Reconstitution of Soils [意大利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Chiara Cassinari
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ricostituzione
technologies_7346 - 意大利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Manfredi Paolo
mcm Ecosistemi
意大利
co-compiler:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
NEW LIFE Project (NEW LIFE)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
m.c.m Ecosistemi (m.c.m Ecosistemi)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Reconstitution is a technology that counters land degradation and according to the theory of "Circular Economy" it's a sustainable land management technology
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [意大利]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- 编制者: Chiara Cassinari
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Reconstitution of soils is a pedotechnique based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials to achieve benefits in areas with barren, degraded, desertified and/ or sealed soils.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
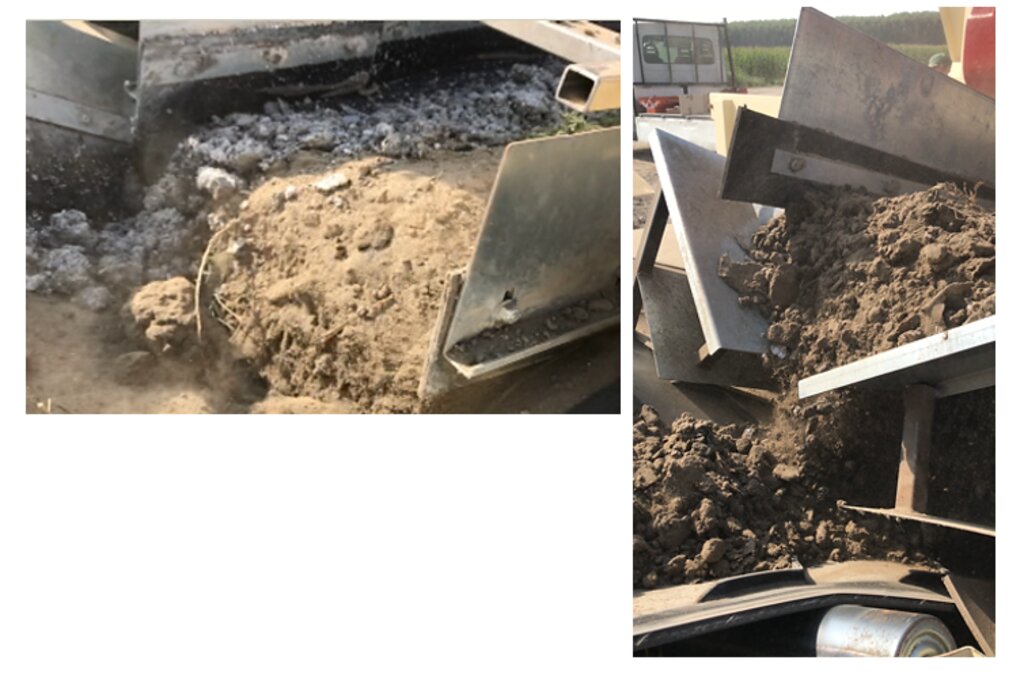
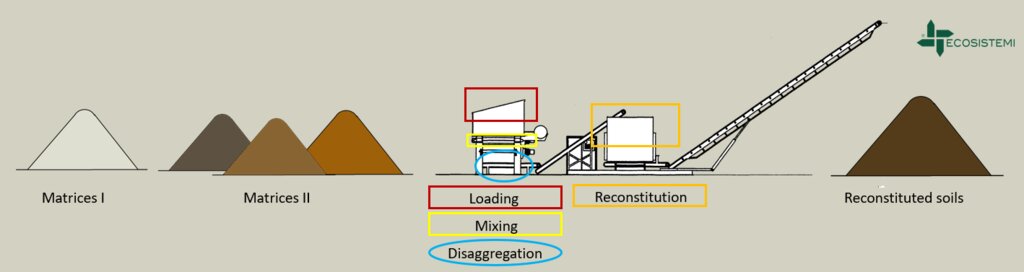
Reconstitution of soils to generate an Anthroposol is a technology based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials or “matrices” (from “matrix” in Latin: everything that is the foundation of something) to achieve ecosystem benefits, especially in areas with degraded, desertified, barren and/or sealed soils. The technology applies a conceptual model based on the production of new soil aggregates with targeted environmental and soil characters generated via a chemico-mechanical process that entails reusing residues of specific origin. The activity is consistent with the principles of a “Circular Economy”, applying restoration ecology, use of compatible waste and saving the non-renewable resource of soil. Reconstitution is covered by two patents of the mcm Ecosistemi s.r.l. company.
