Calcareous soils management [埃及]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Daniel Danano Dale
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_716 - 埃及
- Calcareous soils management: March 18, 2019 (public)
- Calcareous soils management: April 26, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 23, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- Calcareous soils management: March 19, 2017 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
This technology serves many purposes but particularly tackles problem of land degradation due to soil fertility decline, waterlogging and soil surface crust
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Managing calcareous soils through combined structural measures and chemical amendments methods for improving soil productivity and reduce land degradation
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
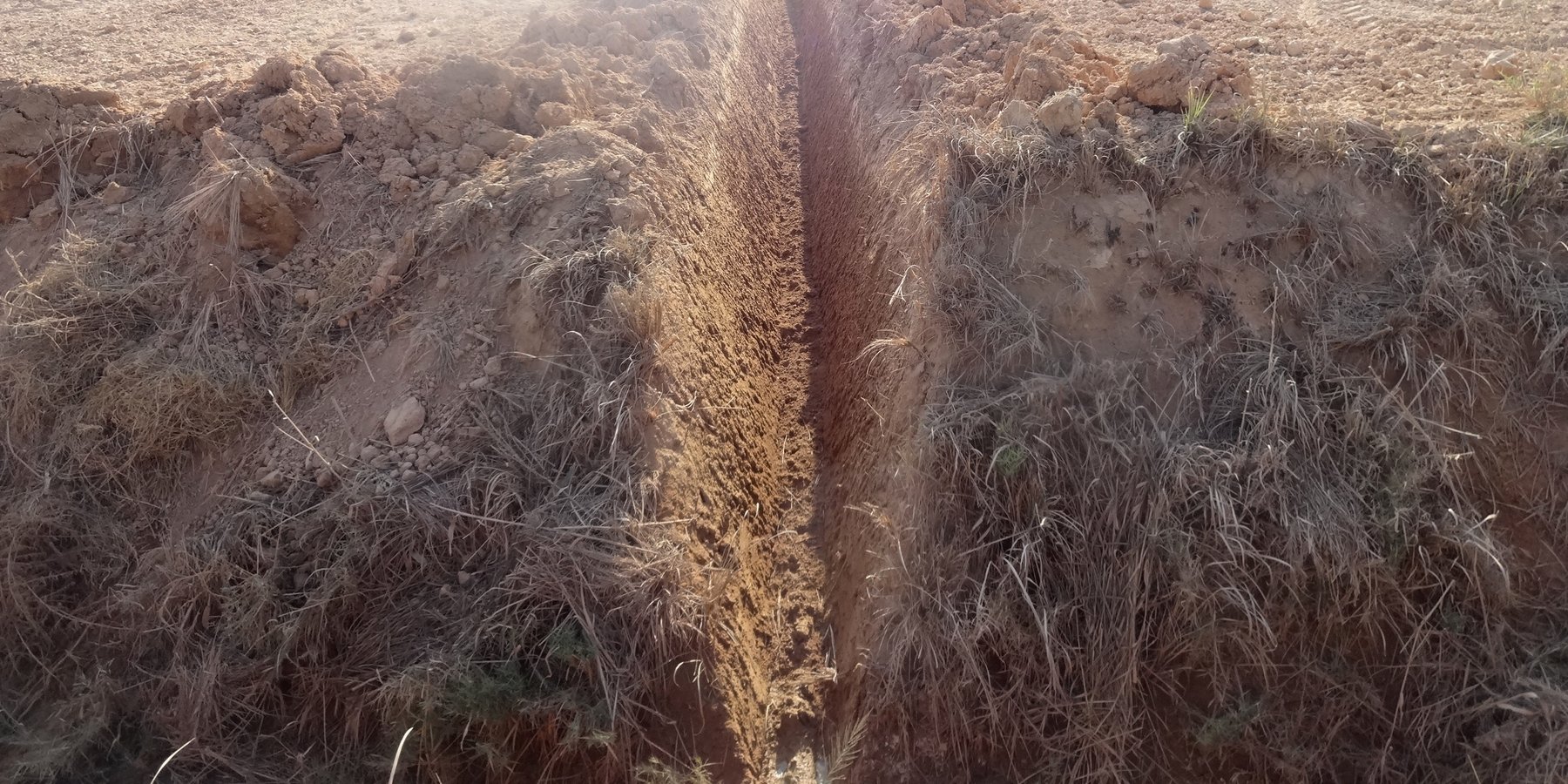
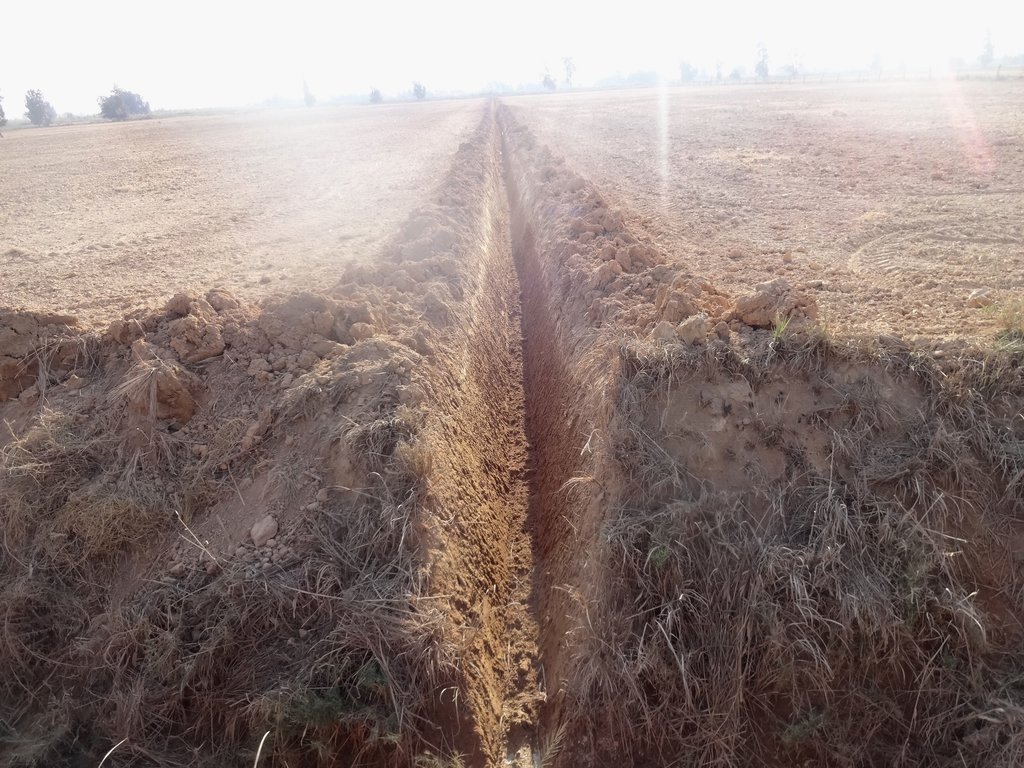
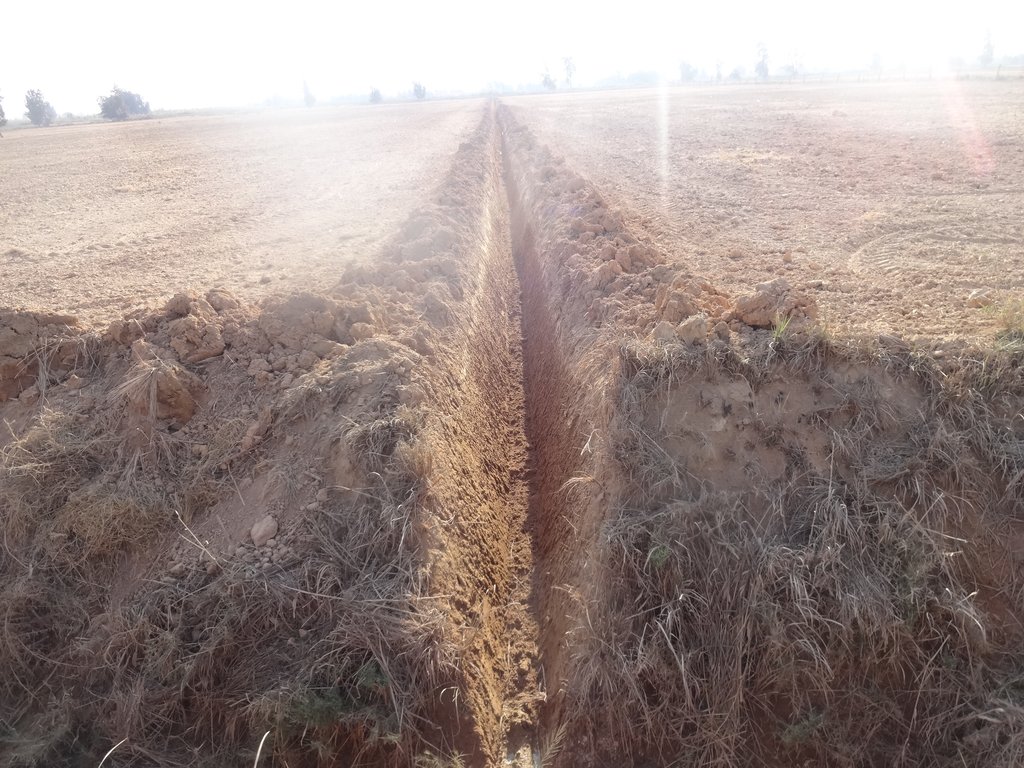
The technology is applied to facilitate drainage in calcareous soils (high calcium carbonate soils) that in addition suffer water logging. The technology is tested in research plots and then demonstrated on farmers field. The research and piloting is carried out by the Soil and Water Research Institute of Egypt. The technology is applied in agricultural fields where variety of cereal crops and vegetables and livestock feed is grown. These fields have been continuously farmed (soil nutrients mining) and have been exposed to varying land uses. The technology area is dominantly owned by smallholder farmers, who are forced to use the land for growing crops for their livelihoods (consumption and market). the fields could be under cultivation for two or more cropping annually and are exposed for varying degradation risks.
