Farmyard manuring [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Toth
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Gudrun Schwilch, Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
Istállótrágyázás
technologies_3063 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Crop Production and Soil Science, University of Pannonia - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
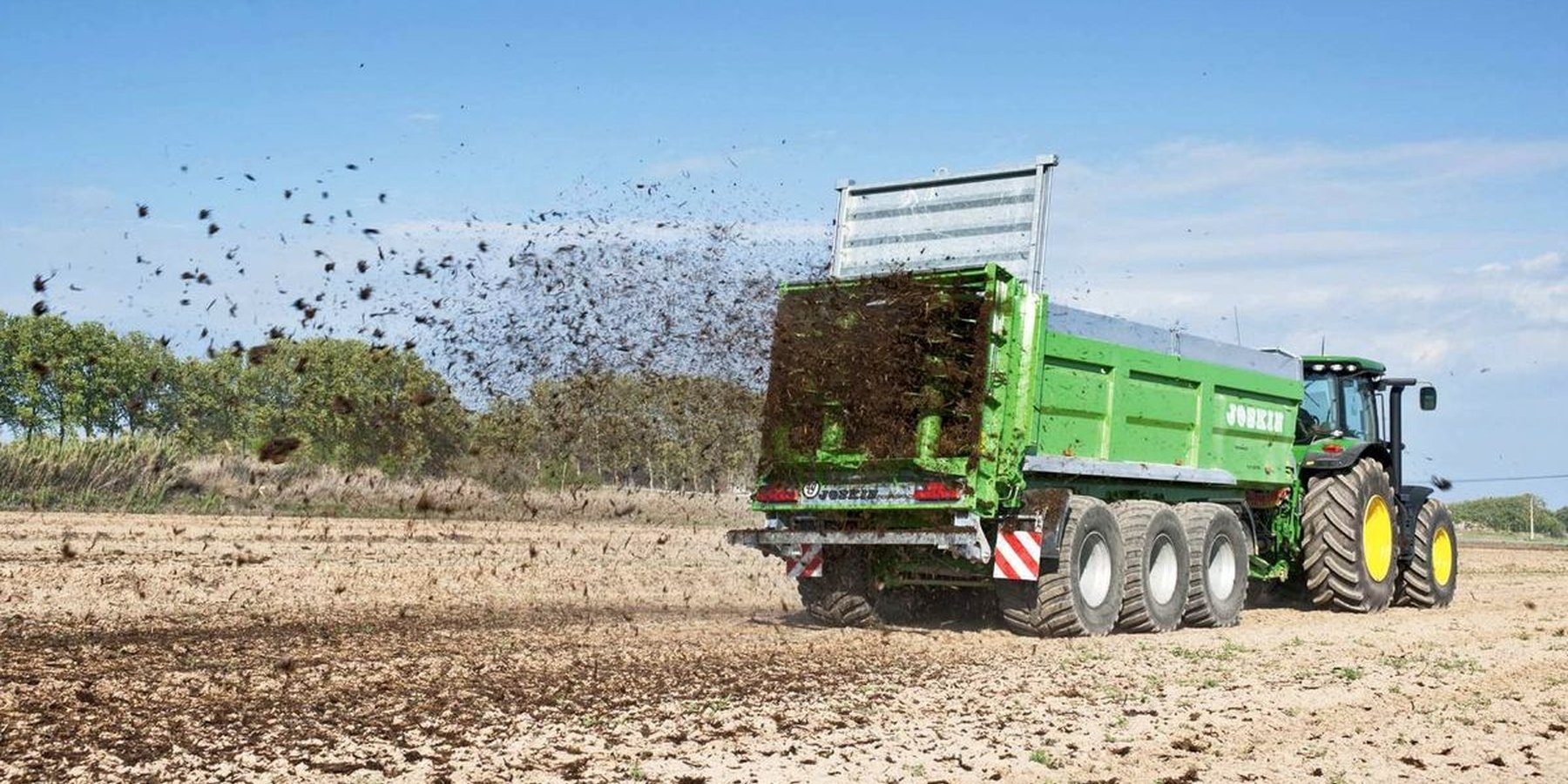
Farmyard manure is a decomposed mixture of cattle dung, urine with bedding material and fodder residues. After rotting the farmyard manure it is incorporated into the ground to increase soil fertility.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
1. The case study area is situated within the catchment of river Zala in western Hungary. 37% of the total catchment area is arable land which is much lower than the national average, 27% is forest, which exceeds the national average. 15% of the land is under grassland management, 5% is horticulture, 3% is pomiculture, 2% is viticulture, 1% is reed management and fish farming. In arable land non irrigated cereals, maize and oil crops are the main farming system classes. Among permanent crops vineyard and fruit trees are the most significant.