Reconstitution applies the process to two groups of pedomaterials. Firstly, primary matrices (matrices I), represent the main material to be converted into fertile soil. These could be degraded soil itself or inorganic mineral pedomaterials. Secondly, secondary matrices (matrices II) refer to byproducts and waste from production activities. Secondary matrices are divided into two. First, organic - from wood and cellulose processing production activities and from textile and agro-food industries. These are characterized by a high organic component with a high carbon/nitrogen ratio, and a high presence of plant fibres. Second, mineral matrices - especially from mining, the preparation of drinking and industrial water and the management of hydroelectric reservoirs and internal canals. There are four stages.
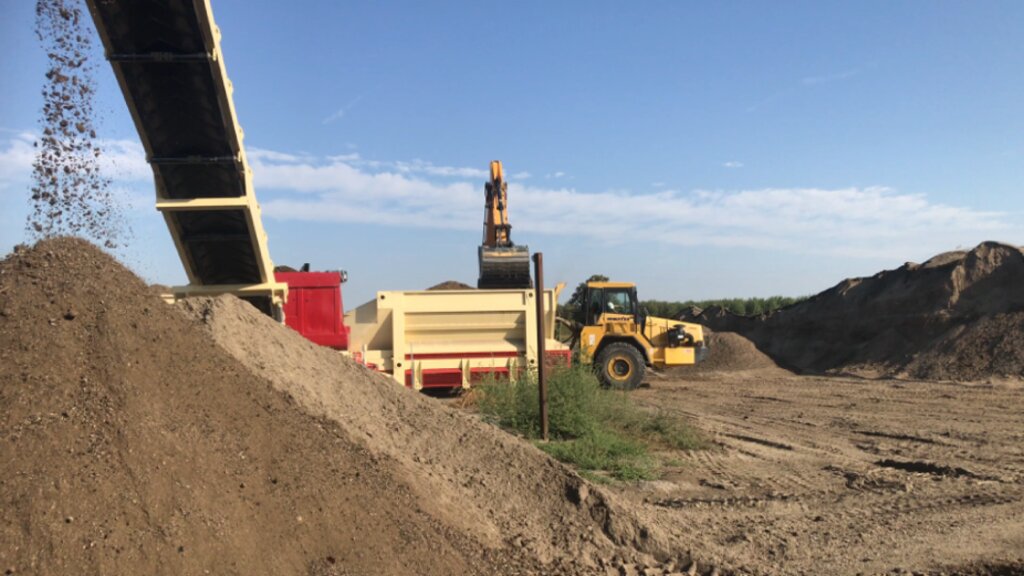
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected according to the type of soil desired and then loaded in the plant. Dosage is calculated through an application program (PEDOGÉNIA), which estimates the chemical properties of the finished product.
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity.
3) Disaggregation: Breakup and defibering through rotating movements at variable power.
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
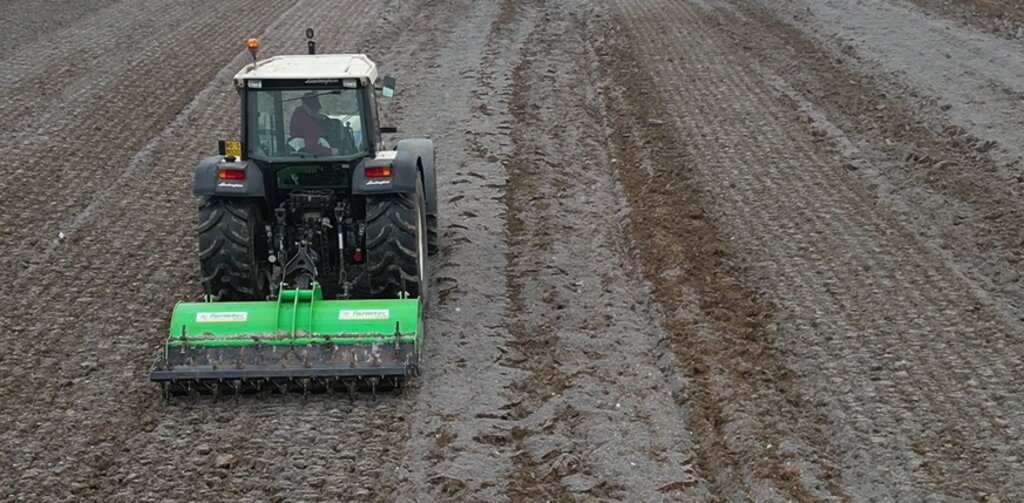
The treatment generates an Anthroposol whose characters and properties are different from the materials of origin.
