INTEGRATED AGRICULTURE-BASED LAND USE IN AREAS WITH SALINE SOILS [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Laksamee Mettpranee
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
technologies_7276 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Siangsunthia Mana
泰国
SLM专业人员:
co-compiler:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Salinity and associated land degradation in parts of the Northeast of Thailand limits production. Knowledge of saline soil management was integrated into an organic agriculture system: dolomite application adjusted pH levels, manure increased the soil's organic matter, while fermented bio-extracts stimulated root systems. Yields of chili pepper and parsley improved greatly.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
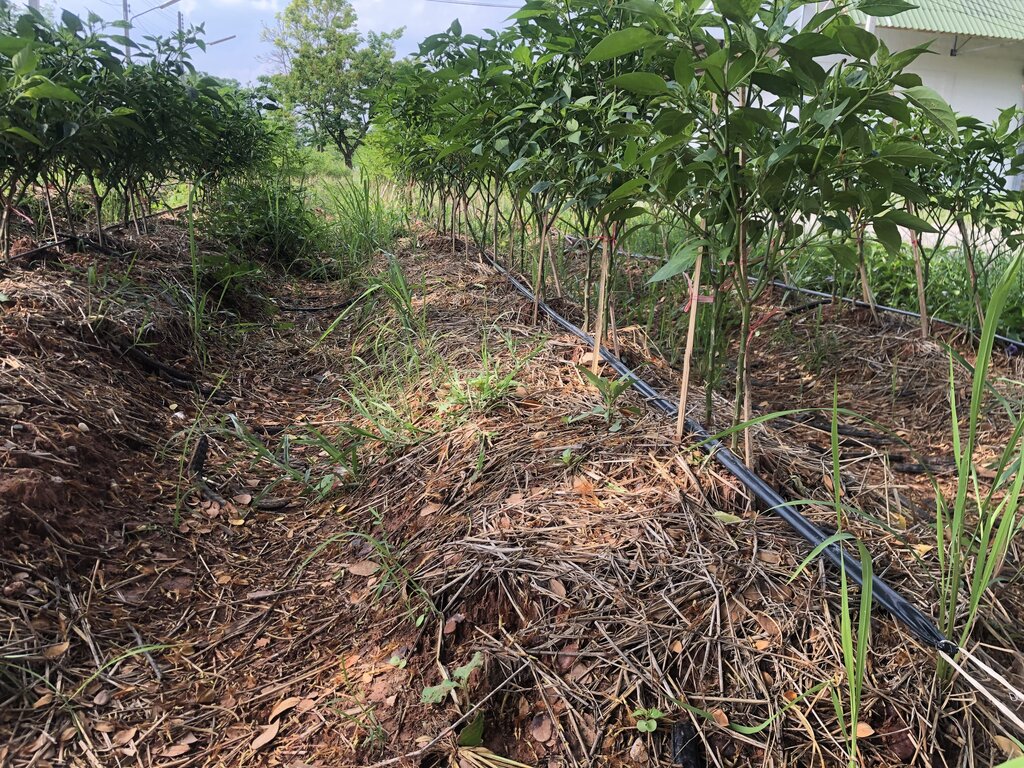
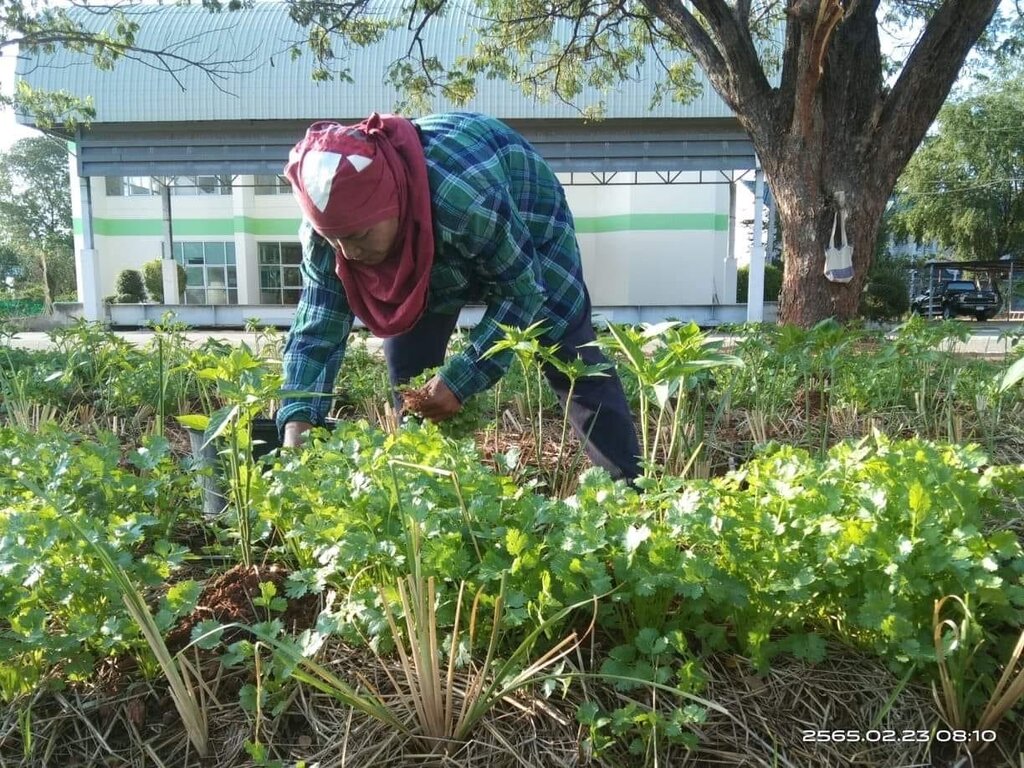
The problem of soil degradation in regions with saline soil such as parts of the Northeast of Thailand shows up as chemical and physical deterioration and low fertility, which are significant limitations to land use. These issues are exacerbated by water shortages in the dry season and excessive rainfall during the cropping season.
To address this, a group of farmers interested in learning effective soil management strategies has formed. Their aim is to mitigate the effects of salinity and improve crop productivity on their farms. The group has received support in the form of production inputs, including microbial activators for producing organic fertilizers and bio-fertilizers, vetiver grass of the Songkhla 3 variety, and dolomite. Additionally, they have implemented guidelines based on learning, observation, and trial and error to develop a 0.04-hectare vegetable plot.
Previously, this area was characterized by low soil fertility and salinity, which resulted in reduced crop yields. The sandy clay loam soil, though slightly saline, had very low moisture content during the dry season. Furthermore, the area lay outside the irrigation zone. To answer these questions, farmers in the community of Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai Sub-district, collaborated to develop sustainable farming practices. With support from the Land Development Department, they integrated knowledge of saline soil management into an organic agriculture system.
This technology began with soil analysis and appropriate measures for managing saline soil before land preparation. Farmers combined their wisdom with Land Development Department technologies, such as dolomite application to adjust pH levels and eliminate pathogenic microorganisms affecting chili pepper growth. Manure was applied to increase the soil's organic matter, while fermented bio-extracts containing beneficial microbes stimulated root systems.
