Rainwater Harvesting for Olive Production [巴勒斯坦国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Joren Verbist
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_6437 - 巴勒斯坦国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
Research Associate – Spatio-temporal assessment – Resilient Agrosilvopastoral Systems (RASP) – Restoration Initiative on Dryland Ecosystems (RIDE):
Haddad Mira
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
约旦
Scientist, Soil and Water Conservation – Resilient Agrosilvopastoral Systems (RASP):
Strohmeier Stefan
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA); Institute for Soil Physics and Rural Water Management (SoPhy) – University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences (BOKU) (Vienna, Austria)
奥地利
Research Team Leader – Soils, Waters, and Agronomy:
Nangia Vinay
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
摩洛哥
Senior Natural Resources Economist – Resilient Agrosilvopastoral Systems (RASP) – Social, Economic, and Policy Team (SEPT):
Dhehibi Boubaker
International Center of Agriculture Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA)
突尼斯
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
ICARDA Institutional Knowledge Management Initiative有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA) - 黎巴嫩1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Microcatchment water harvesting captures, stores and allows safe overflow of excess surface runoff collected during heavy rainfall events. The intercepted and deep-infiltrated water enhances soil moisture at/around the microcatchment structure. This eventually boosts plant productivity in dry areas, mitigates land degradation, and benefits the local farming communities’ livelihoods
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
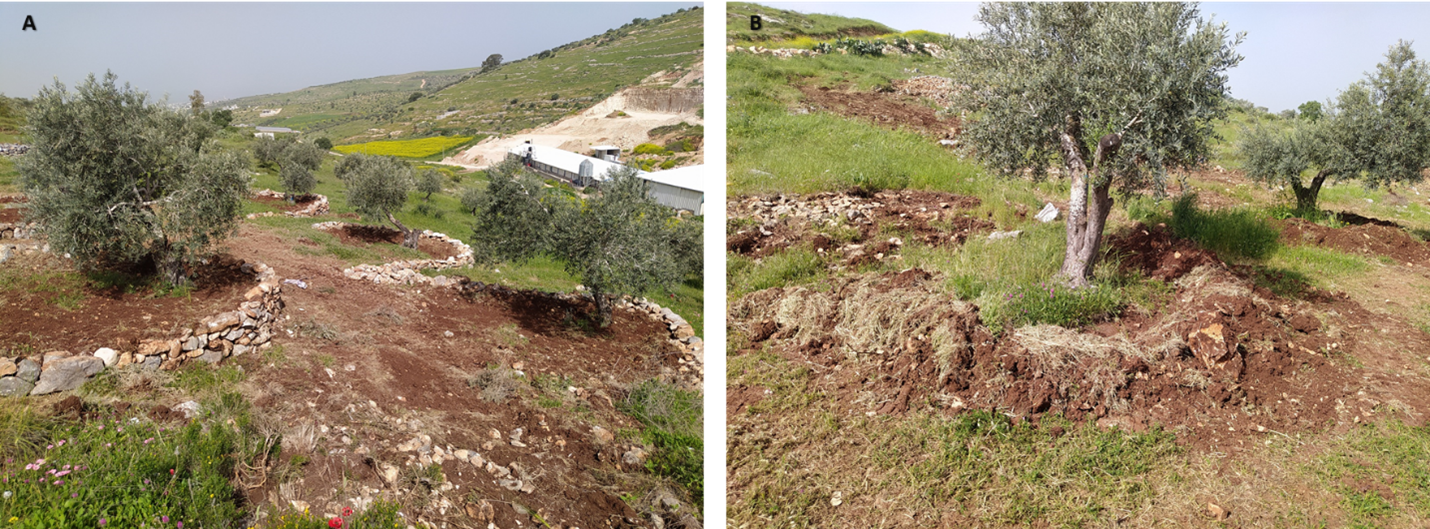
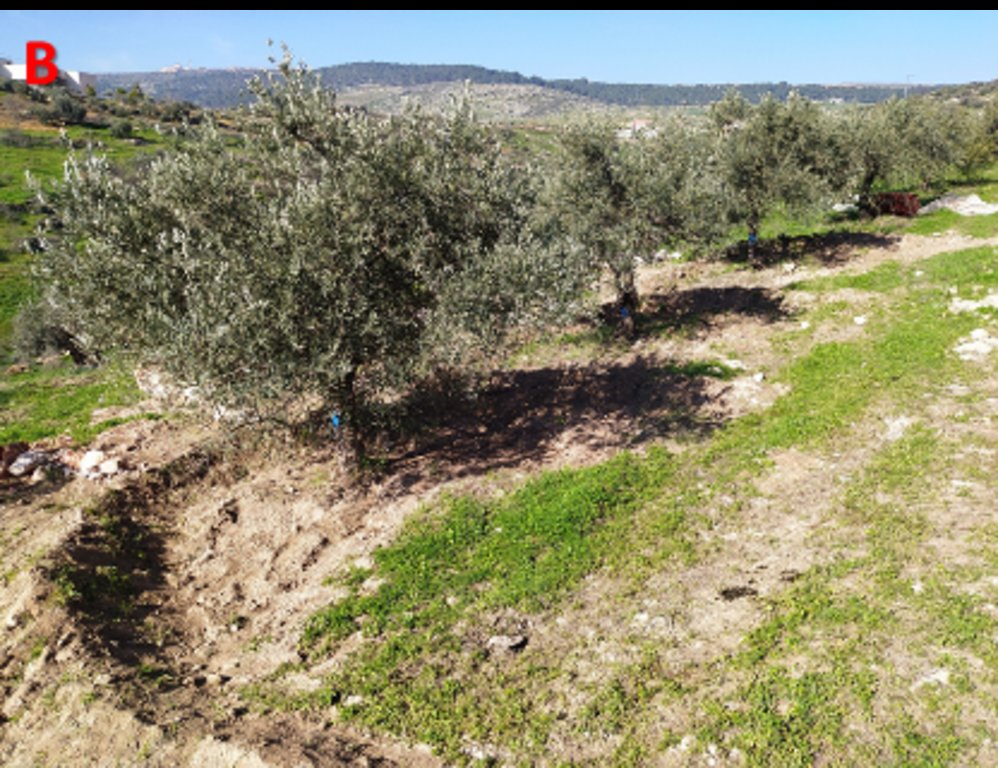
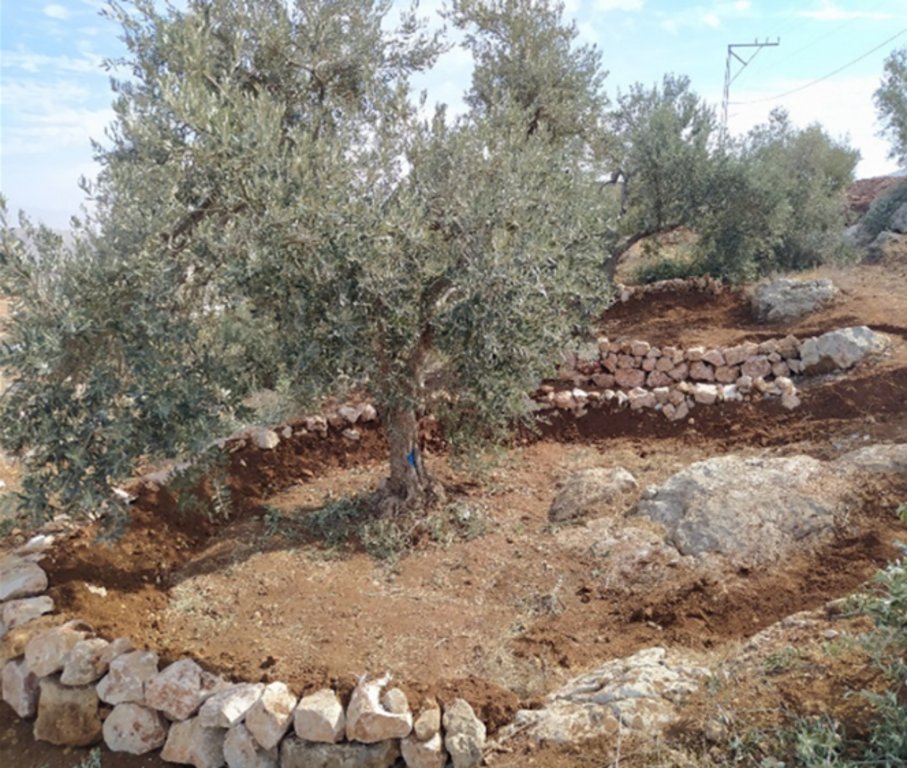
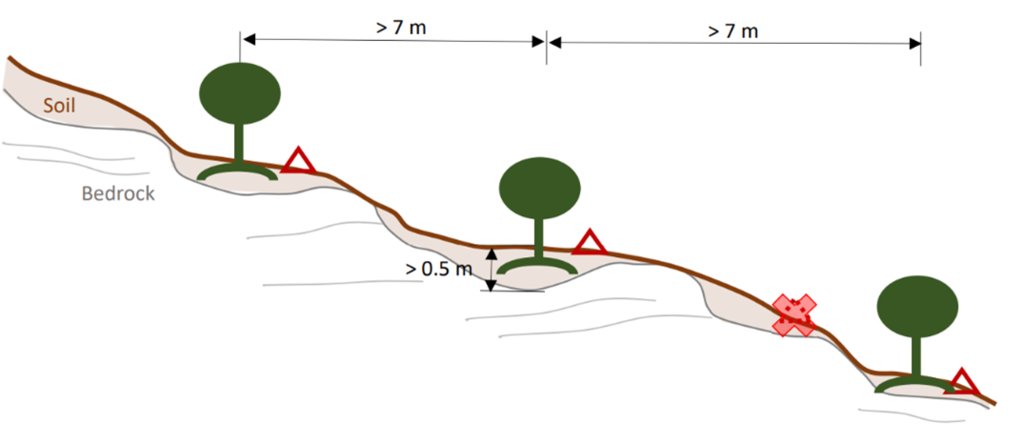
In Palestine, rainfed olives are traditionally cultivated within undulating landscapes with an average annual precipitation ranging between 400 and 700 mm. Olive trees are well known for their resilience to droughts. However, degraded and steeply sloping areas have limited water infiltration and storage capacity: a large proportion of rain forms surface runoff, further speeding up land degradation through erosion and the removal of fertile topsoil, leading to decreased soil health and productivity. The International Center of Agriculture Research in Dry Areas (ICARDA) among others, recognised these issues and superimposed microcatchment water harvesting structures on existing rainfed olive trees in marginal and degraded drylands of Palestine. This technique aims to improve yields by increasing soil moisture through capturing runoff and enhancing infiltration. Thereby, it also decreases the potential for land degradation through surface runoff. This has positive impacts on the local land users and land owners. These are often considered marginalised groups because they lack access to off-farm work and finance to invest in their farms. Additionally, these farmers are directly experiencing the negative impacts of climate change, such as more frequent droughts which can be linked to declining yields, and decreasing farm income. Depending on local climate, topographic and soil conditions, olive trees are usually spaced 5-10 meters apart to avoid competition for water.
