Water Harvesting & Basin tillage [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Cobus Botha
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
In-field water harvesting technique
technologies_968 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Agricultural Research Council (ARC) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Water Harvesting & Basin tillage (WHB) through demonstrations [南非]
Optimising rainwater use, reduce runoff by use of basins and reduce evaporation losses by applying a mulch (stone/reeds) on the runoff strip and in the basins.
- 编制者: Cobus Botha
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
In-field water harvesting technique
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
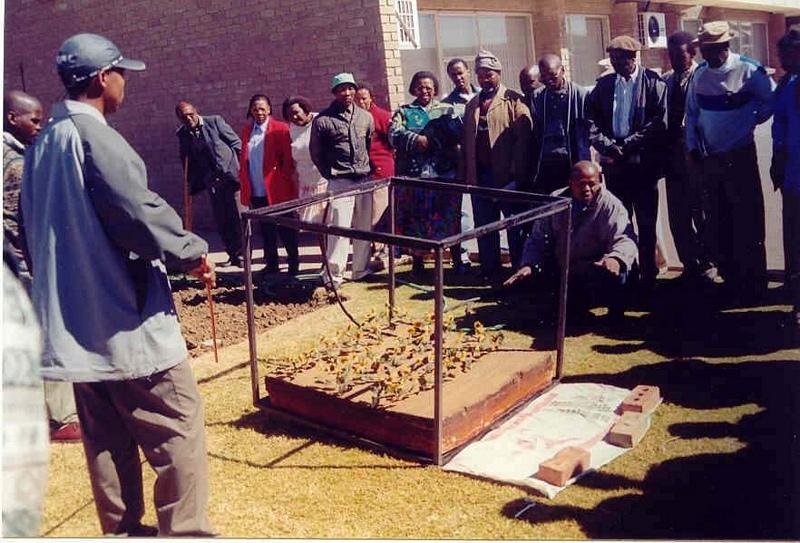
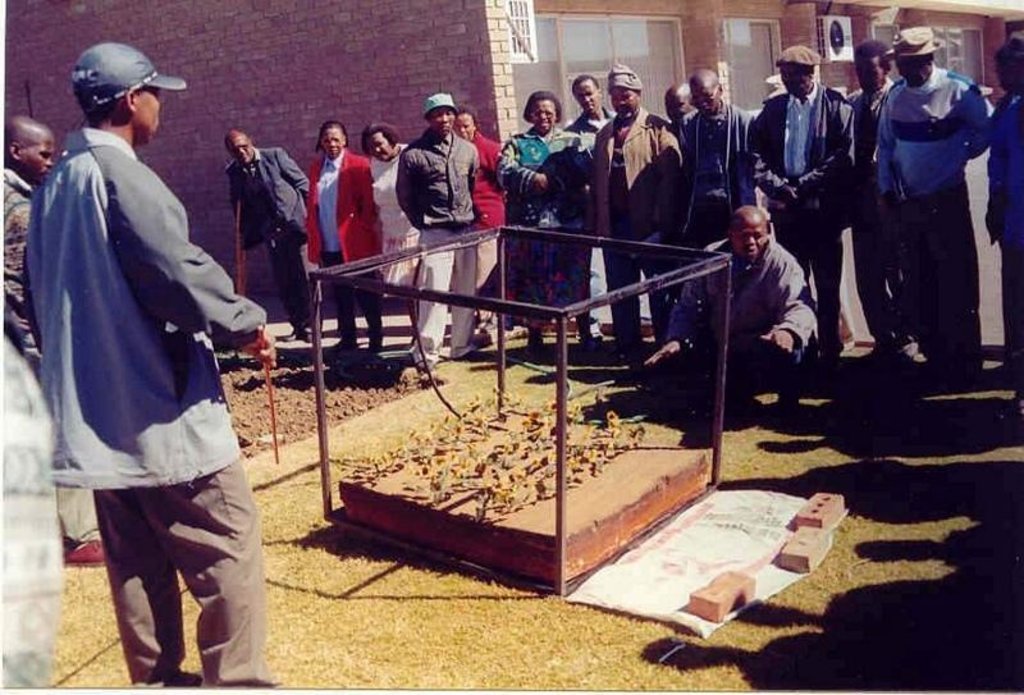
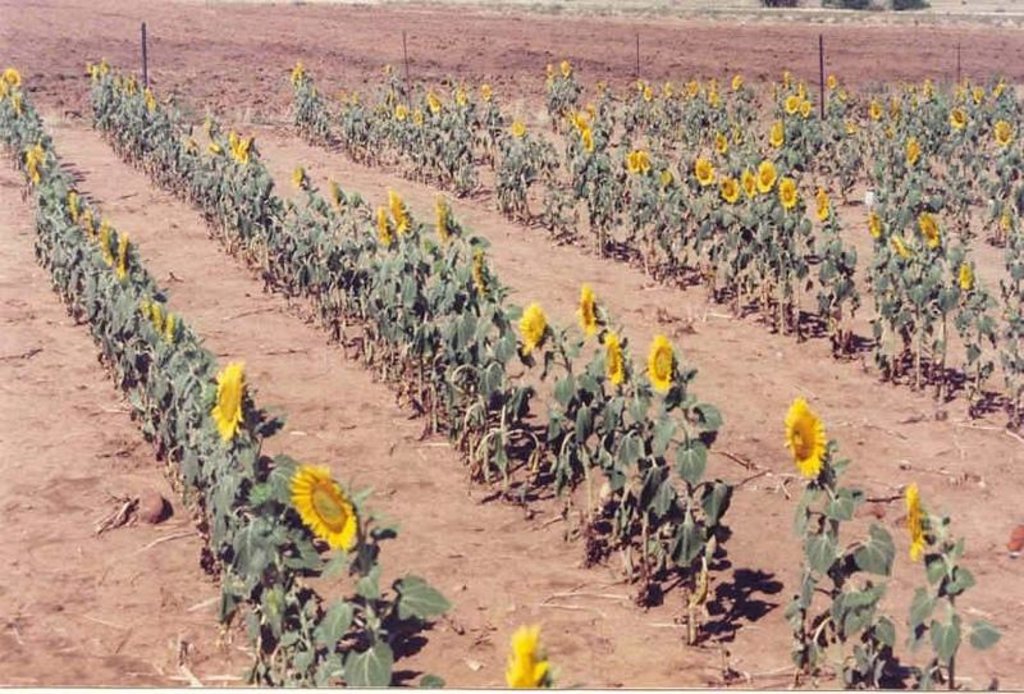
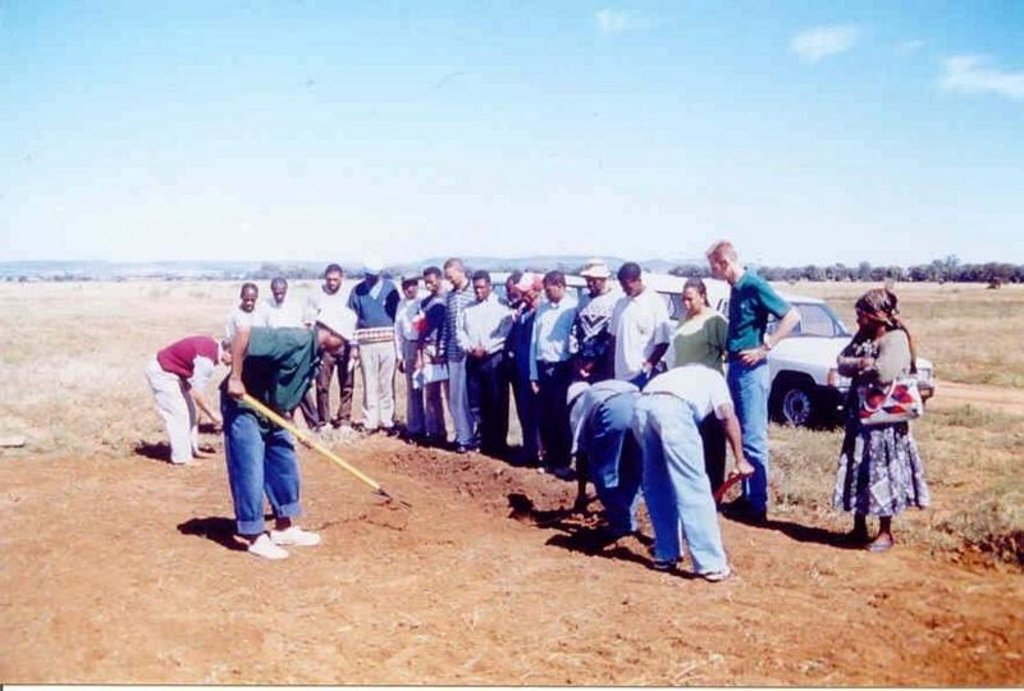
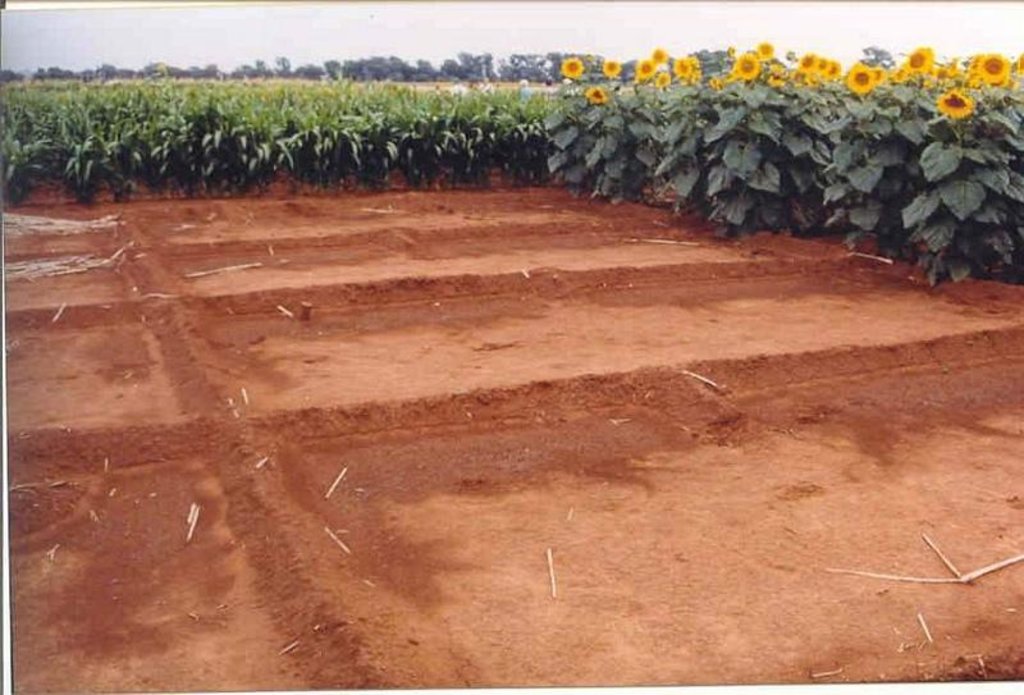
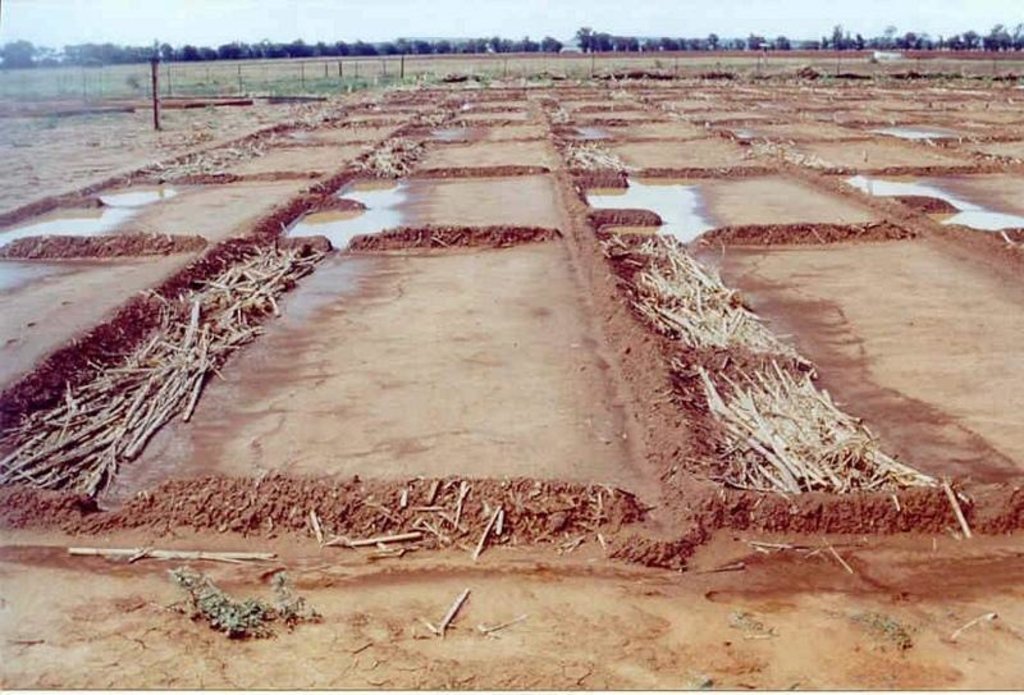
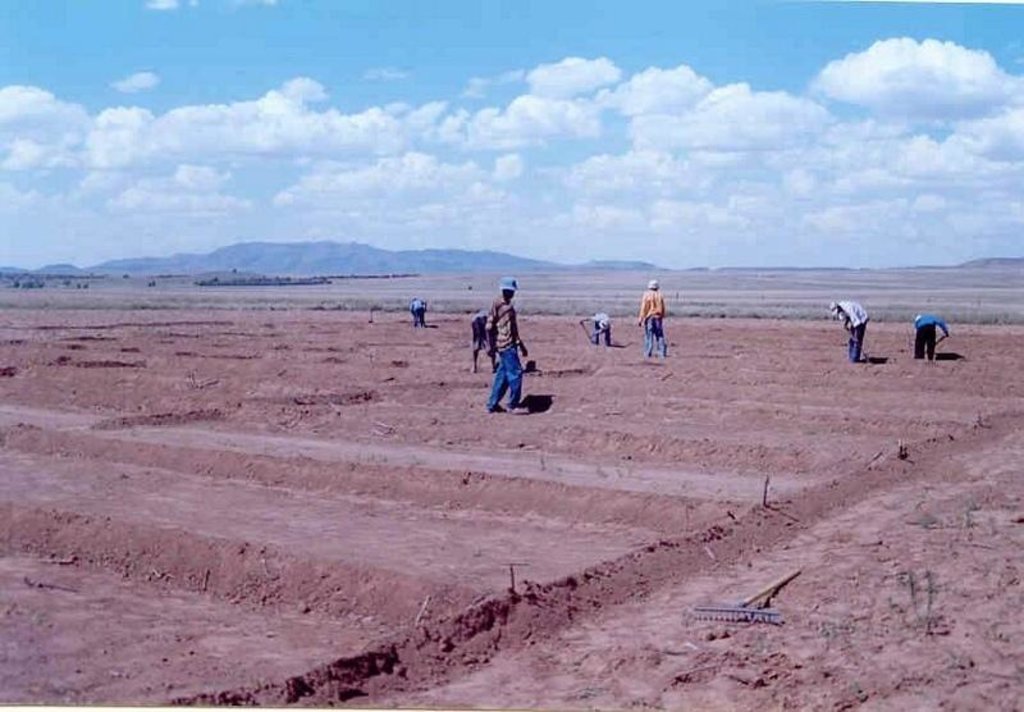