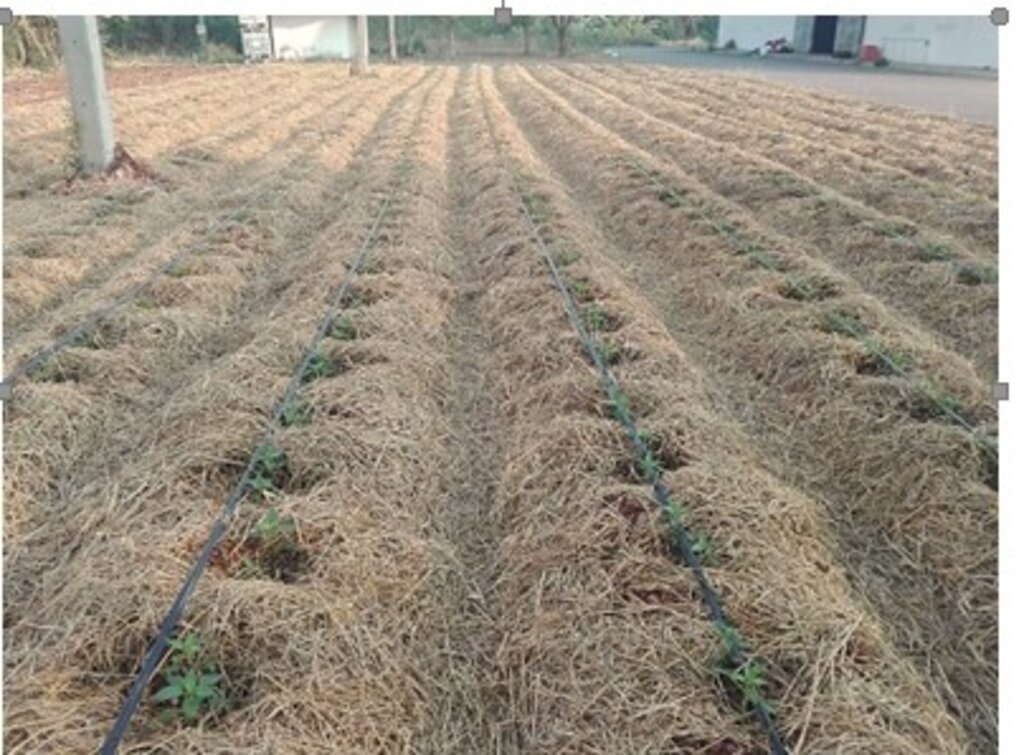
To conserve soil moisture, drip irrigation technology was installed in the chili planting plots, and the soil was covered with straw. Vetiver grass was also used to further conserve moisture as a grass barrier strip. After these soil amendments, the soil structure improved, becoming friable and suitable for planting chili peppers—specifically the Amphawa Gold variety, which has a high market demand.
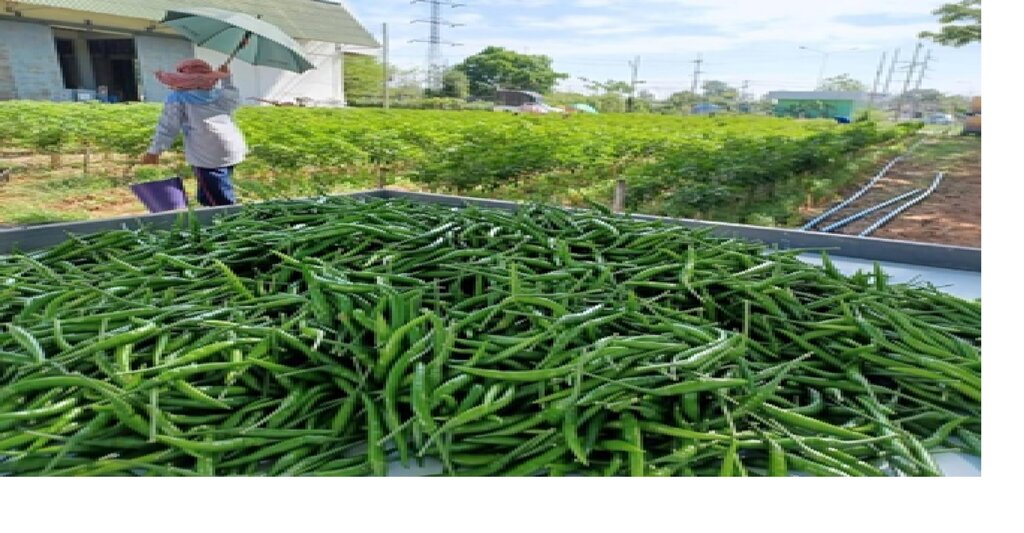
Additionally, parsley was intercropped between plots to optimize land use. On average, the chili pepper yields reached 400 kilograms per 400 square meters over 180 days, with a market price of about 2.50 USD per kilogram. Parsley, as a by-product of watering the chili pepper plants, produced just over 100 kilograms per 400 square meters per production cycle of chili peppers.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
Nakhonratchasima
有关地点的进一步说明:
Moo 5, Ban Kok Phrom, Non Thai sub-district, Non Thai district
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2022
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Farmer groups in Non Thai Subdistrict and nearby areas transfer knowledge through the volunteer soil doctor network.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 蔬菜 - 其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
注释:
The area is outside the full irrigation zone and has a local or community small size water sources.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A5:种子管理,改良品种
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化

生物性退化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Cultivation plot preparation