The properties of the reconstituted soils and the technical-economic sustainability of the pedotechnology have been demonstrated over the years with agronomical tests and experiments, as well as comparative analysis between degraded soils and reconstituted soils. This demonstrates the reconstituted soil’s ability to create a stable pedosystem to carry out its basic functions - storage, filtration, transformation of nutrients and biodiversity pools - for various forms of land use, and ecosystem benefits. Agroforestry restoration with reconstitution has social impact, as it is demonstrated by a EU project (“New Life”), where the Park of Trebbia river has increased utility to people after restoration. Agronomic restoration allows farmers to increase yields using less fertilizer and water. Another environmental and economic advantage is that manufacturing companies which produce waste can reduce costs through the recycling process of reconstitution. For reconstitution, a plant has to be installed near the land to be restored; an overview is presented in 4.1. In addition, earth moving vehicles are needed for the transport and placement of reconstituted soil.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nF3nl4S5X8M
Reconstitution plant
日期:
18/12/2024
位置:
Piacenza, Loc. Mortizza
摄影师的名字:
Paolo Manfredi
注释、简短说明:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kjy95Kz-e70
Construction site: collection of degraded soil to be reconstituted
日期:
18/12/2018
位置:
Piacenza, Gossolengo
摄影师的名字:
Paolo Manfredi
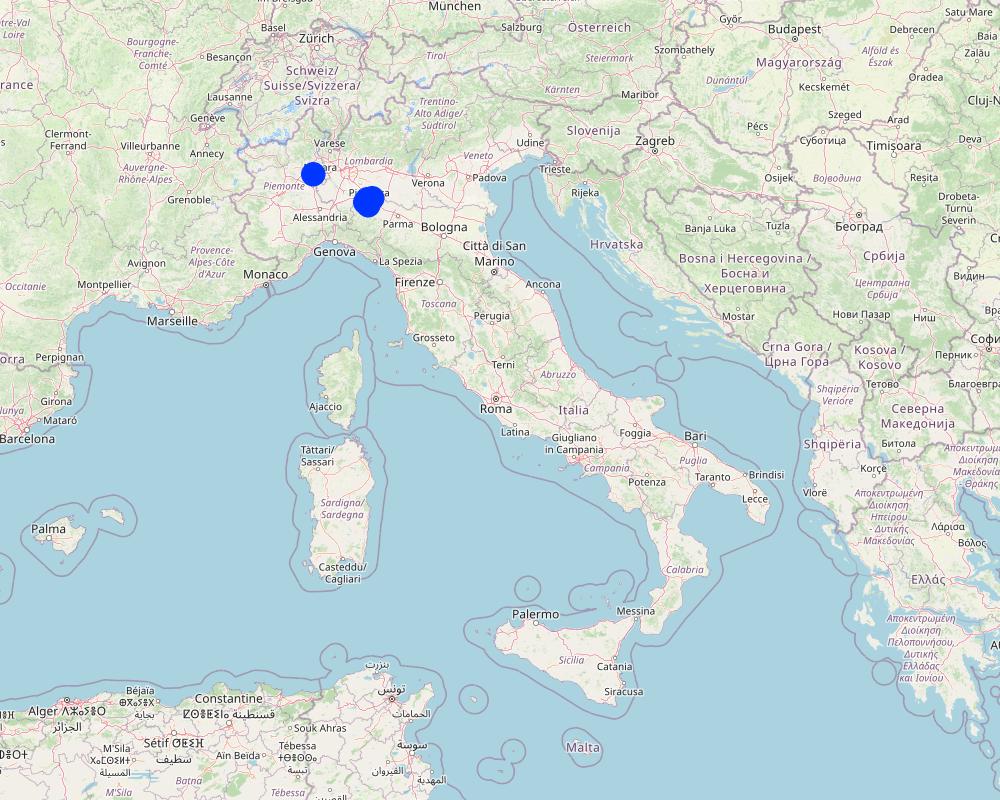
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
意大利
区域/州/省:
Emilia Romagna, Piacenza; Piemonte, Vicolungo
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Regional, National and International projects
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- tomato, fodder crops
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
maize - wheat - tomato

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
- 植树造林
(半)天然林类型:
- 亚热带干燥林天然植被
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
植树造林类型:
- 亚热带旱林人工林
树木类型:
- 金合欢树种
- 山杨
- Salix species
以上的树木是落叶树还是常绿树?:
- 混合落叶或常绿
产品和服务:
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
- 自然灾害防护
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业
矿山、采掘业

不毛之地
具体说明:
degraded, desertified and sealed soils
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 废物管理/废水管理
- ecosystem rehabilitation
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A4:地表下处理

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S11:其它

管理措施
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
- M7:其它

其它措施
具体说明:
addition of organic matter, new soil aggregates, increase water holding capacity
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Ca:酸化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
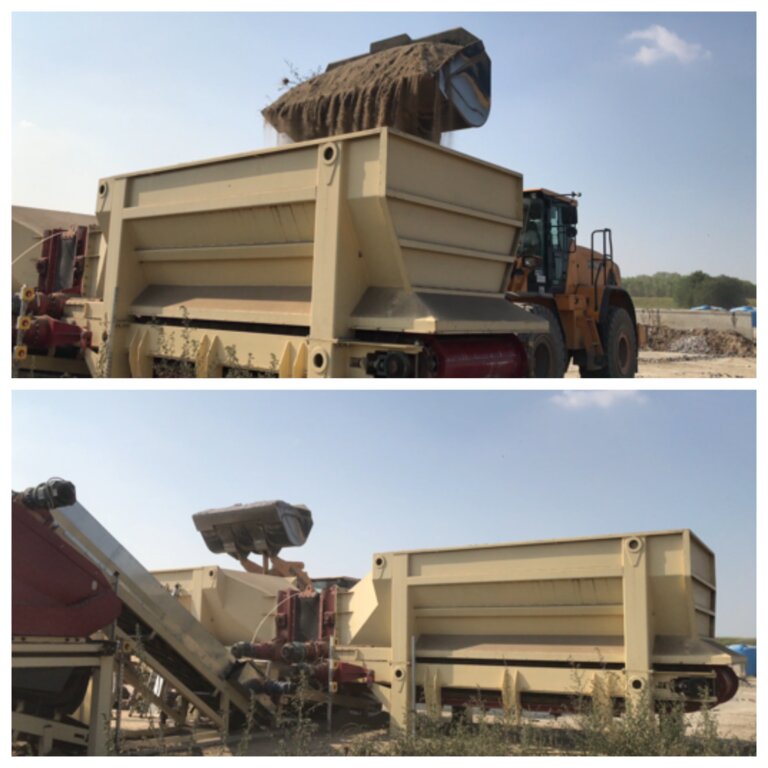
