Improved Tree Nursery Bed [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Jalia Namakula
- 编辑者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Kayubu Kodi
technologies_2797 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Oyet Julius
+256782165103 / +256752165103
Tudakatuba farmers group
Pajak village, Amuru District, Northern Uganda
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Improved fruit tree nursery is a technology comprising of grafted mangoes, grafted citrus, eucalyptus and pines, established with the aim of improving household income and promotion of agro-forestry farming systems within surrounding communities to achieve environmental conservation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
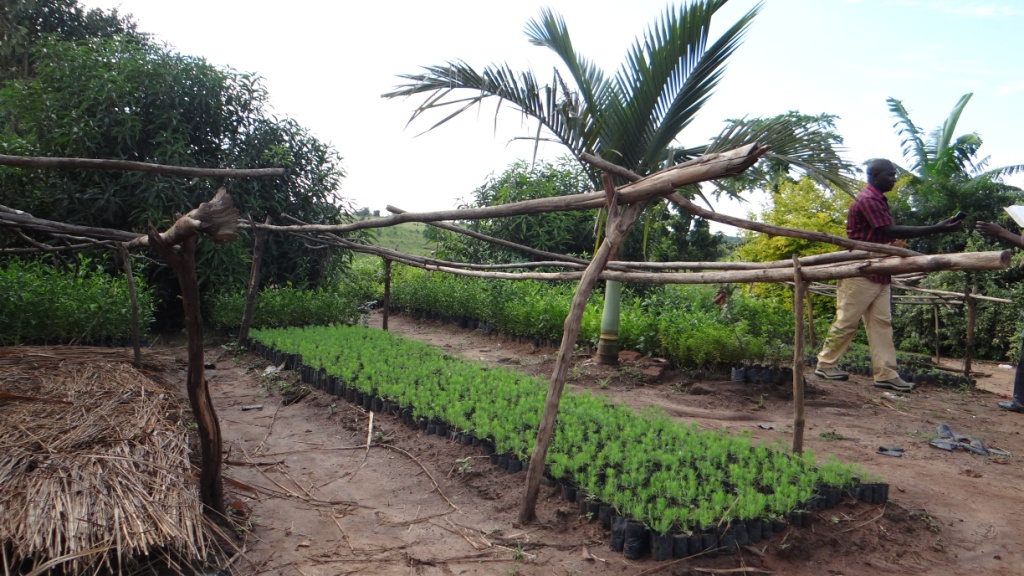
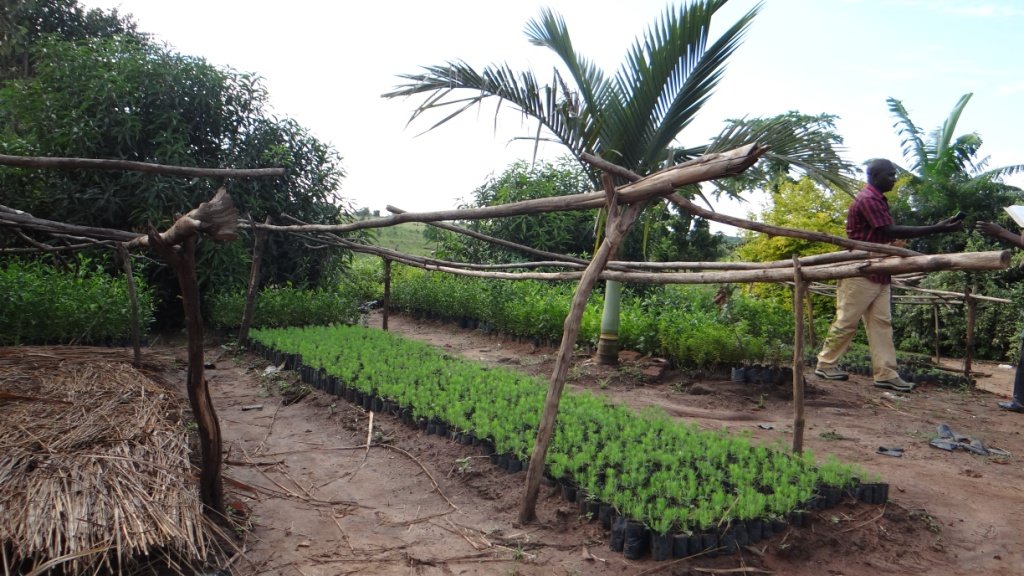
说明:
Tree nurseries are places where tree seedlings are propagated, managed, and grown to a transportable size. They are essential for producing quality seedlings in high quantities for rapid afforestation and sustainable land management.
