Semi-Intensive Goat Farming Practice for Pasture Conservation [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: PRISCILLA VIVIAN KYOSABA
- 编辑者: Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Udo Höggel
Okulisa embuzi
technologies_3363 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Tusiime Edith
Kabarole District farmers association
Kabarole District Farmer Association
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Land Management Practices of South Africa (SLM South Africa)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
17/11/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Goats are stall fed during dry season and open-grazed during rain season. In a semi-intensive system, animals are kept under confinement in which they are stall–fed for some period of time (weeks to months, especially during the dry seasons) followed by another period of open grazing during the rainy seasons.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
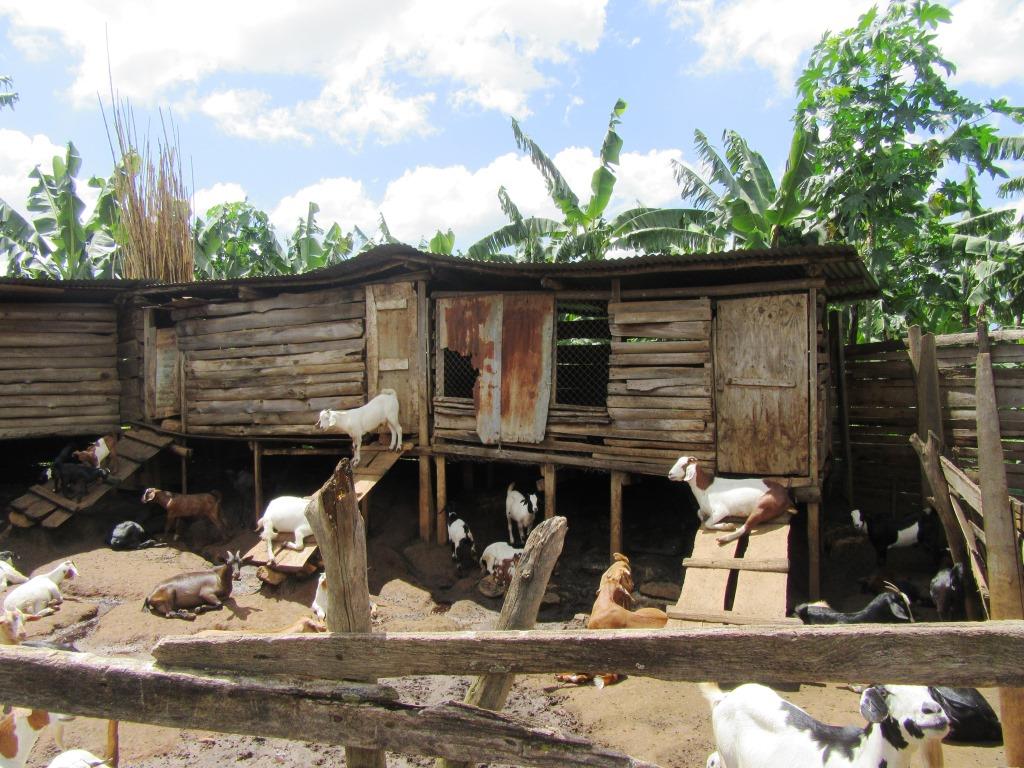
The semi-intensive goat rearing practice is a compromise between extensive and intensive grazing systems limited by shortage of pasture during dry seasons with high chances of spreading diseases requiring for stall feeding goats in an semi-intensive system. The goats are kept under confinement for some period of time (weeks to months, especially during the dry seasons). During dry season, the animals are fed on maize bran; iodized salt; peelings from banana, cassava, and sweet potatoes; and improved grasses (Napier) and forages planted at the boundaries of the banana plantation, which are harvested during the period of need.
