Lab lab inter-crop for improvement of soil fertility for banana production [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aine Amon
- 编辑者: Drake Mubiru
- 审查者: Nicole Harari, Donia Mühlematter, Udo Höggel
Lablab Omurutokye
technologies_3376 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Kabasi Janet
+256784959305
Farmer
Fort portal Municipality, Kabarole District
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Agricultural Research Organisation (NARO) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
13/11/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology is a cover crop that adapts the ground to water scarcity and helps in nutrient replenishing
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
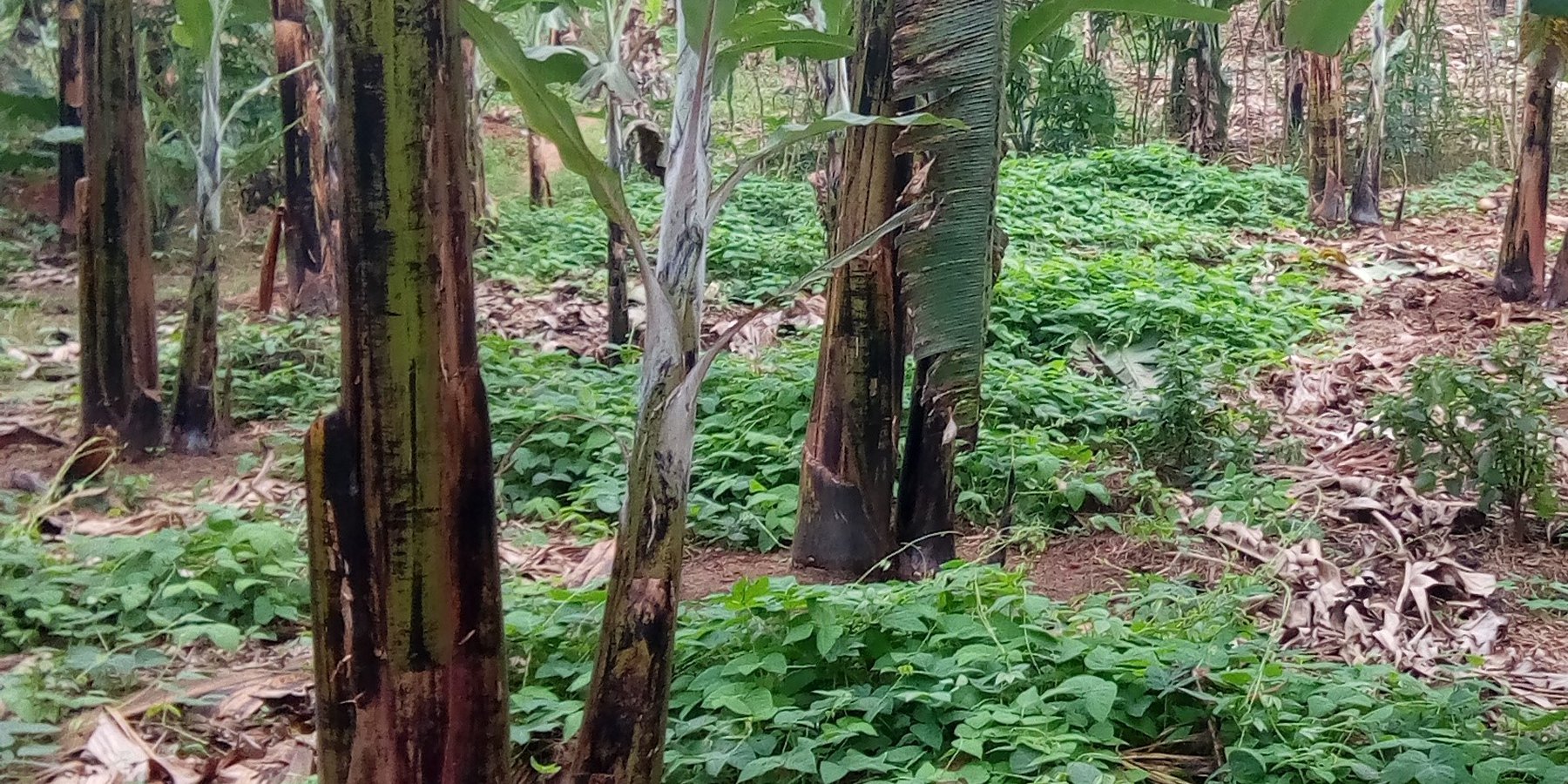
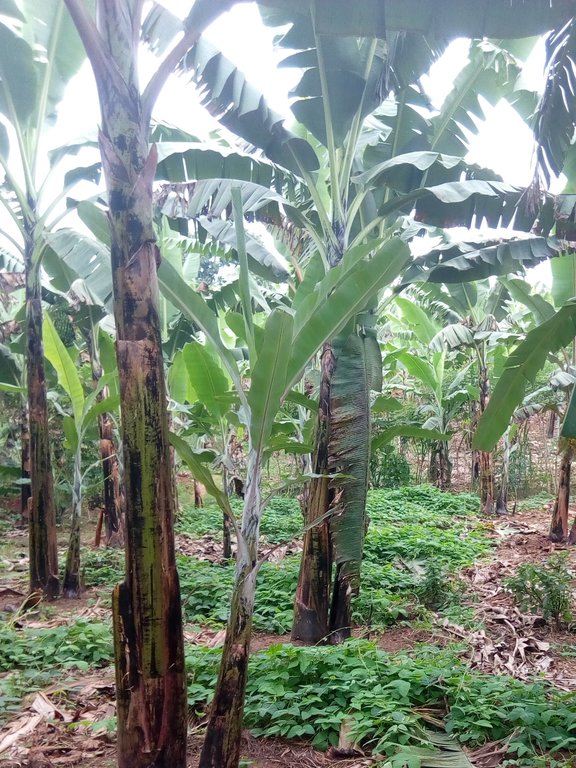
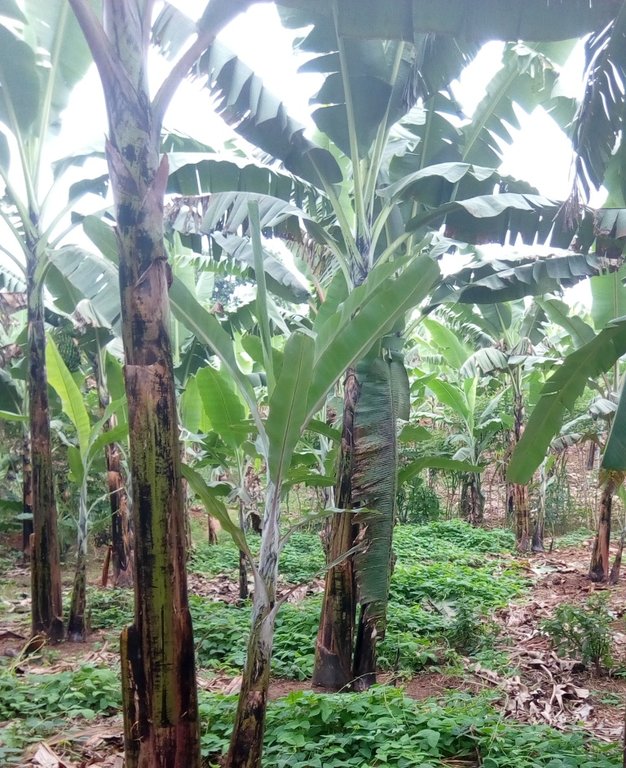
Lab lab (Lablab purpureus) is planted in a banana garden and trained to creep in the empty spaces for suppressing weeds, stabilizing the soil, fixing atmospheric nitrogen and controlling water runoff.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The lab lab (Velvet), commonly called bataw or jarabilla, is widespread throughout the tropics. The legume is characterized by creeping and is normally planted as a cover crop in plantations where it is allowed to cover the open spaces. The leguminous crop is normally promoted and planted in banana gardens for it’s immense potential to control weeds and improve and conserve soil fertility. As an inter-crop, lab lab is usually combined with other crops for its high potential of fixing atmospheric nitrogen, controlling soil erosion, providing green manure and retaining soil moisture in support of the other crops. As a mono crop, lab lab is planted on bare land at all slope angles and at any scale to support the soil structure and to control run off. The leguminous plant is also known to be highly nutritious for livestock farming and is used to add protein content value to other pastures when making good quality fodder, silage and hay.
The lablab in the banana garden was established about 1.5 years ago; establishment of lablab legume in the banana garden is defined by the farmer to be simple and cheap depending on the size of land. The activities involved in establishing the cover crop include (1) weeding the garden to provide a competition free environment for the legume to grow. (2) Sowing of the seeds in the garden a few weeks to the start of the wet season (3) training of the germinating lablab at least 0.75 m away from the banana plants. The main maintenance activity involved is training the cover crops from invading the banana plants to avoid competition for nutrients.
