Conservation tillage [匈牙利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Brigitta Toth
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch, Alexandra Gavilano
Csökkentett és talajkímélő művelés
technologies_3065 - 匈牙利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Crop Production and Soil Science, University of Pannonia - 匈牙利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
-
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Conservation tillage [匈牙利]
Non inversion, conservation (soil and water protective) tillage.
- 编制者: Adam Kertesz
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The aim of conservation tillage is to reduce the soil disturbance. It decreases decomposition of organic matter, enhances cycling of nutrients, soil structure and increases water infiltration.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
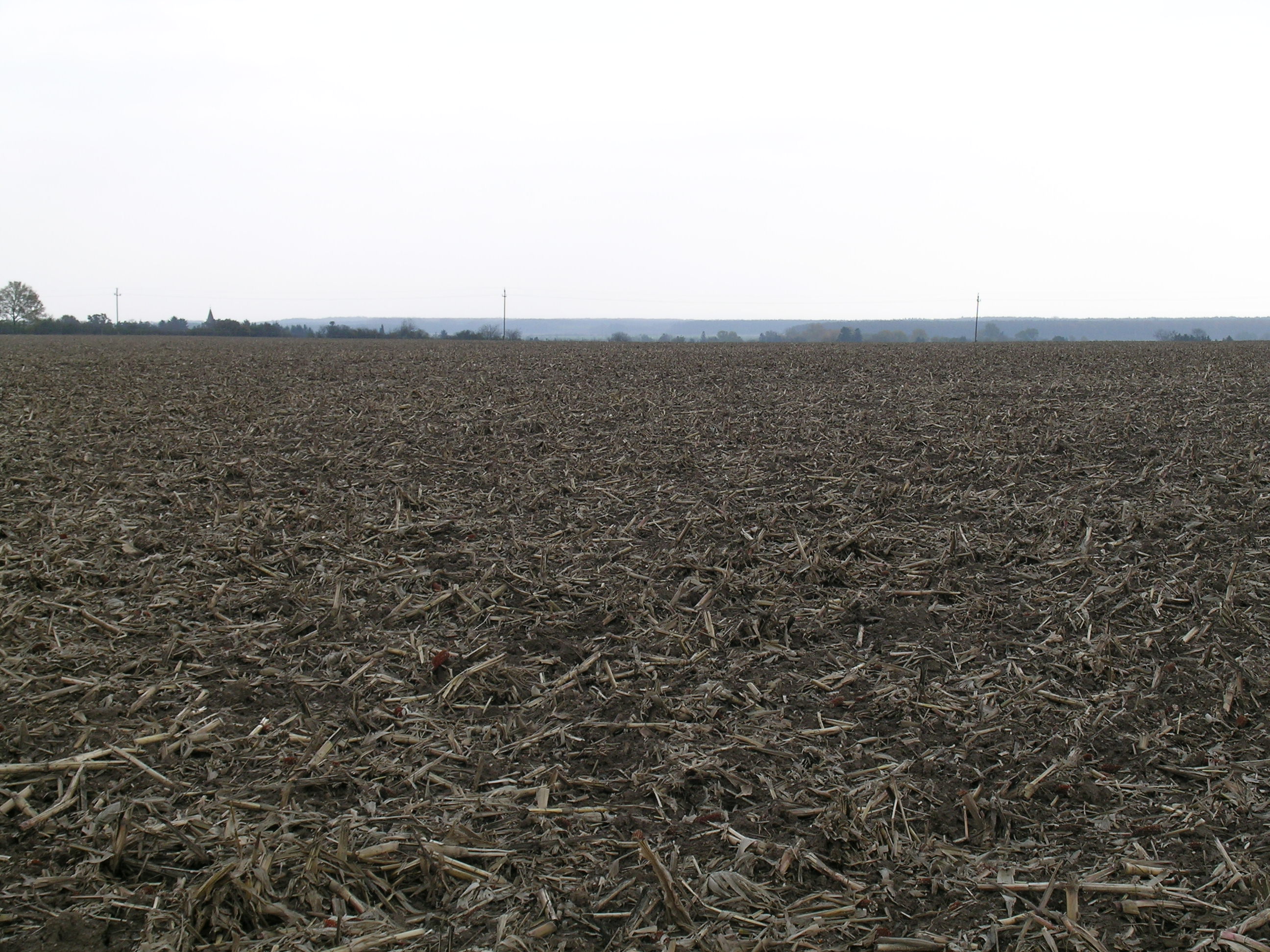
1. The case study area is situated within the catchment of river Zala in western Hungary. The climate is moderately warm, moderately humid, the number of sunshine hours per year are high. Mean annual temperature of the region is about 10 ˚C. The average amount of rainfall is between 600 and 700 mm / year. 37% of the total catchment area is arable land which is much lower than the national average, 27% is forest, which exceeds the national average. 15% of the land is under grassland management, 5% is horticulture, 3% is pomiculture, 2% is viticulture, 1% is reed management and fish farming. In arable land non irrigated cereals, maize and oil crops are the main farming system classes. Among permanent crops vineyard and fruit trees are the most significant.
