Local Food Storage Facility (Granary) [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Bernard Fungo
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson, betty adoch, Sunday Balla Amale
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Dero
technologies_2877 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
12/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
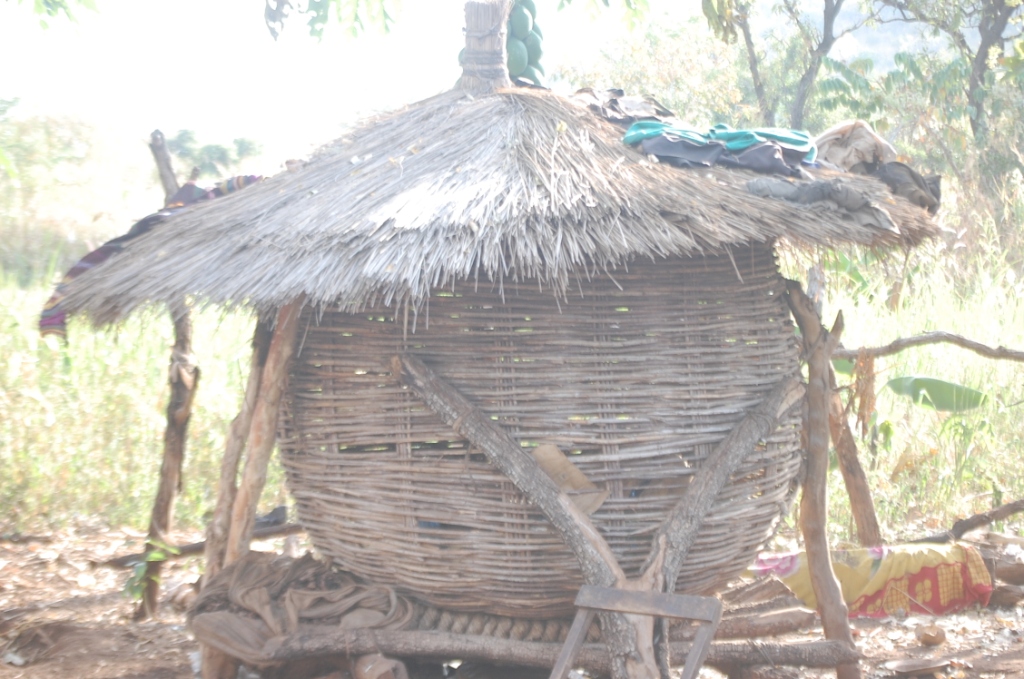
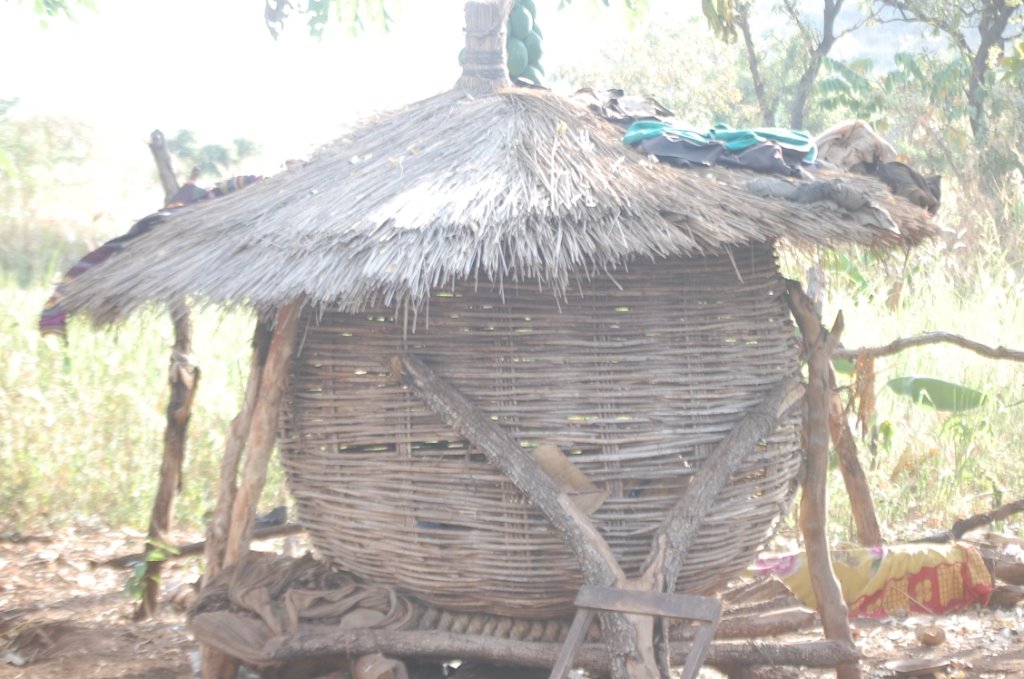
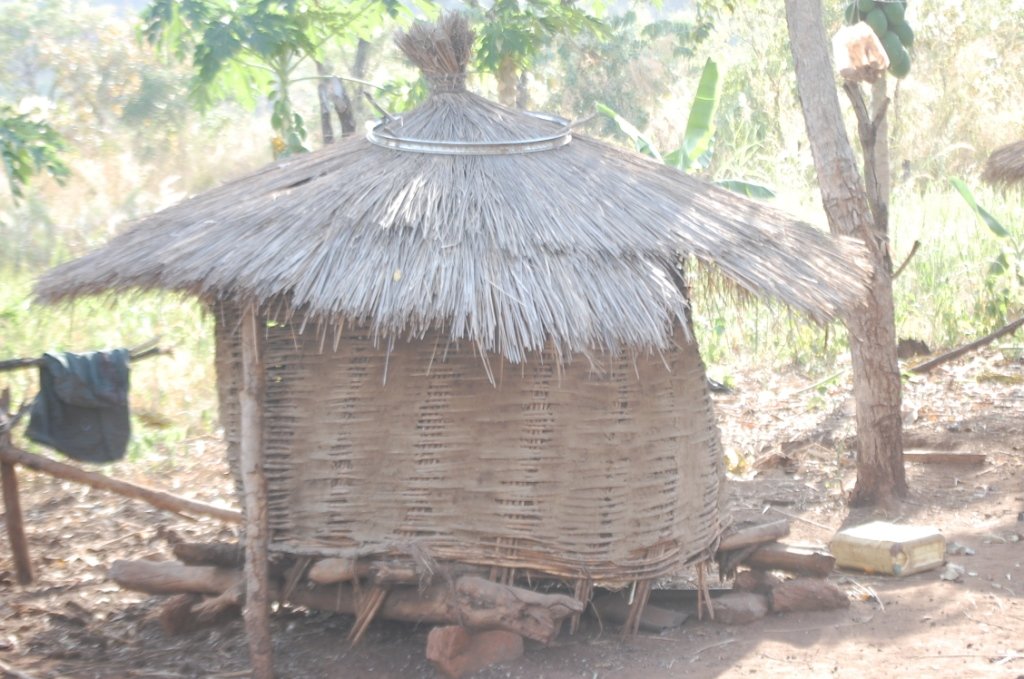
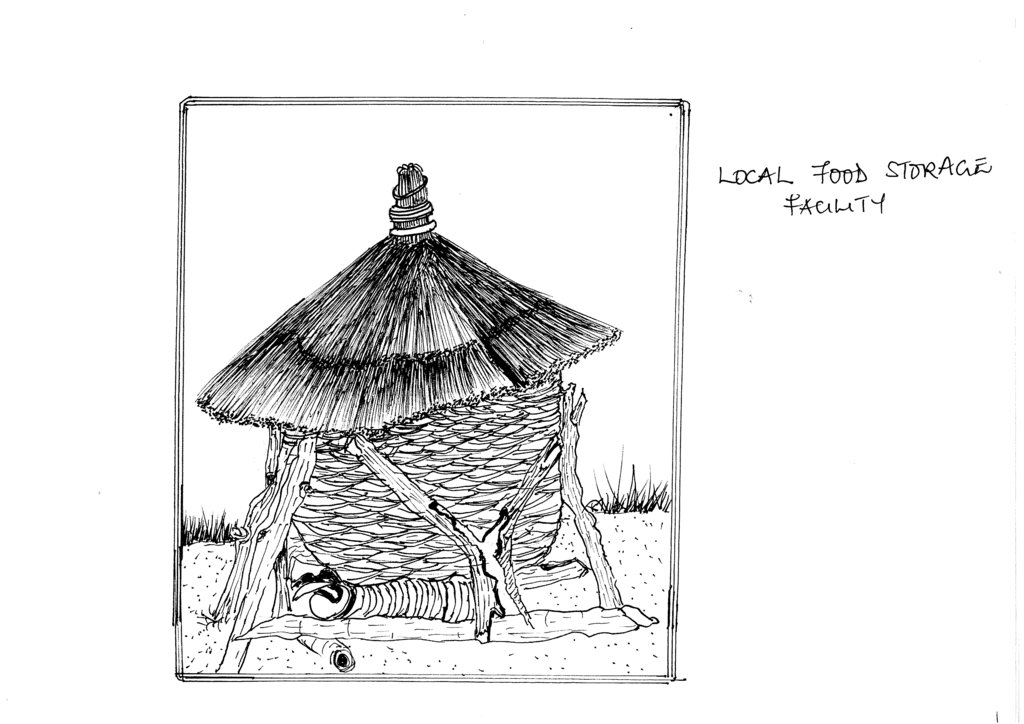
The granary is made of local material for food protection/preservation during bumper harvest
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Drought frequencies are increasing while yields are reducing. Efficient post-harvest handling optimizes the value of the produce in climate-affected contexts hence reducing the vulnerability of the farming sector to climate extremes. Granaries are useful structures for preserving grain crops. They help in food storage as a response to climate change impacts.
The main characteristic of the granary is that it is constructed either using a peeled bamboo, papyrus reeds or small sticks of approximately one cm in diameter. Such sticks are usually from Lantana Camara (Common Lantana or Tickberry) or branches of Eucalyptus spp. The material is woven into a round cylindrical shape of about 2 meters height and 1.5 meters in diameter. The structure is then mounted on wooden poles to keep it off the ground to avoid rodents and water from entering. A round roof made of grass is placed on top as a roof to protect the interior of the granary from rain. A space of about 5 cm is left between the roof and the upper end of the round wall in order to allow for aeration. The way of storage in the granary allows air to flow into and out of the granary and reduce / prevent rotting processes due to moisture accumulation in the granary.