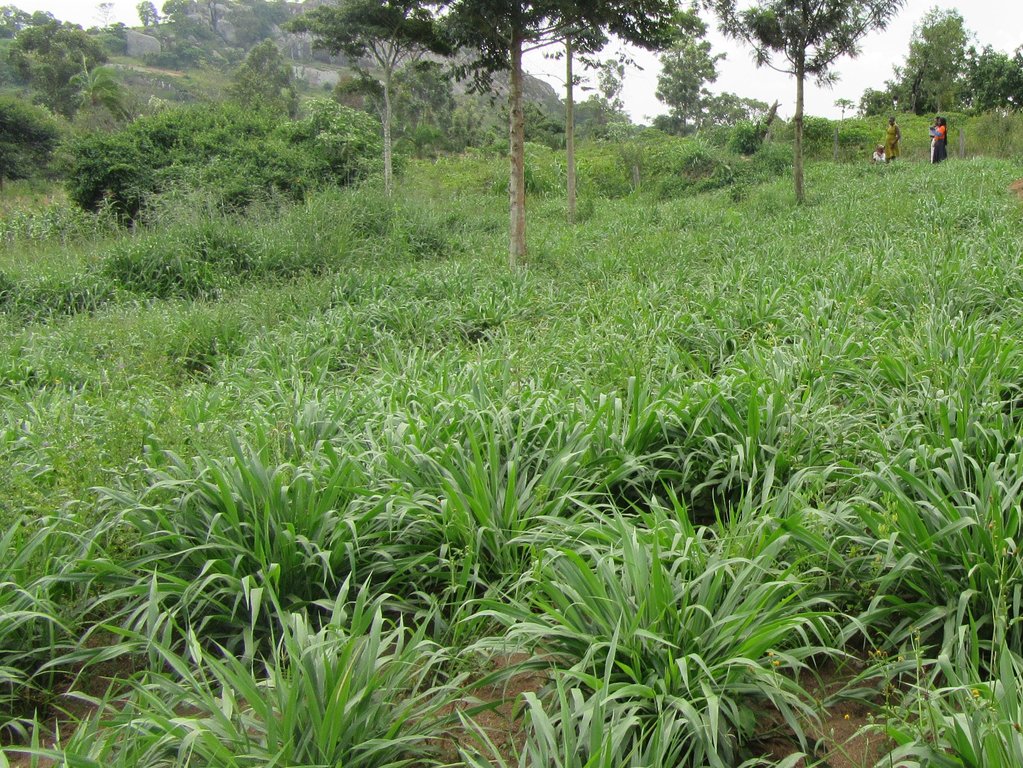
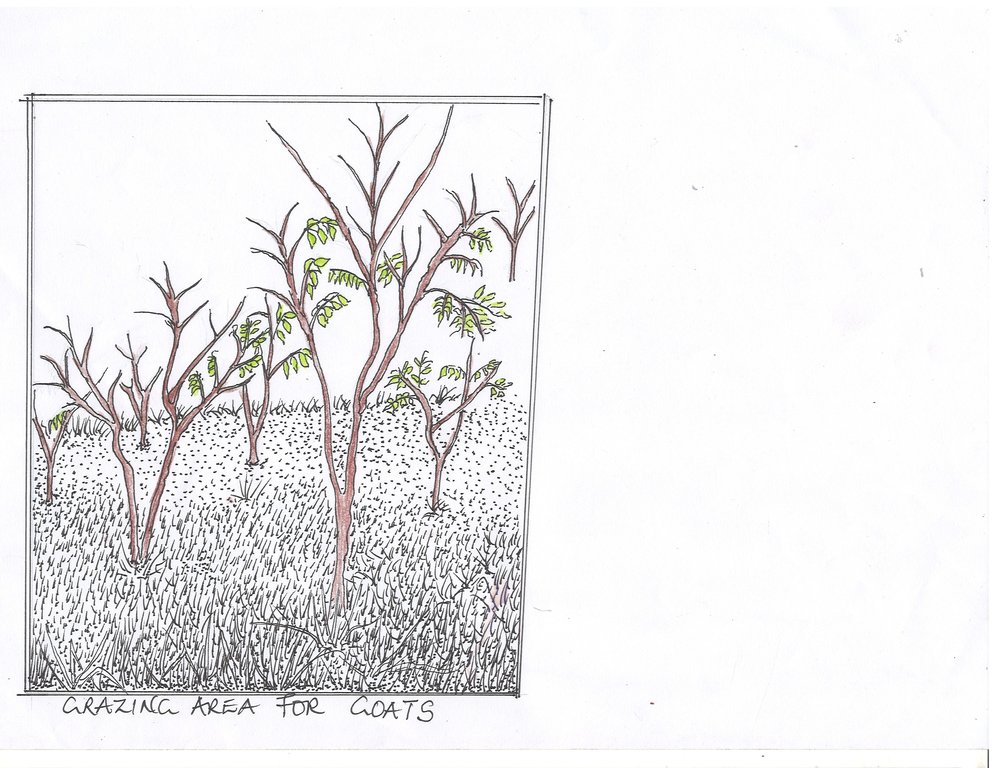
The farmer has got 2 ha of banana plantation. She grows a fodder hybrid called Napier (pennisetum perpureum) around the plantation to be used as fodder for the goats during dry season. Napier grass is a perennial grass fodder commonly called elephant Grass due to its tallness and vigorous vegetative growth. She got the Napier root cuttings from the neighbor practicing the same technology. This is grown around the banana plantation, at a spacing of 60×60cm. It produces more tillers with soft and juicy stem, free from pest and diseases and non-lodging. It can be cultivated throughout the year. Napier grasses contain 6-8% protein. Its optimum cutting interval is about 6 to 8 weeks at grass range of 60 to 90 cm, if sufficient only the tops can be cut and fed. The grass is cut into 5 to 10 cm to reduce loses.
