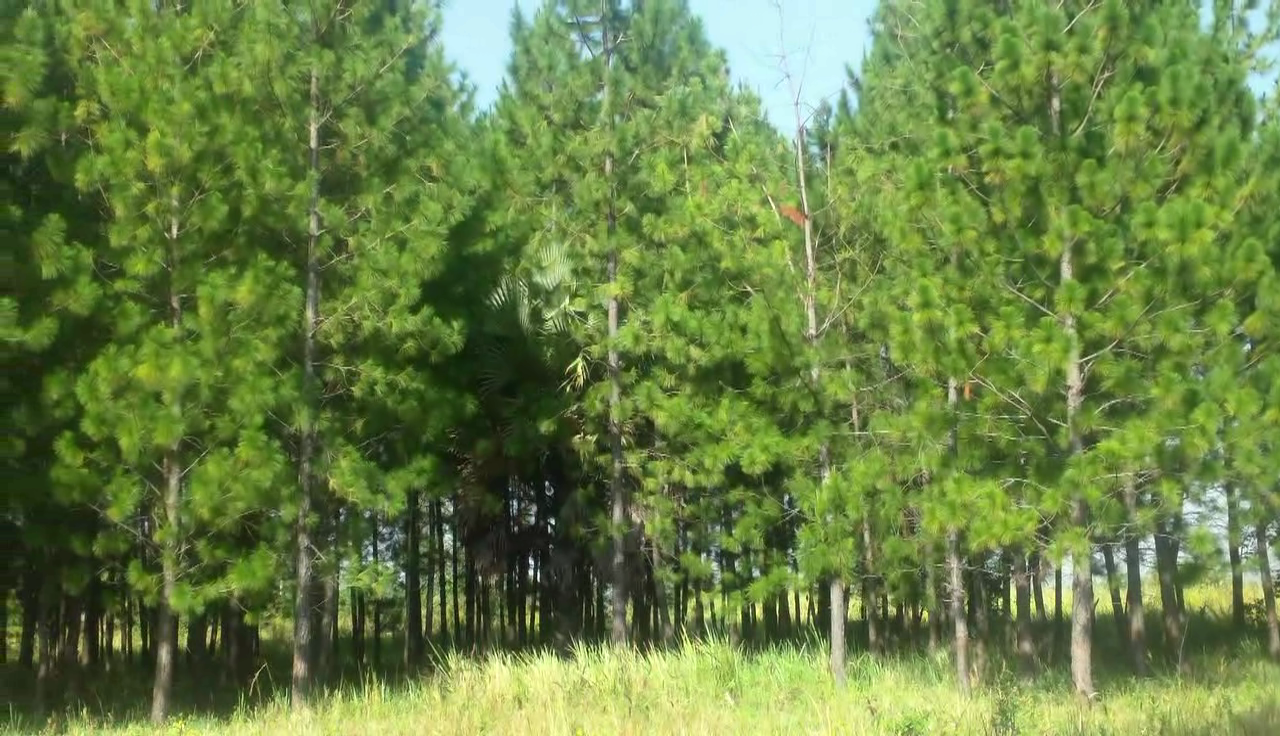
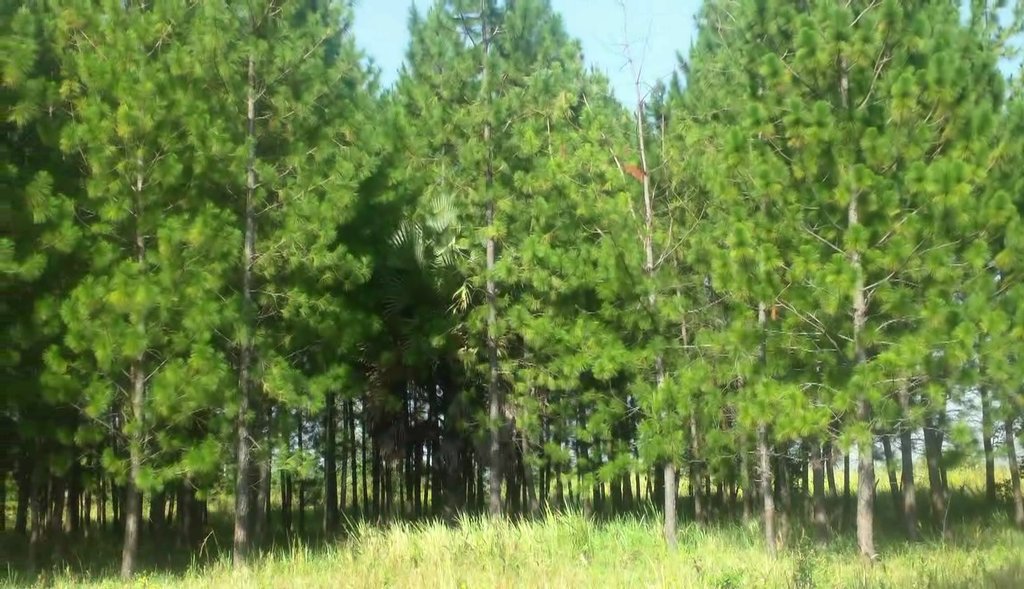
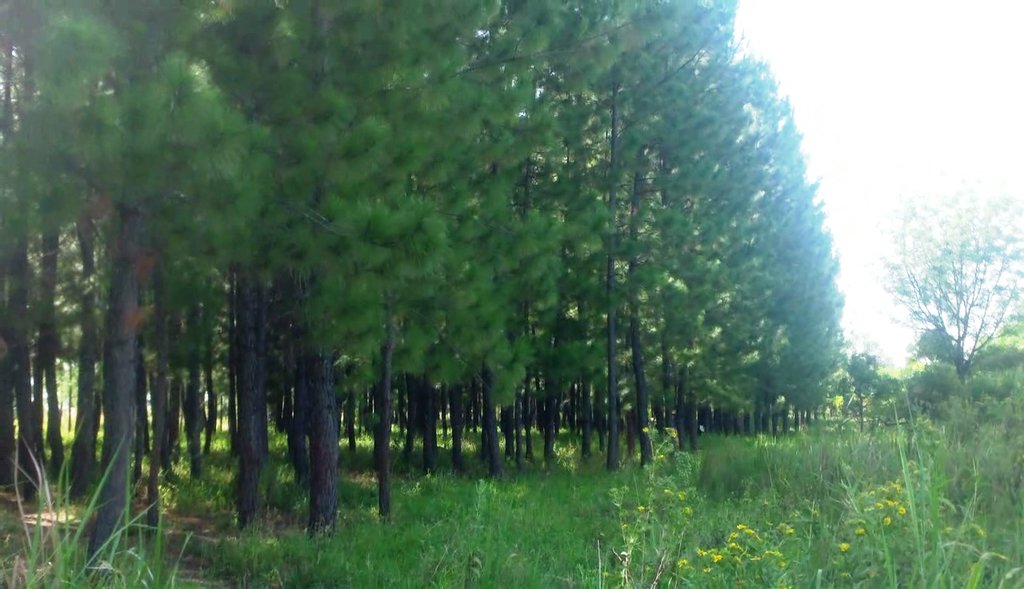
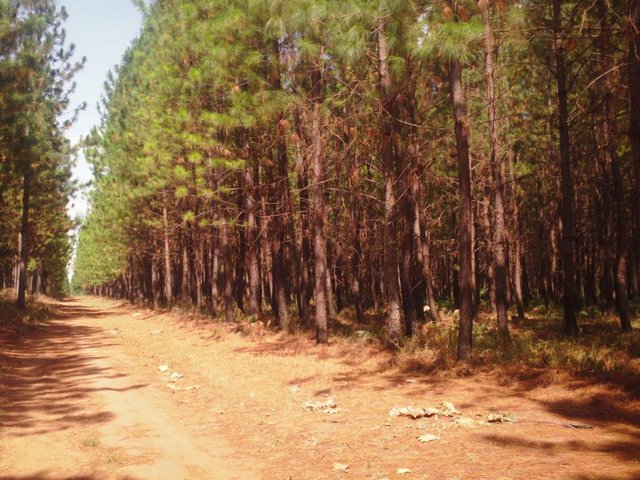
Pine Woodlot [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Bernard Fungo, Sunday Balla Amale
- 审查者: Donia Mühlematter, Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Renate Fleiner, Stephanie Jaquet
Pito Yen pine
technologies_2825 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Okecokon Alex
Farmer
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

WALA Women Group Community Tree planting Approach [乌干达]
A sustainable tree planting group approach involving thirty seven women to serve the most vulnerable community for sustainable development.
- 编制者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
A Woodlot of Pine (Pinus caribaea) is a fast growing, tolerant tree based plantation established to address land cover depletion, soil fertility loss and soil erosion control.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
To establish this technology, the farmer excavates a hole and wait for 4-6 days to allow air that can burn the seedlings first get out and then plant the seedlings. If the planting is done during the dry season, it is important that the farmer water the seedlings regularly to avoid drying.