The equipment required is only a hoe on small scale farms and maybe a tractor or curt on large scale farms. The expenses involved in the establishment process of lablab legume in a garden of 1.5 acres are mainly dependent on the availability of seed and labor. A kilogram of lablab seed was enough and costs the farmer $1.38, the labor to plough the banana plantation was provided by two of family members for 3 days valued at a total of $5.83. The profitability of the technology by the farmer where seen in the improvement in banana bunch size and the ever green banana plants maintained during the wet and dry season. The farmer before establishing lablab harvested banana bunches of sizes valued at US $ 2.78 – US $ 4.17 but today produces bigger bunches and sells at a price between US $ 4.17 – 5.56 on the local market. The average number of bunches harvested per month is also realized to have improved from 112 to 160 bunches. The weeds in the garden are no longer a big problem to the farmer and the soil moisture can be observed on the ground. The leaves of lablab also decompose as manure in addition to the known leguminous function of nitrogen fixation.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
13/02/2018
位置:
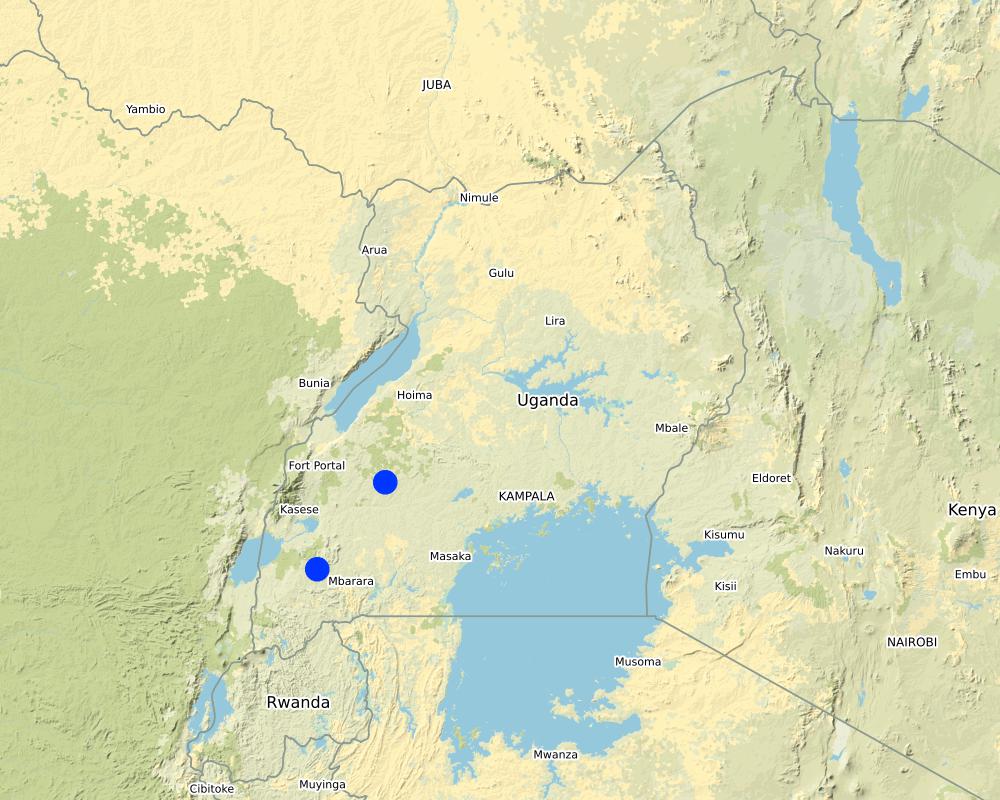
Kabalore, Fort Portal Municipality, Njara Sub County
摄影师的名字:
Mrs. Jalia Namakula
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Western Uganda, Kabarole District
有关地点的进一步说明:
Fort Portal Municipality, Njara Sub County
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The farmer learnt about the technology from another farmer in Bushenyi District South western Uganda.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Bananas
注释:
The farmer also practices livestock farming including piggery and goat farming at a sustainable scale. The lab lab bean leaves are harvested during the dry season to supplement the livestock with leguminous feed.
