Grass reseeding [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kevin Mganga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Donia Mühlematter, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Alexandra Gavilano
Reseeding
technologies_2288 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Range and Wildlife Sciences, South Eastern Kenya University (SEKU) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

On-farm indigenous pasture establishment demonstrations [肯尼亚]
On-farm indigenous pasture establishment demonstrations offer a practical approach to encourage adoption in the arid and semi-arid environments in Kenya.
- 编制者: Kevin Mganga

Projet lutte contre l‘erosion, recuperation et mise en … [布基纳法索]
Une approche intégrée et multipartite au Sud Ouest du Burkina Faso, basée sur l’aménagement des bassins versants et sur la gestion durable des terres avec un fort accent sur la participation locale. Elle réalise des mesures physiques et biologiques de lutte contre l’érosion, d’adaptation au changement climatique et exécute des …
- 编制者: Rebecka Ridder
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
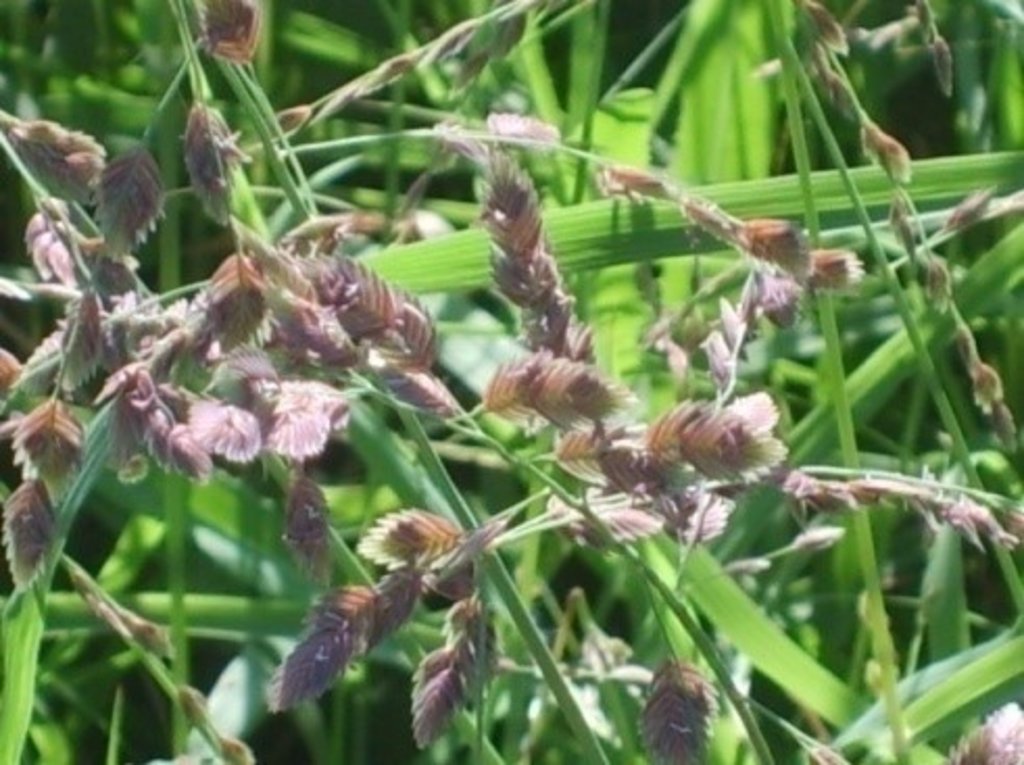