farm fields that are degraded by water logging and high calcium carbonate content (increase in the pH) are treated first in constructing surface drains that are laid out at sloping gradients towards the outlet, so that excess water is safely drained from the field. Ammonia gas 82% is ingested in the soil after seedbed preparation to lower the pH content of the soils. Excess water after irrigation is drained by the drains placed in the field at intervals.
The soils that degrade from water logging and high pH are treated by the combination of measures that are part of the technology. Water is drained by the drains and alkalinity treated by soil amendments in injecting ammonia.
Benefits of the Technology are reduced soil degradation, improved soil quality and health, and productivity increase (crop and fodder).
Land users liked the technology as it helped them increase crop and fodder production. water logged crop fields are safely drained becuse of the drains that remove excess water from the field to safe outlets
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
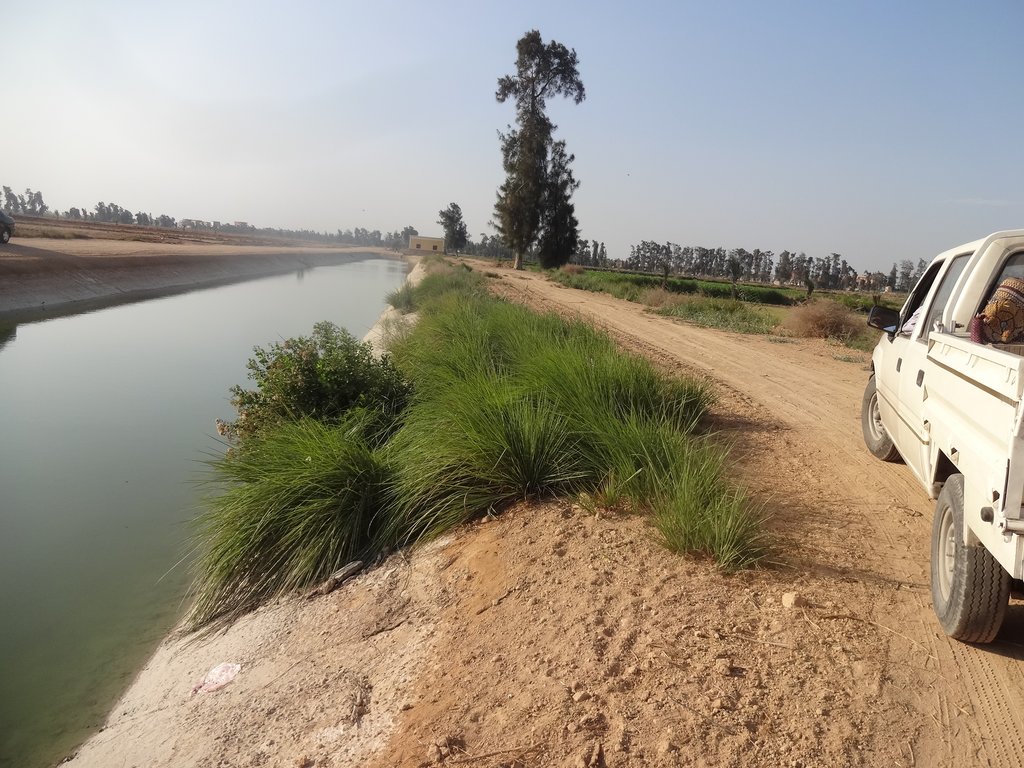
Farmers' field where the technology is implemented: Photo by Daniel Danano , Nile Delta, ElNubaria
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃及
区域/州/省:
El Nubaria
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
注释:
The technology is being applied in many farmers' fields particularly in the newly reclaimed lands of El Nubaria and others
Research and farmers fields demonstration
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 其他
- wheat, rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Minimum 2 or 3 in most cases

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 水牛
- cattle
注释:
In the area, land management is the most indispensable investment, without which livestock and crop productions becomes virtually impossible.
Livestock density: Livestock are mostly stallfed and sometimes let to seasonal grazing after harvest
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
注释:
Land use could change in such a way that some years the land is used for cropping and on the other used to grow fodder for animals (cultivated - pasture- cultivation)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
