Non-winter-hardy honey-producing cover crops [斯洛文尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Gregor Kramberger
- 编辑者: Tamara Korošec
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Neprezimni medonosni posevki
technologies_7463 - 斯洛文尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
土地使用者:
Ropič Andrej
Farmer
斯洛文尼亚
co-compiler:
Horvat Tomotej
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia (KGZS) – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor
斯洛文尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - 斯洛文尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Non-winter-hardy honey-producing cover crops enhance soil fertility, prevent erosion, reduce nutrient leaching, and support biodiversity. These fast-growing, flowering plants are integrated into crop rotation, offering ecological and long-term economic benefits - and are supported by EU agricultural subsidies.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Cover cropping with non-winter-hardy honey-producing mixtures is expanding on arable land in Slovenia, especially in lowland areas near water protection zones, streams, and other water bodies. These plants are often integrated into crop rotations of both conventional and organic farming systems. Together with winter-hardy cover crops, these mixtures are an essential component of good sustainable land management. Supported by the EU's Common Agricultural Policy through SOPO (Schemes for Climate and Environment) and KOPOP (Agri-Environmental-Climate Payments), this technology promotes sustainable agriculture by improving soil structure and health and preventing nutrient leaching.
Cover crops - also referred to as catch crops or green manures - are fast-growing, plants from various families, mostly legumes, grasses and brassicas. After the main crop harvest, these plants are sown and cover the soil during summer, autumn, and winter. We distinguish between winter-hardy and non-winter-hardy cover crops.
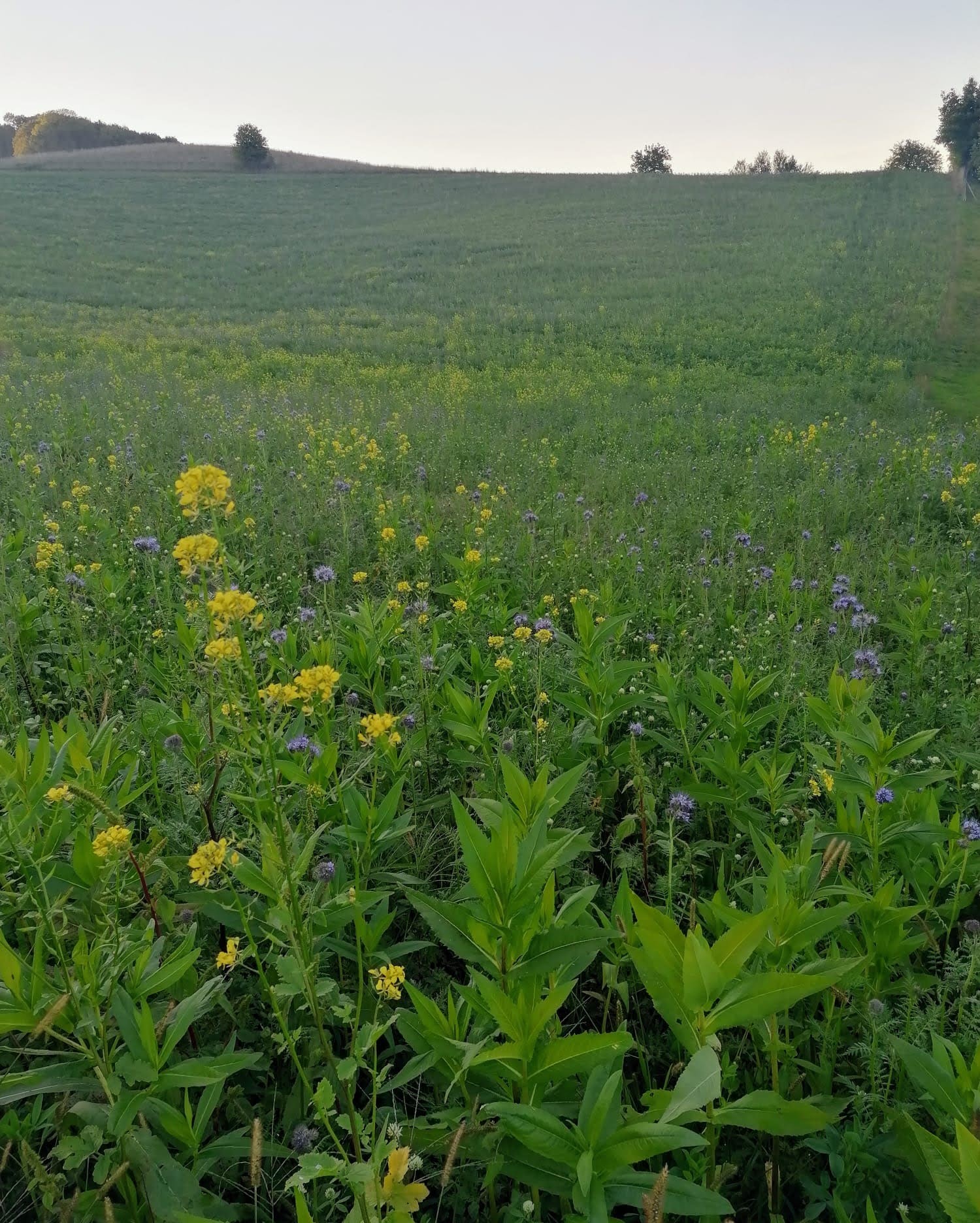
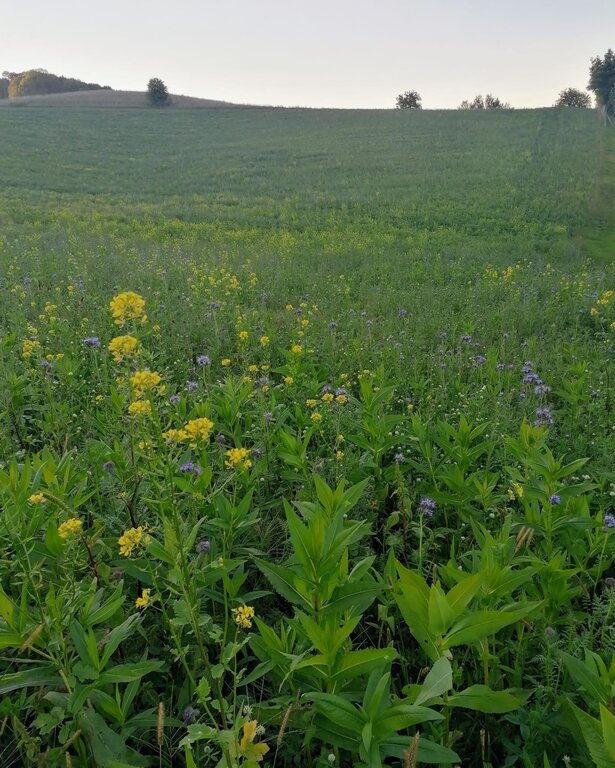