Grass reseeding is a sustainable land management practice aimed at rehabilitating degraded pastures and providing livestock feed. This is mainly carried out with indigenous perennial grass species.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
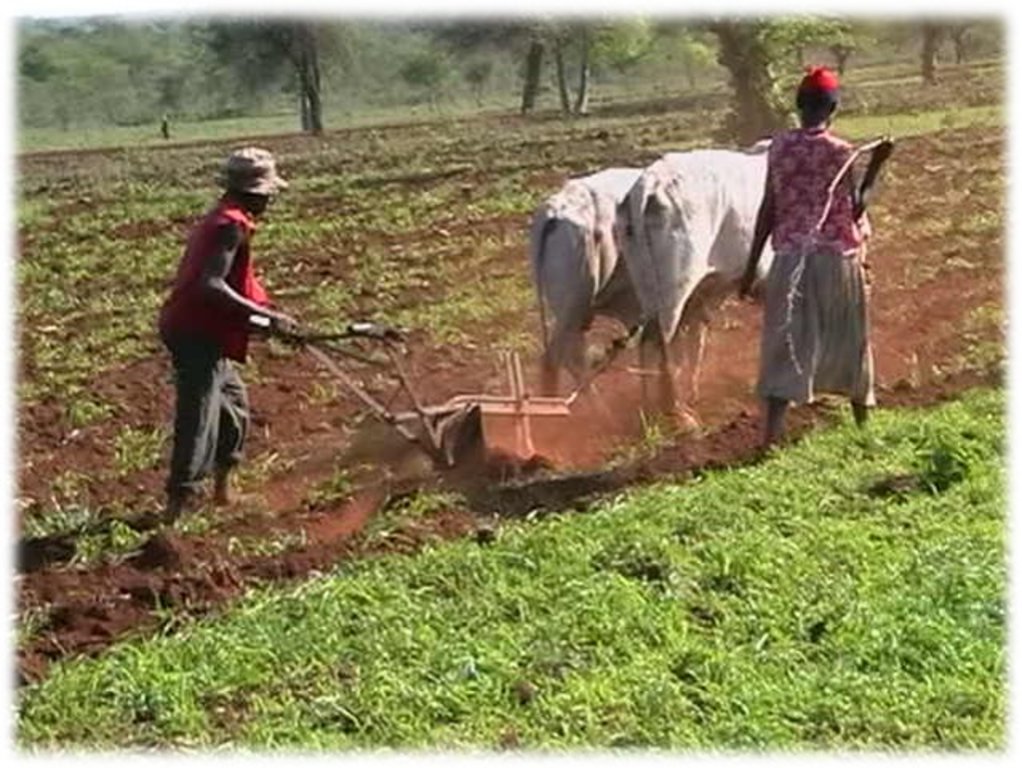
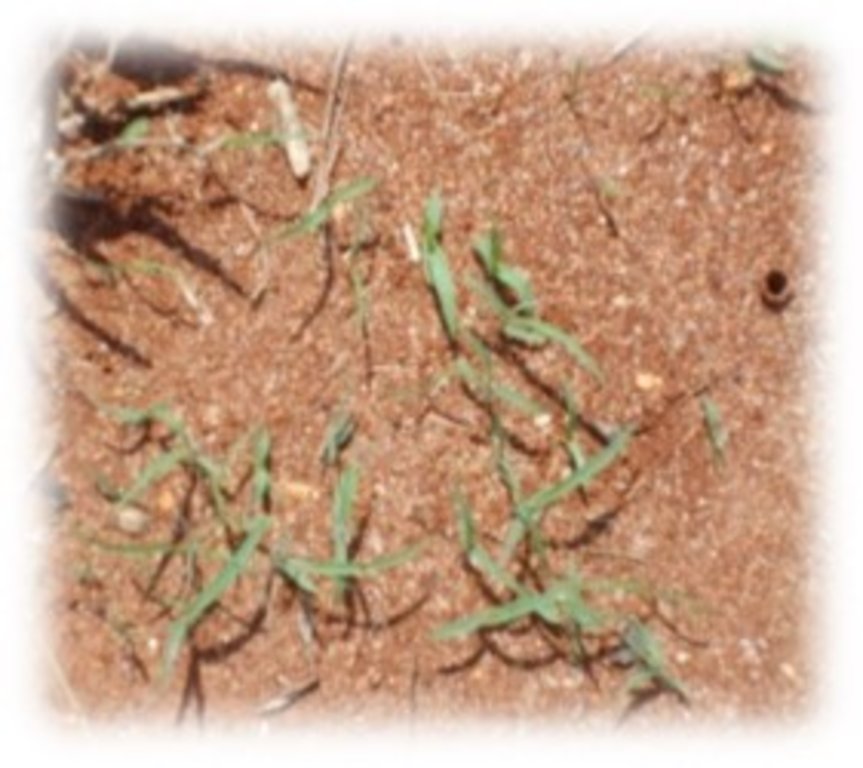
Grass reseeding is a sustainable land management practice especially appropriate for pastoral and agro-pastoral communities inhabiting the arid and semi-arid rangelands of the world. Seedbed preparation involves clearing of invasive bush patches and creation of furrows across the slope using an ox-plough (traditional) or shallow and light ploughing using a tractor (modern). Grass seeds are sown along the furrows which are created directly in the degraded grazing land. The seeds are lightly covered with soil because the indigenous grass seeds are very small. This encourages faster emergence of grass seedlings. The slope should be generally flat or very gentle (<5%) to reduce the speed of runoff, thus prevent soil erosion and consequently the washing away of the grass seeds. Eroded and deposited seeds will eventually lead to uneven establishment of pasture, mainly concentrated downslope. Minimal soil disturbance by ox-plough or tractor facilitates root penetration of the seedlings and also helps breaking the soil surface hardpan formed by continuous hoof action.