注释:
2-3 crops could be irrigated in a year depending on the type of crop
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
- sustainable soils management
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Soil conditioners such as ammonia hydroxide for reducing the pH of soils.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pw:水浸

水质恶化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 适应土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The dimensions of the drains vary from (0.5 m - 1.5 m wide) depending on the spacing of the drains. In the case of narrow spacing's of the drains the width is smaller and when the spacing is larger then the width of the drains gets larger as well (7 - 20m). The depth of the drains is normal bigger near the outlets it could range from 0.3 m at the beginning and could be as deep as 1 meters near the outlet
作者:
-
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
18.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
80 LE (Egyptian Pound)
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | land preparation / seed bed preparation | October -November |
| 2. | constructing drainage ditches | November |
| 3. | injecting soil conditioners | November |
| 4. | stabilizing drainage banks | November |
| 5. | planting | Nov - Dec |
| 6. | weeding and cultivation | Dec-Jan |
| 7. | harvest | April |
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | land tilling | 2-3 times a year |
| 2. | cultivation and weeding | 2 times |
| 3. | repair in channel and ditch breaches | ones a year |
| 4. | removing silt from main drains | ones in a year or ones in 2 years |
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 干旱
Rainfall is less than 25 mm per annum. Desert lands predominate outside the Nile Delta, which are under reclamation in the Nubaria area; few kilometers along the two sides of the Nile River
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
具体说明:
Due to sea water entrusion along the mediterranian coast and in areas where there is no adequate irrigation water
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users could be of both gender. It could be used by all age groups but more dominant users are the middle aged as they have the labor that is needed to do all kinds of farm operation or the land could be contracted out to companies or cooperatives.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Without the technology no production of either crop or livestock fodder is possible
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Land productivity decreased very much and in certain cases it reached to a level where crop farming was impossible because of waterlogging
饲料质量
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
animal feed growth has been increased as the soil conditions to support fodder crops ahs been substantially improved because of the technology
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
生态影响
水循环/径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤有机物/地下C
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 劳动力可用性(例如,由于迁移)
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology has the advantages primarily of reclaiming water logged farm fields to more crop friendly environment. It is not very costly because the drains could be easily made by farm implements the land users have or could be easily rented from cooperatives or companies that provide the service. The amendments used are also within the reach of land users to purchase them and are available in the near vicinities |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Require frequent maintenances. Take away substantial segment of the farm out of cropping interfere in farm operations (pose difficulties for farm machineries and tools to be easily maneuvered as they restrict free turning of machinery and the tractors pulling them. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
08/11/2016
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块