Pitting to restore degraded catchment of Mount Fletcher Dam [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dirk Pretorius
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Joana Eichenberger
Pits
technologies_3377 - 南非
- Pitting to restore degraded catchment of Mount Fletcher Dam : March 21, 2018 (inactive)
- Pitting to restore degraded catchment of Mount Fletcher Dam : April 20, 2018 (inactive)
- Pitting to restore degraded catchment of Mount Fletcher Dam: June 20, 2019 (inactive)
- Pitting to restore degraded catchment of Mount Fletcher Dam: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Buckle Jacob
Department of Environmental Affairs - South Africa
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Working on Ecosystems (Natural Resource Management Programmes – DEA, South Africa)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: Guidelines to Rangeland Management in Sub-Saharan Africa (Rangeland Management)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
SMC Synergy (SMC Synergy) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
Working for Water Wetland rehabilitation [南非]
To improve the quality & quantity of water production and biodiversity in the Blyde River catchment area.
- 编制者: Unknown User
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
To improve infiltration and vegetation cover, by creating small pits on bare soil, which capture runoff and reduce erosion.
2.2 技术的详细说明
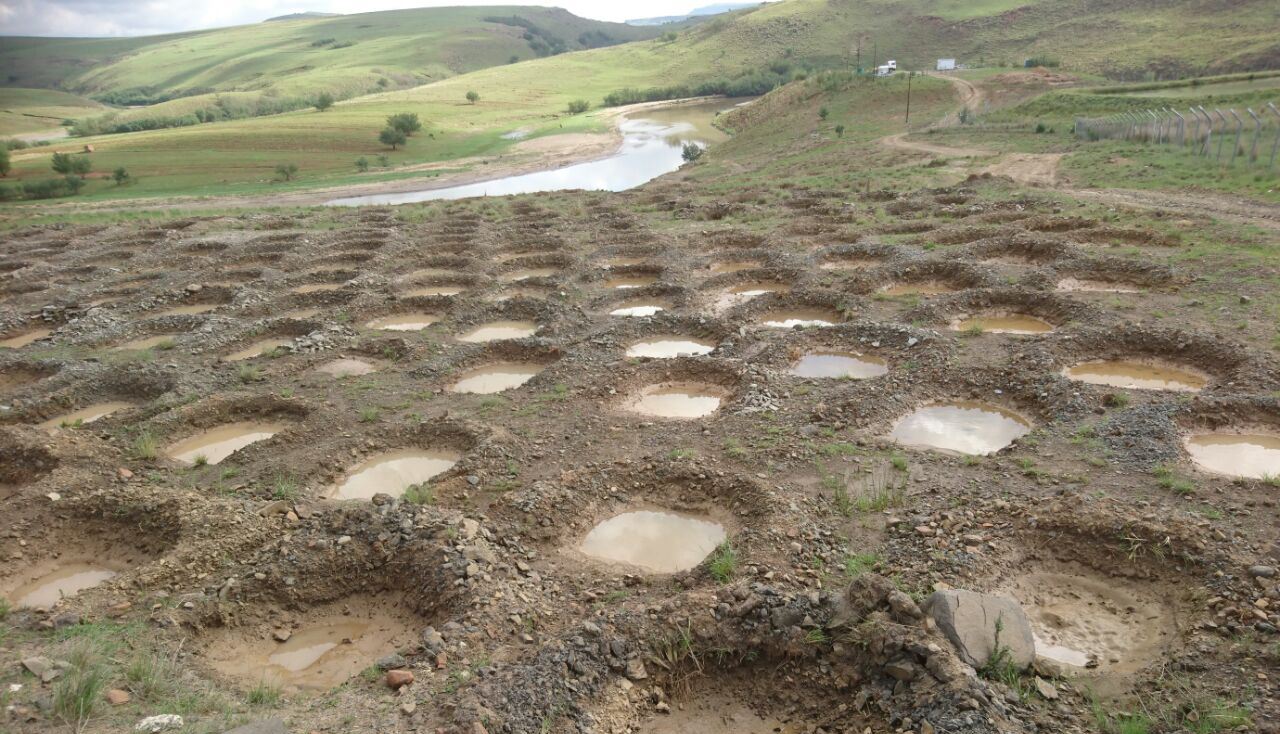
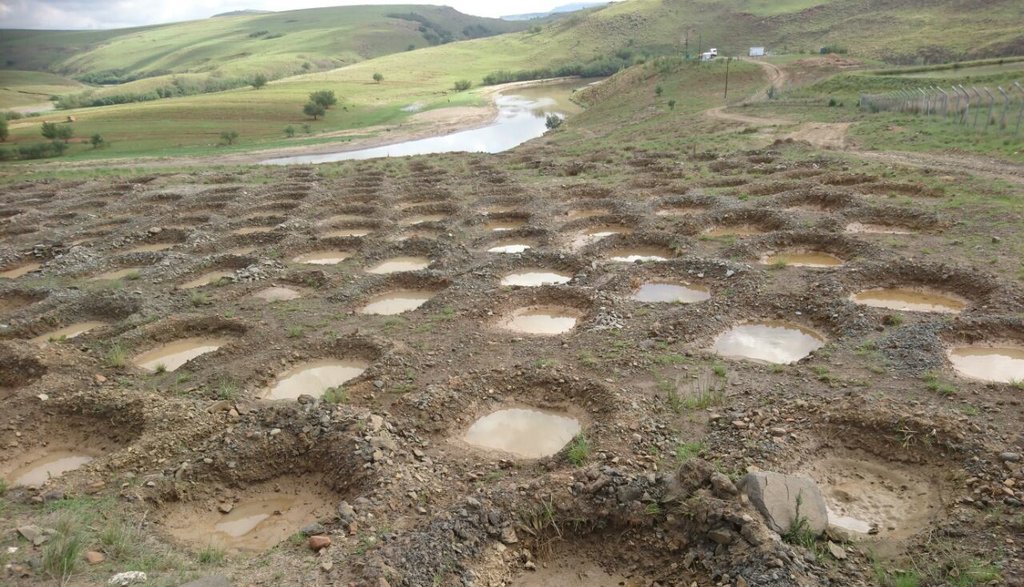
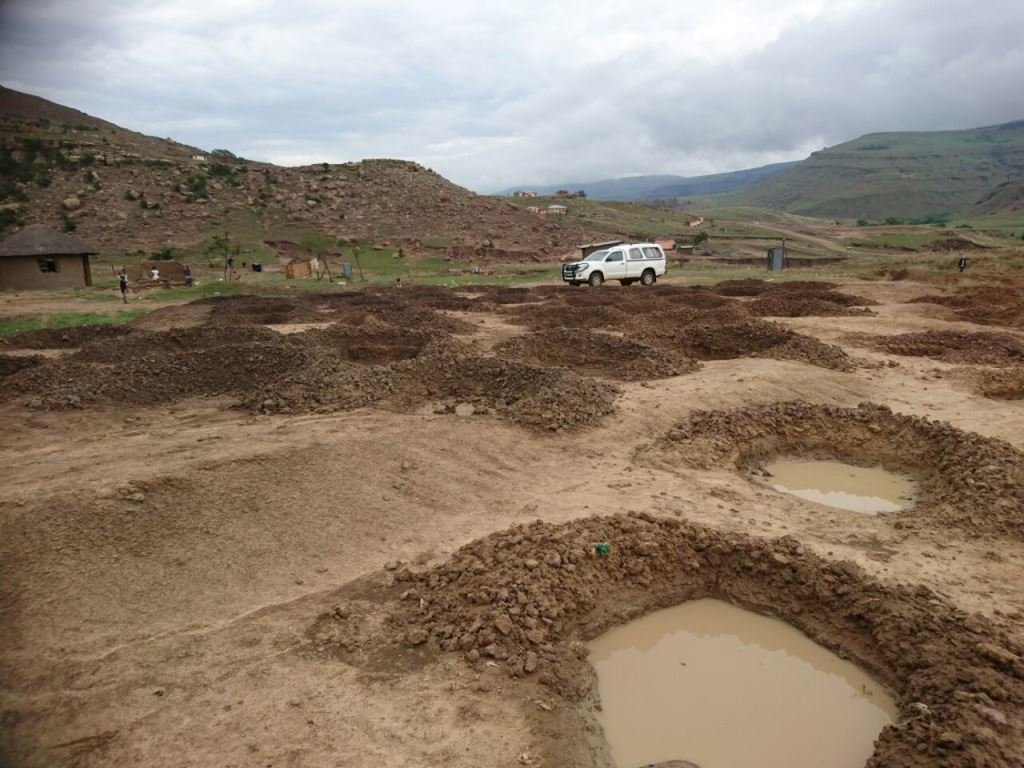
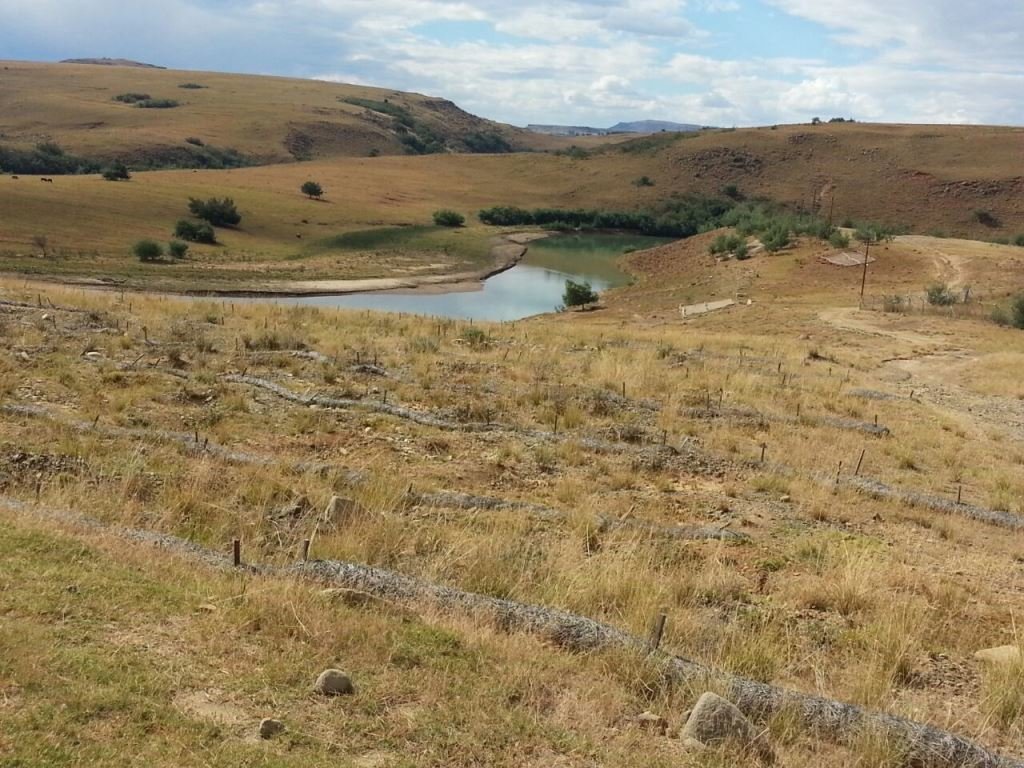
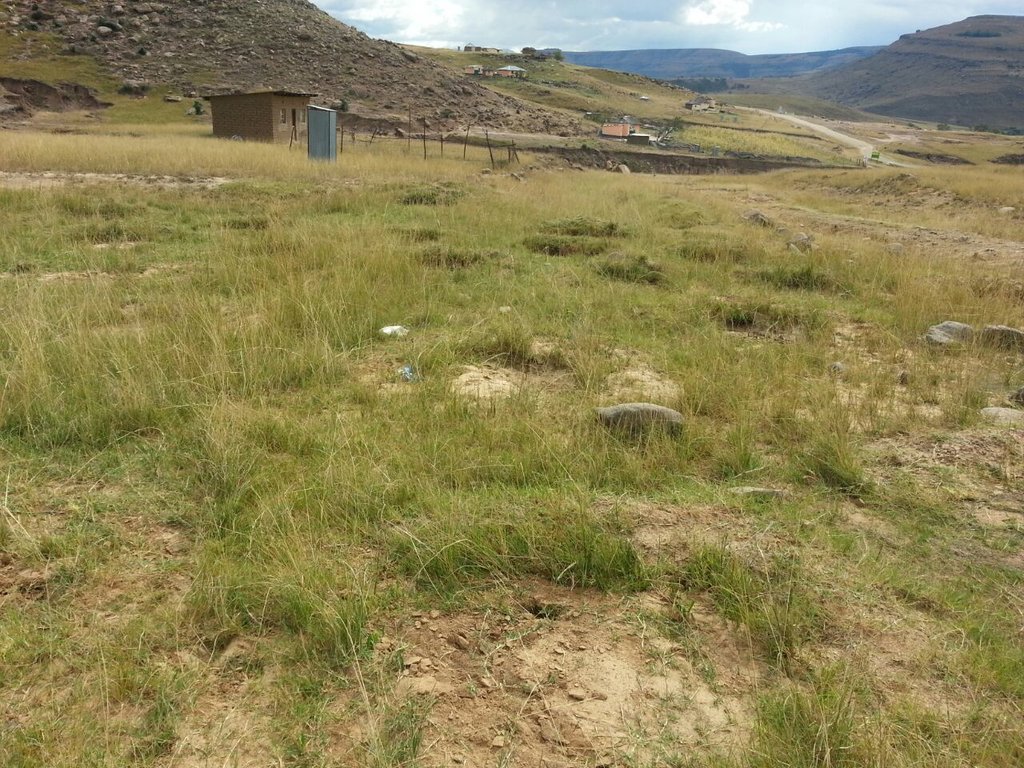
说明:
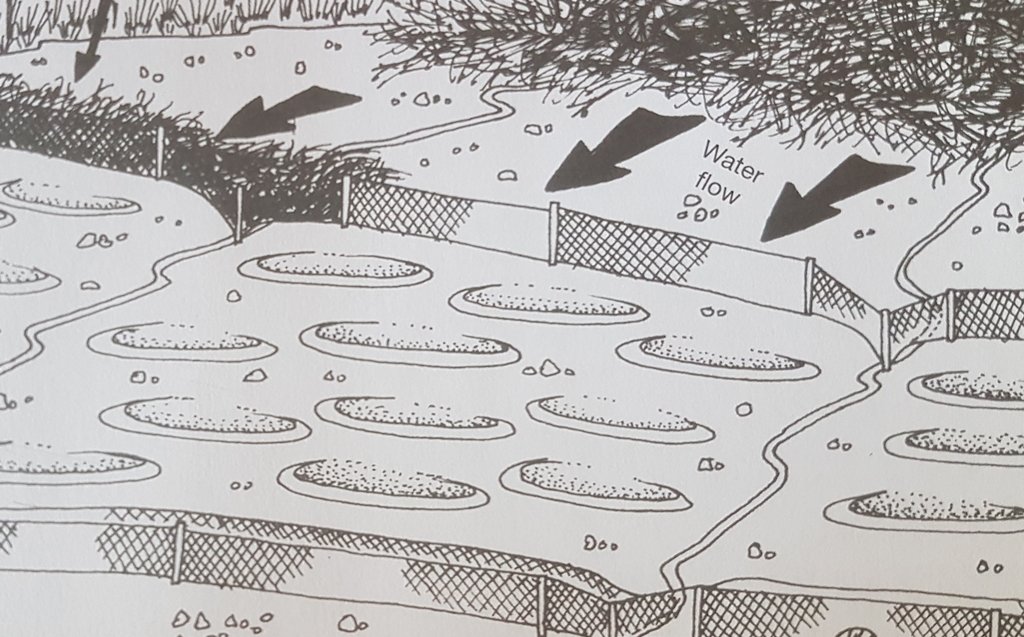
This project on pitting was implemented on the banks of the Mount Fletcher dam in the Eastern Cape of South Africa. The rehabilitation was funded by the Department of Environmental Affairs as part of the “Working on Ecosystems” programme. The programme also focuses on creating jobs and improving skill levels within local communities. The average annual rainfall in the area is 600 to 800 mm and occurs mainly in summer as thunderstorms. Severe sheet and rill erosion occur in the dam’s