Rehabilitation of degraded land [摩尔多瓦共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Valentin Ciubotaru
- 编辑者: Valentin Ciubotaru, UNCCD PRAIS
- 审查者: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Reabilitarea pamanturilor degradate
technologies_1819 - 摩尔多瓦共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/06/2014
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology described here is sustainable land management
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Participatory land management was used to develop, and implement, SLM practices on slopes in order to rehabilitate degraded land. The local population were involved from the beginning. They took part in soil, water and biodiversity research, as well as the formulation and implementation of the land management plan, based on suitable SLM practices. In order to benefit from local knowledge, participatory training included traditional experience in soil conservation, and based on this, appropriate SLM technologies were included in the plan of action.
2.2 技术的详细说明
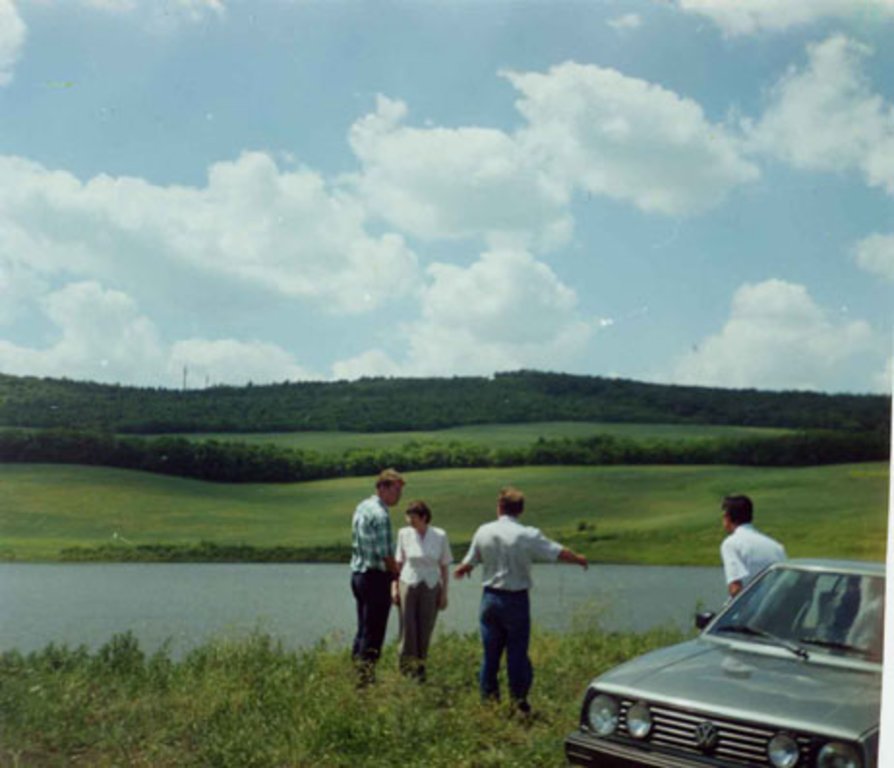
说明:
The distinctive feature of this approach to rehabilitating degraded land on slopes was the involvement of the local population from the beginning. They took part in soil, water and biodiversity research, as well as the development and implementation of the land management plan, based on suitable SLM practices. In order to benefit from local knowledge, participatory training included traditional experience in soil conservation, and based on this, appropriate SLM technologies were included in the plan of action.
The following stakeholders were involved in the overall process:
• Researchers: overseeing soil, water and biodiversity research and presenting results.
• Experts: proposing alternatives in the organization of the land and in the development of integrated management system for the landscape based on research results.
• Local public administration, Joint Stock Company and farmers: contributing with knowledge and experience in analysing land, water and biodiversity resources, preparation and implementation of the action plan.
• NGO BIOS: coordinating all activities, including research, implementation, training and monitoring of activities.
The land management plan was developed together with the local population, then it was implemented. Degraded areas (landslides and heavily eroded soils) were excluded from agricultural production and used for afforestation and grassland. The following soil and water conservation practices are applied:
Vineyards and orchards:
• Conservation tillage
• Forest belts
• Grass inter-rows in vineyards and orchards
Arable land:
• Crop rotation
• Application of mineral and organic fertilizers
• Strip cropping
• Conservation tillage,
• Forest belts.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
摩尔多瓦共和国
区域/州/省:
Central Region of the Republic of Moldova
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
1998
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Vineyards, wheat, barley, maize, sunflower.