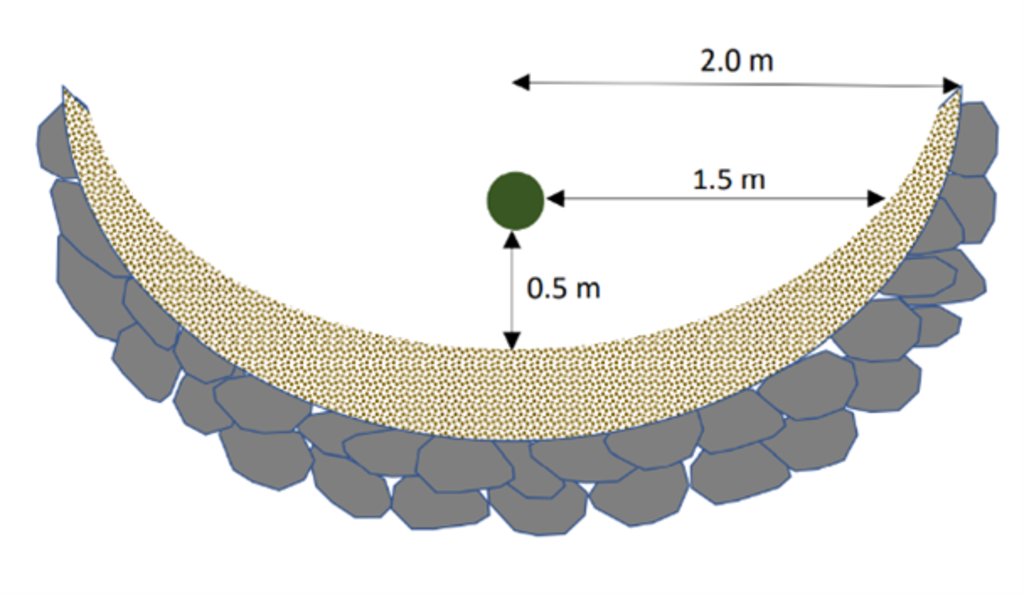
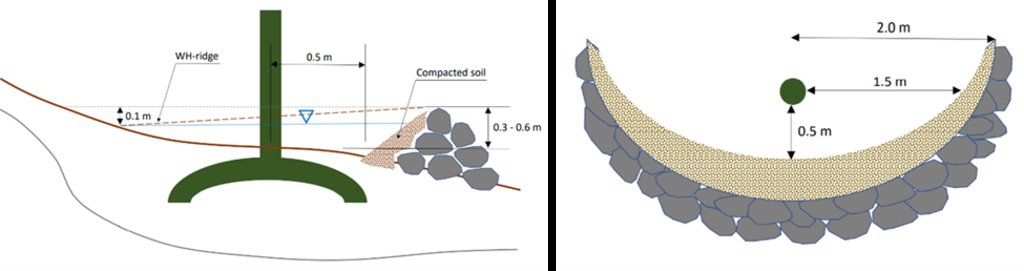
The land is first surveyed and then the microcatchment water harvesting structures (technically termed “semi-circular bunds”) are designed with the tips of the structures on the contour. They are constructed around 0.5 meters downslope of each olive tree in a semi-circle of around 4 meters diameter. The structures are created through stone foundation and bunds topped with a compacted soil layer. The height of the structures varies between 0.3 meters and 1.2 meters. As a first step, stones are placed and fixed in a semi-circular shape. Secondly, the soil inside the structure is slightly levelled. Thirdly, more stones are placed to heighten the bunds. Lastly, excavated and surround soil is put over the stones and thoroughly compacted. The estimation of establishment cost is 7 USD per meter of bund, implying a total cost of approximately 7000 USD per hectare.
The life-duration of the water harvesting system implemented in highly sloping areas, is estimated at 15 years with yearly maintenance cost estimated at 3 USD per tree – 300 USD per hectare. Without maintenance, the life-cycle of the system will be less.
Land users appreciate the technology because it improves their olive yields and thus income. They state that the topsoil maintained in situ, and the improved soil moisture, have positive effects on their harvest. Land users also acknowledge that implementing and maintaining increases the workload. Nevertheless, due to the local material requirements, the costs are low and thus perceived as positive.
Data presented in this documentation are partly made available under the project 'Testing and Out-scaling in situ Water Harvesting Technologies in Palestine' led by ICARDA in collaboration with the Applied Research Institute Jerusalem, Palestinian Ministry of Agriculture, and National Agricultural Research Centre in Palestine. The project is under the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) – a regional project “Implementing the 2030 Agenda for water efficiency/productivity and water sustainability in NENA countries” directly under the Regional Water Scarcity Initiative. The Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency funded the project.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
巴勒斯坦国
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2021
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 橄榄树
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
The area is rainfed and the water for crop use in enhanced due to rain water harvesting.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 森林种植管理
- 横坡措施
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design, with detailed cross-sectional (left) and top (right) views; definition of dimensions
日期:
2022
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design in hillslope direction; definition of spacing constrained by the local ‘soil pocket’ hillslope pattern.
