Trees as Buffer Zones [菲律宾]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Eduardo Alberto, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1709 - 菲律宾
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Manubag Jerry
(088) 221 4302
manubagjerry@gmail.com
Mt. Kitanglad Agri-Development Corporation
Lurogan, Valencia City, Bukidnon , Philippines
菲律宾
Dinamling Djolly Ma.
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Diliman, Quezon City
Pine Baldwin
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Diliman, Quezon City
Bersabe Teodoro
Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Diliman, Quezon City
Betonio Gloria
DA-Northern Mindanao Integrated Agricultural Research Center
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) - 菲律宾1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/12/2015
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [菲律宾]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
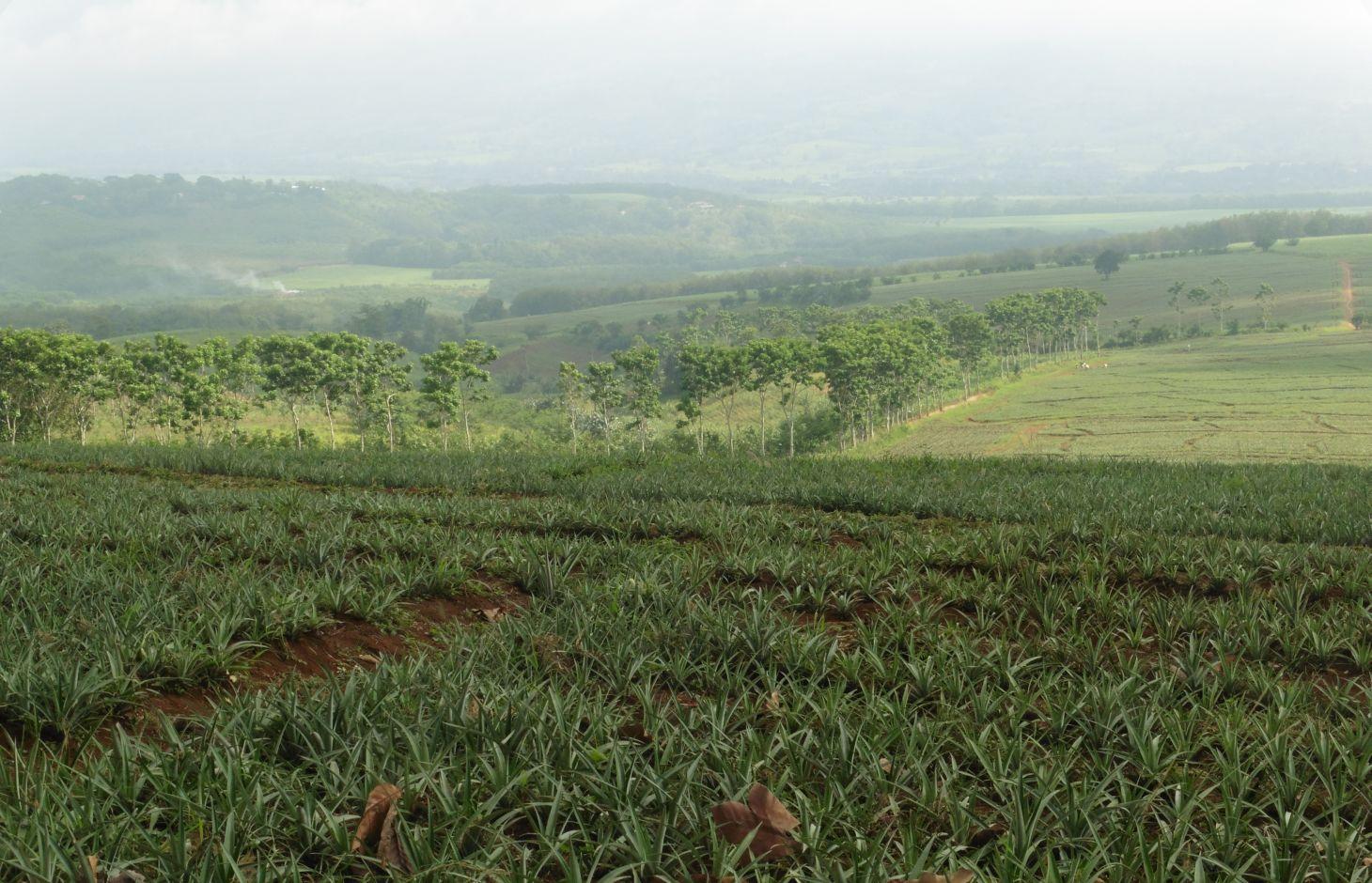
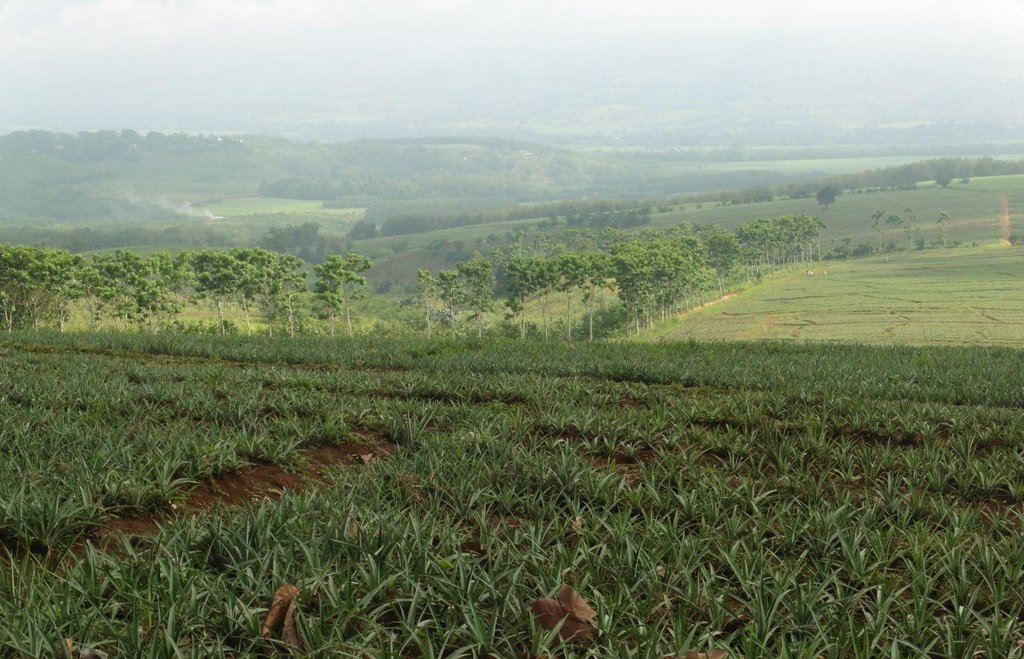
Trees as buffer zones are vegetative measures established in the area to prevent pest from crossing in between blocks. Further, the technology provides haven for flora and fauna which are endemic in the area.