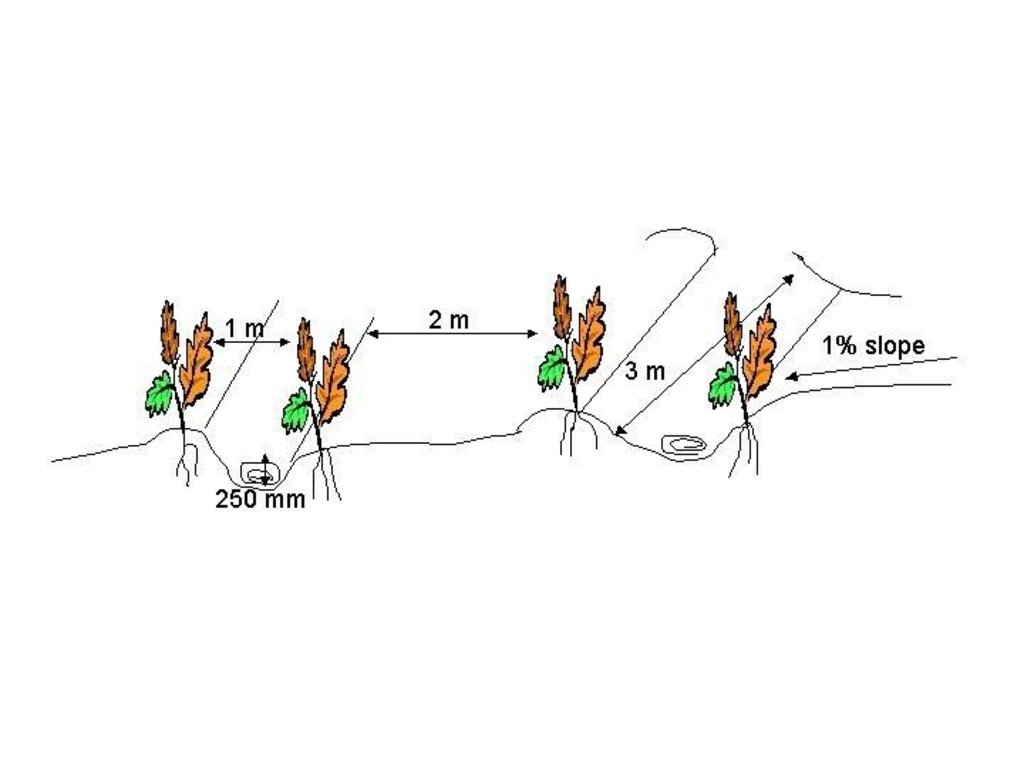
The technique consists of the construction of a 1 m wide basin with a 2 m wide runoff area. They are mulched with either straw or stones and, for the sake of comparison, the runoff area should be left bare. The soil is not tilled to encourage development of a crust, over which water runs off into the basin.