In response to promoting this technology among farmers in Uganda, the Government of Uganda, through its initiatives such as Operation Wealth Creation (OWC), is promoting the growing of high value crops such as fruit trees to improve farmers’ incomes and food security. The technology is established on a gently sloping land lying on a plot of 1725 square meters, some 300 m away from a wetland used as a source of water for the nursery during the dry season. The soils here, on observation, have high clay content and are relatively deep.
The activities for establishing the nursery involved three stages:
1. clearing the bush on site, destroying all the termite mounds, ploughing the area, and levelling the mother beds established on flat or gentle rolling area to avoid water logging during the rainy season
2. preparation of the potting area and the potting medium which was done by mixing black soil with sand and manure in a ratio of 3-1-1 respectively. These activities took 2 person days to finish, followed by potting in 5cm × 12cm potting bags, taking 10 person days. The pots were then laid in a series of 1×10m long beds with paths of 0.75m between them. This activity took 2 persons days. Seeds were planted, watered and pots were covered with grass until germination after 14 days. After germination the seedlings are left for 4 months to mature until they are ready for grafting
3. grafting the then ready root stock with desired scion. The process involves cutting the root stock and scion at an angle and fitting the two together and holding them tightly with a wide plastic thread, the grafted seedlings are then placed in beds and placed in a closed housing unit with enough humidity only to be removed after 21 days. The seedlings are now placed again in rows where they are managed until ready for transportation
Maintenance activities included spraying fortnightly with pesticides and fungicides, watering with clean water twice every week, weeding and regular sorting of the seedlings to encourage proper growth. If any shade was put it is removed when the seedlings are well established to acclimatize them to open environmental conditions before they are transplanted or sold.
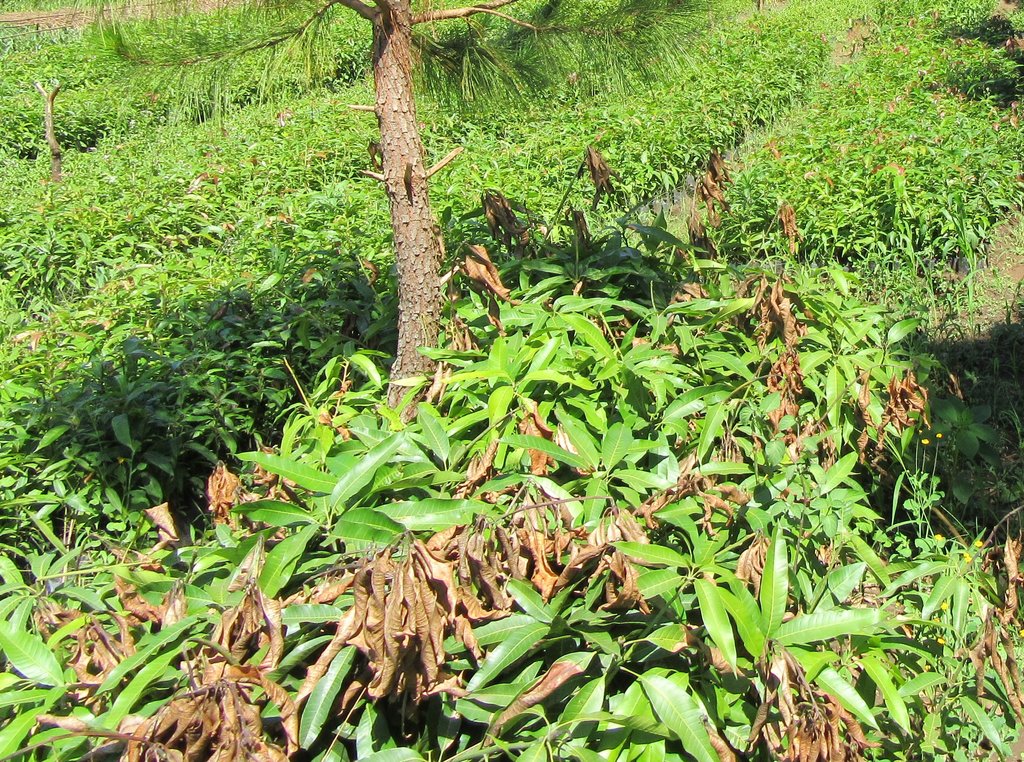
The tree varieties planted include improved mangoes, citrus, clonal eucalyptus and pines. Currently the nursery has over 10,000 citrus seedlings and 15,000 mango seedlings and a few seedlings of both pine and eucalyptus.
Tree nurseries are preferred by farmers because they use small land sizes, generate a lot of income, seedlings, when planted protect the environment and help in rapid production of genetically improved fruit trees in addition to offering employment to a wide spectrum of people including unskilled and skilled persons. There are notwithstanding, challenges such as lack of reliable water source and lack of skilled labor for grafting and high nursery establishment costs.
Limited market opportunities continue to be limiting factors to the tree nursery initiatives with the government being the only big buyer of tree seedlings in North Uganda.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
09/06/2017
位置:
Amuru District, Northern Uganda
摄影师的名字:
Isa Yiga
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Pajak village, Amuru District, Northern Uganda
注释:
Coordinates: 2.812533 and 1.96157
The Nursery beds are s located in Pajak Village, Amuru District
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2002
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
This practice was lean't from a fellow farmer in Mukono District, but technical support is provided by the Amuru local government.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

不毛之地
具体说明:
Bush surrounded by former brick making area
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
The land user constructed a water reservoir close to a wetland to act as a water source especially during the dry season
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
