Longan, Plum interplanting [中国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: zhangsheng LIU
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Development of Southward Fruit Trees
technologies_942 - 中国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Water & Soil Conservation Office of Zhaoan County (Water & Soil Conservation Office of Zhaoan County) - 中国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [中国]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- 编制者: zhangsheng LIU
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Interplanting plum, peach in the Longan orchard to conserve soil and water and improve soil fertility.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
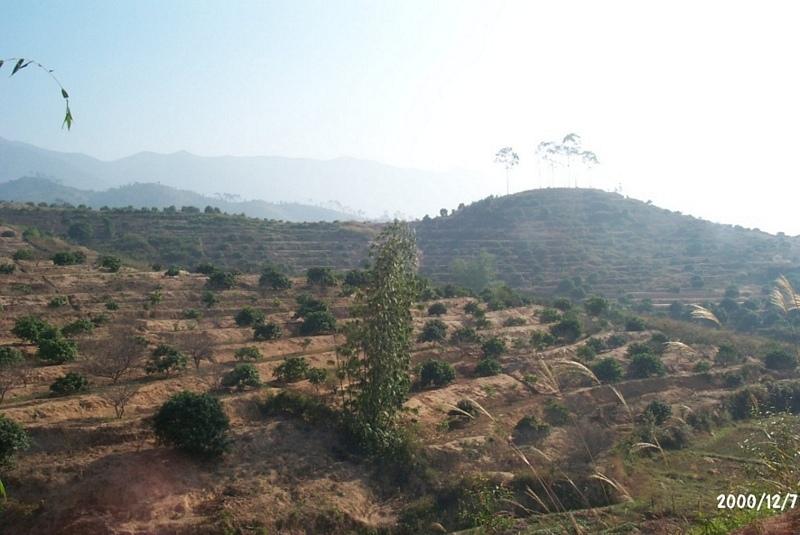
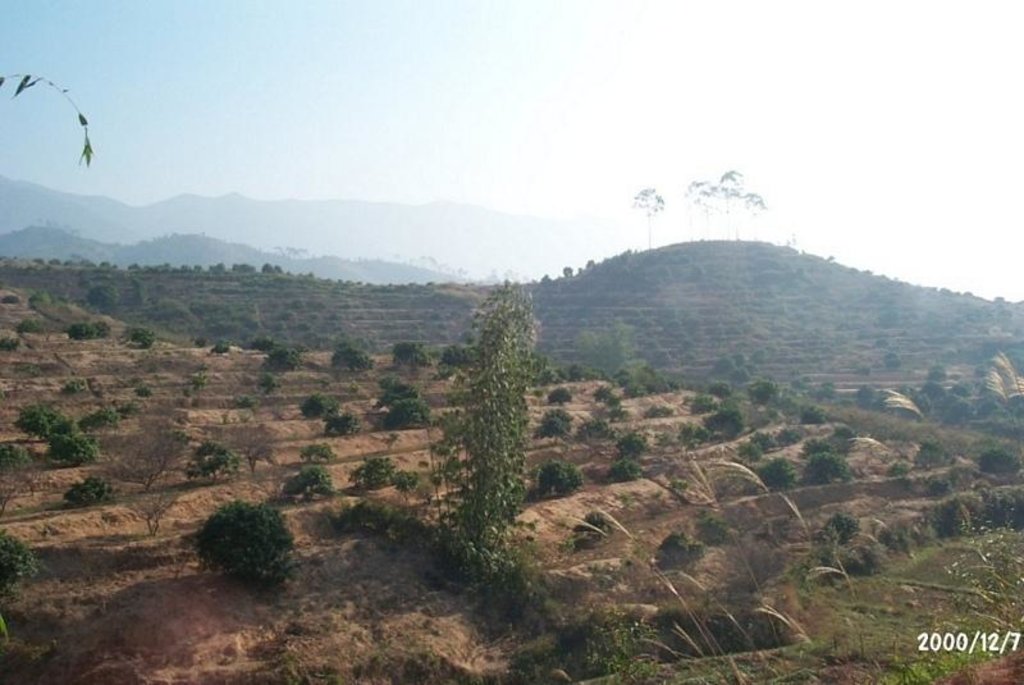
The technology is to interplant fruit trees in orchard so as to prevent water loss and soil erosion. To implement the project, local government gave financial support and SWC specialists gave technologically guide to local land users. The slope land in the hilly and mountain areas were constructed into terraces and plant trees in order to improve surface vegetation cover rate and reduce water and soil loss; the harvesting surplus rainfall in the raining season and irrigate the fruit trees in dry seasons.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
中国
区域/州/省:
Fujian
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
After the land users' arduously cultivating over many years, the former waste mountains have become a picture of vital force, the various growing fruit trees are very vital, water loss & soil erosion is controlled, and cultivated land can be used in a sustainable way.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology originated from Institute of Water & Soil Conservation in Taiwan and improved by the national SWC specialists.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 核果(桃、杏、樱桃、李子等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - OctSecond longest growing period in days: 120Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
采用间作制度了吗?:
是
如果是,说明哪些作物是间作的:
Interplanting plum, peach

森林/林地
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The ground surface of the SWC application area did not plant grass and green manure. The soil in the mountaintop area is lean, where broadleaf forest could be planted.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Because the soil layer is thin and poor, the local farmers wouldn't like to invest in the area where water loss and soil erosion is serious.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Commonly, supplementary planting of trees in the following Spring.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour ridging
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Causing land surface bare, ruderal cluster.), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial: hindering ulterior expanding of the water and soil conservation)
Secondary causes of degradation: Land subdivision (seperated land area can not be entirely developed)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
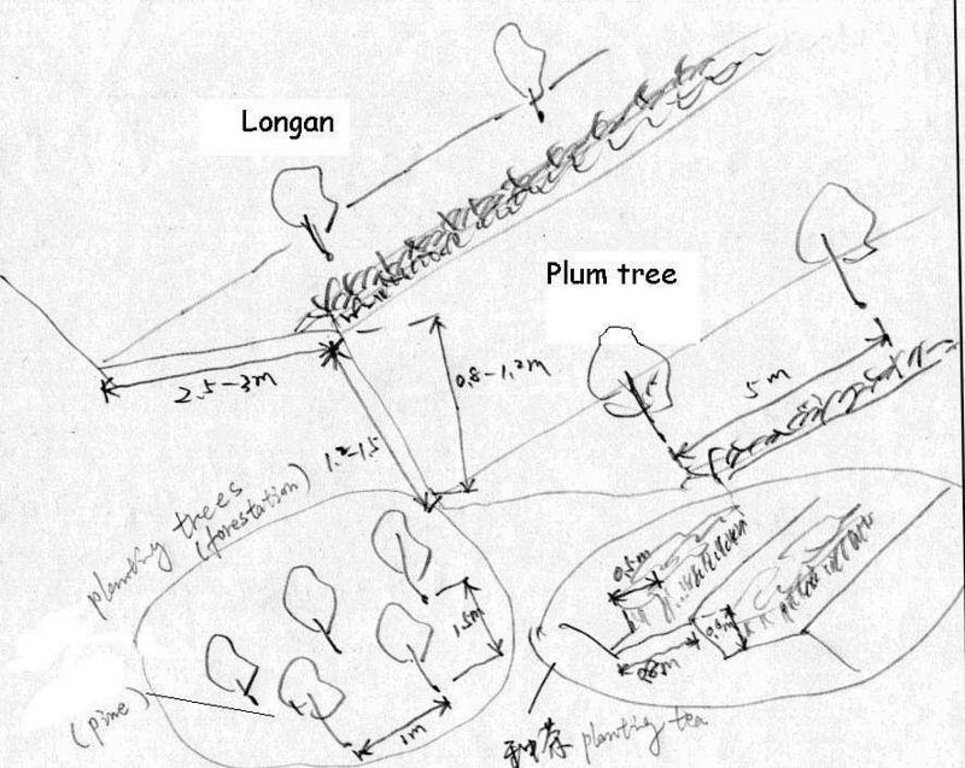
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical drawing of interplanting in orchard.
Location: Zhaoan county. Fujian
Date: 1997
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, wind-break
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Plum trees