The major activity is the construction of the flat granary base structure and later the construction of the superimposed structure using poles on which the granary stands. Periodically the grain is removed and dried in the sun to remove any moisture and pests that may have entered the granary. The granary is also periodically smeared with cow dung to close any holes that develop but also protect it from damage by insects.
What famers like about the technology is that the grain is kept for a long period at the cheapest cost. The materials used to make the granaries are locally available and the skill required in the construction is minimal. Storage space in the house is saved since the granary is established outside.
On the other hand farmers do not like granaries because the food inside them is often prone to theft especially during periods of famine.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
1960
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
牲畜密度(如相关):
N/A
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 收割后的措施
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
Placed within a farm compound
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S9:动植物庇护所
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The diameter of the granary is about 1.5 meters. The height is about 2 meters.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
1 Granary
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Uganda Shillings
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3500.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5000
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and drying sticks and poles | 结构性的 | During the dry season |
| 2. | Making the granary | 结构性的 | During the dry season |
| 3. | Cutting grass | 结构性的 | During the dry season |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cutting sticks and poles | Mandays | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Weaving the granary | Mandays | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cutting grass | Mandays | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Sticks | Sticks | 500.0 | 500.0 | 250000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Grass | Bundles | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Poles | Number | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 425000.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replacing the grass on top | 结构性的 | Once every three years |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cutting grass | Mandays | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Grass | Bundles | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Side poles | Number | 5.0 | 5000.0 | 25000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 75000.0 | |||||
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Weaving the granary
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Materials are getting more and more scarce due to population growth and land clearing, hence more expensive
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Land is less productive, resulting in poor yields and the need for this technology to reduce post harvest losses
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Approximately 300 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Good for storage |
| Cheap |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Fire risk | Keeping away all sources of fire risk, such as ground grass, or cooking near the facility |
| Theft | Make a lockable roof for the granary |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
3
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块