2. Cattle dung, urine with bedding material and fodder residues are decomposed. 4 months are needed for decomposition of the manure. After rotting the manure it is spread to the soil and incorporated. Generally winter rape, corn and sugar beet are the main crops before which manure is applied. Nitrate regulation has to be considered on fields which are defined as sensitive areas, both date and rate of fertilization are limited. Crop rotation is part of the technology, since dairy production is an important activity of the production, so fodder crops have to be produced on a territory determined by the demand of the livestock. Catch crops are rotated on the rest of the field.
3. The purpose of the technology is to increase soil fertility. The following general nutrients are included in the farmyard manure: N%=0.3-0.5, P2O5%=0.20-0.25, K2O%=0.5-0.5 .
4. It is important to have boving holding in a short distance to the plots of the farm where it has to be applied. The manure is spread in each third or fourth year.
5. Impacts of the technology are increased organic matter content, improved biological activity and structure of the soil.
6. Land users like its positive effect on soil health, only one disadvantage can be that it can increase weed infestation.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Zala
有关地点的进一步说明:
Keszthely
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2006
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 黑麦
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
From 10-15 April till 25-30 October
注释:
-
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
It was arable land also before introducing the technology.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 轮作制度(轮作、休耕、轮垦)
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
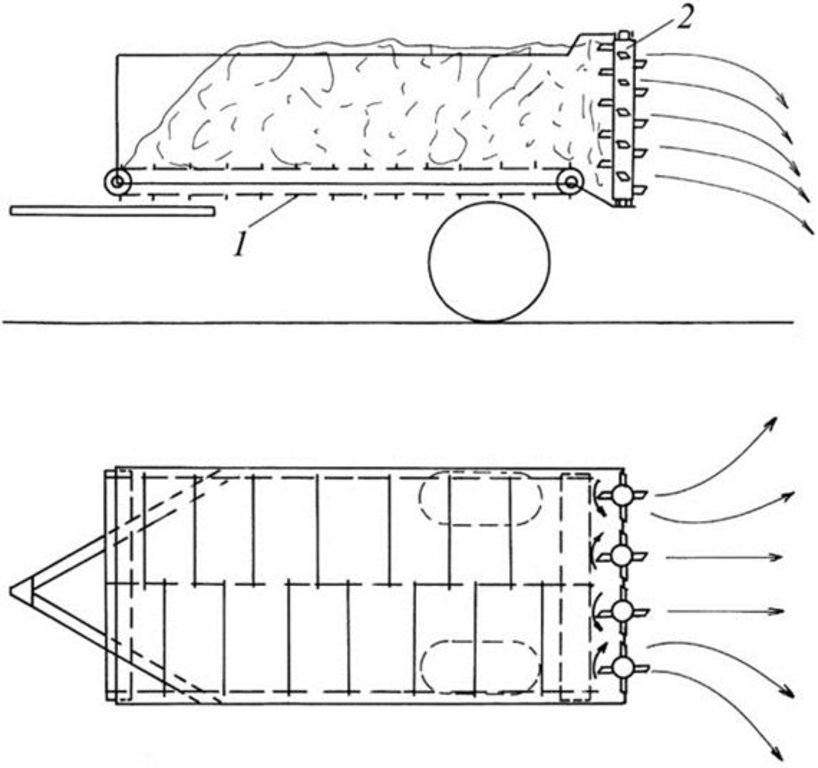
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Figure 1. Equipment to spread farmyard manure.