One of the most popular non-winter-hardy mixtures used in Slovenia, includes Egyptian clover (Trifolium alexandrinum), red clover (Trifolium pratense), phacelia (Phacelia tanacetifolia), and niger (Guizotia abyssinica). These species are drought-tolerant, support pollinators, and naturally perish after the first frost, simplifying subsequent soil preparation.
Their main functions are to improve soil fertility, retain moisture, prevent erosion, and reduce nutrient leaching into waterways. The different characteristics of the species in the mixture combine multiple advantages:
- dissimilar root systems extract nutrients from different layers of the soil;
- the various plant species extract different root exudates, which serve as a nutrient source for soil microorganisms;
- compacted soils become loose and of better structure;
- these species combined lead to enriched organic matter and humus;
- flowering species provide forage for pollinators;
- an overall impact is a reduced need for fertilizers and pesticides which in turn enhances water quality and lowers environmental risks;
- the leguminous species in the mixture fix nitrogen from the air, and follow-up crops like maize require less fertilizer, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Honey-producing non-winter-hardy mixtures are typically included in multi-year crop rotation plans. Activities involve selecting appropriate plant species/varieties or mixtures or species/varieties based on soil, climate, rotation and function requirements.
Shallow cultivation or direct sowing on well-prepared seedbeds takes place after cereal harvest, generally in July and August, with a recommended seeding rate of 12 kg/ha. Farmers usually avoid additional fertilization, as soil nutrients suffice for the growth of cover crops. Minimal maintenance is needed during growth since these plants suppress weeds and reduce pest pressure. Termination involves natural frost die-off, mulching, rolling, or shallow tillage. Detailed record-keeping ensures compliance with subsidy programs and supports long-term benefits.