The trees are planted once a year
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- tree nursery
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The nursery is established on 69m2 × 25m2 of land
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
The nursery was established to improve production of the fruit trees and provide economic benefits to the landuser
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Prossy Kaheru
日期:
09/06/2017
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The nursery is located on a 69m X 25 m (1725 m2) plot size
The nursery beds are a 1m x 10m, with a 75cm pathway between the beds
The beds contain 10,000 citrus seedlings 15,000 mango seedlings and a few clonal eucalyptus and pine trees
The pots used for growing mangoes are 5in x 7in, whereas citrus , eucalyptus and clonal are 4in X 7in
The rivets used to construct the shades are between 2m and1.5cm high. grass is used to shield the young seedlings from direct sunshine
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1725 m2
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3818.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3000/=
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Determine water source | 管理 | June and July |
| 2. | Mix soils with manure | 农业学的 | June and July |
| 3. | Buy planting material (seeds and potting bags) and poles for constructing shelter shelter | 管理 | June and July |
| 4. | Potting and planting seeds | 农业学的 | June and July |
| 5. | Cover pots with grass | 农业学的 | June and July |
| 6. | Put under shade | 管理 | June and July |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Potting and Planting | People | 4.0 | 12000.0 | 48000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Arranging pots | People | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Preparing mango seeds | people | 4.0 | 10000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | 100.0 | |||||
| 设备 | Water pump | Piece | 1.0 | 1000000.0 | 1000000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Wheel barrow | Piece | 2.0 | 80000.0 | 160000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Watering can | Piece | 9.0 | 7500.0 | 67500.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Potting bags | Roll | 12.0 | 6000.0 | 72000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Water storage drum | Piece | 1.0 | 70000.0 | 70000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds (Eucalyptus) | Kg | 5.0 | 30000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds (Pine) | Kg | 10.0 | 10000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds (citrus) | Kg | 4.0 | 60000.0 | 240000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds (mangoes) | Bag | 50.0 | 15000.0 | 750000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Cyons (mangoes) | Piece | 15000.0 | 100.0 | 1500000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Cyons (citrus) | Piece | 10000.0 | 20.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Soil | Truck | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Sand | Truck | 1.0 | 50000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | DAP | Kg | 5.0 | 3500.0 | 17500.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Liquid fertilisers | Litre | 1.0 | 18000.0 | 18000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Construction poles | piece | 50.0 | 3000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Grass | piece | 50.0 | 2500.0 | 125000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Nails | kg | 3.0 | 1000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Polythene bags (6inch) | kg | 100.0 | 6500.0 | 650000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Polythene bags | kg | 120.0 | 6500.0 | 780000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 6341000.0 | |||||
注释:
The land user takes this as a major source of income
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Watering | 农业学的 | 2/week |
| 2. | Pesticides application | 农业学的 | 2/season |
| 3. | Sorting of seedlings | 农业学的 | 2/season |