2.2 技术的详细说明
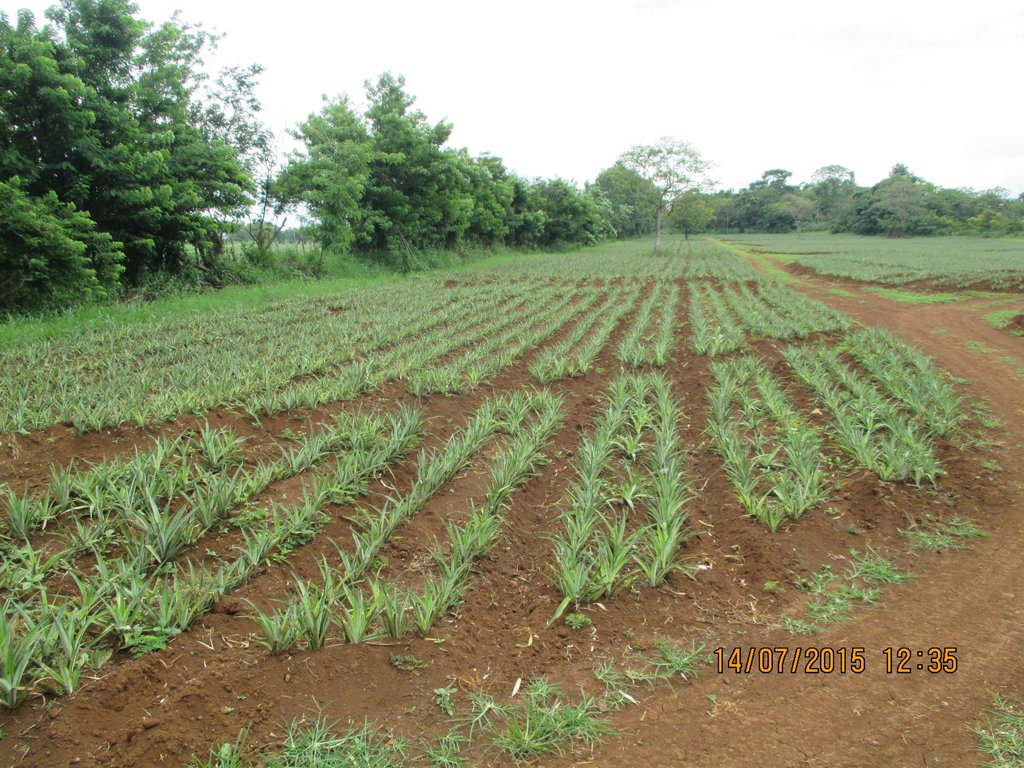
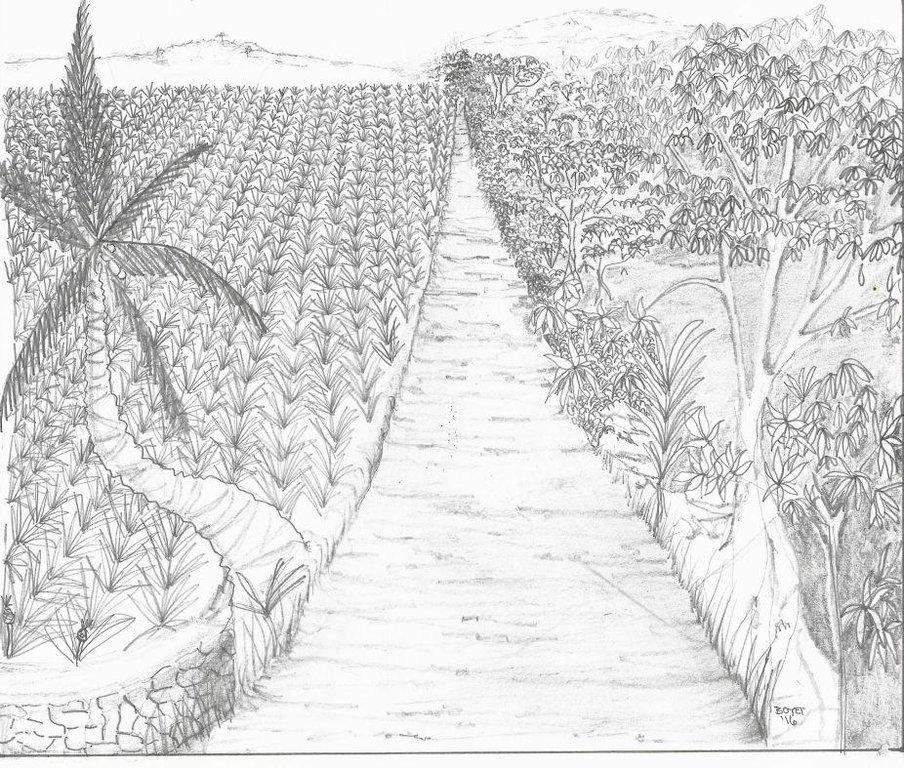
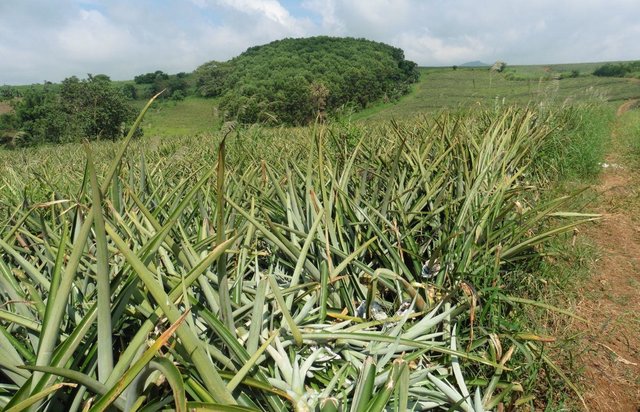
说明:
Trees are planted at strategic locations along the road, between blocks, boundaries or in scattered areas within the pineapple plantation. Indigenous trees,"wildlings", which are considered endangered species were preserved in the plantation. Trees serve as habitat for the different tree of faunal species of birds, reptiles, amphibians and mammals.