Farmers value such cover cropping for its multiple benefits. They very much appreciate the subsidies they get for their additional effort to sow cover crops. However, challenges include higher initial costs, dependency on appropriate weather, complex timing of operations, and potential competition with main crops. Despite these hurdles, many farmers see cover cropping as a critical component of sustainable farming practices.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
斯洛文尼亚
区域/州/省:
Jareninski dol, Pernica
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vosek
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
137.0
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2020
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
The farmer adopted cover cropping as part of his transition to low-tillage farming, supported by experimentation and guidance from the public advisory service. The measure, backed by CAP subsidies, was adopted after research and experimentation, ensuring its effective integration into his farming system.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
The first year of the rotation comprises a mix of grasses and legumes
采用轮作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,请具体说明:
The farmer practices a 4- to 5-year crop rotation plan, primarily involving maize and winter cereals. After the harvest of winter cereals (e.g., wheat) in July, cover crops are sown in early August to protect the soil, enhance fertility, and support low-tillage practices.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 最小的土壤扰动
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A6:残株管理
A6:对残株管理作出具体说明:
A 6.4:保留
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical specifications for sowing non-winter-hardy honey-producing mixture
Sowing time: Sowing is recommended immediately after the harvest of winter cereals, in late July or early August.
Seeding rate: 12 kg/ha
Soil preparation: High-quality seedbed preparation is necessary due to the small seed size. Blind sowing is recommended to destroy or prevent the growth of weeds.
Sowing depth: Seeds are sown shallowly, typically at a depth of 1–2 cm, depending on soil conditions.
Row spacing: Cover crops are typically sown using a grain drill with a row spacing of 12.5 cm (approximately 5 inches) or broadcasted using a fertilizer spreader. Drilling ensures precise seed placement and consistent depth, promoting uniform germination. Broadcasting, on the other hand, involves spreading seeds evenly across the soil surface, often followed by light incorporation to enhance seed-to-soil contact. Both methods are widely used, with the choice depending on specific field conditions and equipment. Plant height: Plants in the mixture grow to a height of 50–100 cm, depending on the varieties used and growing conditions.
Winter hardiness: The plants in the mixture are non-winter-hardy; they perish with the first autumn frost, simplifying autumn or spring plowing.
Suitability for crop rotation: The mixture integrates well into crop rotation as species in it are not related to cash crops. It is sown after the harvest of winter cereals and other early/spring cash crops.
This mixture is particularly suitable for water protection areas as its intense growth prevents the leaching of excess nitrogen from the soil into groundwater, improves the water-holding capacity of the soil and effectively suppresses erosion and weeds. Additionally, its colorful flowers during the summer months enliven the landscape and provide a rich source of nectar for bees and other pollinators.
作者:
Gregor Kramberger
日期:
21/07/2025
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
11.44 ha
如果使用本地面积单位,注明转换系数为1公顷(例如1公顷=2.47英亩):1公顷=:
ha = 10.000 m2
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EUR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
114
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of a disc harrow with cover crops seed drill | 1st year |
注释:
The use of a disc harrow with a cover crop seed drill can support soil preparation and sowing, but it is not strictly necessary. Many farmers use other types of harrows and seeders, which may be more cost-effective or already available on the farm. In some cases, such equipment is shared or acquired through collective investment. While the typical depreciation period for this type of machinery is around 12 years, it is often used for 20 to 30 years, or as long as it remains functional and economically viable.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Disc harrow with cover crops seed drill | piece | 1.0 | 20000.0 | 20000.0 | 70.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 20000.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 23529.41 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Part of the agricultural machinery intended for the implementation of environmental measures can be funded through non-repayable grants from European and national funds under the CAP.
注释:
The cost of such machinery is a key factor, as equipment like a disc harrow with a seed drill can be expensive. However, it should last for 20 years (or more). Furthermore, it is not strictly necessary, many farmers use simpler or existing machinery, and shared or collective investment is also common.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Variable costs of honey-producing non-winter-hardy cover crops | Every year. |
注释:
Variable costs represent the total production expenses for sowing the mixture, including seeds, machinery and labor costs and financing.