| 4. | Construction of shades | 结构性的 | 1/season |
注释:
Sorting of seedlings happens continuously every season
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Watering | People | 5.0 | 3000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Weeding | People | 5.0 | 15000.0 | 75000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Sorting | People | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Strings | People | 2.0 | 8000.0 | 16000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Poles | Piece | 50.0 | 1500.0 | 75000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Grass | Bundle | 25.0 | 2500.0 | 62500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 248500.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Accessibility to quality seed, transportation of materials, drought
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainfall started late. First season rains started in April instead of late March, and second season started in September instead of late August
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Gulu meteorology station
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
The nursery borders with a wetland therefore, water availability is not a challenge
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Only a few tree species planted
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The nursery owner also operates a small maize mill
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
The technology lies on less than an acre of land. The average land holding of this area is 2ha.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
The farmer sold 25,000 seedlings and earned over UGX 37,500,000 ( USD 9,868)
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
continuous watering of the seedlings, maintains soil moisture
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
The water used in the dry season is drawn from the pond constructed in a wetland close. However this is affecting the water flow to other neighbours using this water.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Tree nurseries are very expensive to establish and take close to a year for the seedlings to be sold. Therefore, establishment costs surpass benefits in the short run, however when the trees are sold they fetch a lot of income. Maintenance costs, both in the short and long term are positve.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Optimal space utilisation |
| Maintenance costs are low |
| Nurseries generate high value crops |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Nurseries rehabilitate degraded land |
| Environmental improvements |
| They are used for aesthetic benefits |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishment costs are high | Bulk purchases of inputs |
| Grafting needs technical skills | Hire skilled labour |
| Markets are inaccessible | Register company with the district and sub-county |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive | |
| Markets are highly seasonal | Sourcing from other buyers for examples NGOs promoting agro- forestry |
| Trees do not grow at the same rate | Application of fertilizers |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
one
- 与土地使用者的访谈
one
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Improving Sustainable Productivity in Farming systems and Enhanced livelihoods through Adoption of Evergreen Agriculture in Eastern Africa. Joy Buyinza and Vicent I Opolot
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.cgiar.org/research/publication/improving-sustainable-productivity-in-farming-systems-and-enhanced-livelihoods-through-adoption-of-evergreen-agriculture-in-eastern-africa-shortened-as-trees-for-food-security-project/
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Improving Sustainable Productivity in Farming systems and Enhanced livelihoods through Adoption of evergreen Agriculture in Eastern Africa
URL:
https://www.worldagroforestry.org
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块