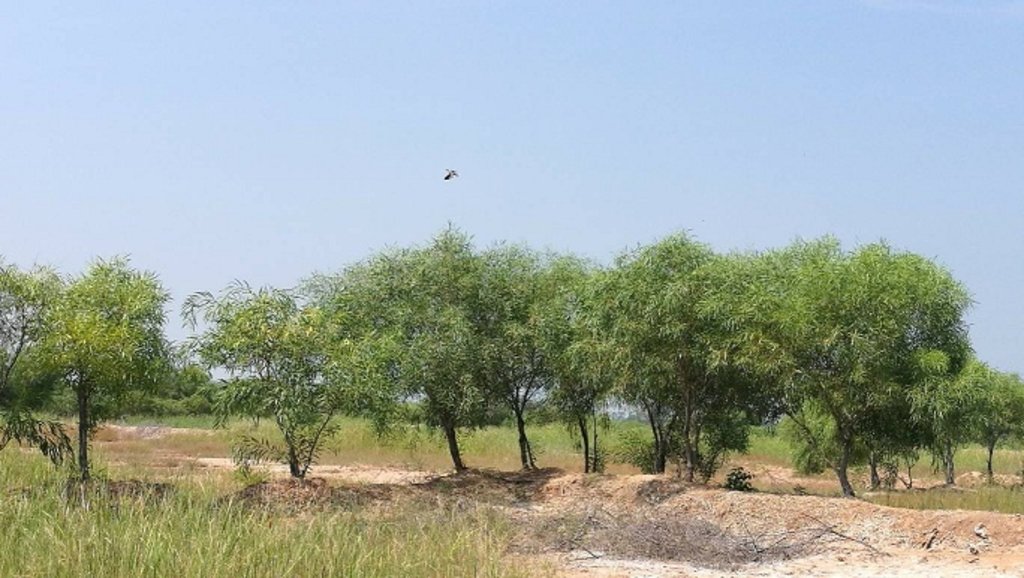
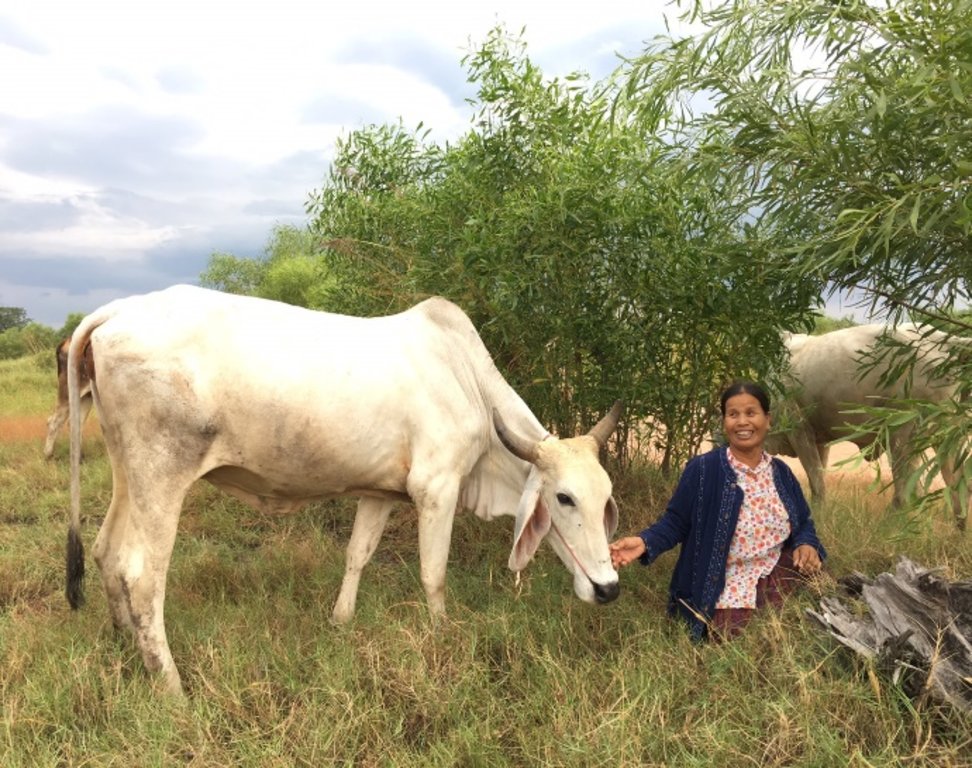
Planting of Acacia ampliceps to control severely salt-affected land. [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Chakkaphan Phaosrakhu
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Samran Sombatpanit, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, William Critchley
Planting Acacia ampliceps on severely salt-affected land leveled with ditches and dikes.