1. Plough and harrow the soil, then plough again using a 65 HP tractor and a small Kubota tractor for further tilling.
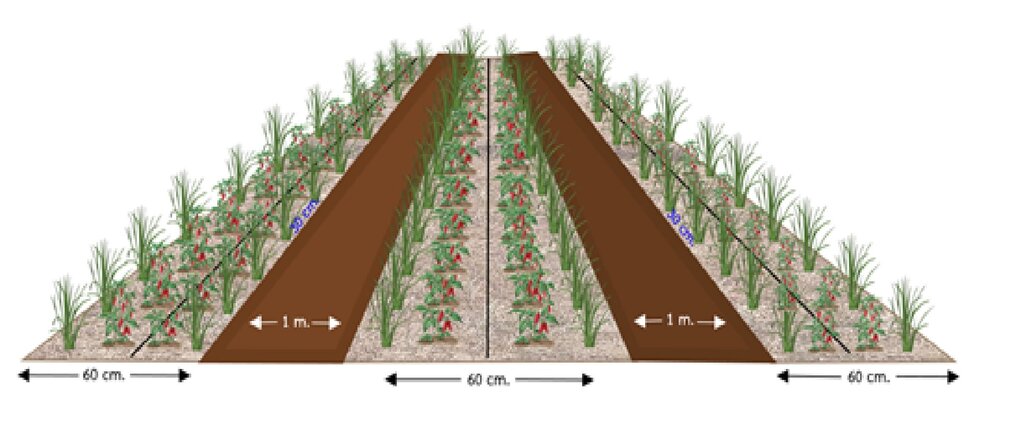
2. Raise ridges to 30 cm high and 60 cm wide, with 1-meter spacing. Burn plant residues to kill bacteria and fungi, then water to extinguish the blaze.
3. Apply dolomite at 156.25 kg/hectare and bioslurry (100 kg/rai) after fermentation. Mix in bio-extract (2 spoons per 20L water) to improve soil and stimulate root growth.
4. Mix soil with 3 handfuls of soil and 1 handful of dung.
5. Dry the soil for 7-14 days, then place a 10 cm banana stem at the bottom of the planting hole before planting.
Planting and maintenance
1. Plant 35-day-old Amphawa Gold chili peppers, sprinkle parsley around the plot, cover with rice straw, and plant vetiver around the edges.
2. Water in the morning and use fermented Indian Laburnum pod extract (2 spoons per 20L water) in the evening. Spray wood vinegar weekly to prevent fungi.
3. When buds appear, spray LDD 2 every 5 days in the evening.
4. Set up a drip system for backup watering in case of labor shortage.
5. If anthracnose occurs, remove affected chili peppers. For aphids, spray plain milk on the affected areas, leave for 20 minutes, then wipe off.
