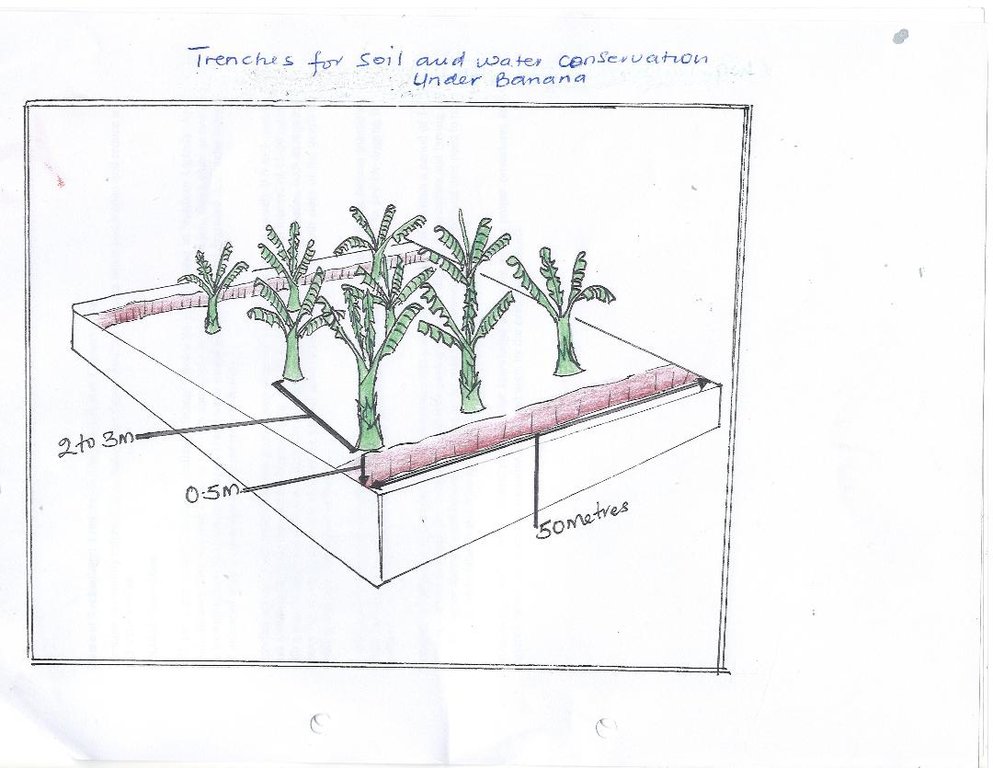
Trenches for soil and water conservation under banana. [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Sunday Balla Amale, Bernard Fungo
- 审查者: Donia Mühlematter, John Stephen Tenywa, Nicole Harari, Renate Fleiner, Stephanie Jaquet, Alexandra Gavilano
Baro kor pii
technologies_2274 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Acen Kaven
Gulu District
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology is useful in controlling soil and water runoffs under banana.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Trenches commonly referred to as “fanny juu, fanya chini” increase water infiltration and reduce soil erosion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
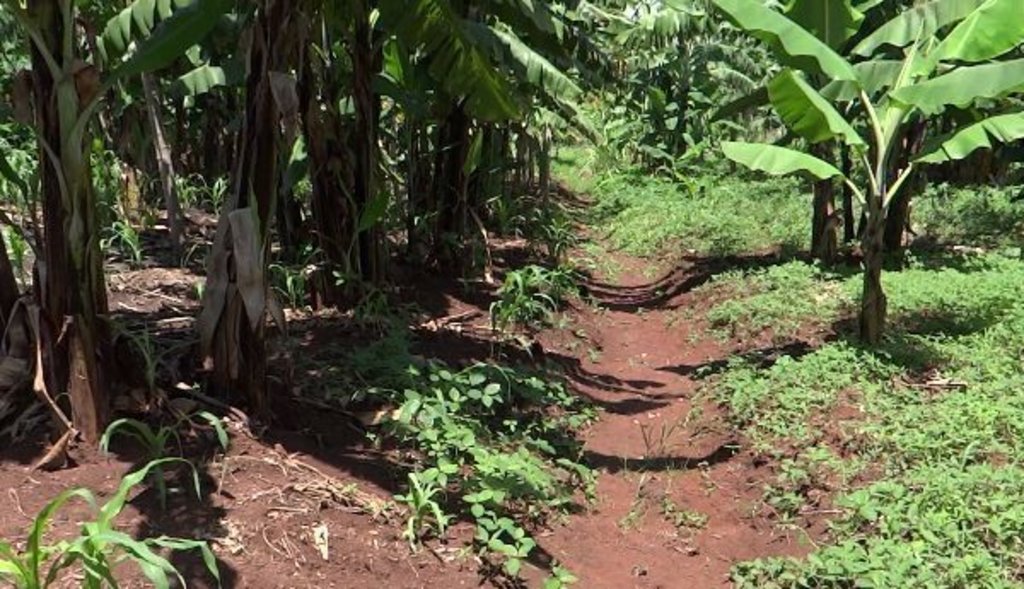
Soil and water runoff is a major challenge encountered by farmers growing banana in Northern Uganda. As a remedy, farmers have started using trenches commonly referred to fanya juu, fanya chini. This is one of the technologies intended to help reduce soil and water runoff on cultivated and degraded land under banana in order to increase water infiltration and improve soil fertility.
The trenches are normally established during the dry season on small pieces of land of about 0.5 to 1 acre, with slopes ranging from 16 to 30% in areas with high rainfall. The trenches are measured, using a tape measure, 0.5 m deep and 50 m long banana planted at a spacing of 3 metres between plants to allow suckers to grow in addition to applying cow dung during maintenance which is locally obtained at no cost.
Implements and materials required to construct the trenches include ropes, spades, and hoes. Once the trenches have been constructed, natural grass can be allowed to grow or elephant grass planted on both sides of the trenches to stabilize the soils and reduce sediments falling into the trenches.
In this practice, the land user starts with identifying soil erosion hotspots within the banana plantation where the trenches are to be established. This is followed by looking for labour and money to pay for digging the trenches.
Trenches are effective in reducing soil and water runoffs under banana production immediately when it starts raining. It is worth to note that, the costs associated with paying labour for digging the trenches and buying inputs are higher during establishment compared to the costs of maintenance; this is because during maintenance the land user only needs to pay for labour to remove sediments from the trenches.
Establishing trenches under banana plantations requires the land user to be provided with prior knowledge and skills through training on the proper procedures on establishing the trench using the correct measurements of 0.5 m deep and 50 m long with banana planted at a spacing of 3 metres with the help of a tape measure, ropes, spades, and hoes and as required inputs.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Video on trenches for soil and water conservation
日期:
26/05/2017
位置:
Gulu District, Northern Uganda
摄影师的名字:
Issa Aiga
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Region,Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Gulu District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The land user started on his own after participating in a field visit in South Western Uganda and later supported by the extension agent through training.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
每年的生长季节数:
- 2