Furrows constitute a form of in-situ moisture conservation, capturing rainwater where it falls, thus increasing availability of water for emerging seedlings. The main purpose of this technology is to rehabilitate degraded natural pastures and provide a continuous source of livestock feed especially during lean periods. Use of indigenous grass species e.g. Eragrostis superba, Cenchrus ciliaris, Enteropogon macrostachyus and Chloris roxburghiana is advocated for better establishment and subsequent development. Ecological impacts of this technology include improved soil cover and reduced soil erosion. In addition to rehabilitating degraded natural pastures and improving quality and quantity for livestock production, grass reseeding has additional socio-economic impacts, thus benefiting rural livelihoods. This is through the sale of hay and grass seed and surplus milk in the local market, which provide supplementary sources of income.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kibwezi
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Arid and Semi-Arid Lands (ASALS) in Kenya.
Practiced among several agropastoral and pastoral households in the arid and semi-arid lands
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 减缓气候变化及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 草

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
- 半游牧畜牧业
- 经营牧场
动物类型:
- 山羊
- 绵羊
- cattle
注释:
Use of indigenous grass species e.g. Eragrostis superba, Cenchrus ciliaris, Enteropogon macrostachyus and Chloris roxburghiana is recommended
Number of growing seasons per year: 2
Bimodal rainfall pattern (March-May) and (October-December).
Livestock density: On average 2-3 cattle, 7-8 goats, 2 sheep per household
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 最小的土壤扰动
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pi:覆土

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
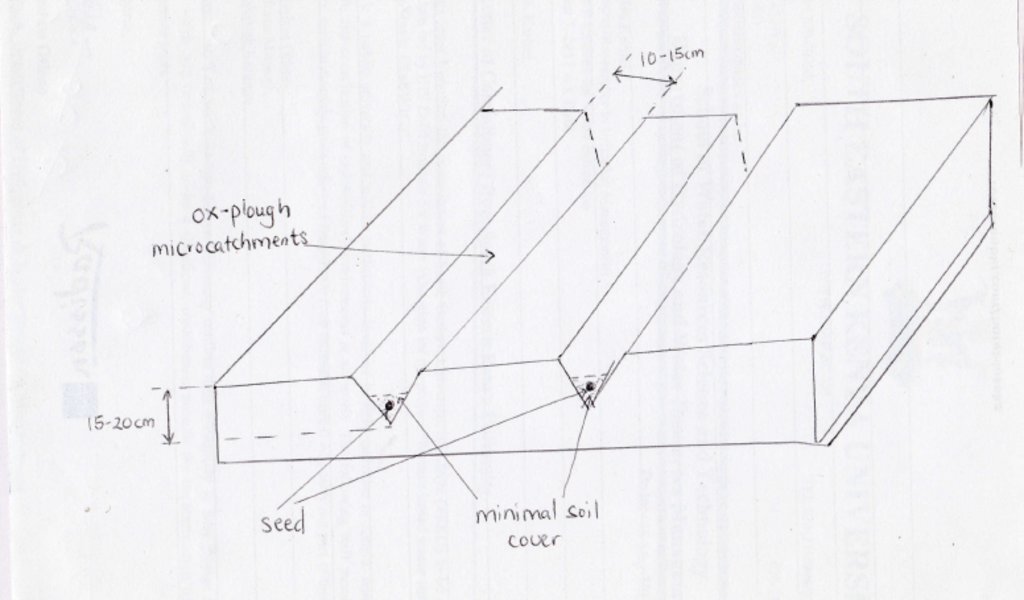
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
15-20 cm deep and 10-15 cm wide furrows across the slope. Spacing between furrows is 15-20 cm and depends mostly on plant species. Seeds are sown along the furrows intentionally built to capture and hold rainwater. Flat or very gentle (<5%) slope to reduce runoff.