catchment. Combined with overgrazing and veld fires on the highly erodible soils, the catchment is severely degraded. Due to the degradation, high loads of sediment have resulted in severe siltation of the Mount Fletcher dam. The pitting technology can help. It is suitable for any low gradient, degraded, landscape as long as duplex soils are not present - due to piping on these soils. The main purpose of pitting is to enhance infiltration of runoff water by capturing, and ponding, it on capped/crusted bare soils. Simultaneously soil loss, due to sheet and rill erosion, is reduced. Secondary benefits of ponding runoff include trapping of sediment and subsequent improvement of vegetation cover. Pitting is combined with brush packing (laying cut bush on the soil’s surface) or mulching, and the construction of silt fences (low barriers across the slope) to further improve sediment trapping. This technology commences with the digging of small pits (70 cm surface diameter and 30 cm deep ) by hand or mechanical implements. The excavated soil is piled up to form a ridge on the down-slope. Pits are placed 2 meters apart in rows 1 meter apart. Re-seeding in pits with commercially available grass seed mixes can be used to enhance vegetation cover. Brush packing over the ponds with local woody (preferably thorny branches) material is recommended (if available locally) to provide protection against grazing and to create a micro-climate for vegetation growth. In between and above the pits silt fences or fiber rolls (can be used to slow water runoff (placed 10 m apart, across the slope).
Silt fences and fiber rolls are temporary sediment control devices used on rehabilitation sites to reduce sediment movement downhill. A typical fence consists of a piece of synthetic filter fabric (also called a geotextile) stretched between a series of wooden or metal fence stakes along a horizontal contour level. A fiber roll is made of wood fiber, straw, coconut fiber or similar material formed into a tubular roll also fixed by wooden or metal stakes.
Maintenance of the structures will include the creation of more pits and repair of silt fences and/or fiber rolls where needed. Further brush packing might be required after 6 months.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Eastern Cape
有关地点的进一步说明:
Near the town of Mount Fletcher on the banks of the Mount Fletcher dam
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
动物类型:
- 牛 - 奶制品
- 山羊
- 绵羊
产品和服务:
- 肉类
- 奶类
注释:
Main animal species and products: Cattle, goats and sheep - meat and milk
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Livestock density: Low
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S4:平沟、坑
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Other structural measures include brush packing (or mulch if available) and the placement of silt fences
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Pitting can be used to restore degraded bare landscapes on slopes up to 30 percent, though not on highly erodible duplex soils. The pits are dug 30 cm deep, with a surface diameter of 70 cm, and sited 2 m apart in rows 1 meter apart. Silt fences or fiber rolls are located 10 m apart across the slope. Brush packing is recommended for protection.