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Reconstituted technology: phases of work:
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected and dosed
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity
3) Disaggregation through rotating movements at variable power
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
作者:
Paolo Manfredi
日期:
12/04/2023
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
10 hectares
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EUR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.89
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
123.00, gross income
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | characterization of the intervention site | no timing |
| 2. | morphological planning | no timing |
| 3. | environmental planning | no timing |
| 4. | pedo-agronomic planning | no timing |
| 5. | moving-plant placement only if the area to be restored is distant from the area where the permanent plant is located | no timing |
| 6. | degraded soil removal and collect | after harvest of crops, if there are |
| 7. | reconstitution | no timing |
| 8. | replacement of reconstituted soil | no timing |
| 9. | final soil placement | no timing |
| 10. | site-specific planting to make soil ready for use | dependence of plants species |
| 11. | land use | no timing |
注释:
The reconstitution plants are 2: one is fixed that is located in an area, the other is a moving-plant: that is it can be located near the area to be restored.
According to the distance between the intervention site and the fixed plant it can be more useful using the moving-plant
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | 3 Workers | person/day | 232.0 | 123.0 | 28536.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Construction area - mobile plant | number | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Earth moving vehicles | number | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Matrices to be used | m3 | 75000.0 | 15.0 | 1125000.0 | |
| 其它 | Reconstitution | m3 | 100000.0 | 2.5 | 250000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1473536.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1655658.43 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Costs related to the matrices to be used and transport (1125000.00 EUR) are covered by company producing waste used. The costs to dispose of matrices II are much higher than taking them to the reconstitution plant.
注释:
degraded land value 0 EUR
restored area value 390000 EUR
restoration using allocation of natural soil (8 EUR/m3, cost of natural soil in Piacenza) added to transport costs = 2100000.00 EUR
restoration using reconstituted soil technology = 28536 + 30000 + 40000 + 250000.00 EUR because 1125000.00 EUR are covered by company producing waste and so not spent for restoration.