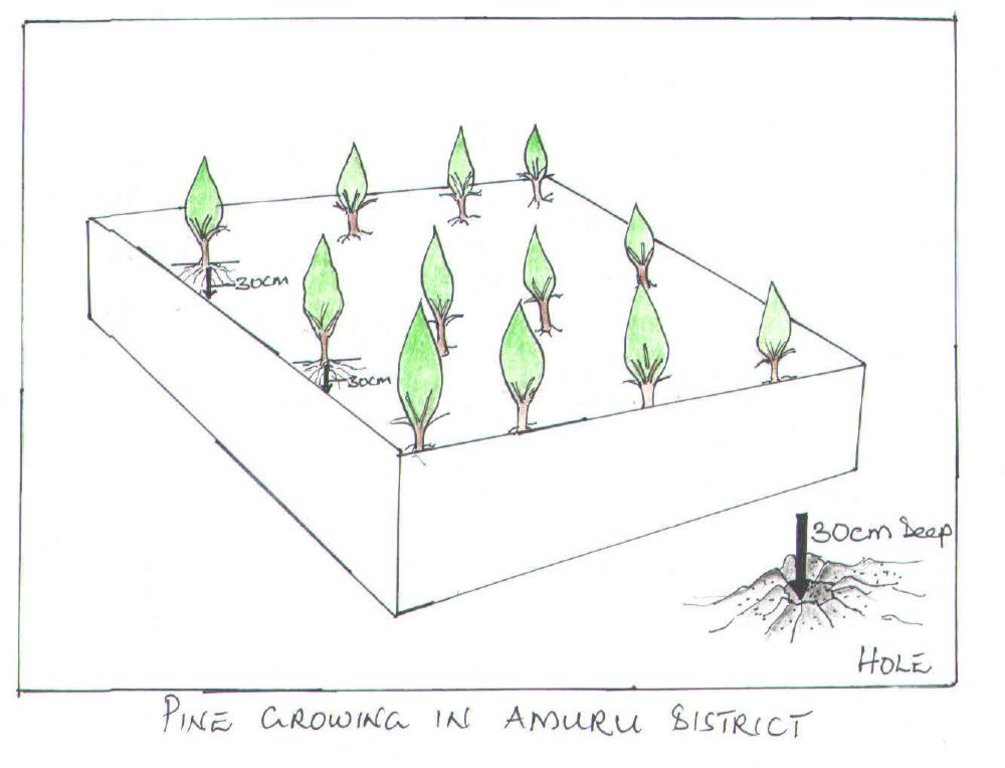
The activities involved in establishing this technology include: (1) Looking for suitable land to establish the technology (2) Looking for labor, and appropriate seedlings and tools to use, (3) Identifying the expert/ trainer to train on how to plant and the right spacing (4) Digging the holes (30cm deep) and waiting for 4-6 days before planting. It is important that the farmer weeds the plantation if weeds develop.
Pinus caribaea is an important forest plantation tree that is fast growing, tolerant to poor soils which don’t retain water and nutrients and often drains too well that may cause the roots to rot or fail to develop and its wood can be milled into timber, pulped or used as poles. The common inputs required for establishing such a technology include a hoe, a panga, a planting string, seedlings, and a trainer.
This technology is easy and cheap to maintain once established. It is good for timber, firewood and environmental conservation with the costs of buying seedlings and payment for labor being high at the time of establishment compared to the costs of recurrent maintenance activities.
What is not liked about this technology is that the benefits are realized after a long time. Secondly, pine is not a source of food until when it is sold and cash is used to buy food unlike fruit trees such as mangoes and oranges.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Video on woodlot plantation in Amuru District, Northern Uganda.
日期:
25/06/2017
位置:
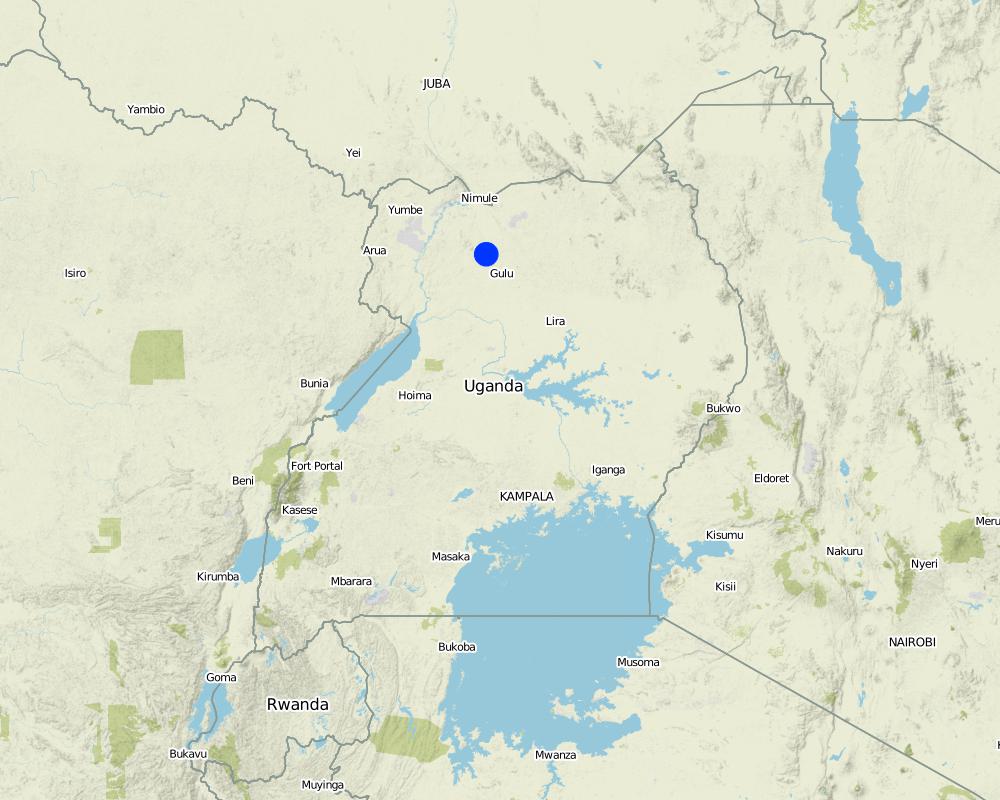
Amuru District, Northern Uganda
摄影师的名字:
Issa
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Region,Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Amuru District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Map showing technology site in Northern Uganda.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
When its dry.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 森林种植管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理
- A5:种子管理,改良品种

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
- Ed:风蚀风积

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 适应土地退化
注释:
Pine is more of timber and firewood.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
2.5 metres within raws
3 metres between raws
10 metres between blocks
5-6 metres wide.
作者:
Kaheru
日期:
25/05/2017
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
0.5 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
3400.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5000 per person per day
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | lookIing for suitable land | Before planting |
| 2. | Looking for tools, labour and seedlings | Before planting |
| 3. | Looking for expert/trainer | Before planting |
| 4. | Preparing land for planting | At the time of planting |
| 5. | Digging the holes (30-60cm) | During planting |
| 6. | Planting with spacing of 3m x3m | During planting |
| 7. | Watering: Dry season | After planting |
| 8. | Monitoring and security provision. | After planting |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | persons | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Panga | Pieces | 1.0 | 7000.0 | 7000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoe | Pieces | 10.0 | 10000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Panga | Pieces | 3.0 | 7000.0 | 21000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | Kgs | 4000.0 | 2500.0 | 10000000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Bamboo- bundles | Bundles | 1.0 | 15000.0 | 15000.0 | |
| 其它 | watering can | Pieces | 3.0 | 25000.0 | 75000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 10268000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 3020.0 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | weeding/slashing | Twice a year: when still young |