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
The farmer previously inter-cropped bananas with beans and maize, the beans planted were for domestic food security. With the introduction of lab lab a perennial crop, the beans and maize are no longer part of the gardening system which has improved the quality and quantity of bananas harvested.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
March - June and September - November
牲畜密度(如相关):
2 goats and 3 pigs kept on zero grazing at subsistence scale
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 地下水管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The farmer has 1.5 acres of land under lab lab bean and banana intercroping system
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
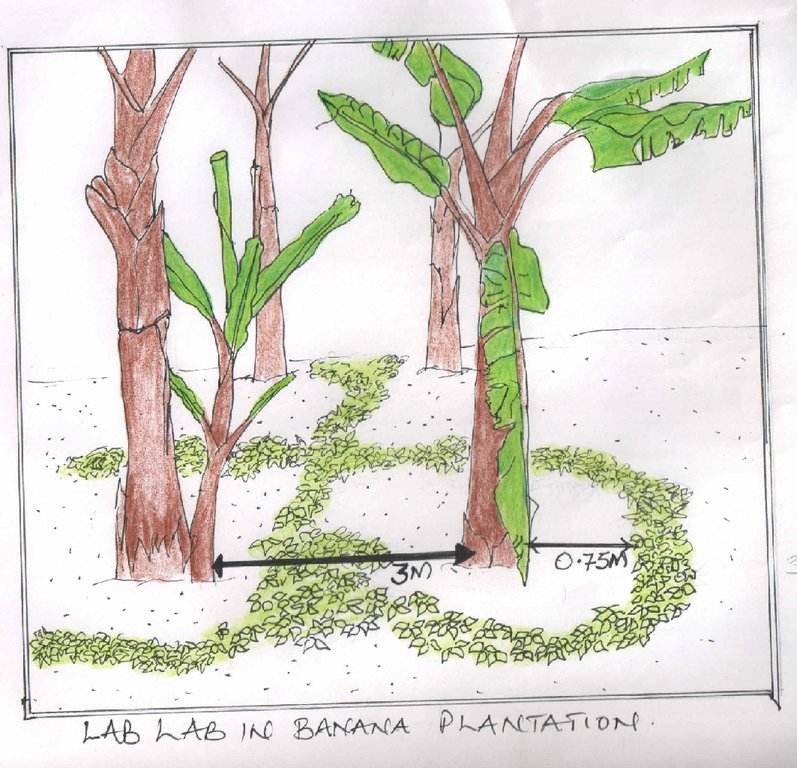
The banana plantains are spaced 3 x 3 m between plants. The lab lab (Velvet) bean is planted and trained to creep in the open spaces, 0.75m away from the base of the banana.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
Acre
如果使用本地面积单位,请注明换算系数为1公顷:
2.5
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Uganda Shilling
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3500
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | weeding the plantation | 管理 | A month to the rain season |
| 2. | Seeding | 农业学的 | Three weeks to the rain season |
| 3. | Training the creeping direction of the legume | 管理 | A month in the rain season |
注释:
Most of the establishment and maintenance activities are done by the family members
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labor for 3days | Man days | 6.0 | 6000.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hire a hoe | Pieces | 2.0 | 1000.0 | 2000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Lablab bean seeds | Kilo grams | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 43000.0 | |||||
注释:
The technology is cheap relative to the farmer's economic capacity
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Training the creeping lab lab bean | 管理 | A month in the rainy season |
| 2. | Harvesting the fodder for pigs and goats | 管理 | Two months after the planting |
注释:
Most of the maintenance activities are simple and labor is provided by the farmer's family
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Training of creeping lab lab beans twice a year | mandays | 2.0 | 6000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting the ready lab lab for goats and pig fodder | Manhours | 30.0 | 1000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 42000.0 | |||||
注释:
These activities are simple and the labor was provided by the farmer
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The availability of lablab bean seeds for planting and the availability of labor required for preparing the garden
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
The water used for domestic use is mainly tap water and rooftop harvested water
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The landuser belongs to the community elite as he/she working as a teacher in a secondary school.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
50
SLM之后的数量:
65
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Bigger bunches of matooke at all times of the year.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
More leave-material for feeding goats and pigs is available.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
The dry season normally retards banana production. However, this is now minimized through the moisture retention capacity of lab lab.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Weeding expenses no longer incurred.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Lab lab is a cover crop and contributes to reducing the rainwater run-off.
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
干旱影响
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 季节性温度 | 旱季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Manure from falling leaves |
| Suppresses weeds |
| Feed for animals |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improves moisture retention in the soil |
| Reduces run off |
| Nitrogen fixation into the soil |
| Establishment is cheap and needs simple tools like hoes |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The cover crop is invasive and doesn't favor inter cropping |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The foliage may be a habitat to vermins like snakes and rats | Setting traps in case of infestation |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Two farmers
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
LABLAB Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet
URL:
https://plants.usda.gov/plantguide/pdf/pg_lapu6.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块