日期:
2022
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
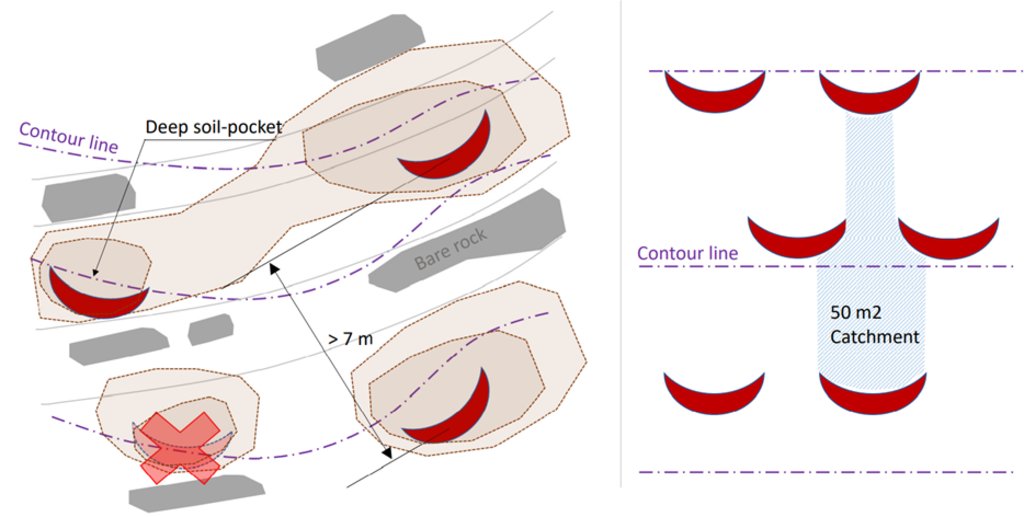
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design from a top view; definition of minimum microcatchment areas contributing to the rainwater harvesting pits.
日期:
2022
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Microcatchment rainwater harvesting design, with detailed cross-sectional (left) and top (right) views; definition of dimensions.
日期:
2022
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1 Hectare
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Field survey for contours | |
| 2. | Place Stones | |
| 3. | Soil Removal | |
| 4. | Stone bund around tree | |
| 5. | Stone bund topped with excavated soil |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
7000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The project met the total costs for establishment.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Incidental repairs |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
300.0
注释:
The land users are expected to continue to carry out maintenance themselves.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Improved soil moisture provides resilience for droughts, reducing failure risk
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Not damaging the bunds may hinder land management
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Inputs for repair and implementation is required
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Because soil moisture is increased, yield is as well and risk is decreased
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Building and repairing the bunds requires labour
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Local farmers were included in the process, improving their knowledge
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased yield |
| Decreased land degradation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduced and reversed land degradation |
| Increased yield |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Increases the workload | In the current state this cannot be overcome. However, alternative structures may be considered e.g., pre -fixed. |
| Limited availability of suitable stones | The purchase of stones or alternative materials such as wood or clay, or alternative structures such as pits. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
2021/2022
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Boubaker Dhehibi, Mira Haddad, Abdallah Alimari, Sameer Shadeed, Stefan Strohmeier, Issam Nofal, Anas Sayeh, Ibtisam I. O. AbuAlhaija, Mohammad Besharat, Imad Ghenma, Vinay Nangia. (6/3/2023). Potential Of Water Harvesting as a Strategic Tool for Resilience, Sustainable Livelihoods, and Drought Mitigation in the Olive Farming System in Palestine. Beirut, Lebanon: International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas (ICARDA).
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11766/68288
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块