technologies_4149 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Tathaisong Nurean
-
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Phaosrakhu Chakkaphan
Land Development Regional Office 3
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Chuaysanoi Phatranit
Land Development Regional Office 3
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Oechaiyaphum Kaewjai
Land Development Regional Office 3
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Prachansri Saowanee
Land Development Regional Office 3
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Phiprakon Apisit
Land Development Regional Office 3
泰国
SLM专业人员:
Prawanna Prasit
Land Development Regional Office 3
泰国
National consultant:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology is very well accepted by the land users.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Acacia ampliceps is a very salt-tolerant species that can grow well in severely salt-affected areas. Land leveling with ditches and dikes is needed, and they are planted along an east-west direction. The technology is very well accepted by land users.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
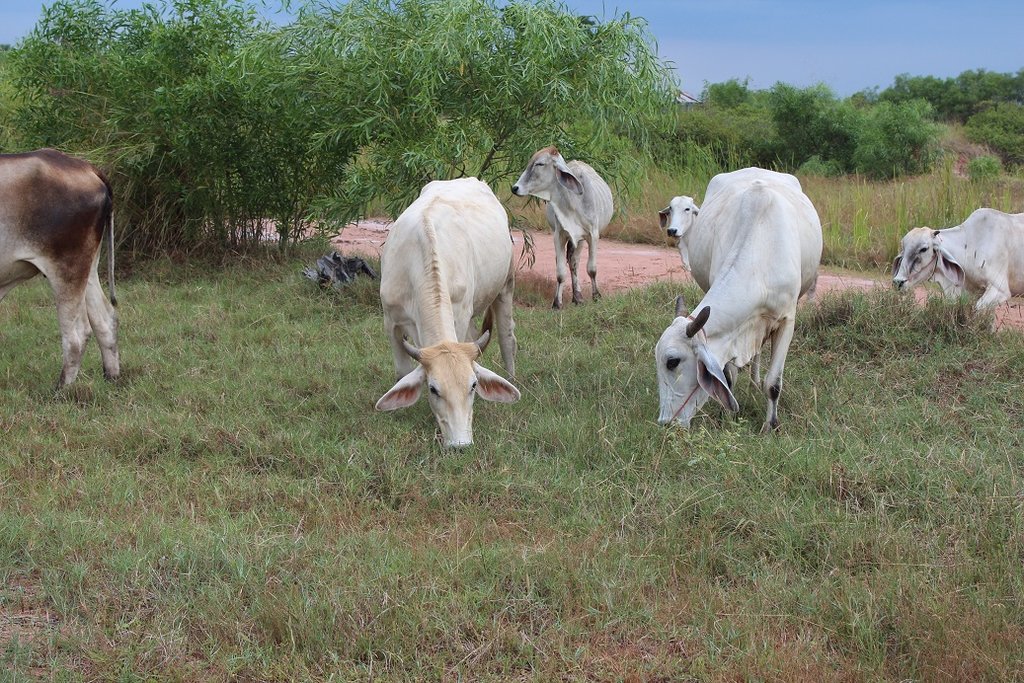
Acacia ampliceps (salt wattle, a leguminous Australian shrub), has been introduced in salt-affected areas in the Northeast of Thailand for the remediation of saline soils. It is a very salt-tolerant plant that grows well on severely salt-affected land. Leveling the land and furnishing with ditches and dikes is needed first, and then the trees are planted in the affected area, along an east-west orientation on the dikes. The technology is very well accepted by land users. Planting such trees in the severely salt-affected land in Kham Tale Sau, Nakhon Ratchasima Province is a subproject of the LDD project on "Planting Perennial Salt-tolerant Trees in Salt-affected Areas in the Northeast of Thailand", which started since 1997. In the subproject, Acacia ampliceps was grown on 68 rai (approx. 11 hectares) covering >50% of the salt patches in heavily salt-affected barren land owned by Mrs. Nurian Tathaisong at Ban Kok Sa-ad Village, Dansay Sub-district, Buayai District, Nakhon Ratchasima Province. In a recent study, after planting the acacia tree in 2015, her land had changed noticeably from its barren state to being covered with trees that provided shade; native grasses had returned to form a source of fodder for her 14 cattle. The purposes of the project have been to maximize the use of the land with a low level of inputs and to decrease salinity to the level that other less salt-tolerant plant species can survive - and crops can be grown for higher income. Eventually it is hoped that better soil properties will be created.