作者:
K. Coetzee
日期:
2005
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
2 hectares
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Rand
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
12.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
140 (excluding transport)
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig pits (5000/2ha) | 2 to 3 months before onset of summer rains |
| 2. | Install silt fences or fibre rolls | 2 to 3 months before onset of summer rains |
| 3. | Add grass seed mix in ponds and cover with layer of soil | 2 to 3 months before onset of summer rains |
| 4. | Brush packing between pits | 2 to 3 months before onset of summer rains |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Unskilled labour (including transport) | per day | 160.0 | 240.0 | 38400.0 | |
| 设备 | Picks, spades, hand compactor, pliers, hopper, bow saws, hammer, wheel barrow (renting the equipment) | per day | 14.0 | 20.0 | 280.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Grass seed | kilogram | 2.0 | 75.0 | 150.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Silt fences or fibre rolls | per meter | 2000.0 | 15.0 | 30000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | 1.0 | |||||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 68830.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 5735.83 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Department of Environmental Affairs - South Africa
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Add more ponds if necessary | After floods |
| 2. | Restore silt fences | After floods |
| 3. | Brush packing of ponds | After 6 months |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Unskilled labour | per day | 6.0 | 240.0 | 1440.0 | |
| 设备 | Picks, spades, hand compactor, pliers, hopper, bow saws, hammer, wheel barrow (renting the equipment) | per day | 6.0 | 20.0 | 120.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Grass seed | kilogram | 0.5 | 75.0 | 37.5 | |
| 施工材料 | Silt fences | per meter | 200.0 | 15.0 | 3000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 4597.5 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 383.13 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Department of Environmental Affairs - South Africa
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labor availability, soil hardness, availability of material, transport cost.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
750.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Summer thunderstorms
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不可用
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Steep slopes in the catchment with frequent high rainfall events contribute to high levels of sheet and rill erosion casing the siltation of the Mount Fletcher dam (affecting the usability of the water and storing capacity of the dam).
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Degraded grassland
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
- 老年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Poor rural communities far from markets - very little goods and services
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Initially, animals are not grazed on restored areas to allow vegetation recovery – but the long term impacts should be positive.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Brush packing is used to prevent animals from grazing on rehabilitated areas.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Infiltration improves - less runoff
饮用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Less sedimentation from runoff.
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Infiltration improves - less runoff
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Over the long-term farm income will increase - improved rangelands.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Jobs are created for community members.
其它社会经济效应
Job creation
Improved skills
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Skill levels increased for some community members.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Household income increased for some community members.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Less runoff
水质
注释/具体说明:
Less sedimentation from runoff.
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Improved species composition due to seeding in pits.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Less runoff
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
More biomass to burn (including fencing and fibre rolls)
微气候
注释/具体说明:
Improved micro-climate due to brush packing.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Impact only slightly positive due to the extent of the erosion problem in the catchment - more pitting necessary to have a larger impact on the Mount Fletcher dam.
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
Same as above.
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
Impact of ponding only slightly positive due the the extent of the erosion problem in the catchment - more ponding necessary to have a larger impact on the Mount Fletcher dam. The Mount Fletcher dam is currently severely silted and the off-site effects of ponding is difficult to quantify at this stage.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地雷暴 | 适度 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
| 陆地火灾 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
droughts
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Adapted grass seed mixes for better drought tolerance.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Cost effective technology that can be applied to large areas (part of Extended Public Works Programme – job creation). |
| Improve infiltration of runoff. |
| Improve vegetation cover and therefore productivity of livestock. |
| Help to reduce the poverty level of communities and improve skill levels. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Cost effective technology that can be applied to large areas. |
| Improve infiltration of runoff. |
| Improve vegetation cover and therefore productivity of livestock. |
| Help to reduce the poverty level of communities and improve skill levels. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Silt fences can be damaged by fire and vandalism. | Fire breaks and community engagement. |
| Very little local woody material for brush packing. | Replace brush packing with mulch from nearby areas (can be expensive due to transport). |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Silt fences can be damaged by fire and vandalism. | Fire breaks and community engagement. |
| Very little local woody material for brush packing. | Replace brush packing with mulch from nearby areas (can be expensive due to transport). |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/01/2018
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Wetland Rehabilitation Guidelines, W Russel, 2009, ISBN 978-1-77005-640-4: Water Research Commission - South Africa - WRC report TT 341/09
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Water Research Commission - South Africa
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Caring for Natural Rangelands, Ken Coetzee, 2005, ISBN 1-86914-071-0
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Ken Coetzee, University of KwaZulu-Natal Press
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Working for Water Wetland rehabilitation [南非]
To improve the quality & quantity of water production and biodiversity in the Blyde River catchment area.
- 编制者: Unknown User
模块
无模块