1. scraper chain
2. broadcaster
作者:
http://www.tankonyvtar.hu/hu/tartalom/tkt/zoldseg-disznoveny/ch02s05.html
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
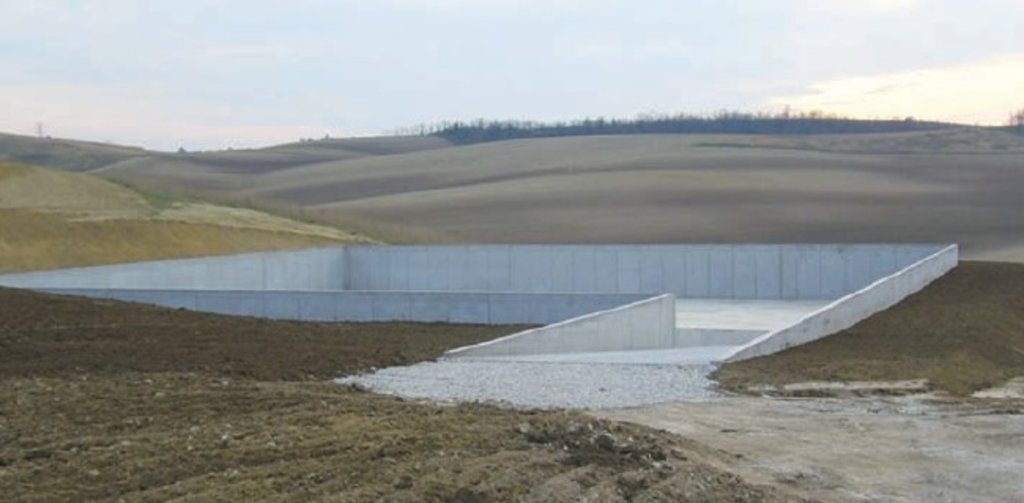
Figure 2. Construction of manure storage facility.
The stack of manure is built gradually in order to control the aerobic and anaerobic processes inside. Between the placement of two layers some days is left for the oxidative degradation processes.
作者:
https://agrarium7.hu/
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Forint
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
260.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10000
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | construction of manure storage facility |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | construction of manure storage | 1000 t | 1.0 | 4600000.0 | 4600000.0 | 50.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4600000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 17692.31 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The farmer could apply for financial support (tender).
注释:
Construction costs include labour and material. The facility can store 1000 t of manure.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | farmyard manure application | autumn before primary tillage |
注释:
Incorporation of manure is done with the normal ploughing and therefore does not cause extra costs.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | sum of labour cost for spreading the manure | day/ha | 0.02 | 15000.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | farmyard manure application (1 ha 0.16 hour) | machine hours | 0.16 | 80000.0 | 12800.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 13100.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 50.38 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of constructing the manure storage facility.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
680.00
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Keszthely
农业气候带
- 半湿润
moderately warm, moderately wet
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
-
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Cambisol, pH is 7.3; OM is 1.5
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
-
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
-
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
-
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 租赁
注释:
-
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
+30 % increase in yield
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
+30 % increase in yield, positive for nutrient recycling within the farm, better soil conservation due to perennial crops e.g. alfalfa
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
it results in more stable market position
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
transporting manure for long distances is not economical
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
stabilization of the whole system of farming
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
better soil condition is a feedback for the farmer
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
due to better soil structure
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
due to better soil structure
土壤
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
positive for nutrient recycling within the farm
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
OM increases with 30 % in temperate climate on Luvisol
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
yield is increased
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
more earthworms
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
increase cation exchange capacity
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
higher SOC results in better C sequestration
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
注释:
-
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Manure is used only if it is available within a few km around the farm.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increases the soil organic content and improves the soil structure. |
| Increase of soil fertility. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improved microbiological activity resulting in improved nutrient utilization. |
| Improved soil health, due to better microbial activity. Soil structure improves. |
| In this way it improves soil fertility. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Risk of weed infestation. Labour and cost intensive. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Risk of weed infestation. Labour and cost intensive, heavy field work causing compaction. | Precise pest management. Timing of field applications should be better adapted to soil moisture conditions. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/10/2016
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
-
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
-
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
-
URL:
-
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块