The basins collect the maximum amount of water during rain and because it accumulates in the basin, it is allowed more infiltration time. Mulch minimises evaporation and the efficiency varies with the type of mulch used.
The construction of basin and runoff areas and mulching maintenance involves keeping basins open and mulch intact.
This technique is used under semi-arid conditions on soils with very high clay contents. The depth of the profile must be greater or equal to 900 mm and the A-horizon must also be 250 mm or more.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Free State
有关地点的进一步说明:
Botshabelo, De Wetsdorp, Bloemfontein, Thaba Nchu
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
An area of approximately 750 000 ha east of Bloemfontein has been earmarked for developing farmers. The Water harvesting and Basin tillage technique has been employed in the scattered villages and two towns Thaba Nchu & Botshabelo.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Other methods of water harvesting is used elsewhere in Africa.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
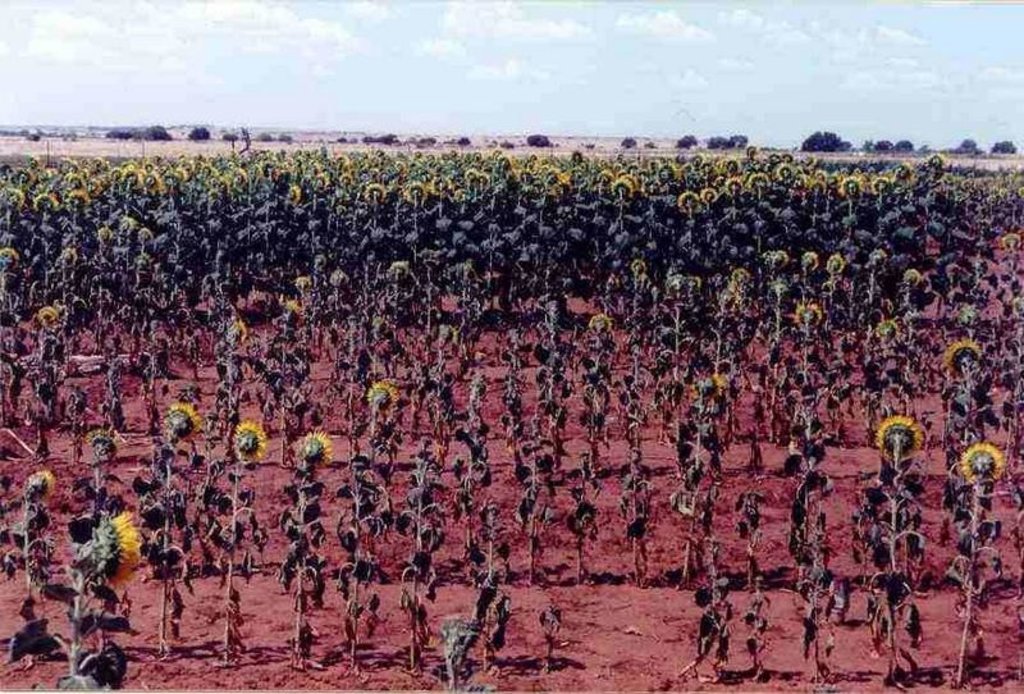
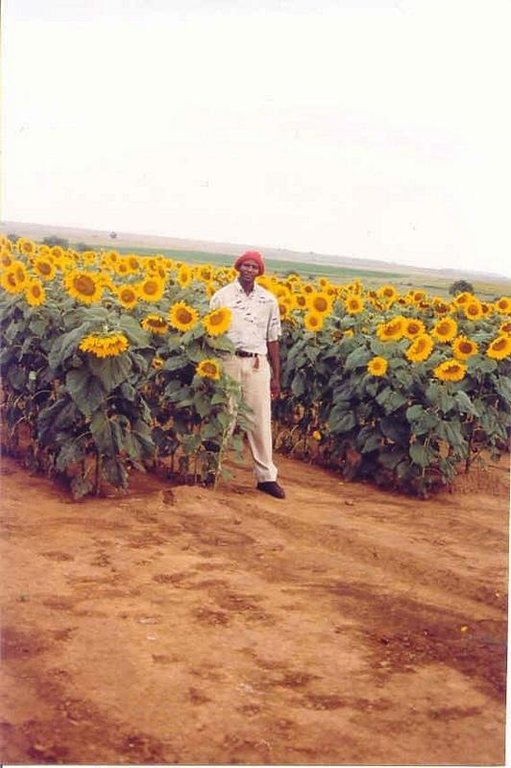
- 油料作物 - 向日葵、菜籽、其他
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Jan - April
注释:
major cash crop: Sunflower
major food crop: Maize
other: Beans
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The area is marginal for crop production because of relatively low and erratic rainfall and dominantly clay soils with high water losses due to runoff and evaporation from the soil surface.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of good fertile soils and to little rain to produce a good crop.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 集水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理
- A7:其它
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.1:免耕
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Agricultural causes - Traditional, conventional cultivation methods not feasible), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Lack of knowledge)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Low and erratic rainfall events), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial - No resources to cultivate)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical specifications