Cost related to construction area and mobile plant are the costs for the set up of the area where to put the mobile plant and for it' transport to the intervention site.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ordinary plant maintenance | every 6 months or when needed |
| 2. | Reconstituted soil analysis | every 6 months |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | 1 Worker | person/day | 20.0 | 123.0 | 2460.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | 3 Laboratory staff | person/day | 100.0 | 115.0 | 11500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 13960.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 15685.39 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most important factor affecting costs could be the transport of degraded soil or matrices I to be used to the restoration site in the case of soil sealed
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
891.02
有关降雨的规范/注释:
May: average monthly regionally anomaly +230% (heavy rains); October: heavy rains
February 2023 is the month with less rain 27.6 mm; in May is the rainiest 250.7 mm
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Bulletin ARPAE 2023
农业气候带
- 半湿润
mean annual temperature 14.4 °C Bulletin ARPAE 2023
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Following the soil characterization (data are mean of 30 soil samples) of the last area of intervention with reconstitution; the data describes soil condition before reconstitution.
The soil texture is silty-loam
The aggregate stability index describes soils with poor stability
pH (1:2.5 in H2O) 6.98 ± 0.37
EC (saturated paste) 0.93 ± 0.41 dS m-1
tot CaCO3 10.33 ± 4.36 g kg-1 SS
active CaCO3 3.08 ± 1.24 g kg-1 SS
tot C 10.62 ± 3.68 g kg-1 SS
organic C 10.26 ± 3.44 g kg-1 SS
tot N 1.47 ± 0.43 g kg-1 SS
HA + FA 2.54 ± 1.26 g kg-1 SS
Olsen P 87.83 ± 44.19 mg kg-1 SS
available Fe 74.68 ± 32.97 mg kg-1 SS
available Mn 27.92 ± 15.78 mg kg-1 SS
available Zn 2.30 ± 1.72 mg kg-1 SS
available Cu 4.32 ± 1.34 mg kg-1 SS
soluble B 0.71 ± 0.25 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable K 21.61 ± 34.72 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable Mg 92.68 ± 28.13 mg kg-1 SS
CEC 26.22 ± 4.42 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Mg2+ 2.39 ± 0.50 cmol(+) kg-1
exch K+ 0.42 ± 0.33 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Na+ 0.48 ± 0.22 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Ca2+ 11.82 ± 4.75 cmol(+) kg-1
Chemical fertility is low, intrinsec fertility is poor, global fertility lower-intermidiate
In the link other data about soil analysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Hb0PcmSYGY&list=PLXcG4R_rAdFaqGnKCa0qaL6FcrafvU0VE
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地下水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
是
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
60%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKrAG6jrqXA
作物质量
SLM之前的数量:
70%
SLM之后的数量:
95%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 70% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that wheat quality. in terms of proteins, increased in reconstituted soils
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
65%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
these increment are estimation
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
0
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 40% to 0: this decreasing is an estimation, it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D0II3SGNhKo
土地管理
SLM之前的数量:
40
SLM之后的数量:
100
注释/具体说明:
simplified from 40% to 100%; because of the physical properties of reconstituted soils; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ld8YzGcx6Qw
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
60%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 60% to 10%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
60%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils and so also farm income increases
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
60%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 60% to 100%; because of it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
文化机会
SLM之前的数量:
10%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in a EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJ8gFmV1Onc
娱乐机会
SLM之前的数量:
10%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
15%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 40% to 15%, this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMazUuMaa6o
多余水的排放
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; some laboratory tests demonstrated that reconstitution improves soils permeability
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oDhW-YlBjHA
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 40% to 100%; analyzing the water retention curves in many experimentation sites and comparing them with degraded soils, reconstituted soils has demonstrated to have better water holding capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yqtl4-xYMeo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qy_B3oCyIAM
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
20%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species were sprouted naturally
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils as soil stability index
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g1GhoyIy4sk
土壤结壳/密封
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
0%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 50% to 0%; we tested a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aPQRoaYmrIQ
土壤压实
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 50% to 100%; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil compaction in reconstituted soils
养分循环/补给
SLM之前的数量:
60%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 60% to 100%; the high chemical fertility of reconstituted soils has been demonstrated in a lot of field tests
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
10%
SLM之后的数量:
80%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 10% to 80%; reconstituted soils has high organic carbon with a high C/N ratio; the SOC/clay is optimal
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
SLM之前的数量:
20%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 100% in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFnUsjYLwfw
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
20%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
20%
SLM之后的数量:
100%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
