Organic Farming of Table Grapes [意大利]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Pandi Zdruli
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Agricoltura biologica nella coltivazione di uva da tavola
technologies_7648 - 意大利
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
REACT4MED (Inclusive Outscaling of Agro-Ecosystem Restoration Actions)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Centre International de Hautes Etudes Agronomiques Méditerranéennes, Istituto Agronomico Mediterraneo di Bari (CIHEAM IAMB)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Organic farming avoids contamination of soil and water by eliminating the use of chemical fertilisers and other synthetic inputs.
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
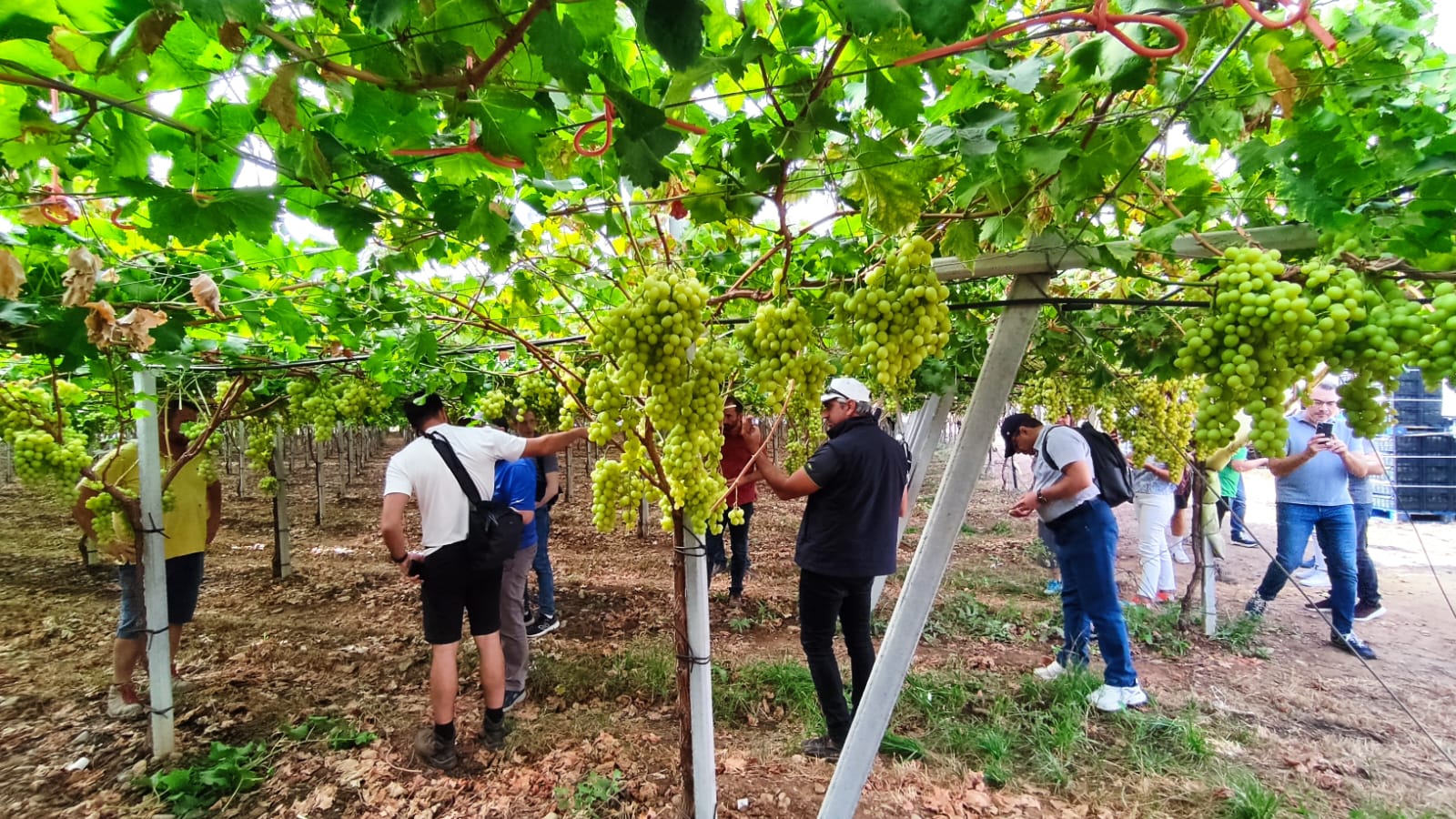
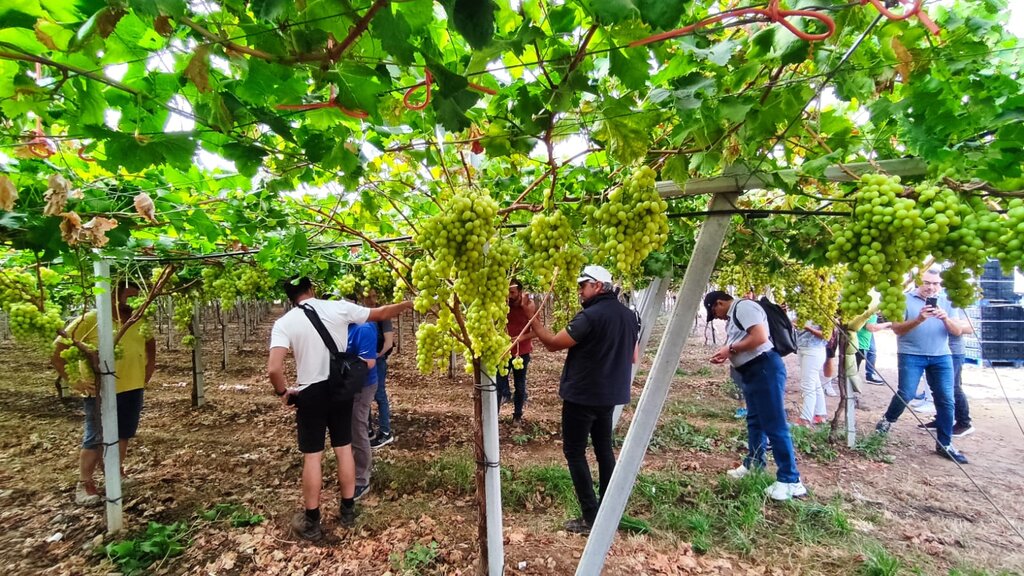
Organic Farming (OF) of table grape production in Apulia region is estimated at 8.5% of the total area. The advantages of OF include an increase in soil organic matter, better water holding capacity and lower soil salinity.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The EU Green Deal programme targets the conversion of 25% of agriculture into organic farming. Italy is close to 20% (as of 2024), and progress is being made towards the 25% target. Organic farming (OF) of fresh table grape production in Apulia region is estimated at about 8.5% of the total area of 35,000 ha. There are clear advantages of OF over conventional production methods in terms of soil heath. Soil organic matter is increased and water holding capacity is improved. Lower levels of soil salinity are also observed, principally due to the elimination of chemical fertilisers. Production is supported by modern, digitised, drip irrigation systems that increase water use efficiency.
Organic table grapes are produced at farm level. The main characteristics are based on the principles of organic farming, namely those of Health, Ecology, Fairness and Care. These principles guide the production system in (i) promoting soil, plant, animal, and human health, (ii) sustaining healthy ecological systems, (iii) ensuring fairness for all involved, and (iv) taking a precautionary and accountable approach to protect the environment for now and for future generations. Organic farming aims to produce food that sustains the health of the soil, plants, animals, humans, and thus the planet as an indivisible whole. This involves nurturing living systems rather than trying to control them, while promoting a strong and healthy environment.