Location: Glen. Free State
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply
Mulching
Material/ species: Stone/straw
Remarks: <80 % stone; straw varies
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: N, P, K
Remarks: Basins/runoff areas
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Basins/runoff areas
作者:
Cobus Botha
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of basins | Before planting / Once in 10 years7 |
| 2. | Preparing seed bed | At planting / annual |
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
100% of the land users are poor and own 100% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Also commercial/ market but less common
Level of mechanization: Also mechanized, but less common
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
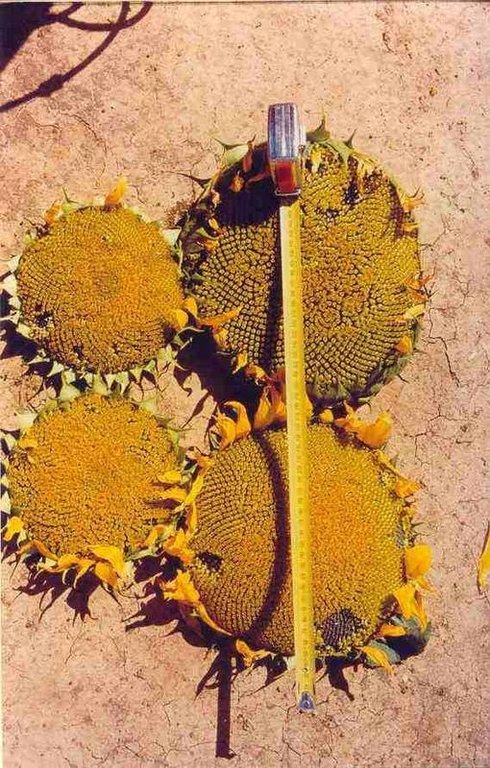
生产
作物生产
社会文化影响
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
19
SLM之后的数量:
0
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
22.6
SLM之后的数量:
9
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Can obtain higher crop yields in dry seasons. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Minimize runoff and evaporation losses. |
| More water available for plant growth that leads to higher yields. |
| Save on input costs (Use no-till). |
| Unemployed people in rural semi-arid areas can produce food for themselves. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Initially labour intensive to construct basins. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Some soil movement into the basins. | |
| Organic mulch may absorb some rainwater. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Water Harvesting & Basin tillage (WHB) through demonstrations [南非]
Optimising rainwater use, reduce runoff by use of basins and reduce evaporation losses by applying a mulch (stone/reeds) on the runoff strip and in the basins.
- 编制者: Cobus Botha
模块
无模块