| 2. | Watering | During dry season: trees still young |
| 3. | Prunning | Twice a year |
| 4. | Security and moniroring | Daily |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour on monthly basis | Persons | 10.0 | 150000.0 | 1500000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1500000.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 441.18 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Seedlings and labour takes most of the costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1500.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
from the planted pine trees.
森林/林地质量
注释/具体说明:
Due to prunning.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Slashing and weeding.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
for labours.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
From the sale of timber and fuel wood.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Timber and fuel wood.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Planting, watering, thinning and pruning and harvesting.
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Where the pine trees are planted.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Due to planted trees.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Especially where the trees are planted and was originally degraded.
生物多样性:植被、动物
外来入侵物种
注释/具体说明:
Causing serious problems to natural habitat.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Due to Invasive species.
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
If not protected with fireline.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Benefits are low in the short run and high in the long run.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Good at providing fire wood in the short run after prunning. |
| The costs are low after establishment (prunning, monitoring). |
| Easy to establish once the seedlings are available and can easily be replicated by other farmers. |
| Suitable for both small scale and large farmers with similar or different land sizes. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The land user is managing the technology well and is likely to reap long term benefits (income and Timber). |
| The technology is easy to manage after establishment. Maintenance is not laborious. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology is not very much appropriate for soil fertility improvement as compared to other agroforestry trees (callindra, Grivellea and Alnus). | The land user need to integrate other agroforestry and fruit trees in the technology. |
| The technology is costly in terms of securing seedlings. The land user has to travel long distances 15km to buy the seedlings. | The land user can be trained on how to raise her own seedlings. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The benefits of the technology are long term and may not help the land user to meet urgent needs (school fees, medical care etc) | The land user need to look at other alternative sources of income which are short term and multi-purpose e.g integrate tree planting with livestock for milk, manure and other benefits. |
| The benefits of the technology are long term from 5 to 10 years. | Explore alternatives and integrate other sources of income which are short term and multi-purpose but also good at addressing land degradation problems e.g poultry keeping. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
25/05/2017
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

WALA Women Group Community Tree planting Approach [乌干达]
A sustainable tree planting group approach involving thirty seven women to serve the most vulnerable community for sustainable development.
- 编制者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
模块
无模块