Organic matter application to enhance soil health [英国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Alan Radbourne
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_5968 - 英国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Fisher Karen
Soil Association
英国
土地使用者:
Corp Nicholas
Wasing Farm
英国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
European Interreg project FABulous Farmers有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Soil Association (Soil Association) - 英国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (CEH) - 英国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The addition of organic matter, such as compost, to soils on farms can enhance soil health with benefits for soil organisms, soil structure, carbon sequestration and plant production.
2.2 技术的详细说明
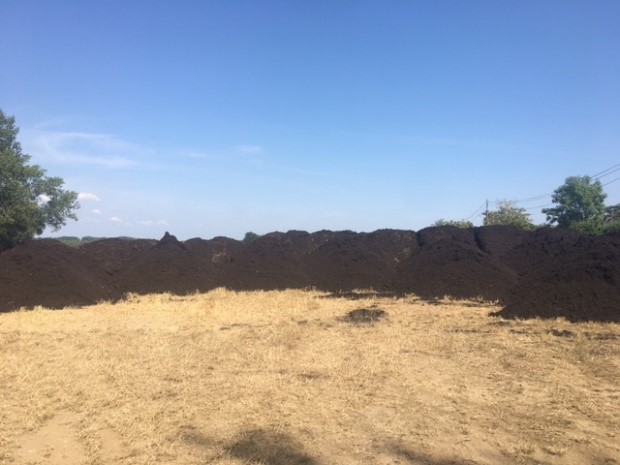
说明:
Application of organic matter to soils, in the form of compost, helps enhance soil organisms and structure for improvements in overall soil health. This technology has been applied to 36 hectares of a 300 hectare organic arable farm that practices a rotation of 2 years grass ley, followed by a winter cereal and then two spring cereals with cover crops in the period between the two spring crops. The technology has been trialed in the south of England (Berkshire) where the average annual rainfall is around 690 mm and the soil is mostly gravel, silt and clay soil with low organic matter – making it challenging to cultivate.
The practice has been to import certified green waste compost to apply to fields on a rotational basis before the winter crop, as it requires more nitrogen than the spring crops. The application was planned for this period in the rotation as spring spreading can damage the soil through compaction after the winter crop has been harvested.
The sources of green waste varied, with 900 tonnes of composted PAS 100 certified green waste from a local waste company, and 500 tonnes of green waste from a local camomile producer, both in 2019/2020. The compost was stored in windrow heaps for 6 months on the grass leys turning once during this time. For the application, a contractor then used a spreader before soil cultivation for the winter crop. This technology is ongoing.
The primary aim of the application of organic matter is to improve soil fertility and the soil's health. This in turn results in better crops.
Challenges to overcome with this technology are issues with compaction from spreading activities and the cost of compost purchase and haulage. Compaction can be alleviated through autumn spreading, yet costs can be prohibitive. So, far the benefits of the technology application are limited as it will take a long time achieve the full impacts of increasing soil organic matter, especially in the soil type that is present on the farm, yet the hope is it will have a large impact in the future.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
英国
区域/州/省:
Berkshire
有关地点的进一步说明:
Reading
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2019
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 燕麦
- 谷类 - 黑麦
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 饲料作物 - 草
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
A rotation of 2 years grass ley, followed by winter cereal and then two spring cereals with cover crops in-between spring cereals.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
36 hectares
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
£GBP
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
£150
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Procurement of compost | Spring |
| 2. | Application of compost (27.4t/ha) | Autumn |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost purchase, haulage and spreading (£11 per tonne) | ha | 36.0 | 303.0 | 10908.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 10908.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 12832.94 | |||||
注释:
Compost was sourced, delivered, arranged in windrows and later spread by a single contractor for a set price (£11 per tonne @27.4t/ha over 36 ha).
4.5 维护/经常性活动
注释:
No ongoing maintenance as organic matter will incorporate into soil over time. Ongoing maintenance would be to repeat the procedure to continue adding matter to the soil over time.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
No ongoing maintenance costs as organic matter will incorporate into soil over time. Ongoing maintenance would be to repeat the addition at the right time of the crop rotation again to continue adding organic matter to the soil over time.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost of contractor haulage and spreading, which is partly driven by current fuel costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
693.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
具体说明:
Leased long term on a business farming tenancy
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Yield remains the same, yet this could be offset by any loss linked with organic conversion. Difficult to quantify at this time.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Quality remains the same, yet this could be offset by any change linked with organic conversion. Difficult to quantify at this time.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
More expensive technology than conventional fertilisers
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil water infiltration evident
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Slightly improved moisture capacity of soil evident and will improve long-term
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
Slightly reduced soil crusting evident and will improve long-term
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Slightly reduced soil compaction with more soil air space evident and will improve long-term
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Improvements in available soil nutrients
土壤有机物/地下C
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Increased potential for carbon sequestration with addition of carbon rich green waste
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 冬季 | 增加 | 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Good fertiliser option for organic system |
| Improvements in soil health will benefit farm for many years |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Sustainable method of soil health improvements and crop fertilisation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Relatively expensive to implement | The farm is organically certified so costs offset from higher organic food prices as this technology fits within certification. Additional farm subsidy to support technology would also be beneficial in the future if policy changes. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Expense to implement | Recognition through farm subsidy |
| Have to take a long-term approach, this is not a quick fix | Set a long-term sustainability and soil health plan for repeated application management |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
30/09/2020
注释:
Ongoing meetings and support to land user by SLM specialist
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块