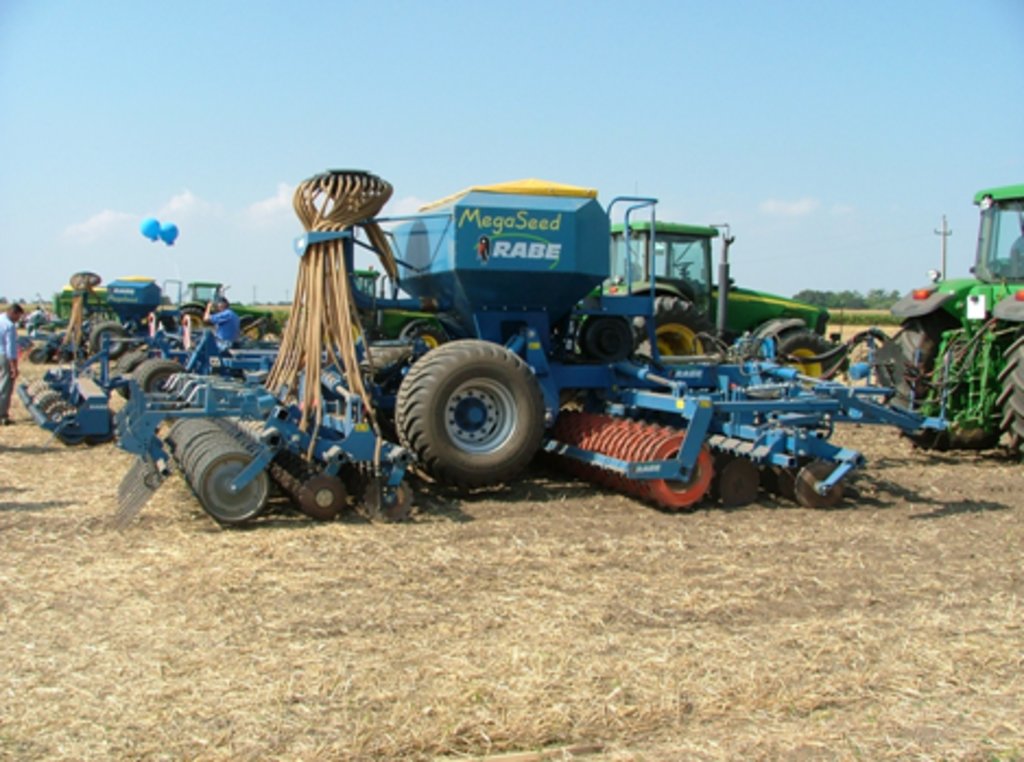
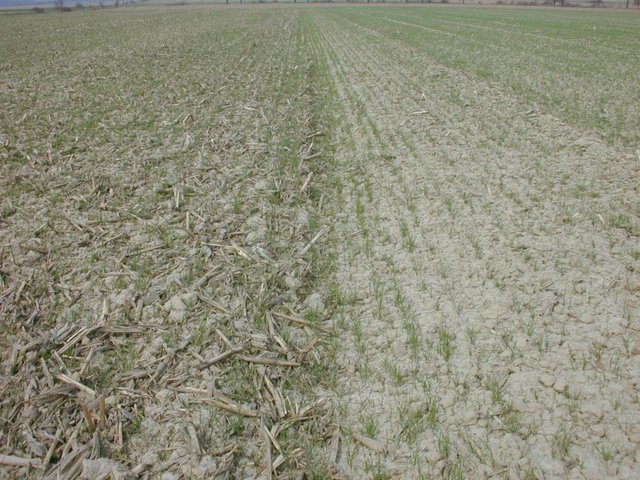
2. In this technology reduced disturbance of the soil is used, non-inversion of soil is applied. At least 30 percent of crop residues are left on the field. Primary tillage is usually carried out by rippers or combinated disk rippers. Machinery is usually supplied by agricultural contractors in case of farms smaller than 100 ha.