The extensive system is practiced during rainy season where the farmer grows a mixture of fodder species including Sesbania and Napier grass grown on land size of 0.5 ha. Sesbania is a fast-growing tree with regular and rounded leaves. The flowers are white and red in color according to its species but the ones at the farm are yellow. The leaves of Sesbania trees are highly palatable and mostly liked by goats. The protein content in this is about 25%. 1kg of seed was planted at a spacing of 100 cm x 100 cm. In this field Napier grass is planted in rows at a spacing of 60×60cm. The seeds for Sesbania were supplied to the farmer by the Kabarole District Production Office.
Farmers in Kabarole District use the Semi-intensive system for rearing both local and improved breeds of goats. As dry spells are increasingly becoming common, this technology helps farmers to go through the dry season with enough feed for the goats. Farmers prefer rearing goats because they don’t have complicated feeding and medical requirements. As the human population grows and land fragmentation increases, farmers in this area are now moving towards intensive feedings systems.
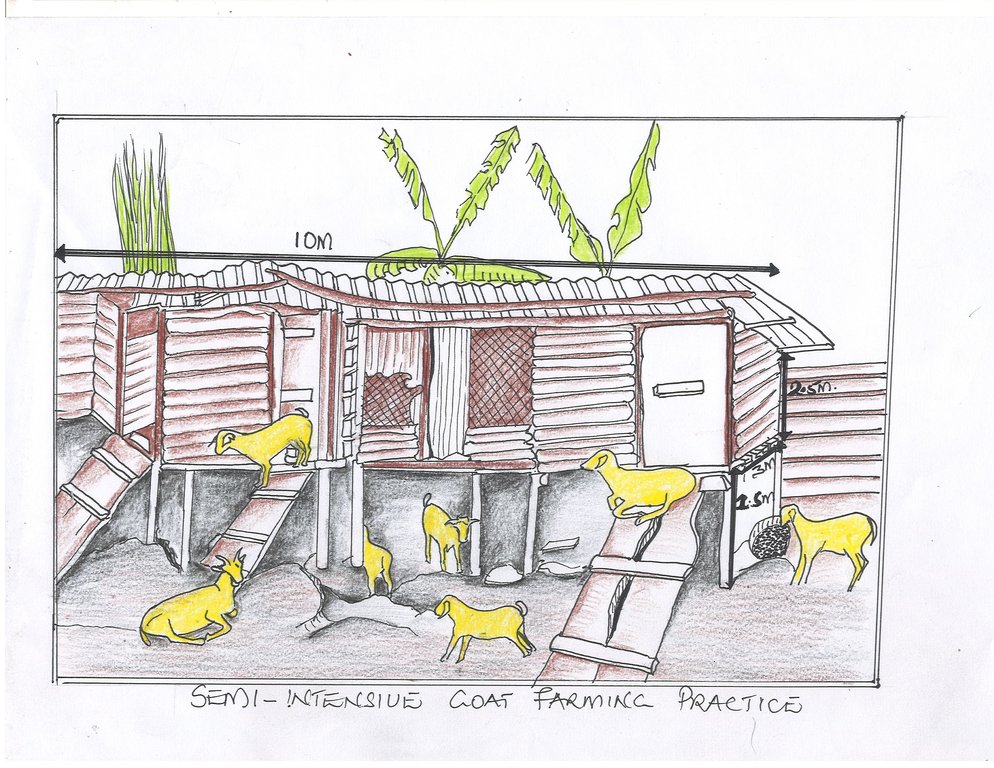
Throughout seasons of abundant forage, farmers harvest the forage together with grasses and make hay to feed the goats during the dry season when pastures are scarce. The cost of harvesting the hay is comparable to the cost of paying a herdsman in open grazing systems. Besides, the establishment of the shelter for goats is not cumbersome compared to those of other animals. The constructed structure occupies an area of about 12 ×12 meters squared with length of 10 meters and width is 3 meters. It is lifted ground to floor 1.5 meters and floor to roof by 2.5 meters. Further partitioned in 4 units and each unit measurement is 3 meters with a slope angle of 20 degrees. The Capacity of each unit is 18,17,17 and 18 goats respectively.