The technology started with locating severely salt-affected sites, leveling the land and furnishing it with ditches and dikes. Each dike is 2 m wide at its base, 0.5 m high, and 1.5 m wide on top. The ditch is 0.5 m deep and 1 m wide. Acacia ampliceps seeds are treated to break the dormancy by soaking in hot water (80°C) for 10 min before planting in the nursery. The 2-month-old seedlings are planted in pits of 0.3 x 0.3x 0.3 metres on the dike, with the addition of 1 kg each of compost and rice husks. Spacing between planting pits is 2 m as a single row in the middle of the dike. According to the land user, 1 year after planting native grasses had returned while the salt crusts had disappeared. At 2-years old, the average plant height was 1.65 m and continued growing, producing 8-10 coppices per tree, and leafy shade for cattle. Acacia ampliceps wood is used to produce charcoal. Three years after planting, the land user had converted 23 rai (approx. 3.7 hectares) of less saline land to paddy fields. After a period of 3 years, the technology induced a better microclimate and richer diversity of flora and fauna species, e.g. wild flowers, native grasses, frogs, dragonflies, earthworms, birds and rats. The fragrant Acacia ampliceps flowers attract bees, thus in the near future the land user intends to undertake apiculture as well as producing essential oil, and making charcoal. The only visible threat to Acacia ampliceps is a forest-fire risk due to its high oil content; fires could cause damage to crops.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
日期:
28/11/2018
日期:
28/11/2018
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Nakhon Ratchasima
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ban Kok Sa-ard, Moo 10 T. Danchang, A. Buayai, Nakhon Ratchasima, Thailand
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
On farmer's land.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Land Development Department and Local authorities had demonstrated Acacia ampliceps plantation on farm ridges in the salt-affected area, under the project of salinity-tolerant crop plantation to suppress salt-affected soil distribution, at A. Buayai, Nakhon Ratchasima since 2014 up to now.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- Desalination
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

不毛之地
具体说明:
Barren land
注释:
There are salt crusts in the heavily salt-affected barren land.