3. The purpose of the technology is to improve soil structure, reduce decomposition of organic matter, increase water infiltration, reduce soil erosion and soil compaction.
4. Special equipment is needed for soil management: soil loosener and minimum-tillage equipment to perform tillage and seeding in one pass. Primary tillage is due in autumn, secondary tillage (surface preparation) is performed in early spring.
5. It improves soil microbial activity, biodiversity, deeper rooting. Further to it fuel efficiency is better compared to conventional tillage.
6. Its disadvantage is the higher risk of weed infestation.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
匈牙利
区域/州/省:
Zala
有关地点的进一步说明:
Rádóckölked
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
-
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2002
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
-
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
- wheat
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
From 18-23 April till 14-16 October
注释:
Main crops (cash and food crops): wheat, maize, oilseed rape
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Remained the same.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
-
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 最小的土壤扰动
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理
注释:
-
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pw:水浸

生物性退化
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
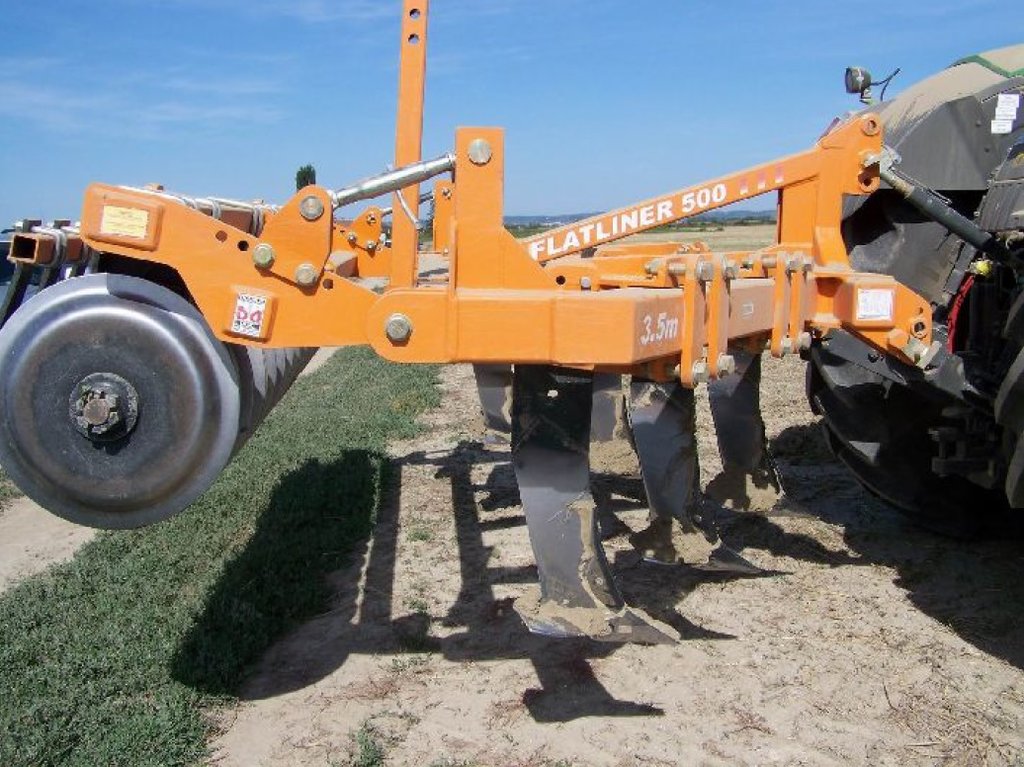
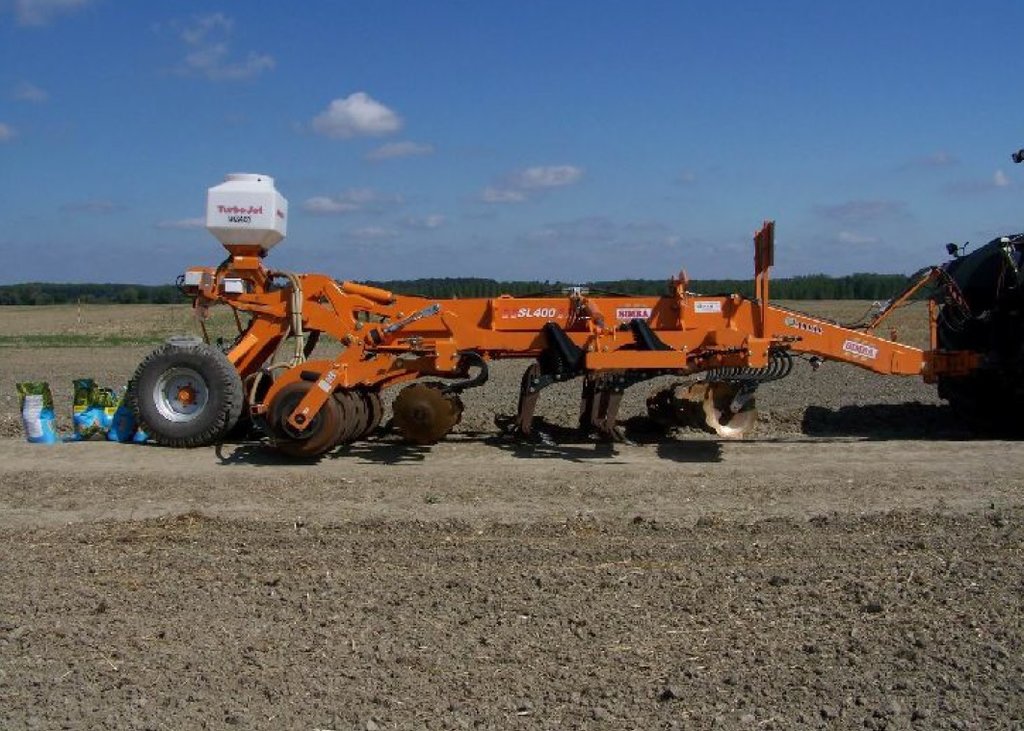
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
This turbo drill machine used in this conservation tillage technology perform seedbed preparation and sowing in one operation.
作者:
Zoltán Tóth
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Forint
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
257.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
10000
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Primary tillage (Seedbed preparation and sowing) | autumn |
注释:
Compared to conventional tillage no further activities are required in conventional tillage. Primary tillage is indicated because it needs different equipment, such as ripper or disk ripper.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | primary tillage | day/ha | 0.1 | 15000.0 | 1500.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | primary tillage machine (0.67 hour 1 ha) | machine hours | 0.67 | 14570.0 | 9761.9 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 11261.9 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 43.82 | |||||
注释:
Cost of primary tillage in conventional tillage would cost 38200 Ft (equipment: 35200 Ft + labour: 3000 Ft). Therefore primary tillage costs 27000 Ft/ha less in conservation tillage than in conventional tillage.