Purpose of the Technology: It assimilates carbon from carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. It also provides shelter/habitat for wildlife species such as birds and temporary shades for laborer during rest time. The trees also improve the aesthetic value of the plantation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The initial step is the identification of specific tree planting areas for supplementation of natural cover. Along road networks are usually utilized as buffer zones. Prior to planting, grass brushing is done followed by hole digging. Maintenance in the area includes brushing of grasses and pruning of the canopy by 5-6 laborers.
Natural / human environment: The area is under humid agro-climate condition with a topography ranging from 1-10% slope. It receives an average annual rainfall of approximately 3072 mm. The elevation ranges from 370-890 meter above sea level.
Mt. Kitanglad and Agri Development Corporation (MKADC) operates the area where the technology is being practiced. Farmers living within the area are the laborers of the company.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
菲律宾
区域/州/省:
Valencia City
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bukidnon
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The company integrated trees along roads and between blocks ,years later and trees were grown enough ( around 10 years) , they found its efficiency as habitats for endangered species.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Major cash crop: Pineapple
Other crops: Mangium, mahogany and other trees
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water logging, soil erosion and monocropping ( pineapple production throughout the year).
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
具体说明:
Longest growing period from month to month: trees grow for more than a year
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Estimated area planted as buffer zones is 5% of the gross area of the plantation.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind, aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed, in blocks
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

生物性退化
- Bh:栖息地丧失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bh: loss of habitats
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Cutting of trees, excessive pruning)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Trees planted between blocks of pineapple and access roads
Location: Barangay Lurogan. Valencia City, Bukidnon
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use, Improve of biodiversity
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): <10
In blocks
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Spectabilis, Calliandra, Mangiam
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Coconut, Mulberry
Other species: Oranamental
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2-5%%
Construction material (other): Trees (hard wood and fruit trees)
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Philippine Peso
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
46.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
6.45
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grass Brushing | 植物性的 | |
| 2. | Hole Digging | 植物性的 | |
| 3. | Planting | 植物性的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Grass brushing, hole digging and planting | ha | 1.0 | 117.0 | 117.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 117.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Brushing of grasses | 植物性的 | Every 3 months |
| 2. | Pruning | 植物性的 | Every after cropping season/at maturity |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Brushing of grasses and pruning | ha | 1.0 | 78.0 | 78.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 78.0 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Pruning Shear
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
3072.00
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altidudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. (497m)
Landforms: valley floors (256)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
100% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
Market orientation: Commercial/market (pineapples are exported in neighboring Asian countries)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
文化机会
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
风速
其它生态影响
Operating conditions
注释/具体说明:
Serves as temporary shade for laborers/workers
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Land user's view agree with experts opinion. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Protection of wildlife by providing food and shelter How can they be sustained / enhanced? Inclusion in the protocol of the company the prohibition of hunting and preying of alien or wildlife species present in the area. |
|
Preservation of wildlings and endemic species by retaining native tree species during clearing operation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintenance and protection of these trees by marking them. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land user's view agree with experts opinion. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Reduction of the pineapple production area due to the area allocated for growing trees. | Planting of trees that could be beneficial to the company and to the employees such as fruit bearing trees and those that improve the soil condition. |
| Trees shades some areas for pineapple production. | Regular pruning of the canopy. |
| Vulnerability to extreme event such as strong winds/typhoons | Introduce new species tolerant to those events |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Integrated Soil and Water Conservation Approach in Improving … [菲律宾]
Integration of soil and water conservation technologies primarily aim to protect the area from loss of biodiversity and land degradation.
- 编制者: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
模块
无模块