Quantity/ density: 238
Remarks: increasing ground cover
Contour ridging
Remarks: reasonable layout
Trees/ shrubs species: jequirity tree
Perennial crops species: Plum, peach lichi trees
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 15.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 60.00%
Construction material (earth): cheaper, local materials, good effect
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 28.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 13.00%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 26.00%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:2.00
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Forbidding disafforest in mountain areas for 3 years.
作者:
LIU Zhangsheng, Zhaoan, China
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
8.3
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.40
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | plant trees | spring |
| 2. | Level off land | winter |
| 3. | weed | winter |
| 4. | digging ditch | spring |
| 5. | Level off land | Autumn |
| 6. | costruct bank of field | winter |
| 7. | Closure and forbidding disafforest | 3 years |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging ditch(interplant) | winter / Annually |
| 2. | irrigate | spring / Each cropping season |
| 3. | fertilization | Mar.Jun.Sep. /Annual |
| 4. | spew pesticide | Apl.Jul. /Annual |
| 5. | reinforce banks of level terrace | autumn/Annual |
| 6. | complementing seedling | spring / 1 |
| 7. | Fertilizing | Mar. Jun. / 2 |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Slope angle degree, and earth volume being moved.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Main factor influencing the SWC cost is steeper slope. Since the slope steeper is, much more cost needed to level off terrace. In some places, the earth needs to be moved from one place to another which will spend a lot of labor forces.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
- 半湿润
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
slopes on average also moderate
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth als moderatly deep
Soil fertility very low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration medium - good
Soil water storage capacity medium - high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
12% of the land users are very rich and own 12% of the land.
44% of the land users are rich and own 44% of the land.
35% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land.
9% of the land users are poor and own 9% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Mainly in transport of goods and travelers, such as transport service. It needs much more idle labor forces.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1253 households
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
注释:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
690 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
563 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The farmers have known that the SWC technology could produce benefits of improving agricultural production.
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Interplanting fruit trees of Longan, Peach, Plum etc. [中国]
Interplanting plum, peach and other fruit trees in longan orchard on level terraces in order to prevent soil and water loss and improve production of the fruit trees.
- 编制者: zhangsheng LIU
模块
无模块