It might be needed to use wider range herbicides for killing higher number of weed species, which can cost extra 10000 Ft/ha.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of pesticides can be higher than in conventional tillage, but cost of fuel is significantly less.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
-
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Rádóckölked
农业气候带
- 半湿润
moderately cool, moderately wet
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
-
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Luvisol; pH is 6.5.; CEC = 20 cmol(+)/kg
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
-
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
-
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
-
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
-
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Productivity is increased through improved soil health, decreased surface runoff, better nutrient and water holding capacity, which can be seen in medium to longer term.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Productivity is increased through improved soil health, decreased surface runoff, better nutrient and water holding capacity, which can be seen in medium to longer term.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Production failure is decreased through improved soil health, decreased surface runoff, better nutrient and water holding capacity.
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Less labour time and cost are required due to fewer tillage trips and cultivation operations for seedbed preparation, and soil management needs significantly less fuel as well.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Less labour time is required due to fewer tillage trips and cultivation operations for seedbed preparation.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Through improved productivity and decreased production failure risk food security is improved.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Farmers applying conservation tillage practices will get a wider knowledge about factors causing land degradation and management practices which can decrease or prevent it.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
注释/具体说明:
Nutrient and pesticide losses are decreased through decreased runoff which increases water quality.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Surface runoff is reduced due to increased soil cover by leaving at least 30% of crop residue on field before and after planting the next crop.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Soil moisture content is increased due to the mulch on the soil surface which reduces evapotranspiration and also due to improved soil pore system in which storage pores are increased, so available water for plants is increased as well.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Soil cover is increased due to leaving at least 30% of crop residue on field before and after planting the next crop.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Soil loss is decreased due to decreased runoff.
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
Crop residues left on the filed help to protect the soil aggregates from splash erosion and crusting through raindrops. Aggregates are more stable in the topsoil also due to reduced soil disturbance resulting in higher total porosity which enhances downward water movement.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Crop residues left in the field return the carbon fixed in the crops to the soil. The carbon sequestration potential of the soil depends on the crop type, soil moisture content, soil mineralogy, soil texture, porosity and temperature. Different carbon categories have different turnover rates. Reduced runoff reduces the organic matter loss.
生物多样性:植被、动物
动物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Accumulation of crop residues and organic matter in the surface layer creates favourable feeding conditions, therefore microbial biomass increases.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Due to improved soil structure and porosity soil moisture storage is increased which can buffer the impact of drought.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emission is reduced by less tillage operations emitting less CO2 by tractor engine and decreased oxidative breakdown of soil organic matter through minimized mechanical tillage.
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
-
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 未知 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 未知 |
注释:
-
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
If equipment (ripper or disk ripper) is landed for the primary tillage there is no establishment cost for the farmer. If he has to buy the equipment it will benefit in long-term return. The maintenance/recurrent costs both short and long-term is positive, because cost of fuel is significantly less than in conventional tillage.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
-
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Non-inversion tillage results in better water infiltration, soil aeration and helps to avoid subsoil compaction. |
| Deeper rooting and all its benefits. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Non-inversion tillage results in better water infiltration, soil aeration and helps to avoid subsoil compaction. |
| Deeper rooting and all its benefits. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Higher risk of weed infestation. | Precise stable tillage and weed control technologies. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Higher risk of weed infestation. | Precise stable tillage and weed control technologies. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
27/10/2016
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Busari, M. A., Kukal, S. S., Kaur, A., Bhatt, R., & Dulazi, A. A. (2015). Conservation tillage impacts on soil, crop and the environment. International Soil and Water Conservation Research, 3(2), 119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iswcr.2015.05.002
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095633915300630
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Corsi, S., Friedrich, T., Pisante, M., & Sà, J. D. M. (2012). Soil Organic Carbon Accumulation and Greenhouse Gas Emission Reductions from Conservation Agriculture: a literature review (Vol. 16).
URL:
http://www.fao.org/fileadmin/user_upload/agp/icm16.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Conservation tillage [匈牙利]
Non inversion, conservation (soil and water protective) tillage.
- 编制者: Adam Kertesz
模块
无模块