森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:
- 选伐
植树造林:
- 混交品种
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 放牧/啃牧
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
About 150 ha of degraded land (landslides) were taken out of agricultural production and transferred to afforestation
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V3:植被的清理
- V4:更换或清除外来/入侵物种

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

化学性土壤退化

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bf:火灾的有害影响
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
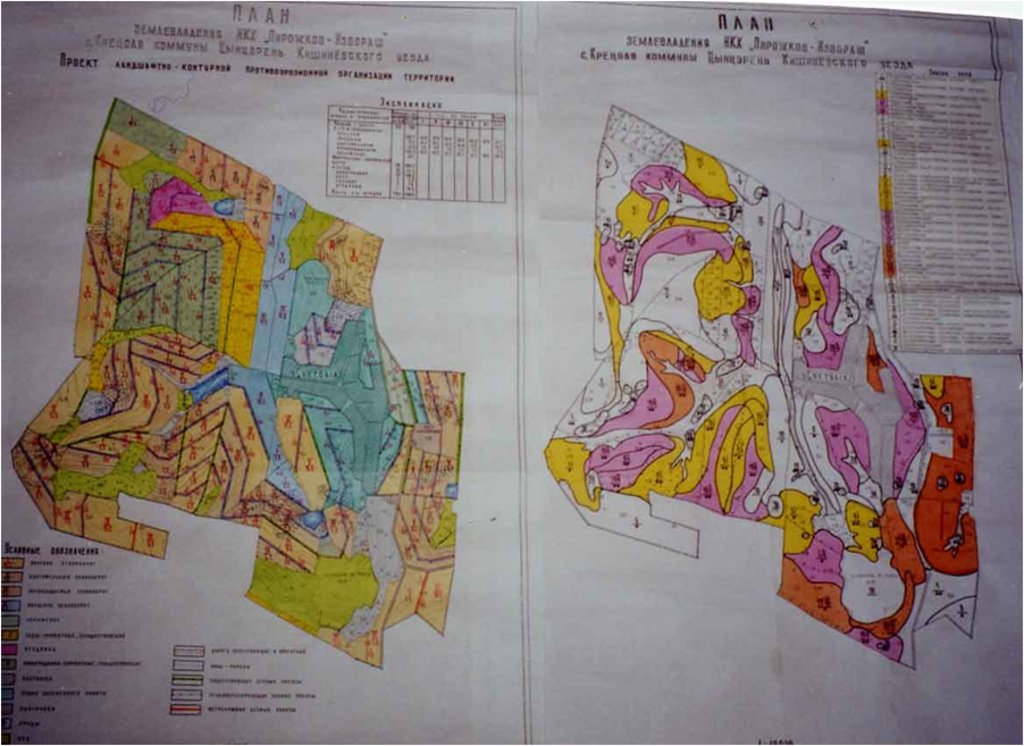
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Regeneration of degraded commune forest as well as existing forest protective belts | ||
| 2. | Soil conservation tillage | ||
| 3. | Planting of grass in inter raw of vineyards and orchards together with contour tillage and other soil conservation | ||
| 4. | Earth dam structure |
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
550.00
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
State Hydrometeorological Service
农业气候带
- 半湿润
The climate is moderately continental: the summers are warm and long, with temperatures averaging about 20°C, and the winters are relatively mild and dry, with January temperatures averaging -4°C. Annual rainfall, which ranges from around 500 millimetres; long dry spells are not unusual. The heaviest rainfall occurs in summer; heavy showers and thunderstorms are common.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The territory of Cretoaia village is situated in the Central Moldavian Plateau, at an average elevation of about 350 m. It is interlaced by deep, flat valleys, ravines, and landslide-scoured depressions.|
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Chernozems (black soils) prevail (80% of the area), however they are degraded. About 50% of the land has a gradient from 2 to 6 degrees, while 30% of the land has an inclination exceeding 6 degree. Water erosion processes are widespread and quite intense. The predominant length of the hillsides in Cretoaia is over 900 m.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The estimated average income per capita in the community over the last 3 years was 70 US dollars per month. The principal activity in the commune is agriculture. The farmers cultivate arable crops, grapes, fruits and vegetables. People also have cattle, sheep and goats in their household, mainly for home consumption and some extra for sale. There is a foodstuffs and a macaroni factory in the village, where the local population work.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
People in the community have plots of about 4 hectares per household - which belong to them - and they have title deeds and land maps to prove it.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
土地管理
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
有关影响评估的意见:
The expected environmental impact of the initiated actions are significant, especially in the long run. Expected changes include diminishing landslide activity, the soil erosion rates, changes in existing land use management, changes in the landscape, etc.|
The sustainable technologies were proposed and implemented for the soil to be productive. The increased production on the land were fertilizers applied in combination with soil conservation practices.
Men found another occupation - fishing in the constructed water reservoir, while for the community is meant a recreation facility. The expected social impact of implemented practices include increased jobs for people, and increases in agricultural productivity.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 10-50%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
1. Highly motivated local governments. 2. Bad weather which has led to intensifying activity against landslides 3. Clearly expressed objectives and expectations in respect to individual benefits. All these can be replicated anywhere. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
10
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Elena Bivol, Valentin Ciubotaru Urban Agriculture in Chisinau, Republic of Moldova / NGO BIOS, Chisinau, 2005, 60 p.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NGO BIOS 72/3 Columna str., office nr. 3, Chisinau, MD-2009, Republic of Moldova Tel./Fax: +(373-22) 545733; +(373-22) 723372 GSM: +(373) 69134294 .
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块