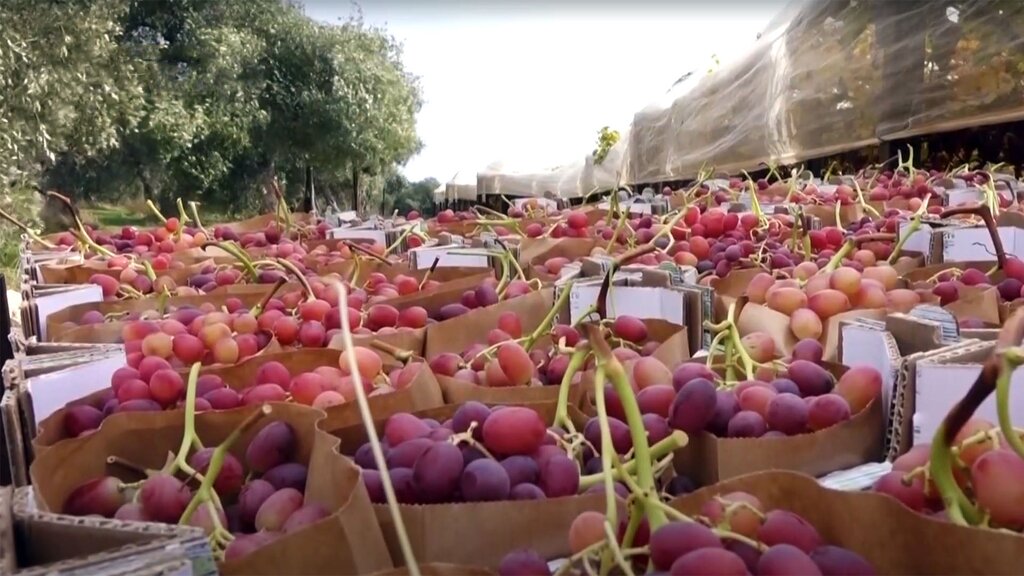
The main purpose of organic table grape farming is to produce healthy grapes without hurting the environment, and in particular protecting soil and water from contamination. In the production system, inputs include organic manure to increase and maintain soil organic matter, and the encouragement of beneficial insects for pest control. The major benefits of farming this way are the production of better-quality grapes, while simultaneously improving soil health. Furthermore, the selling price of organic grapes attracts a premium of about 30%. This compensates for the lower yields that often occur as a result of eliminating synthetic chemical inputs.
Organic farming in Italy is regulated by the DECRETO LEGISLATIVO of 6 October 2023, no. 148 that sets out standards of production that are the basis of official certification.
However organic farming is not mainstream in fresh grape production, and many farmers remain reluctant to adopt it. This is mainly related to the need for biological means of pest and disease control that do not work effectively all the time, unlike synthetic chemical pesticides and fungicides that are not permitted under OF. This has consequences on yields and potentially on farmers’ income.
2.3 技术照片
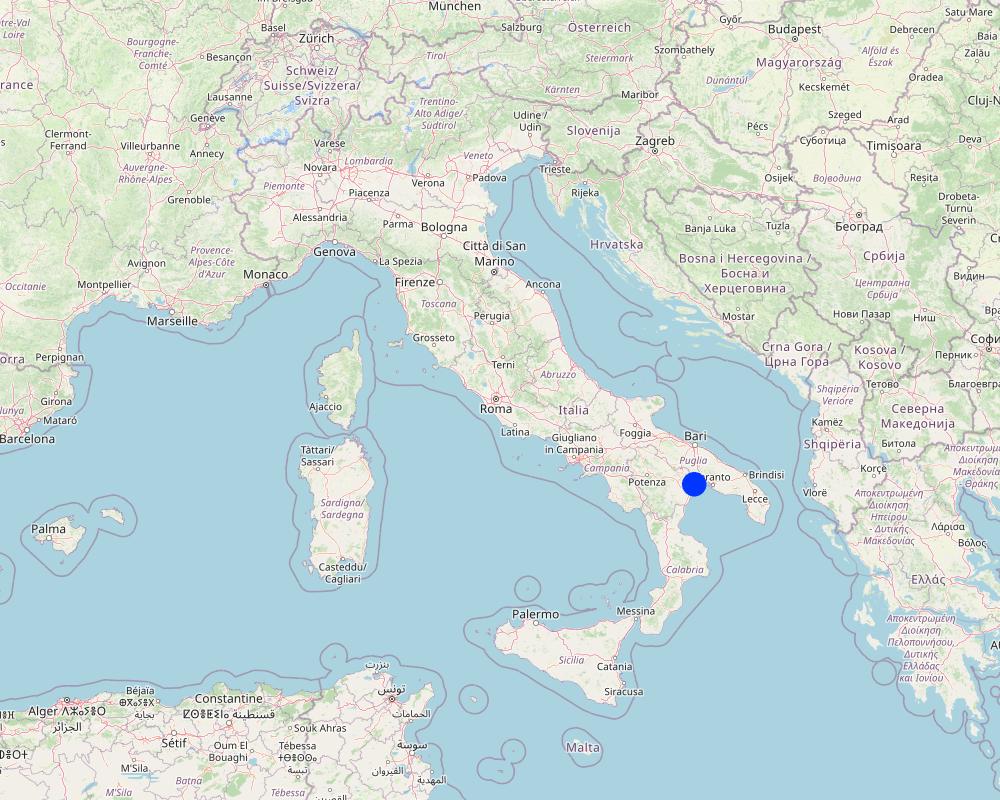
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
意大利
区域/州/省:
Apulia Region, Taranto
有关地点的进一步说明:
Dioemede Farm
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
300.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The technology is found in farmlands cultivated over long periods.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The technology is also promoted by the EU Green Deal where the targets are to convert 25% of EU agriculture into OF by 2030.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
- Grapes
- Table grapes cultivated for a period of max 20 years
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
One harvest per year
采用间作制度了吗?:
否
采用轮作制度了吗?:
否

其它
具体说明:
