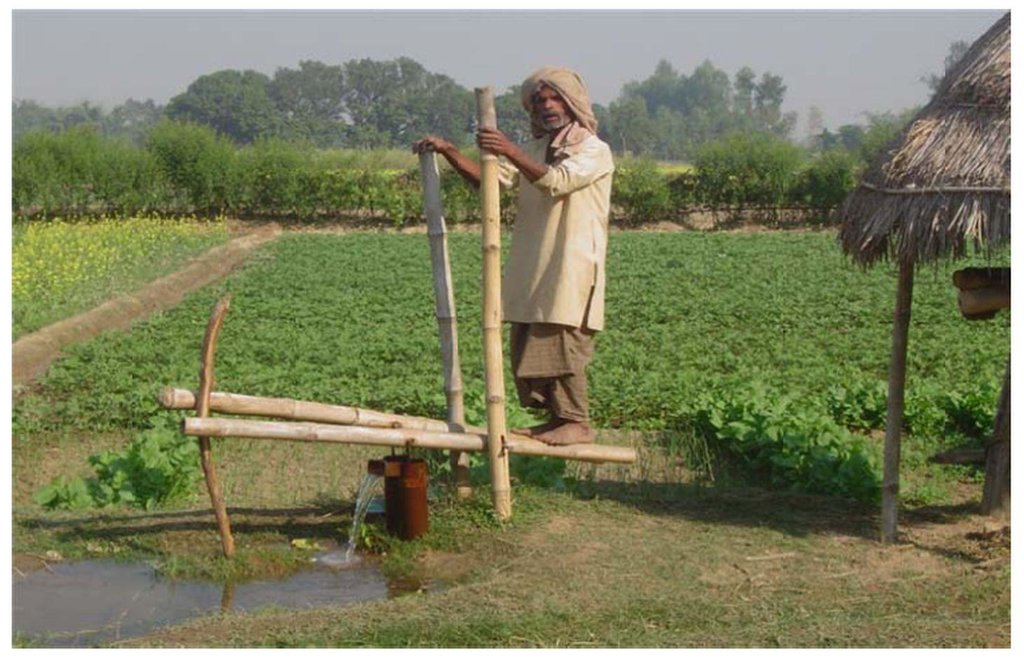
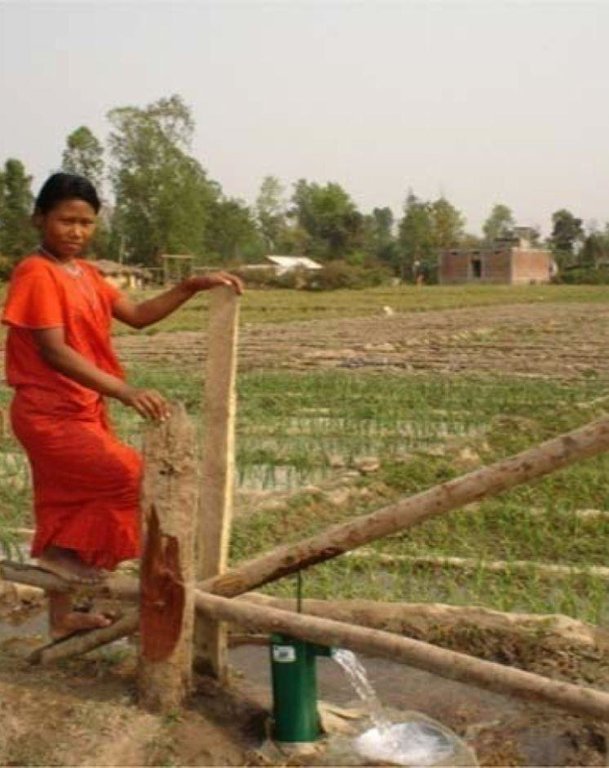
A treadle pump is a foot operated water lifting device that can be used by smallholder farmers to irrigate their land in places where the water table is high.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A treadle pump is a simple, cheap, and effective device for lifting water. In this technology, bamboo levers are pushed repeatedly by foot to provide the driving power to lift water. This simple device is relatively easy to install and maintain and is environmentally friendly. Three types of treadle pumps are in common use; all three use the cylinder and paddle concept, but the model which uses a cylinder 8.9 cm in diameter and has bamboo paddles is the one most commonly favoured by farmers in the region. It is cheaper and can lift more water than a comparable hand pump. On average, a treadle pump can be used to lift water from about 6 m underground and one such pump can irrigate as much as 0.34 ha of land (depending on the soil type and other conditions). In addition to lifting water for irrigation, the treadle pump can also be used for a variety of domestic purposes. In the Terai areas of Nepal, it is also widely used as a means of generating income.