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Work with machines | hour | 52.0 | 9.0 | 468.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Seedbed preparation and sowing | hour | 23.0 | 35.2 | 809.6 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Mulching | hour | 29.0 | 32.0 | 928.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seed | ha | 11.44 | 79.2 | 906.05 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Financing cost | % | 0.03 | 3089.94 | 92.7 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3204.35 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 3769.82 | |||||
注释:
The farmer cultivates a total of 28.6 hectares of arable land. The area is theoretically divided into five equal parts, as it follows a 5-year crop rotation system. Additionally, a cover crop is sown after barley and wheat. Therefore, we have accounted for costs on 2/5 of the additional total area.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The total area is theoretically divided into five equal parts, following the 5-year crop rotation system. However, in practice, this division is not perfectly even. Other important cost factors include variations in input prices (such as seeds, fertilizers, and plant protection products), machinery costs, labor availability, and weather conditions that impact yields and operational efficiency.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1032.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Most precipitation falls in summer, the months with the highest average precipitation are August and September, the least precipitation falls in winter, in January and February at least, and in principle more precipitation falls in autumn than in spring.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Jareninski Vrh (1991-2020)
农业气候带
- 半湿润
The average annual air temperature at Jareninski Vrh during the reference period 1991–2020 was 10.1 °C.
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Hydromelioration was carried out in the area, a drainage system and water retention systems (e.g. ponds and basins) were arranged.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
In 2023, the average agricultural holding in Slovenia manages 8.8 hectares of utilized agricultural land.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
具体说明:
Based on national legal system.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops improve soil fertility, moisture retention, and nutrient availability, leading to slight yield improvements in the following crop. The impact depends on crop rotation, soil conditions, and cover crop management.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops used in this system are not intended for grazing or fodder production; their role is primarily soil conservation and fertility enhancement. Usually, they are incorporated into the soil.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops enhance soil conservation, reduce the need for intensive tillage, and improve crop rotation efficiency.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops reduce the need for fertilizers and herbicides, but additional costs for seeds and labor partially offset these savings.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops require an initial investment, but long-term benefits such as reduced input costs and improved soil fertility may positively impact farm income over time.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Additional labor required for sowing and managing cover crops.
生态影响
水循环/径流
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops reduce direct soil exposure, lowering evaporation and improving water retention.
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops enhance soil moisture by reducing evaporation and improving water infiltration.
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops provide continuous ground cover, protecting the soil from erosion, nutrient loss, and extreme weather conditions.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops significantly reduce soil loss by stabilizing the soil, preventing erosion, and improving infiltration.
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops provide continuous plant cover, reducing bare soil exposure and enhancing biodiversity.
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops contribute significantly to above-ground biomass accumulation, increasing organic carbon input into the soil.
植物多样性
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops introduce multiple species into the cropping system, enhancing plant diversity and ecosystem resilience.
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops support pollinators, natural pest predators, and soil organisms, enhancing ecosystem balance.
栖息地多样性
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops create diverse habitats for pollinators, beneficial insects, and soil organisms, improving ecosystem resilience.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops help break pest and disease cycles, support beneficial insects, and improve soil health, reducing outbreaks.
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops enhance water retention, reduce evaporation, and improve soil structure, making fields more resilient to drought.
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
The data have not been obtained through specific measurements but rather through a questionnaire with the farmer and insights from other farms and agricultural advisors.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
缓冲/过滤能力
注释/具体说明:
Cover crops act as a natural buffer, reducing runoff, filtering pollutants, and preventing nutrient loss.