Grapes vineyards
注释:
Table grape production is widely spead in the Provinces of Bari and Taranto in Apulia Region
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 否(继续问题3.4)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
注释:
Irrigation is crucial for table grape production. Water comes from several dams in the area and from groundwater.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A4:地表下处理

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pw:水浸

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
- Hs:地表水良变化
- Hg:地下水/含水层水位的变化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hq:地下水水质下降
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
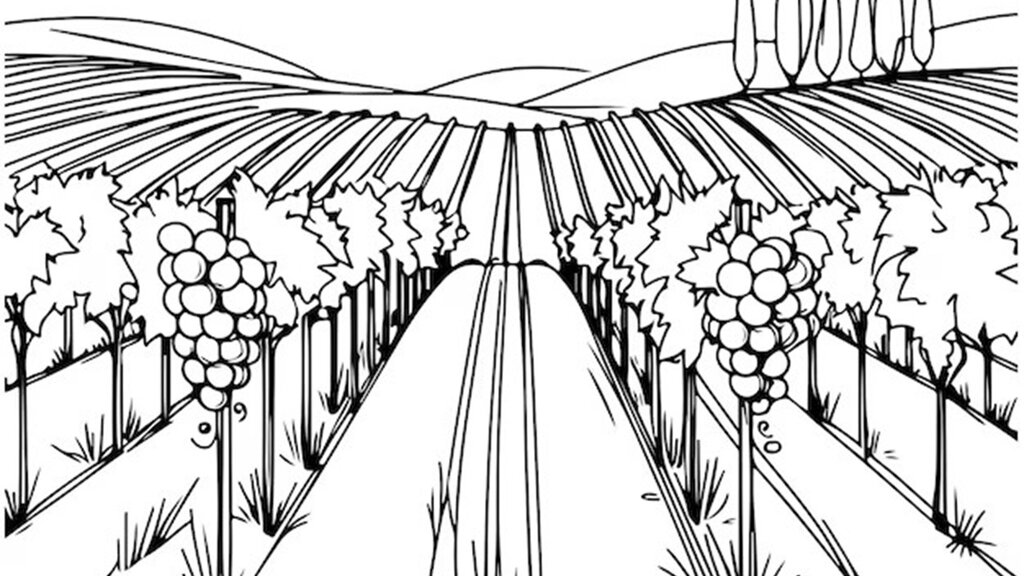
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The sketch gives an overview of an organically farmed table grape plantation. The grape rows are spaced at 2.5 metres apart, and the grape vines then pruned to reach 2.0 metres high (making management and harvesting easier). Drip irrigation pipes are situated alongside the rows of grapes - allowing precisely controlled and thus efficient application of water to each plant. Fertilizer is delivered in the irrigation water - thus it constitutes a "fertigation system".
作者:
Pandi Zdruli
日期:
06/10/2025
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
Hectare
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
EUR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
0.85
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Soil preparation | Winter |
| 2. | Location of cemented piles | Winter |
| 3. | Rootstock planting | Winter |
| 4. | Grafting | Winter |
| 5. | Establish irrigation and fertigation system | Winter |
| 6. | Fall |
注释:
Grape cultivation requires first soil preparation, followed by establishing the cemented piles that form the framework to support the grapes. Then planting is carried out using rootstock filoxera resistant varieties upon which the grafting is carried out. All of this is supported by an irrigation system.