作者:
Kevin Mganga
日期:
18/05/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
Hectare
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Creation of furrow micro-catchments with ox-plough | Before onset of the rains |
| 2. | Sowing (seed placement and covering with soil) | Before onset of the rains |
| 3. | Gapping (reseeding gaps with poor establishment and cover) | After establishment |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Casual and Household labour | person-days | 4.0 | 5.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hiring ox-driven plough | person-days | 4.0 | 100.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | kgs | 5.0 | 10.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 470.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 470.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Gapping (i.e. reseeding bare areas (patches) with poor germination and cover) | Seasonal |
注释:
Gapping is done to ensure uniform plant cover
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Casual and household labour | person-days | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Ox-driven plough | person-days | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seed | kg | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 115.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 115.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Seed availability in the 'informal markets' i.e. between farmers and farmer groups, research organisation, influences the cost of grass seed. This is mainly determined by the preceding rainy season.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
700.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Highly variable in space, time and season.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Meteorological Station - South Eastern Kenya University
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitude 900 m above sea level
Slope angle - flat 0-2% and gentle 3-5 % slopes
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Seasonal flactuation depending on rainfall
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Due to intensive utilisation of natural pastures, notably due to overgrazing, indigenous pasture species are depleted and replaced by less preferred invasive plant species. However, reseeded pastures reverses this trend by re-introducing various species the indigenous pastures which can naturally co-exist and reduce competition with other herbaceaous plant species, thereby increases biodiversity.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
- 半游牧的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
注释:
Communal land use right - e.g. common grazing land, reserved and seasonal grazing areas (large scale)
Individual land use right - e.g. individual pasture establishment within individual owned land
Communal water use rights - e.g. watering point, river, lake, stream, community water reservoir, boreholes
Individual water use rights - e.g. individual tap water, roof water catchment
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
收入和成本
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Reseeded areas improve the soil hydrological properties by reducing the impact of raindrops thus reducing soil disturbance and increasing water infiltration capacity. Consequently, runoff, and sediment production - an index of soil erosion, are greatly reduced.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased quantities of livestock forage especially during the dry season (fodder reserves). |
| Diversification of source of income through sale of grass hay and seeds. |
| Improving the environment i.e. rehabilitating degraded grazing land. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reliable source of livestock forage especially during periods of drought. |
| Diversification of source of income through sale of grass hay and seeds. |
| Improving the environment i.e. rehabilitating degraded grazing land. |
| Climate change mitigation through carbon (C) sequestration. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Successful establishment is dependent on amount, distribution and duration (rainy days) of rainfall in the area. | Improved rainwater capture and storage technologies. |
| Seed availability - quantity and quality | Large-scale production of good quality indigenous seed to supply the pastoral and agropastoral communities at a subsidized price. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Rainfed and climatic (rainfall dependent) | Improved rainwater harvesting and storage technologies |
| Seed availability - quantity and quality | Large-scale production of good quality indigenous seed to supply the pastoral and agropastoral communities at a subsidized price. |
| Low uptake/interest among the youth, students | Sensitization of the youth as a source of income (business) |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/01/2016
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
KZ Mganga, NKR Musimba, DM Nyariki. 2015. Competition indices of three perennial grasses used to rehabilitate degraded semi-arid rangelands in Kenya. The Rangelands Journal 37: 489-495
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
The Rangeland Journal website, US Dollars $25
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
KZ Mganga, NKR Musimba, DM Nyariki. 2015. Combining sustainable land management technologies to combat land degradation and improve rural livelihoods in semi-arid lands in Kenya. Environmental Management 56: 1538-1548
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Environmental Management Journal website, US Dollars $38
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
KZ Mganga, NKR Musimba, MM Nyangito, DM Nyariki, AW Mwang’ombe. 2015. The choice of grass species to combat desertification in semi-arid Kenyan rangelands is greatly influenced by their forage value for livestock. Grass and Forage Science 70: 161-167.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Grass and Forage Science Journal website, US Dollars $38
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Competition indices of three perennial grasses used to rehabilitate degraded semi-arid rangelands in Kenya
URL:
http://www.publish.csiro.au/rj/RJ15023
标题/说明:
Combining sustainable land management technologies to combat land degradation and improve rural livelihoods in semi-arid lands in Kenya
URL:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00267-015-0579-9
标题/说明:
The choice of grass species to combat desertification in semi-arid Kenyan rangelands is greatly influenced by their forage value for livestock
URL:
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/gfs.12089/abstract
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

On-farm indigenous pasture establishment demonstrations [肯尼亚]
On-farm indigenous pasture establishment demonstrations offer a practical approach to encourage adoption in the arid and semi-arid environments in Kenya.
- 编制者: Kevin Mganga

Projet lutte contre l‘erosion, recuperation et mise en … [布基纳法索]
Une approche intégrée et multipartite au Sud Ouest du Burkina Faso, basée sur l’aménagement des bassins versants et sur la gestion durable des terres avec un fort accent sur la participation locale. Elle réalise des mesures physiques et biologiques de lutte contre l’érosion, d’adaptation au changement climatique et exécute des …
- 编制者: Rebecka Ridder
模块
无模块