注释:
Acacia ampliceps plantation on land leveled with ditches and ridges, had potential salinity watertable control.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田

不毛之地
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Average annual rainfall 900-1,100 mm.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- desalination
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S1:阶地

其它措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pw:水浸

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
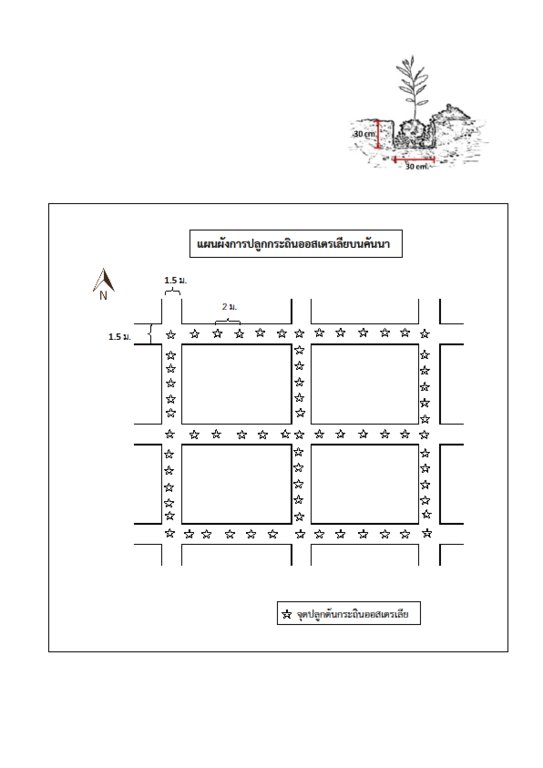
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The technologies start with locating severely salt-affected sites and land leveling with ditches and dikes. The dike is 2 m wide, 0.5 m high, the top of the dike is 1.5 m wide. The ditch is 0.5 m deep and 1 m wide. Acacia ampliceps seeds are treated to break the dormancy by soaking in 80°C hot water for 10 min before planting in the nursery. The 2-month-old seedlings are planted in a pit of 0.3x0.3x0.3 m on the dike, with an addition of 1 kg each of compost and rice husk, at a spacing of 2 m as a single row in the middle of the dike. The ridges are 20 m apart.
作者:
Chakkaphan Phaosrakhu
日期:
09/10/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
45 rai
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
1 ha = 6.25 rai
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
THB
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
32.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300 THB/day
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nursery of Acacia ampliceps. | May-July |
| 2. | Preparing the pit for planting | May-July |
| 3. | Planting Acacia ampliceps | May-July |
注释:
There is no irrigation water, therefore planting time depends directly on the period of early rainy season which is May-July.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cost of hired labour on planting process (cost of hired labour/ day is 300 THB, 1 rai needs 2 labourers. Hence, the total cost of hired labour is 600 THB) | rai | 1.0 | 600.0 | 600.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Cost of Acacia ampliceps nursery (1 young seedling costs 1.50 THB). 1 rai needs 80 young seedlings. So, the total cost of young seedlings is 120 THB. | seedling | 80.0 | 1.5 | 120.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | The cost of compost is 3.5 THB/kg. Rate of application is 0.5 kg/pit | kg | 40.0 | 3.5 | 140.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | The cost of rice husk is 4 THB/kg. Rate of application is 1 kg/pit | kg | 80.0 | 4.0 | 320.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | The cost of chemical fertilizer (15-15-15) is 20 THB/kg. Rate of application is 0.1 kg/pit | kg | 8.0 | 20.0 | 160.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1340.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 41.88 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
-
注释:
Land Development Department supports the operational budget particularly cost of Acacia ampliceps plantation, while land users are in charge of maintenance and forest fire control during dry seasons.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Forage harvesting after 1 year of Acacia ampliceps plantation | rainy season, 4 times |
注释:
After 1 year of planting, the native grasses that did not exist have returned while salt crusts disappear.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Cost of hired labour on trimming process: 1. The cost of hired labour: 300 THB/8-hr day and 2. Trimming process for 1 rai requires 4 hours each time, twice a year. Hence, the total cost of hired labour on trimming process is 300 THB/rai/yr) | time | 2.0 | 150.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 300.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 9.38 | |||||
注释:
Land users operate trimming process; however, labour cost is calculated.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Land Development Department supports the operational budget particularly cost of Acacia ampliceps plantation at first year, then users are in charge of maintenance and forest fire control.
At the first year, the initial cost for Acacia ampliceps plantation is about 1,340 THB. This includes: the cost of hired labour on planting process, 600 THB/rai; the cost of young seedlings, approximately 120 THB/rai and the cost of compost, rice husk and chemical fertilizer, about 620 THB/rai. For the expenditure part on the 1st year, there is a hired labour for harvesting fodder in a period of 6 months, approximately 300 THB/rai (from the early to the end of rainy season). However, land user can produce fodder and have grazing land for 14 cattle for around 180 days/yr. Each cattle needs about 30 kg of fodder a day. The cost for the fodder is 1 THB/kg. Land user can save the cost for cattle feeding approx. 5,400 THB/cattle/yr. In conclusion, land user can save the cost for fodder production and grazing land approximately 1,680 THB/rai. For the expenditure part on 2nd and 3rd year, there is fodder harvesting, trimming process and charcoal production. Land users may obtain approx. 10 bags of charcoal that costs 120 THB/bag. Thus, there is a direct income from charcoal production (about 26.7 THB/rai/yr) and an increase of rice production (up to 5%). Land users can have increased income from selling rice at 100 THB/rai.