6. Remove old leaves at 45-50 days to expose the trunk to sunlight, promoting better growth and higher yields
Harvesting yields
1. Harvest the first generation of chili peppers at 65 days, then harvest every 5 days for the next 6 months.
作者:
Ms. Nisa Sahoh
日期:
01/04/2025
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
1.12ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
6.25rai
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
8.82 USD
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Drip irrigation system installed | Before mulching/ cropping (March) |
| 2. | None | |
| 3. | None |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Drip lines | metre | 4.6 | 1.76 | 8.1 | |
| 劳动力 | PVC tubes | metre | 10.0 | 0.59 | 5.9 | |
| 劳动力 | 1000 litre tank | piece | 1.0 | 67.65 | 67.65 | |
| 劳动力 | None | None | ||||
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 81.65 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 81.65 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cultivation plot preparation | |
| 2. | Planting and maintenance | |
| 3. | Harvesting yields | |
| 4. | In case of an anthracnose epidemic, destroy the chili pepper stricken with the disease. During an outbreak of aphids, spray with plain milk at the point of the outbreak. Leave it for 20 minutes and then wipe it off. | |
| 5. | Remove leaves of the chili peppers when they are 45-50 days in order to make the trunk expose to the sun. This helps chili peppers grow well and increase their yields. |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Ploughing to prepare plot | Person days | 1.0 | 8.08 | 8.08 | |
| 劳动力 | Soil preparation | Person days | 1.0 | 4.41 | 4.41 | |
| 劳动力 | Cultivation, watering, plot maintenance | Person days | 1.0 | 24.25 | 24.25 | |
| 劳动力 | Harvesting | Person days | 1.0 | 137.64 | 137.64 | |
| 设备 | Tractor/ cultivator maintenance | Fuel etc | 1.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Chili peper plant | plant | 1200.0 | 0.029 | 34.8 | |
| 植物材料 | Parsley seeds | gram | 600.0 | 0.01 | 6.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Rice straw | kilogram | 180.0 | 0.1 | 18.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fermented bio-extracts | liter | 120.0 | 0.29 | 34.8 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Dolomite | kilogram | 13.6 | 0.73 | 9.93 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Dung | bag | 35.0 | 2.5 | 87.5 | |
| 其它 | Drip line | meter | 4.6 | 1.76 | 8.1 | |
| 其它 | PVC tube | meter | 10.0 | 0.59 | 5.9 | |
| 其它 | 1,000 liter bucket | bucket | 1.0 | 67.65 | 67.65 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 522.06 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 522.06 | |||||
注释:
Drip irrigation systems have no maintenance costs but they are replaced after 2 to 3 years.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
1. Labour costs
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 老年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
Degraded soil, and poor fertility
SLM之后的数量:
Soil amendments make the soil better
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
Plants could not grow
SLM之后的数量:
Plant thrive and give good quality yields continuously.
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
产品多样性
SLM之前的数量:
Plants cannot be planted.
SLM之后的数量:
Integrated cultivation, namely chili peppers, parsley and vetiver for soil amendment
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
There was no cultivation.
SLM之后的数量:
The quantity of products can be sold and exported.
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
社会文化影响
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Conducting natural farming by avoiding fertilizer and chemical application
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
社区机构
SLM之前的数量:
Studied how to solve problems by themselves
SLM之后的数量:
Building interaction of farmers groups in the area based on consulting and mutual problem solving
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
There was no knowledge propagation
SLM之后的数量:
Farmers in the area accept the technology and gather together to learn methods of soil management so that they can grow plants and implement them in their own areas.
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
SLM之后的数量:
Mulching with plant debris, rice straw and growing plants.
注释/具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
养分循环/补给
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Nutrients increase from integrated cropping such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etcnts increase from integrated cropping such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc
注释/具体说明:
Using a questionaire
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Plant varieties which are cultivated in the area grow more such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc.
注释/具体说明:
Using a questionaire
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
--
SLM之后的数量:
Plant varieties which are cultivated in the area grow more such as chili peppers, parsley, vetiver etc.
注释/具体说明:
Using a questionaire
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
Information from a questionnaire
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 |
注释:
Rainfall has decreased due to climate change, a result of global warming.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
The land users are responsible for covering the cost themselves. Supported by agricutural production factors from LDD.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Yes. Use the drip system for morning watering with organic fertilizer.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Farmers manage soil and water and use integrated farming methods, leading to additional income opportunities. |
| Farmers in the area are committed to overcoming challenges and limitations related to soil, water, and environmental conditions. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Support for forming farmer groups in the area to exchange knowledge on soil management for increasing crop yields and addressing local farming issues, as well as developing professions for community farmers. This includes promoting the production of safe, non-toxic crops and creating value for products, leading to increased household income for farmers. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farmers who use the technology must learn to follow procedures carefully. | Training and experience |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology used is precision farming. Farmers who use the technology must pay attention to every step. | Training |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
10
- 与土地使用者的访谈
10
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
2
注释:
https://lddmordin.ldd.go.th/web/data/Tank_Soilmanagement/Soil_58.pdf
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Sustainable soil management practices in Asia
URL:
https://e-library.ldd.go.th/library/Ebook/bib10906.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块