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算建立该技术所需要的总成本。:
30000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
100% by the land users
注释:
The costs of establishing fresh table grape plantations are covered 100% by the land users - mostly big companies with adequate financial resources.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Irrigation | Every 10 days during the irrigation season |
| 2. | Application of organic inputs | Once per year in winter |
| 3. | Weeding | Frequently during the growing season |
| 4. | Pruning | Once a year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果您无法分解上表中的成本,请估算维护该技术所需要的总成本。:
10000.0
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
100% by the land users
注释:
All maintenance costs are covered by land users
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Raw materials, like rootstock, irrigation systems, tractors and labour costs
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
650.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Typical Mediterranean climate with dry and hot summers and mild wet winters
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Ginosa
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Semi arid climate, with annual rainfall about 650 mm/year
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Flatlands
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Cambisol/Fluvisol soil types, basic pH above 7.5, good CEC values, lower salinity, low soil organic matter less than 1.5%
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水质请参考::
地下水和地表水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
具体说明:
Areas located close to the Ioanian Sea expose salinity problems
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
偶然
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Water quality deriving from the above ground dams is of good quality but during the summer irrigation season is not enough to satisfy farmers needs, then many of them have drilled wells and pump groundwater for their needs. Often such water is saline.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Mostly herbacous plants along the drainage canals. Soil biodiversity dominated by earthworms and billions of microorganisms.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 合作社
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 公司
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
土地使用权是否基于传统的法律制度?:
否
具体说明:
Not traditional, regulated by the Government laws
注释:
All land rights are in line with EU rules
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Grapes are free of pesticide and fungicide residues
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Minimum tillage makes field operations simpler and quicker
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Infiltration and water holding capacity are increased, making more water available downstream for pumping
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Water demands are reduced because of efficient systems of irrigation
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
A result of increased prices of grapes: value addition through organic farming
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The major lever for conversion to OF is awareness among farmers that this form of farming brings economic soil health benefits.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地下水位/含水层
注释/具体说明:
Water infiltrates better under this system
蒸发
注释/具体说明:
Reduced by better ground cover
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Increased by better ground cover
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Improved as a result of minimum tillage
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Less erosion as ground cover improved
土壤结壳/密封
注释/具体说明:
A positive result of minimum tillage
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
A positive result of minimum tillage
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
The overall system supports and encourages this
盐度
注释/具体说明:
Less irrigation water used
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
The overall system supports and encourages this
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Fewer beneficial insects killed because of elimination of chemical pesticides
减少气候和灾害风险
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
The overall system supports and encourages irrigation water efficiency
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
A result of minimum tillage
对现场影响的评估(测量)进行具体说明:
Data were collected in the context of the PRIMA funded REACT4MED project: a combination of data, expert assessment and farmer testimony
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
注释/具体说明:
Better infiltration of rainwater etc
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
Better infiltration of rainwater etc
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Better infiltration of rainwater etc
对场外影响(测量)的评估进行具体说明:
Data were collected in the context of the PRIMA funded REACT4MED project: a combination of data, expert assessment and farmer testimony
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 季雨量 | 夏季 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
3000 hectares
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
In some cases there are EU subsidies to convert to OF but farmers complain about bureaucracy and red tape.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Organic Farming in fresh table grapes requires dedication from farmers and rigorous application of technology. |
| Production may be lower in terms of quantity but the quality is better, translated into higher selling price |
| This requires however, raising awareness of customers for such products and willingness to pay a higher price for a healthy product. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Organic Farming has also benefits for soil health, biodiversity and overall environment |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses are mostly related to the willingness of some farmers to change their methods of farming | Spread the positive results, show concrete examples where the technology worked out well. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Converting to OF is not easy and straightforward. Many farmers fear that they will lose income and will be subject to severe controls from the regional authorities and their product may not be certified, so they could lose the market. | Correct application of the methodology. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Several visits in the area
- 与土地使用者的访谈
25
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
5
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
8
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
19/09/2023
注释:
Data were collected in the context of the PRIMA funded REACT4MED project
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Restoration, Indicators, and Participatory Solutions: Addressing Water Scarcity in Mediterranean Agriculture. Perrino, E.V.; Zdruli, P.; Piscitelli, L.; D’Agostino. 2025
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Agronomy 2025, 15, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071517
7.4 一般注释
Results reported here are based on the work done by CIHEAM Bari team in the REACT4MED project.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块