Integrated runoff water management [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Alex Lwakuba
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1749 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Erabu John
MMAIF, DEPT of Agriculture
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of agriculture, animal industry and fisheries (MAAIF) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
This is a system of integrated runoff water and drainage management that allows cultivation in a swampy valley bottom.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
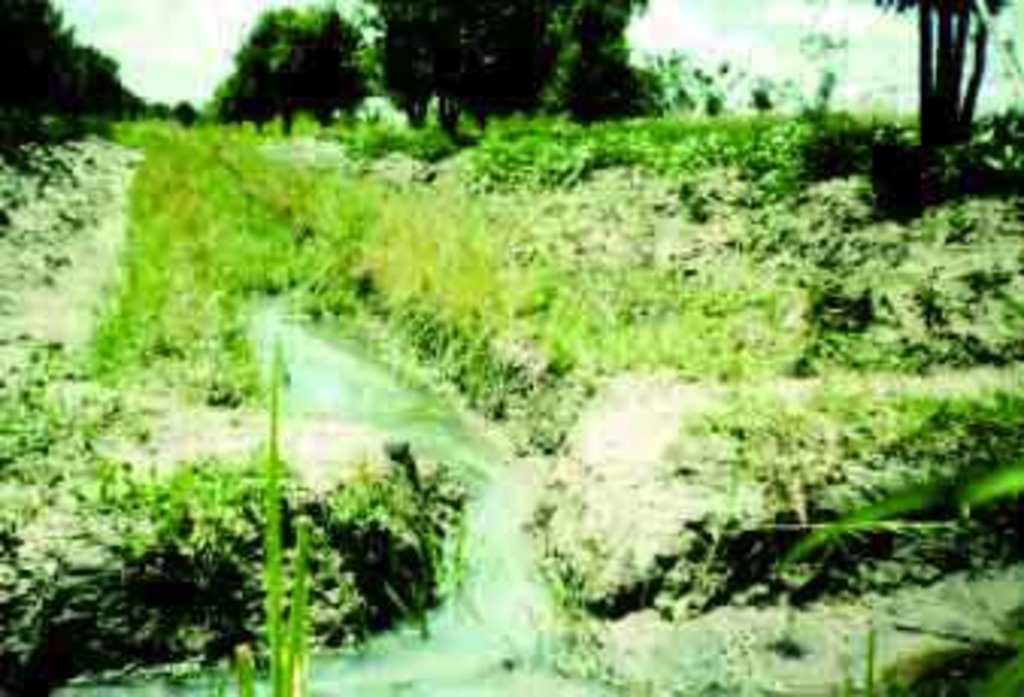
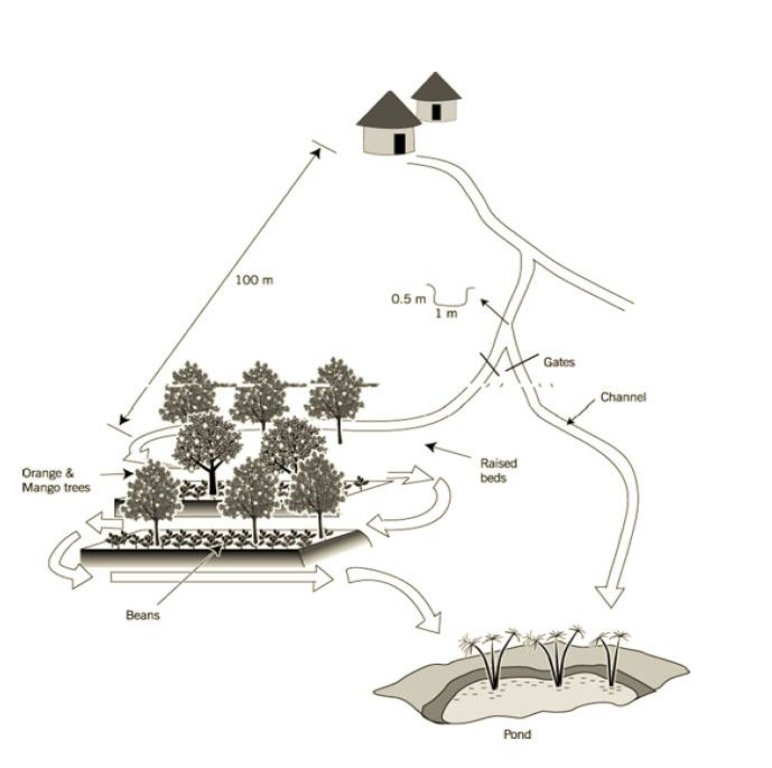
Setting up the infrastructure involves dividing the land in the valley into raised beds of ±10 m x 20 m which are separated by furrows, acting as drainage channels. Below the furrows is a pond. These furrows, however, can also fulfil the opposite role – distributing runoff water from upslope in the valley bottom if required. A diversion channel has been constructed to guide runoff from a track towards the valley. The channel is 0.5 m deep, 1 m wide, over 100 m in length and with a gradient of 0.5% - 1.0%. It is estimated that the ratio of catchment to cultivated area is 10:1. The channel is left open to divert runoff in times of shortage (though, naturally, as with any rainwater harvesting system, there has to be rain locally before it can be harvested). This water then can be held by the furrows whose outlet can be blocked. Citrus fruits (oranges) and mangoes are planted on the beds, and intercropped with annuals.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose is production of cash crops, based on reclamation of land and control of concentrated runoff. The impact is achieved through a flexible method
of drainage/water harvesting, which helps ensure suitable moisture conditions for growth.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main maintenance aspect is clearing inlets, channels and removing vegetation, using common household hand tools such as spades and hoes.
Natural / human environment: The technology is situated in a valley near a swamp. It consists of growing both annual and perennial crops throught the year. The farm is located in a semi-arid area. The soil is sandy loam and shallow.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Katakwi
有关地点的进一步说明:
Katakwi
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 5 km2.
the area under the technology reported covers farmers in one parish which approximates 5 km2
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
an adoption from another district by the landuser but with a lot of modifications and technology
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 水稻(旱地)
- 谷类 - 高粱
- 根/块茎作物 - 木薯
- 蔬菜 - 根茎类蔬菜(胡萝卜、洋葱、甜菜等)
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 柑橘属
- 饲料树木(朱缨花属、银合欢、前庭草等)
- Eucalyptus

牧场

森林/林地
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): the major land use problem in the area are cutting down of trees, burning of bushes lack of crop roatation and water and soil conservation methods.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): continous cultivation leading to low yields lack of soil and water conservation methods eg ploughing across the slope
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
ketch of the runoff harvesting system
Uganda
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting
Structural measure: diversion ditch/cut-off drain
Spacing between structures (m): 10
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.45