有益物种
SLM之前的数量:
20%
SLM之后的数量:
80%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Q8tqJNai3o
栖息地多样性
SLM之前的数量:
10%
SLM之后的数量:
80%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, physical reconstituted soil properties
干旱影响
SLM之前的数量:
40%
SLM之后的数量:
0%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 40% to 0%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, phisical reconstituted soil properties
碳和温室气体的排放
SLM之前的数量:
40
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; this is an estimation considering reconstituted soils microbial activity (tests about biological fertility), soil water content (humidity), soil temperature, nutrient availability and pH-value
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag5wzRVFg9s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Anetp8gKaQg
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
SLM之前的数量:
20%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
注释/具体说明:
increasing from 20% to 50%; because of the CaCO3 content of some matrices II
风力搬运沉积物
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
10%
注释/具体说明:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 极端冬季条件 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The recycle of suitable waste materials used defrays the reconstitution technology in short and long term
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
其它(具体说明):
the Technology is partly modified to face every restoration project
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
design, matrices to be used
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Strengths: to change soil class in Land Capability Classification, to improve soil workability, to create new soil aggregates (the organic matter is covered by fine soil mineral fractions) |
| Advantages: to increase soil fertility, to implement Circular Economy |
| Opportunities: to create a non-renewable resource (soil) and/or to restore it, to implement Circular Economy |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Strengths: to produce the suitable soil for the environment where it will be placed |
| Advantages: to reduce the use of fertilizers |
| Opportunities: to restore soil using suitable waste, Circular Economy |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: demand exceed supply, concerning current number of workers employed in the reconstituted plant | formation of new workers |
| Risks: crisis of industries producing suitable waste | non-stop search for suitable waste to use |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: contamined soils | studies about possibility of using reconstitution to clean soils |
|
Risks: the pedotechniques include all the anthropic activities that determine a growing influence of man on pedogenesis and pedolandscapes; they have to satisfy man needs while avoiding any undesirable environmental consequences (Dazzi et al., 2010). This is the main core of reconstitution of soils, but sometimes, the use of waste material, even if, environmental suitable, isn't understood because of waste are considered materials only for disposal. |
Dissemination concerning the laboratory analysis before the waste use, studies and research projects with University to test environmental suitability of reconstituted soils |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
2 visits/survey a year
- 与土地使用者的访谈
each land user where technology was adopted
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
15/03/2023
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
The reconstitution pedotechnique: Applications, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., 10.1016/j.eti.2021.102246
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
The reconstitution: environmental restoration assessment by means of LCC and FCC, 10.6092/issn.2281-4485/8500
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Trees and shrubs monitoring using an ecological approach: the conclusion of the restoration project of Borgotrebbia landfill (Northern Italy), Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Meloni F., Stragliati L., Trevisan M., Giupponi L., 10.31031/EAES.2019.06.000635
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
A new technology to restore soil fertility: Reconstitution, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Francaviglia R., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201933
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Growth and yield response of tomato (Solarium lycopersicum L.) to soil reconstitution technology, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Gatti M., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201916
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Test on the effects of reconstituted soil on emergency speed and root growth in maize, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Salvi R., Battaglia R., Marocco A., Trevisan M., 10.1515/contagri-2018-0035
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Osservazione di Lycogala terrestre Fr. e Stemonitis axifera (Bull.) T. Macr. su suoli ricostituiti sabbiosi, Manfredi P., Salvi R., Bersan M., Cassinari C., Marocco A., Trevisan M.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Relationship between hydraulic properties and plant coverage of the closed-landfill soils in Piacenza (Po Valley, Italy), Cassinari C., Manfredi P., Giupponi L., Trevisan M., Piccini C., 10.5194/se-6-929-2015
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil temperature fluctuations in a degraded and in a reconstituted soil, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., ISBN 20385625
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Confronto tra dati produttivi di mais coltivato su terre ricostituite e terre naturali, Manfredi P., Tassi D., Cassinari C.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Scientific Journal
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Ecosistemi web site
URL:
https://www.mcmecosistemi.com/
标题/说明:
Paolo Manfredi ResearchGate
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paolo-Manfredi-2
标题/说明:
Chiara Cassinari ResearchGate
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chiara-Cassinari
标题/说明:
All the publications with DOI mentioned above
标题/说明:
Ecosistemi YouTube channel
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCOloFv-BLgvIVt9kBZuZyZg
7.4 一般注释
Very useful questionnaire
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [意大利]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- 编制者: Chiara Cassinari
模块
无模块