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
The data have not been obtained through specific measurements but rather through a questionnaire with the farmer and insights from other farms and agricultural advisors.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 季节性温度 | 春季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 季节性温度 | 秋季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 季节性温度 | 冬季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 季雨量 | 春季 | 增加 | 适度 |
| 季雨量 | 秋季 | 减少 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 热浪 | 好 |
| 干旱 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
注释:
In the short term, establishment costs are high machinery investment, with no direct financial return. However, in the long term, benefits such as improved soil fertility, reduced input costs, and better yields in crop rotation help offset initial expenses. In the short term, maintenance costs, such as seed, labor for sowing and termination, are balanced by reduced expenses on herbicides and fertilizers. Over the long term, cover cropping leads to lower input costs, improved soil health, and better yields in crop rotation
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
The composition of the cover crop mix was adjusted to better fit the crop rotation, improving soil fertility and weed suppression.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improvement of soil fertility (improved soil structure, increased humus - organic matter content) |
| Soil erosion control (e.g., Pernica lake) |
| Weed control – suppression of weeds |
| Moisture retention in the soil (protection of soil against direct sun rays) |
| Long-term pest control |
| Easier soil cultivation - suitable for minimum tillage |
| Beneficial for bees and wild pollinators |
| Improved aesthetic value of the landscape |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Non-winter-hardy cover crops improve soil structure, increase organic matter content, increase the number and variety of soil (micro)organisms and enhance nutrient cycling, leading to more fertile and resilient soils. They also help in nutrient retention. |
| The root systems of cover crops help anchor the soil, reducing erosion caused by wind and water. |
| Continuous cover with cover crops can suppress weeds, reducing the need for herbicides. |
| Certain cover crops can break pest and disease cycles, contributing to healthier crops. |
| Honey producing non-winter-hardy cover crops support pollinators. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Time- and labor-intensive, requiring significant coordination in terms of timing, weather, and other conditions to meet the deadlines set within the framework of the Common Agricultural Policy – CAP, if the farmer wants to get subsidies for this planting cover crops. | Farmers have greater influence in policy making. Bottom-up approach. |
| Additional seed cost. | The farmer enrolls in CAP measures to receive a subsidy for this measure. |
| Initial costs when purchasing equipment, additional investments, and changes in work technology. | Equipment rental, applying for funding grants for equipment, and modifying already existing machinery. |
| Complexity of management, more demanding planning, and necessary knowledge. | Education |
| Farm conditions vary, and the effectiveness of cover crops depends on soil type, climate, and local conditions, which can affect growth and overall benefits. | Selecting suitable cover crop mixtures adapted to local soil and climate conditions. Flexible management practices, regular monitoring, technical support, education. |
| Inappropriate use | Education |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Establishing and terminating cover crops require additional time and labor, which can be a limiting factor for some farmers. | Good planning, collaboration with other farmers, subsidies, and awareness of the long-term benefits of this method encourages the farmer to be more willing to invest effort. |
| Additional costs for seed purchase and extra labor. | The farmer enrolls in CAP measures to receive a subsidy for this measure. |
| Potential challenges in soil preparation. | Appropriate equipment, planning, selection of the right plant varieties. |
| Complexity of crop management and planning. | Education, planning, record keeping. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1 (Andrej Ropič, farmer)
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
2 (Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia (KGZS) – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor; Tamara Korošec and Timotej Horvat)
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
CAP and Slovenian Strategic Plan 2023-2027.
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
17/01/2023
注释:
Visit to the farm and farmer interview.
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Quintarelli, V., Radicetti, E., Allevato, E., Stazi, S. R., Haider, G., Abideen, Z., Bibi, S., Jamal, A., & Mancinelli, R. (2022). Cover Crops for Sustainable Cropping Systems: A Review. Agriculture, 12(12), 2076.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://doi.org/10.3390/agriculture12122076
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Food. (2024). Unified Application 2024: Guidelines for the implementation of interventions under the Strategic Plan of the Common Agricultural Policy 2023–2027. Ljubljana, Slovenia.
URL:
https://www.kgzs.si/uploads/eiv24/NAVODILA%201/00_VELIKA_NAVODILA_2024_-_CELOTA_-_28_5_24.pdf
标题/说明:
SARE: Cover Crops for Sustainable Crop Rotations
URL:
https://www.sare.org/resources/cover-crops/
标题/说明:
Recommendations for sowing catch crops and winter cover crops for the sustainable use of arable land (Priporočila za setev naknadnih in prezimnih posevkov, za trajnostno rabo njiv)
URL:
https://www.kmetijskizavod-nm.si/uploads/kgz_nm/travni%C5%A1tvo/Priporo%C4%8Dila_za_setev_naknadnih_in_prezimnih_posevkov.pdf
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块