When farmers consider installing a treadle pump, they first need to verify whether there is sufficient groundwater to merit the expense. Treadle pumps should be installed by trained technicians and properly maintained throughout their lifetime. If possible, an extra set of spare parts should always be kept on hand and a trained technician should be consulted for major repairs.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Banke, Bardiya, Dailekh, Surkhet, Kaski, Dhanusha, Kapilbastu, Rupandehi, Jhapa, and Salyan District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1,000-10,000 平方千米
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- Simplified irrigation
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Most agriculture in Nepal is rainfed. There is a general scarcity of water for irrigation and the availability of the water that exists is limited by economic and energy constraints.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: Water not available for Irrigation, Soil moisture is decreasing, crop productivity is declining
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
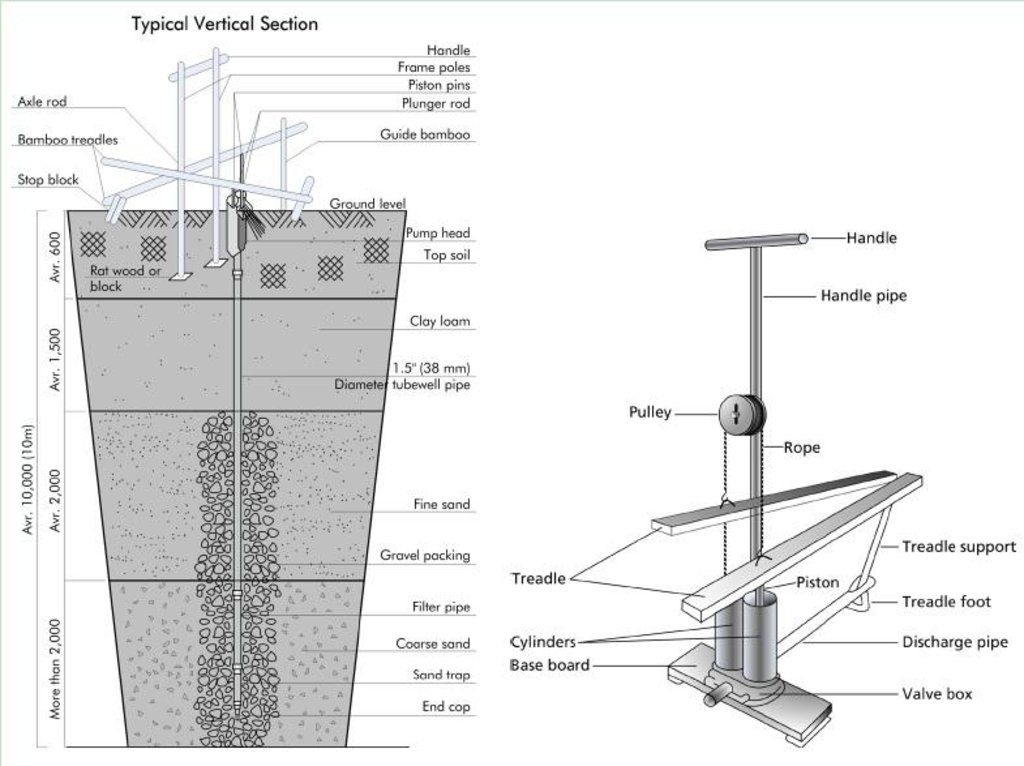
Components of a treadle pump
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Technical knowledge required for Field Technician:
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil, Increase supply of water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), spreads water
作者:
Purusottam Gupta, AK Thaku
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Waterpump
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.33
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The site first needs to be evaluated in order to verify whether sufficient groundwater is available. | |
| 2. | The pump should be installed by a trained technician. |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Evaluate site and installing pump | persons/day/unit | 3.0 | 5.3333 | 16.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Various materials | unit | 1.0 | 43.0 | 43.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 59.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 59.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | The pump needs to be maintained on a regular basis and, if possible, an extra set of spare parts should be kept on hand. A trained technician should be consulted for major repairs | |
| 2. | Routine maintenance activities are: Repairing or replacing the treadle frame |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintaining pump | persons/day/unit | 2.0 | 4.0 | 8.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Various material | unit | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 13.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 13.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
This is an average cost estimate, the actual cost will be a function of the soil type, how far the water table is below the surface, and the type and quality of the materials used (metallic vs. non-metallic, timber vs. bamboo) and the cost of labour.All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
All services access (low to moderate):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Increase crop diversification
生产区域
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Farming can continue through period of drought
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
社会文化影响
文化机会
娱乐机会
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Increased farm income helps to improve the lives and livelihoods of smallholder farmers, and of other socially and economically disadvantaged groups
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
其它生态影响
natural water table if water is continuously drawn
the land close to the pump area remains wet and swampy
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| seasonal rainfall extremes | 好 |
注释:
A larger bore (12.7 cm) treadle pump can be used to access deeper in the water table where more water may be available
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Land users are quick to adopt this technology voluntarily even without any external support.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It meets the need for a low-cost irrigation measure and is accessible to farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sustained effort by the government to disseminate information, assist INGOs and local people to get started. |
|
Can be manually operated and does not require any sophisticated or skilled manpower How can they be sustained / enhanced? Make it even easier, simpler, and cheaper to buy and maintain by introducing improved methods and techniques |
|
Does not require electricity or any other external form of energy so it is easy to implement even in remote places How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue efforts at research and development to make the pumps even more effective |
|
It is an affordable technology for growing vegetables. Purchase and installation are within the means of most farmers and it is easy to maintain. Technical know-how for installation is available locally. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Continue research and development to make pumps even more effective. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Requires manpower. It irrigates only a limited area. | Continue research and development to make it even simpler to use, possibly even by those who are not so physically fit. |
| Requires continuous inspection and maintenance and a supply of spare parts (washer, check valve, bamboo poles) | Continue research and development to make it even more robust without the need for vigilant maintenance. |
| Over time, the pumps pump less water, there is frothing, and sand is also lifted | The joints and sockets need tightening. The right place should be selected for boring and, after installation; the area needs to be packed with gravel. |
| At times the pump has trouble lifting water, it is not working properly | Check the treadle frame installation. Check that the size of the washer is appropriate. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Technical guideline for treadle pump installation and maintenance. Kathmandu, Nepal, IDE-Nepal
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块