The shelter for the goats is made from relatively cheap materials that are readily available to the farmers. The farmer rears 70 goats on 1-acre piece of land using this technology. By planting improved forages in the grazing areas, the farmer receives increased amount of forage harvested as well as the quality of grass available to the goats during the open grazing periods and income after sale.One challenge of this technology is the dependence on family labor that is not always sufficient for all the tasks involved in the technology both at establishment and maintenance in addition to complications with of rural-urban migration of youth, thereby leaving the workload to the elderly.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
A video Showing Semi intensive goat farming practice in Kabarole District, Western Uganda
日期:
15/11/2017
位置:
Kabarole District,
摄影师的名字:
Aine Amon
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Western Region
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
1960
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
- Prevention of diseases
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
主要动物种类及产品:
It is a mixture of cross and local breed and the main product aimed for is meat
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
牲畜密度(如相关):
The farmer has got 70 goats, the number of animals per each constructed unit is variable. She constructed 1 unit, partitioned into 4 sections measuring to 3×3 meters each accommodating 15 goats.
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S9:动植物庇护所
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
It is an elevated floor housing unit with 10 X 3 meters squared with a height of 2.5m.
From ground it is elevated 1.5 m. The structure is partitioned into 4 units
The Capacity of each unit is 18,17,17 and 18 goats respectively.
Construction materials are timber peelings, iron sheets, nails.
Animal species are both crosses and local breeds.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Per shelter as described
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
shillings
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3650.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
25,000
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Constructing animal shelter | 结构性的 | Once |
| 2. | Buying kids | 管理 | Once |
注释:
These were the activities mentioned by farmer required to establish the technology
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Animal housing Structure construction labor | Man days | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Buying kids | Kids | 20.0 | 20000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Poles | 35.0 | 7000.0 | 245000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | Iron sheets | 50.0 | 21000.0 | 1050000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | Nails | Kilograms | 30.0 | 3000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Ropes | 20.0 | 1000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Unit doors | 5.0 | 25000.0 | 125000.0 | 100.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1980000.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Acquiring animal feeds | 管理 | Everyday |
| 2. | Animal water | 管理 | Everyday |
| 3. | De_worming the animals | 管理 | After 2 months |
| 4. | Buying iodine salt to mix in animal feed | 管理 | When needed |
| 5. | Repairing damaged patches of the animal shelter | 结构性的 | When needed |
| 6. | Cleaning the animal housing | 管理 | Daily |
| 7. | Giving feeds to the goats | 管理 | Daily |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Animal Vaccine | Bottles | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Iodine salt | Kilograms | 360.0 | 800.0 | 288000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Labor | 100.0 | ||||
| 其它 | Stocking animal feeds | Bundles | 1300.0 | 500.0 | 650000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 988000.0 | |||||
注释:
Maintenance cost as reported by farmer are on yearly basis. As for labor, cost is at zero because its family labor used all through.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The organisaton and purchase of feedstuff
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
2000.00
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 儿童
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
An elderly widow who carries out this goat farming project to raise income to pay her children and grand children's school fees plus also taking care of her personal need.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Reason given is that a farmer can now comfortably pay children school fees plus take-care of the family necessities
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Cut and carry method requires much labor
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Manure collected from the goats shelter is piled and later applied in the garden hence increasing crop yields
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Goats confined.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 减少 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 适度 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 适度 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improved standards of living because of the incomes generated. |
| Animal manure acquired and then applied in the farmers banana plantation |
| Serves as employment opportunity for the youths in the home. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Easy access for feeding and watering |
| Nutrient requirement are met both from grazing and stall feeding. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Relatively expensive to maintain | |
| Vaccinating every after two months a bit tiresome | |
| In dry season they usually face a problem of water scarcity |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Stall feeding relatively increases the feeding cost | Supplementing stall feeding with grazing and pasture growing |
| Management and knowledge of forage storage is needed | Through training on forage management |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2 people the elderly lady owning the farm plus her son helping in the smooth running of the farm activities
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Commercial Goat Farming in India: An Emerging Agri-Business Opportunity
URL:
http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/47443/2/7-Shelanderkumar.pdf
标题/说明:
Expert System for sheep and goat
URL:
http://agritech.tnau.ac.in/expert_system/sheepgoat/Housing%20of%20sheep%20and%20goats.html
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块