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 140
Construction material (earth): soil dug out to make channel and ditches
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 1.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 1.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:10.00
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Uganda shillings
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1000.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | ploughing, 2nd plough, diving the blocks, digging | dry season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 270.0 | 270.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 42.0 | 42.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost manure | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 345.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.34 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | cleaning inlets | during rains/each cropping season |
| 2. | cleaning channels | during rains/each cropping season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 340.0 | 340.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 315.0 | 315.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 71.0 | 71.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 726.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.73 | |||||
注释:
structures; channels 140mts long, W 1m depth 0.45m
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour intensive and time consuming in the digging of channels
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
- 非常丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 30% of the land (with over 10 cows).
10% of the land users are rich and own 25% of the land (with 5 - 10 cows).
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (with 3-5 cows).
25% of the land users are poor and own 15% of the land (with 1-3).
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land (without cows).
Off-farm income specification: majority of farmers are poor have no access to loans
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (cleaning, weeding and harvest) and animal traction (both ranked 1)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
注释:
Land ownership: group, individual, not titled, individual, titled
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
其它社会经济效应
Input constraints
社会文化影响
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Negative: Can lead to waterlogging
土壤流失
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
动物多样性
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
500 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Only one close neighbour has shown interest in copying him. ‘A few’ others from further away, also have. One constraint to adoption is the large amount of labour involved in setting up the system.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| increased incomes |
|
increased soil moisture content How can they be sustained / enhanced? adopt mulching |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
water runoff can be managed easily How can they be sustained / enhanced? constantly maintain the structure |
|
increased yields How can they be sustained / enhanced? adopt composting |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| need skills for the adopters | adopter need training |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| labour intensive | encourage group work |
| costly to construct | encourage household savings |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块