牧场
- 2 cows

其它
具体说明:
Trenches
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A5:种子管理,改良品种

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S1:阶地
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

物理性土壤退化
- Pw:水浸

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Hw:湿地缓冲能力下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Trenches reduces the speed of water which when not controlled washes away the soil nutrients.
Desilitation restores fertility removed from the trench and taken back to the banana garden.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Trenches are normally established during the dry season on small pieces of land of about 0.5 to 1 acre, with slopes ranging from 16 to 30 % in areas with high rainfall. The trenches are measured using a tape measure, 0.5 m deep and 50 m long banana planted at a spacing of 3 metres between plants to allow suckers grow.
作者:
Acen Kaven
日期:
10/05/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.5 to 1 acre
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
3350.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5000
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Identify erosion hot spot area | During the dry season/ after heavy rains |
| 2. | Look for the tools and labour | During the dry season |
| 3. | Measure the size of trench | During the dry season/ before rains set |
| 4. | Dig the trench | During the dry season/ before rains set |
| 5. | Desilt when it fillsup with soil | During the dry season/ after rains |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Persons days | persons | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spade | Pieces | 10000.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | Wheel barrow | Pieces | 10000.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 设备 | Ropes | Pieces | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tape measure | pieces | 1.0 | 25000.0 | 25000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 78000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 23.28 | |||||
注释:
Planting material (natural grass or elephant grass planted on the trenches is obtained free and no costs involved on purchase of planting material.
Total costs for establishing trenches are much higher at the time of establishment compared to the costs of maintenance and the benefits are high both in the short and long term.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desiliting | At least every year after heavy rains/ during dry season |
注释:
The farmer uses cow dung to maintain the technology which is locally obtained at no cost.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Persons | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertiliser | Kgs | 2.0 | 3500.0 | 7000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Biocides | litres | 2.0 | 3500.0 | 7000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 39000.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 11.64 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour for digging trenches, desilting and re-applying the silt in the garden.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1350.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Two rainy season March -May and September to November.
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Trench making is a technology that is more labour intensive and is usually not appropriate for women to do.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
土地管理
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
High at the time digging trenches but over a period of time reduces
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
From the sale of banana.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
More tasks at establishment and over a period of time reduces which affects labour costs.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Extension workers extend knowledge to the farmers and other farmers come to learn from other farmers promoting the technology.
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
As a planted grasses (elephant grass) on the trench.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Due to the presence of the trenches and grasses planted as stabilizers.
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Water runoff is controlled by the trench.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 适度 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 滑坡 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
More costs for labour and inputs for digging trenches at estsblishment than costs required for maintaing and desilting.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Those who have adopted are those that are outiside the group as a resulting of copying from the group.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
Around 40%.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
By planting natural and elephant grass to reduce soil and water run off.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Good at reducing soil and water runoff. |
| The costs of maintaining trenches in a banana plantation are rather low compared to the costs of estsblishment. Costs may be only high when it comes to weeding the banana. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Trenches are effective in controlling soil erosion. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive with high costs at estsblishment than maintenance. | Work in groups. |
| Requires knowledge and skills which a farmer may not have at the time of establishment. |
Consult extension agents to provide technical guidance. Provide trainings on proper procedures for estsblishment. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Trenches alone may not be a measure for reducing land degradation. | Plant agrofrestry trees (Callindra , Grivellea, and Elephant grass where trenches are established. Fodder). |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
01
- 与土地使用者的访谈
01
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/05/2017
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块