In conclusion, there is a cost of maintenance during 3 years for approx. 900 THB/rai. Part of the income, the land user can have income from the increased rice yield approx. 100 THB/rai/yr. Otherwise, charcoal production can reduce fuel’s expenditure in daily life for approx. 26.7 THB/rai/yr. Fodder production and grazing land can reduce cost of cattle feeding for approximately 1,680 THB/rai/yr. The land user, however, wants to leave the branches of Acacia ampliceps for watertable control and for cattle shading.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Meteorological Department
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
森林/林地质量
非木材林业生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
土地管理
能源生产
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
酸度
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
干旱影响
飓风、暴雨的影响
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
微气候
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
| 森林火灾 | 适度 |
| 陆地火灾 | 适度 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 不好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Plantation cost in the 1st year is the main cost; the rest is the maintenance cost after 1-2 years of the growing period, including weed control. All kinds of weed can be used for raising animals. Hence, there is not much maintenance cost after establishing the Acacia trees.
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
4,665 rai (approx. 745 ha)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
Land users claimed that planting Acacia ampliceps on the severely salt-affected land can decrease salinity to about 50% after 3 years of planting. This project made farmers understand the methodology of desalination.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
Acacia ampliceps plantation
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
The farmer attempted to grow Acacia ampliceps on the leveled land with two methods. The first one: 1) To grow by removing the plastic bag and 2) To grow without removing the plastic bag. The farmers found that removing the plastic bag before planting is better, as the plant growth will not be disrupted.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| 1) Desalination to 40% after 3 years of planting; |
| 2) Branches of Acacia ampliceps are used as forage and for producing charcoal; |
| 3) The plants provide shade, with increased air humidity, resulting in a better atmosphere to live in; and |
| 4) The plants increase the amount of flora, especially the forage crop. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| 1) Desalination, thus preventing the spread of salt-affected soil; |
| 2) To increase rice yield and, thus, farmers’ income; |
| 3) To induce better microclimate and biodiversity of both flora and fauna species, e.g. wild flowers, native grasses, frogs, dragonflies, earthworms, birds and rats. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| One year after Acacia ampliceps planting, farmers had to investigate their technology, to prevent their technology from animal and fire attack. | 1) The farmer had to investigate his technology, to prevent their technology from trapping animals. They have to build firebreak. |
| 2) The farmer should request his neighbors who raise buffalos and cows to prevent their animals from destroying the technology. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farmers who do not join this project do not know how to plant Acacia ampliceps on farm dikes. Moreover, they do not know where to buy the seeds. Thus, LDD officers or farmers who are engaged with this project have to inform them. | LDD officers or farmers who are engaged with this project have to educate other farmers. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Visit 1 farmer/land user.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Interview with 1 farmer.
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
The Land Development Department officers and planners (7)
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
5
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
03/11/2018
注释:
The interviewer on field visit and interview process must be by a person who is knowledgeable about the background of this project.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Land Development Department
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.ldd.go.th/ LDD project on planting perennial salt-tolerant trees in salt-affected areas in Northeast Thailand, Mr. Pramote Yamklee,2005
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
LDD project on planting perennial salt-tolerant trees in salt-affected areas in the Northeast. Thailand, Mr. Pramote Yamklee,2005
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.ldd.go.th/Lddwebsite/web_ord/Technical/HTML/Technical03030.html
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/library/media/27/
标题/说明:
where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/en/projects-and-countries/projects/drr
7.4 一般注释
The questionnaire is very complicated.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块